Abstract
Background
Chromium (Cr) contamination in soil poses a serious hazard because it hinders plant growth, which eventually reduces crop yield and raises the possibility of a food shortage. Cr’s harmful effects interfere with crucial plant functions like photosynthesis and respiration, reducing energy output, causing oxidative stress, and interfering with nutrient intake. In this study, the negative effects of Cr on mung beans are examined, as well as investigate the effectiveness of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid in reducing Cr-induced stress.
Results
We investigated how different Cr levels (200, 300, and 400 mg/kg soil) affected the growth of mung bean seedlings with the use of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid. Experiment was conducted with randomized complete block design with 13 treatments having three replications. Significant growth retardation was caused by Cr, as were important factors like shoot and root length, plant height, dry weight, and chlorophyll content significantly reduced. 37.15% plant height, 71.85% root length, 57.09% chlorophyll contents, 82.34% crop growth rate was decreased when Cr toxicity was @ 50 µM but this decrease was remain 27.80%, 44.70%, 38.97% and 63.42%, respectively when applied A. brasilense and Salicylic acid in combine form. Use of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid significantly increased mung bean seedling growth (49%) and contributed to reducing the toxic effect of Cr stress (34% and 14% in plant height, respectively) due to their beneficial properties in promoting plant growth.
Conclusions
Mung bean seedlings are severely damaged by Cr contamination, which limits their growth and physiological characteristics. Using Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid together appears to be a viable way to combat stress brought on by Cr and promote general plant growth. Greater nutrient intake, increased antioxidant enzyme activity, and greater root growth are examples of synergistic effects. This strategy has the ability to reduce oxidative stress brought on by chromium, enhancing plant resistance to adverse circumstances. The study offers new perspectives on sustainable practices that hold potential for increasing agricultural output and guaranteeing food security.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The sixth most common transition metal and the seventh most prevalent element in the earth’s crust is chromium (Cr) [1]. Due to the weathering of the earth’s crust and the deposition of waste from industrial operations, including the chemical (leather, pigments, electroplating, and other industries) and metallurgical (mostly steel and metal) sectors, it is present in the environment [2]. Environmental conditions severally effect on the growth and development of the plants [3, 7]. Due to their abundance in protein, certain minerals, vitamins, and calories, pulse crops are considered nutritional crops for the consumption of human beings, and mung bean can be eaten in a variety of ways boiled, fried, sprouted, and in powdered form, and most nutrient dense form of mung bean is mung bean sprout, which has greater than 200% more protein than other consumable forms. 100-gram mung bean sprouts have a nutritional content of 7 g of protein, 18 g of carbohydrate portion, 0.026 g of sodium, 24 gram of fat, 0.0029gram of calcium, and 103.5 calories and other significant vitamins [8]. Mung bean is the 2nd largest cultivated crop in Pakistan after chickpea. It is planted as a cash crop in summer and spring season. Mung bean cultivated on 0.25 million hectares of land with the annual production of 178 tones and averaged yield of this crop is around 515 kg/ha [9].
Inoculating plants with Azospirillum, which principally stimulates plant root development, may help to boost and stabilize crop yield. Although they have been carried out on various crops and in various regions, evaluations of Azospirillum’s effectiveness under current cultivation practices and at typical environmental conditions are rare [10]. Under field conditions, Azospirillum brasilense can colonize hundreds of plant species and significantly enhance their growth, development, and efficiency. The most researched observed the mechanism for Azospirillum to promote plant growth in inoculated plants, in addition to nitrogen fixation, has been linked to its capacity to produce a number of phytohormones, primarily auxins and particularly indole-3-acetic acid [11], abscisic acid (ABA), polyamines, ethylene, and nitric oxide [12]. Under controlled agronomic conditions, Azospirillum brasilense can colonize the soil rhizosphere and in the internal tissues of many plants that directly enhancing their proliferation, development, and yield. Azospirillum has both direct and indirect effects on plant development. Increases in the bioavailability of nutrients for plants (such as nitrogen, phosphorus, iron, and potassium) or the creation of enzymes and plant growth regulators (phytohormones) are examples of direct methods. Plant resistance to infections and tolerance to abiotic stress are two examples of indirect processes [13]. Under abiotic stress conditions, SA’s ability to restore growth is correlated with its impact on physiological aspects of the plant, including water content, nutrient uptake, synthesis of chlorophyll pigments, growth, stomatal regulation, suppression of ethylene biosynthesis, hormonal profile regulation, and protein kinas synthesis [14]. In extremely modest amounts, SA is an endogenous growth regulator that occurs naturally in plants [15]. There is a need to assess the impact of metals such chromium on the crop production and the impact on important cash crops of Pakistan. The impact of chromium on the mung bean’s germination and growth efficiency is poorly understood. The current study planned to evaluate the impact of differing chromium concentrations on seed germination and plant growth performance. We hypothesized that the combine application of A. brasilense and SA might have the positive impact on mung bean under Cr toxicity and can improve the plant growth. This study explores a novel approach to enhance plant tolerance to heavy metal stress by using combine application of A. brasilense and a natural plant hormone (CA), providing valuable insights into sustainable agricultural practices for managing metal-contaminated soils.
