Abstract
Background
Glioblastoma (GBM) has a high incidence rate, invasive growth, and easy recurrence, and the current therapeutic effect is less than satisfying. Pyroptosis plays an important role in morbidity and progress of GBM. Meanwhile, the tumor microenvironment (TME) is involved in the progress and treatment tolerance of GBM. In the present study, we analyzed prognosis model, immunocyte infiltration characterization, and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network of GBM on the basis of pyroptosis-related genes (PRGs).
Methods
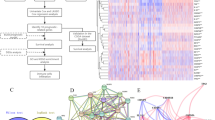
The transcriptome and clinical data of 155 patients with GBM and 120 normal subjects were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx). Lasso (Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator) Cox expression analysis was used in predicting prognostic markers, and its predictive ability was tested using a nomogram. A prognostic risk score formula was constructed, and CIBERSORT, ssGSEA algorithm, Tumor IMmune Estimation Resource (TIMER), and TISIDB database were used in evaluating the immunocyte infiltration characterization and tumor immune response of differential risk samples. A ceRNA network was constructed with Starbase, mirtarbase, and lncbase, and the mechanism of this regulatory axis was explored using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA).
Results
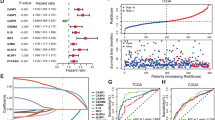
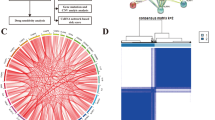
Five PRGs (CASP3, NLRP2, TP63, GZMB, and CASP9) were identified as the independent prognostic biomarkers of GBM. Prognostic risk score formula analysis showed that the low-risk group had obvious survival advantage compared with the high-risk group, and significant differences in immunocyte infiltration and immune related function score were found. In addition, a ceRNA network of messenger RNA (CASP3, TP63)–microRNA (hsa-miR-519c-5p)–long noncoding RNA (GABPB1-AS1) was established. GSEA analysis showed that the regulatory axis played a considerable role in the extracellular matrix (ECM) and immune inflammatory response.
Conclusions
Pyroptosis and TME-related independent prognostic markers were screened in this study, and a prognosis risk score formula was established for the first time according to the prognosis PRGs. TME immunocyte infiltration characterization and immune response were assessed using ssGSEA, CIBERSORT algorithm, TIMER, and TISIDB database. Besides a ceRNA network was built up. This study not only laid foundations for further exploring pyroptosis and TME in improving prognosis of GBM, but also provided a new idea for more effective guidance on clinical immunotherapy to patients and develo** new immunotherapeutic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common malignant tumor of the central nervous system [1]. It is characterized by invasive growth and easy recurrence [2]. Recently, despite continuous developments in treatment methods, such as surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy have been reported, the median survival time of patients remains 12–15 months, and no substantial improvement has been achieved yet [29]. Changes in lncRNA expression and its mutation can promote the occurrence and metastasis of tumors [30]. lncRNA plays a key role in TME intracellular signal transduction [31]. GABPB1-AS1 is an lncRNA in the cytoplasm. Recently, many studies have pointed out that lncRNA is a poor prognosis marker of glioma [32], cervical cancer [33], breast cancer [34], and prostate cancer [35]. According to this study, significant differences in GABPB1-AS1 expression was found between tumor and normal tissues. Similarly, Li et al. [36] found high expression of GABPB1-AS1 in the glioma tissues, and in vitro and in vivo experiments have demonstrated that GABPB1-AS1 knockdown reduced the proliferation and invasiveness of glioma cells. According to our results, Hsa-miR-519c-5p can be regulated by GABPB1-AS1 specifically, thus regulating the transcriptional levels of CASP3 and TP63. On this basis, Hsa-miR-519c-5p can control ECM-related signaling pathways (e.g., ECM receptor interaction, adherens junction, and TGFβ signaling pathways) and immune-related signaling pathways (e.g., Toll-like receptor and NOD-like receptor signaling pathways). This demonstrated that ECM and immune inflammation reactions played the key role in occurrence, invasion and metastasis of GBM. The TGF-β in the tumor tissues can inhibit immune cells, decrease local inflammation, and promote the reconstruction of ECM [37]. ECM components and high expression levels on the corresponding cell surface receptors are closely related with the progression of GBM [38]. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) can recognize non-self-molecules and activate the inflammation process. TLR expression had been observed in various samples, such as GBM cases and GBM cell lines, indicating that TLR plays an important role in tumor invasion and metastasis [39]. Therefore, we speculated that the mechanism by which GABPB1-AS1 regulates the transcriptional levels of CASP3 and TP63 and relevant signaling pathways through Hsa-miR-519c-5p might play a crucial role in the occurrence and development of GBM.