Materials and methods
Experimental design
An approved mung bean variety “PRI Mung-2018” seeds were obtained from the Pulses Research Institute, Faisalabad for research. Six mung bean seeds were planted in a clay pot at a depth of 10 cm, containing 2 kg of that soil that had been carefully rinsed and dried to examine the effects of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid on mung bean plants under chromium-contaminated soil. To create the chromium toxicity, Soil was contaminated with the chromium compound {potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7)} @200, 300, and 400 mg/kg of the soil as per the treatments. Cr was applied in the soil 5 days before the sowing and uniformly mixed in each pot. Soil sampling and analysis are represented in Table 1. Azospirillum brasilense (FCBP-SB0025) (B3) pure culture was obtained from the Fungal Culture Bank of Pakistan (FCBP) at the Faculty of Agriculture Sciences, University of Punjab, Lahore. A total of 39 plastic pots were arranged in three replications of 13 treatment combinations using randomized block design (RBD) in a greenhouse at the Botanical Garden, Government College, University of Lahore. The greenhouse environment includes controlled temperature (often 20–30 °C), relative humidity (commonly 50–70%), photoperiod (12–16 h of light), and additional lighting to promote optimal plant growth, producing a space suited for study and experimentation. The pot trial was performed from March 28 to April 27, 2022, in a greenhouse.
Parameters studied
Plant height, shoot root length, fresh and dry weight
Measuring the vertical plant height from the base to the tallest shoot tip is the first step in gathering information on “Plant height, shoot root length, fresh and dry weight” in mung bean plants. Measure the longest root and main stem, respectively, to determine the length of the shoot. Immediately weigh the entire uprooted plant to determine its fresh weight. Dry the plant in an oven to determine dry weight, and then weigh it once it has reached a steady weight. The plant dry weight was determined by drying the 3 tallest plants from each replicate for each concentration, were dried in a hot air oven at 60 °C for 48 h. Repeat the procedure for numerous plants in each treatment, using averages to improve data accuracy. All the relevant data was collected after 1 month of the seed germination.
Crop growth rate (CGR)
Crop growth rate was noticed by the following formula as reported by Karimi and Siddique [16].
Where:
W2: Final dry weight of the crop (grams per square meter)
W1: Initial dry weight of the crop (grams per square meter)
t2: Final time (days)
t1: Initial time (days)
Chlorophyll contents and relative water contents
Chlorophyll contents (a, b, and total) were also estimated by using the procedure described by Arnon [17]. Relative water content in the leaf was noticed by Barrand Weatherley’s equation [18] as follows,
5 g of fresh leaves were acquired, and they were mashed in a pestle and mortar with 80% acetone to detect the chlorophyll a and b. After being ground, each sample was boosted in volume by 10 mL using acetone before being centrifuged for five minutes at 4000 rpm. This sample’s absorbance was determined using a UV/visible spectrophotometer (Spectro scan 80D, Kyoto, Japan) at 663 and 645 nm. The following formulas were used to determine the concentrations of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total chlorophyll as reported by Du et al. [19]:
Where A665 and A652 are the absorbance figures discovered through spectrophotometric analysis at the appropriate wavelengths.
Enzymatic activities
Harvesting plant tissue and making a homogenised extract in a cold buffer solution are the first steps in measuring the activity of various enzymes in mung bean plants, such as catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), peroxidase (POD), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). 240 nm hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) breakdowns should be observed for catalase, and enzyme activity should be calculated based on the change in absorbance. By detecting the ascorbate’s reduction by H2O2 at 290 nm, one can measure the activity of ascorbate peroxidase. Track the oxidation of the substrate (such as guaiacol) in the presence of H2O2 to determine the activity of the peroxidase. Determine the superoxide dismutase’s ability to prevent the photoreduction of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) at 560 nm and express activity in accordance with that finding. Ensuring correct reporting of enzyme activity per gramme of fresh or dry plant tissue weight. Ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT), Peroxidase (POD), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities were noticed according to the Nakano and Asada [20], Vanacker et al. [21], Ghanati et al. [22], and Beyer and Fridovich [23], respectively. All local, national or international guidelines and legislation were adhered to for the use of plants in this study.
Statistical analysis
All data was analyzed at a 95% probability level by using Fisher’s test, and least significant difference (LSD) with the use of Statistix 8.1 computer software.
Results
Effect of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid on growth related parameters of mung bean under chromium toxicity
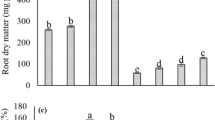
Chromium (Cr) toxicity showed the significant negative effect on the mung bean seedlings Highest plant height, shoot length, root length, shoot fresh weight, root fresh weight, shoot dry weight and root dry weight was noticed in T1 under control condition when no Cr stress was applied having no soil amendment. Highest plant height (32.22 cm), shoot length (21.07 cm), root length (11.05 cm), shoot fresh weight (16.64 g), root fresh weight (1.01 g), shoot dry weight (9.82 g) and root dry weight (0.65 g) was noticed in T1 under control condition when no Cr stress was applied having no soil amendment followed by T5 (plant height: 30.18 cm, shoot length: 19.43 cm, root length: 9.02 cm, shoot fresh weight: 13.41 g, root fresh weight: 0.96 g, shoot dry weight: 8.43 g and root dry weight: 0.60 g, respectively) when Cr toxicity was 200 mg/kg of soil having seed inoculation of A. brasilense and foliar application of SA. Lowest results were noticed in T10 (plant height: 20.25 cm, shoot length: 11.13 cm, root length: 3.11 cm, shoot fresh weight: 6.12 g, root fresh weight: 0.68 g, shoot dry weight: 3.02 g and root dry weight: 0.13 g, respectively) when Cr toxicity was 400 mg/kg soil having no amendment (Table 2).
Effect of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid on chlorophyll contents of mung bean under chromium toxicity
Data regarding the chlorophyll contents shows that all studied treatments significantly effected on the chlorophyll contents (Table 2). Highest chlorophyll a (2.15 mg/ml), b (1.16 mg/ml) and total chlorophyll contents (3.31 mg/ml) were noticed in T1 under control conditions having no toxicity followed by T5 (chlorophyll a: 2.09 mg/ml, chlorophyll b:1.12 mg/ml and total chlorophyll: 3.21 mg/ml, respectively) when Cr toxicity was @200 mg/kg of soil with the combine application of A. brasilense and SA. Lowest results (chlorophyll a: 0.81 mg/ml, chlorophyll b: 061 mg/ml and total chlorophyll: 1.42 mg/ml, respectively) were noticed in T10 when Cr toxicity was @ 400 mg/kg of soil having no amendment.
Effect of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid on enzymatic activities of mung bean under chromium toxicity
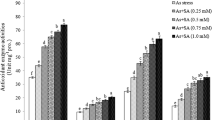
Enzymatic activities of mung bean were significantly affected by the application of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid under chromium toxicity (Table 3). Higher negative effects were noticed with the increase of Cr toxicity and combine application of A. brasilense and SA is effective to control their negative effect. Highest CAT (Catalase), APX (Ascorbate peroxidase), POD (peroxidase) and SOD (superoxide dismutase) activities was noticed in T1 (CAT: 1.32 units/mg of protein, APX: 4.52 units/mg of protein, POD: 0.82 units/mg of protein, SOD: 4.01 units/mg of protein) followed by T5 (CAT: 1.21 units/mg of protein, APX: 4.20 units/mg of protein, POD: 0.71 units/mg of protein, SOD: 3.81 units/mg of protein) and lowest results were seen in T10 (CAT: 0.68 units/mg of protein, APX: 1.22 units/mg of protein, POD: 0.08 units/mg of protein, SOD: 2.62 units/mg of protein).
Enzymatic activities of mung bean were significantly affected by the application of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid under chromium toxicity (Table 3). Higher negative effects were noticed with the increase of Cr toxicity and combine application of A. brasilense and SA is effective to control their negative effect. Highest CAT (Catalase), APX (Ascorbate peroxidase), POD (peroxidase) and SOD (superoxide dismutase) activities was noticed in T1 (CAT: 1.32 units/mg of protein, APX: 4.52 units/mg of protein, POD: 0.82 units/mg of protein, SOD: 4.01 units/mg of protein) followed by T5 (CAT: 1.21 units/mg of protein, APX: 4.20 units/mg of protein, POD: 0.71 units/mg of protein, SOD: 3.81 units/mg of protein) and lowest results were seen in T10 (CAT: 0.68 units/mg of protein, APX: 1.22 units/mg of protein, POD: 0.08 units/mg of protein, SOD: 2.62 units/mg of protein).