Conclusions
In conclusion, pyroptosis and TME-related independent prognostic markers were screened, and a prognosis risk score formula was established for the first time on the basis of prognosis PRGs. TME immunocyte infiltration characterization and immune response were assessed with ssGSEA, CIBERSORT algorithm, TIMER, and TISIDB database. A ceRNA network was then constructed. This study not only laid the foundation for the further exploration of pyroptosis and TME for the improvement of GBM prognosis but also provided novel insights for clinical immunotherapy and development of novel immunotherapeutic drugs. Deep experimental and clinical studies are still needed to elucidate the molecular mechanism of GBM and clinical applications of biomarkers and immunotherapy.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the TCGA (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/), GTEx (https://www.gtexportal.org/), GSEA-MSigDB (http://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/login.jsp), Reactome (https://reactome.org/), Harmonizome (https://maayanlab.cloud/Harmonizome/), R software (version 4.1.1, https://www.r-project.org), STRING (version 11.5, https://string-db.org/), Cytoscape software (version 3.8.2, https://cytoscape.org), Gene Ontology (GO) http://geneontology.org/), KEGG (https://www.kegg.jp/kegg/kegg1.html), TIMER (http://timer.cistrome.org/), TISIDB (http://cis.hku.hk/TISIDB), Starbase (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/), MirTarbase (http://mirtarbase.cuhk.edu.cn/), Oncolnc (http://www.oncolnc.org/), Lncbase (https://carolina.imis.athena-innovation.gr/diana_tools/web/index.php?r=lncbasev2/) and GEPIA2 (http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn/).
References
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P. The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(4):764–72.
Lucki NC, Villa GR, Vergani N, Bollong MJ, Beyer BA, Lee JW, et al. A cell type-selective apoptosis-inducing small molecule for the treatment of brain cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(13):6435–40.
Hu J, **ao Q, Dong M, Guo D, Wu X, Wang B. Glioblastoma immunotherapy targeting the innate immune checkpoint CD47-SIRPα Axis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:593219.
Patel AP, Tirosh I, Trombetta JJ, Shalek AK, Gillespie SM, Wakimoto H, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science. 2014;344(6190):1396–401.
Fang Y, Tian S, Pan Y, Li W, Wang Q, Tang Y, et al. Pyroptosis: a new frontier in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121:109595.
Wang L, Qin X, Liang J, Ge P. Induction of Pyroptosis: a promising strategy for Cancer treatment. Front Oncol. 2021;11:635774.
Tsuchiya K. Switching from apoptosis to Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-elicited inflammation and antitumor immunity. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(1):426.
Kong Y, Feng Z, Chen A, Qi Q, Han M, Wang S, et al. The natural flavonoid Galangin elicits apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and autophagy in glioblastoma. Front Oncol. 2019;9:942.
Ren LW, Li W, Zheng XJ, Liu JY, Yang YH, Li S, et al. Benzimidazoles induce concurrent apoptosis and pyroptosis of human glioblastoma cells via arresting cell cycle. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00752-y.
Jiang M, Qi L, Li L, Li Y. The caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:112.
Dapash M, Hou D, Castro B, Lee-Chang C, Lesniak MS. The interplay between glioblastoma and its microenvironment. Cells. 2021;10(9):2257.
Da Ros M, De Gregorio V, Iorio AL, Giunti L, Guidi M, de Martino M, et al. Glioblastoma Chemoresistance: the double play by microenvironment and blood-brain barrier. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):2879.
Chen Z, Hambardzumyan D. Immune microenvironment in glioblastoma subtypes. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1004.
Broekman ML, Maas SLN, Abels ER, Mempel TR, Krichevsky AM, Breakefield XO. Multidimensional communication in the microenvirons of glioblastoma. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14(8):482–95.
Huang R, Meng T, Chen R, Yan P, Zhang J, Hu P, et al. The construction and analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cell and ceRNA networks in recurrent soft tissue sarcoma. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(22):10116–43.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature. 2008;455(7216):1061–8.
GTEx Consortium. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet. 2013;45(6):580–5.
Gene Ontology Consortium. The gene ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(Database issue):D322–6.
Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):27–30.
Zhang B, Wu Q, Li B, Wang D, Wang L, Zhou YL. m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):53.
**e J, Li H, Chen L, Cao Y, Hu Y, Zhu Z, et al. A novel Pyroptosis-related lncRNA signature for predicting the prognosis of skin cutaneous melanoma. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14:6517–27.