Effect of Azospirillum brasilense and salicylic acid on relative water content (RWC) and crop growth rate (CGR) of mung bean under chromium toxicity
Relative water content (RWC) significantly affected by all studied treatments (Fig. 1). Highest RWC was noticed in T1 (75.15%) under control condition followed by T5 (69.57%) when Cr toxicity was @200 mg/kg of soil with A. brasilense and SA. Lowest RWC were noticed in T10 (27.64) when Cr toxicity was @ 400 mg/kg of soil having no soil amendment. Crop growth rate (CGR) also affected by the application of A. brasilense and SA under Cr toxicity (Fig. 2). Highest CGR was noticed in T1 (8.12 g m−2 day−1) followed by T5 (7.52 g m−2 day−1) and lowest CGR was observed in T10 (1.43 g m−2 day−1).
Discussion
Variety of growth parameters in mung bean plants were examined in our study, including plant height, shoot and root length, root-shoot dry and fresh weights, chlorophyll content, enzymatic activities, relative water content (RWC), and crop growth rate. Salicylic acid (SA) and Azospirillum brasilense have the significant impact on all studied treatments and can improve the growth under Chromium (Cr) toxicity. Environmental conditions severally effect on the growth and development of the plants [3, 46]. As a result of Azospirillum brasilense promotion of root growth, plants are better able to reach water in deeper soil layers, which improves overall water intake and leads to enhanced RWC [31]. Plants are able to better utilize water resources for growth and stress adaption thanks to the increased nutrient availability brought on by Azospirillum inoculation, thus boosting RWC and CGR. SA and A. brasilense work together to maximize water use, improving both RWC and CGR and enabling mung bean plants [28, 29].
Conclusion
Chromium stress has a negative effect on growth and productivity of mung bean but seed inoculation of Azospirillum brasilense and foliar application of salicylic acid together mitigate the adverse effect of Cr stress. Higher Cr toxicity has the higher negative effect. Sole application of A. brasilense and SA is effective to improve the mung bean growth but it is not enough to control negative effect of Cr toxicity. Combine application of A. brasilense and SA is more effective to mitigate the negative effect of Cr toxicity. Use of A. brasilense and SA is very effective for sustainable crop production even under adverse environmental conditions. In future, there is need to investigate and make an approach with the use of A. brasilense and SA by which farmers can get fully control on Cr toxicity.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bibi M, Khan S, Khan N, Tareen AH, Bibi S, Taj H. Determination of essential and non-essential elements in Xylanthemum macropodum of Balochistan, Pakistan. Baghdad J Biochem Appl Biol Sci. 2021;2(02):94–103.
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Mol Clin Environ Toxicol. 2012;101:133–64.
Yan Y, Jarvie S, Liu Q, Zhang Q. Effects of fragmentation on grassland plant diversity depend on the habitat specialization of species. Biol Conserv. 2022;275: 109773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2022.109773.
Huang W, Wang X, Zhang J, **a J, Zhang X. Improvement of blueberry freshness prediction based on machine learning and multi-source sensing in the cold chain logistics. Food Control. 2023;145: 109496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109496.
Velma V, Vutukuru SS, Tchounwou PB. Ecotoxicology of hexavalent chromium in freshwater fish: a critical review. Rev Environ Health. 2009;24(2):129–46.
Murtaza S, Iqbal MZ, Shafiq M, Kabir M, Farooq ZUR. Effects of chromium on seed germination and seedling growth of Mung Bean Vigna Radiata (L.) R. Wilczek (Fabaceae). Res J life Sci Bioinf Pharm Chem Sci. 2018;4(6):357–64.
Wang L, Bai P, Yuan X, Chen H, Wang S, Chen X, Cheng X. Genetic diversity assessment of a set of introduced mung bean accessions (Vigna radiata L). Crop J. 2018;6(2):207–13.
Hanif M, Khattak MK, Haq U, Gul I, Khan K, Ullah A, Ali K. Effects of temperature and water purity on germination and yield of mungbean sprouts. Sains Malaysiana. 2019;48(4):711–7.