** L, Zhang K, Ou X, Qiu X, **ao X. A novel Pyroptosis-associated long non-coding RNA signature predicts prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment of patients with breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:727183.
Cao Y, **e J, Chen L, Hu Y, Zhai L, Yuan J, et al. Construction and validation of a novel Pyroptosis-related gene signature to predict the prognosis of uveal melanoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:761350.
**e J, Chen L, Tang Q, Wei W, Cao Y, Wu C, et al. A necroptosis-related prognostic model of uveal melanoma was constructed by single-cell sequencing analysis and weighted co-expression network analysis based on public databases. Front Immunol. 2022;13:847624.
DeCordova S, Shastri A, Tsolaki AG, Yasmin H, Klein L, Singh SK, et al. Molecular heterogeneity and immunosuppressive microenvironment in glioblastoma. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1402.
Wang Q, Hu B, Hu X, Kim H, Squatrito M, Scarpace L, et al. Tumor evolution of glioma-intrinsic gene expression subtypes associates with immunological changes in the microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2017;32(1):42–56.e6.
Castriconi R, Daga A, Dondero A, Zona G, Poliani PL, Melotti A, et al. NK cells recognize and kill human glioblastoma cells with stem cell-like properties. J Immunol. 2009;182(6):3530–9.
Lee SJ, Kang WY, Yoon Y, ** JY, Song HJ, Her JH, et al. Natural killer (NK) cells inhibit systemic metastasis of glioblastoma cells and have therapeutic effects against glioblastomas in the brain. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:1011.
Wang J, Su Z, Lu S, Fu W, Liu Z, Jiang X, et al. LncRNA HOXA-AS2 and its molecular mechanisms in human cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;485:229–33.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and Cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017;77(15):3965–81.
Botti G, Scognamiglio G, Aquino G, Liguori G, Cantile M. LncRNA HOTAIR in tumor microenvironment: what role? Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2279.
Luan F, Chen W, Chen M, Yan J, Chen H, Yu H, et al. An autophagy-related long non-coding RNA signature for glioma. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(4):653–67.
Ou R, Lv M, Liu X, Lv J, Zhao J, Zhao Y, et al. HPV16 E6 oncoprotein-induced upregulation of lncRNA GABPB1-AS1 facilitates cervical cancer progression by regulating miR-519e-5p/Notch2 axis. FASEB J. 2020;34(10):13211–23.
Suvanto M, Beesley J, Blomqvist C, Chenevix-Trench G, Khan S, Nevanlinna H. SNPs in lncRNA regions and breast Cancer risk. Front Genet. 2020;11:550.
Alkhateeb A, Rezaeian I, Singireddy S, Cavallo-Medved D, Porter LA, Rueda L. Transcriptomics signature from next-generation sequencing data reveals new transcriptomic biomarkers related to prostate cancer. Cancer Inform. 2019;18:1176935119835522.
Li X, Wang H. Long non-coding RNA GABPB1-AS1 augments malignancy of glioma cells by sequestering MicroRNA-330 and reinforcing the ZNF367/cell cycle signaling pathway. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021;17:2073–87.
Bryukhovetskiy I, Shevchenko V, Arnotskaya N, Kushnir T, Pak O, Victor Z, et al. Transforming growth factor-β mimics the key proteome properties of CD133- differentiated and CD133+ cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2020;151:219–42.
**ao W, Wang S, Zhang R, Sohrabi A, Yu Q, Liu S, et al. Bioengineered scaffolds for 3D culture demonstrate extracellular matrix-mediated mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance in glioblastoma. Matrix Biol. 2020;85-86:128–46.
Moretti IF, Franco DG, de Almeida Galatro TF, Oba-Shinjo SM, Marie SKN. Plasmatic membrane toll-like receptor expressions in human astrocytomas. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0199211.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by Medical Innovation Research Program of Shanghai Municipality (grant number 21Y11920900), and Scientific and Technological Innovation Projects of Longhua Hospital (grant number CX202052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HMA and BH designed the study, coordinated technical support and funding. BH revised the manuscript. MRD performed the study and drafted the manuscript. YJQ, XP, JFC, MXZ and TZ participated the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Correlation analysis of prognostic PRGs expression with immunocyte levels in TIMER database.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, MR., Qu, YJ., Peng, X. et al. Pyroptosis-related prognosis model, immunocyte infiltration characterization, and competing endogenous RNA network of glioblastoma. BMC Cancer 22, 611 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09706-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09706-x