Habib N, Anwar MZ, Saeed I. Comparative profitability analysis of recommended mungbean varieties at narc experimental station Islamabad Pakistan. Pak J Agric Res. 2014;27:8–14.
Okon Y, Labandera-Gonzales C, Lage M, Lage P. Agronomic applications of Azospirillum and other PGPR. Biological nitrogen fixation. New Jersey: John Wiley; 2015. p. 921–33.
Coniglio A, Mora V, Puente M, Cassán F. Azospirillum as biofertilizer for sustainable agriculture: Azospirillum brasilense AZ39 as a model of PGPR and field traceability. In: Microbial Probiotics for Agricultural Systems. Cham: Springer; 2019. p. 45–70.
Molina-Favero C, Creus CM, Lanteri ML, Correa‐Aragunde N, Lombardo MC, Barassi CA, Lamattina L. Nitric oxide and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: common features influencing root growth and development. Adv Bot Res. 2007;46:1–33.
Glick BR. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica. 2012;2012:963401.
Es-sbihi FZ, Hazzoumi Z, Amrani Joutei K. Effect of salicylic acid foliar application on growth, glandular hairs and essential oil yield in Salvia officinalis L. grown under zinc stress. Chem Biol Technol Agric. 2020;7(1):1–11.
Tamás L, Mistrík I, Alemayehu A, Zelinová V, Bočová B, Huttová J. Salicylic acid alleviates cadmium-induced stress responses through the inhibition of Cd-induced auxin-mediated reactive oxygen species production in barley root tips. J Plant Physiol. 2015;173:1–8.
Karimi MM, Siddique KHM. Crop growth and relative growth rates of old and modern wheat cultivars. Aust J Agric Res. 1991;42:13–20.
Arnon DI. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949;24(1): 1.
Barrs HD, Weatherley PE. A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficit in leaves. Australian J Biol Sci. 1962;15:413–28.
Du E, Dong D, Zeng X, Sun Z, Jiang X, de Vries W. Direct effect of acid rain on leaf chlorophyll content of terrestrial plants in China. Sci Total Environ. 2017;605:764–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.044.
Nakano Y, Asada K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981;22(5):867–80.
Vanacker H, Carver TLW, Foyer CM. Early H2O2 accumulation in mesophyll cells leads to induction of glutathione during the hyper sensitive response in the barley-powdery mildew interaction. Plant Physiol. 2000;123:1289–300.
Ghanati F, Morita A, Yokota H. Induction of suberin and increase of lignin content by excess boron in tabacco cell. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2002;48:357–64.
Beyer WF, Fridovich I. Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Anal Biochem. 1987;161:559–66.
Zhang Y, **ao X, Feng H, Nikitina M, **aoshuan Z, Zhao Q. Stress Fusion Evaluation Modeling and Verification Based on Noninvasive Blood Glucose Biosensor for Live Fish Waterless Transportation. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems. 2023;7:1172522. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2023.1172522.
Méndez-Gómez M, Castro-Mercado E, Alexandre G, García-Pineda E. Superoxide anion production in the interaction of wheat roots and rhizobacteria Azospirillum brasilense Sp245. Plant Soil. 2015;400:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2709-9.
Lu H. Dissection of salicylic acid-mediated defense signaling networks. Plant Signal Behav. 2009;4:713–7. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.4.8.9173.
Agnihotri A, Gupta P, Dwivedi A, Seth CS. Counteractive mechanism (s) of salicylic acid in response to lead toxicity in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. Cv. Varuna. Planta. 2018;248:49–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2867-0.
El-Ballat EM, Elsilk SE, Ali HM, Ali HE, Hano C, El-Esawi MA. Metal-resistant PGPR strain Azospirillum brasilense EMCC1454 enhances growth and chromium stress tolerance of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by modulating Redox Potential, Osmolytes, antioxidants, and stress-related gene expression. Plants. 2023;12: 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112110.
Huda AKMN, Swaraz AM, Reza MA, Haque MA, Kabir AH. Remediation of Chromium Toxicity through Exogenous Salicylic Acid in Rice (Oryza sativa L). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016;227:278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2985-x.
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Ok YS. Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2016;23:17859–79.
Zaheer MS, Raza MAS, Saleem MF, Khan IH, Ahmad S, Iqbal R, Manevski K. Investigating the effect of Azospirillum brasilense and Rhizobium pisi on agronomic traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Arch Agron Soil Sci. 2019;65:1554–64.
Husain T, Suhel M, Prasad SM, Singh VP. Ethylene and hydrogen sulphide are essential for mitigating hexavalent chromium stress in two pulse crops. Plant Biol. 2022;24(4):652–9.
Martínez-Ballesta MDC, Egea-Gilabert C, Conesa E, Ochoa J, Vicente MJ, Franco JA, Fernández JA. The importance of ion homeostasis and nutrient status in seed development and germination. Agronomy. 2020;10(4): 504.
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA, Oves M. Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in the remediation of metal contaminated soils. Environ Chem Lett. 2009;7:1–19.
Gill RA, Zhang N, Ali B, Farooq MA, Xu J, Gill MB, … Zhou W. Role of exogenous salicylic acid in regulating physio-morphic and molecular changes under chromium toxicity in black- and yellow- seeded Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2016;23:20483–20496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7167-2.
Kashif M, Sang Y, Mo S, Rehman SU, Khan S, Khan MR, et al. Deciphering the biodesulfurization pathway employing marine mangrove Bacillus aryabhattai strain NM1-A2 according to whole genome sequencing and transcriptome analyses. Genomics. 2023;115(3):110635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110635.
Yadav M, Gupta P, Seth CS. Foliar application of α-lipoic acid attenuates cadmium toxicity on photosynthetic pigments and nitrogen metabolism in Solanum lycopersicum L. Acta Physiol Plant. 2022;44:112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03445-z.
Kumar D, Dhankher OP, Tripathi RD, Seth CS. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles potentially regulate the mechanism(s) for photosynthetic attributes, genotoxicity, antioxidants defense machinery, and phytochelatins synthesis in relation to hexavalent chromium toxicity in Helianthus annuus L. J Hazard Mater. 2023;454: 131418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131418.
Kumar D, Seth CS. Photosynthesis, lipid peroxidation, and antioxidative responses of Helianthus annuus L. against chromium (VI) accumulation. Int J Phytoremediation. 2021;24:590–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1958747.
Gupta S, Seth CS. Salicylic acid alleviates chromium (VI) toxicity by restricting its uptake, improving photosynthesis and augmenting antioxidant defense in Solanum lycopersicum L. Physiol Mol Biology Plants. 2021;27:2651–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01088-x.
Zhang Q, Cheng Z, Wang Y, Fu L. Dietary protein-phenolic interactions: characterization, biochemical-physiological consequences, and potential food applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61:3589–615. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1803199.
Hayes JD, McLellan LI. Glutathione and glutathione-dependent enzymes represent a co-ordinately regulated defence against oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 1999;31:273–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715769900300851.
Lu L, Zhai X, Li X, Wang S, Zhang L, Wang L,… Wang F. Met1-specific motifs conserved in OTUB subfamily of green plants enable rice OTUB1 to hydrolyse Met1 ubiquitin chains. Nat Commun. 2022;13:4672. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32364-3.
Herrera-Vasquez A, Salinas P, Holuigue L. Salicylic acid and reactive oxygen species interplay in the transcriptional control of defense genes expression. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:171. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00171.
Mariyam S, Bhardwaj R, Khan NA, Sahi SV, Seth CS. Review on nitric oxide at the forefront of rapid systemic signaling in mitigation of salinity stress in plants: crosstalk with calcium and hydrogen peroxide. Plant Sci. 2023;336: 111835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111835.
**dal A, Seth CS. Nitric oxide mediated post-translational modifications and its significance in plants under abiotic stress. In: Nitric Oxide in Develo** Plant Stress Resilience. 2023. p. 233–250. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-91209-9.00006-3.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R941), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Statement of ethical approval in compliance with institutional, national, or international guidelines for using animals
All local, national or international guidelines and legislation were adhered to for the use of plants in this study.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R941), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.H.A, M.S.Z. supervised the experiment, W.HU.D.K and M.I. conduct whole experiment and write the initial manuscript, A.H., K.I and R.I. validate the results and T.H.A. improve technical language of the manuscript, M.R. and A.E.M.A.M. review the manuscript and write the discussion, M.S.E. and M.S.Z. do the data interpretation and provide the resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
An approved “PRI Mung-2018” mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) a cultivated variety seeds were obtained from the Pulses Research Institute, Faisalabad for research. All local, national or international guidelines and legislation were adhered to for the use of plants in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, H.H., Ilyas, M., Zaheer, M.S. et al. Alleviation of chromium toxicity in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) using salicylic acid and Azospirillum brasilense. BMC Plant Biol 23, 535 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04528-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04528-w