Abstract
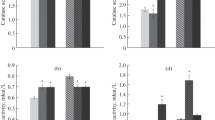
The effect of treatment of wheat seeds with a suspension culture of cells of endophytic bacteria of the strain Bacillus subtilis 26D and lines B. subtilis 26D+n, selected for tolerance to crude oil components, on the growth and biochemical characteristics of wheat plants Triticum aestivum L. in conditions of oil pollution of the soil was studied. It has been shown that seed inoculation with the line B. subtilis 26D+n stimulated the growth of seedlings and suppressed the development of oxidative stress under conditions of exposure to oil pollution in plants in comparison with the control and plants inoculated with the strain B. subtilis 26D. Accordingly, bacteria B. subtilis 26D+n contributed to more successful growth of wheat plants on oil-contaminated soils, which can be used to stimulate the growth of plants in such areas and to return some of them to economic circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Odukoya, J., Lambert, R., and Sakrabani, R., Understanding the impacts of crude oil and its induced abiotic stresses on agrifood production: A review, Horticulturae, 2019, vol. 5, p. 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae5020047
Alotaibi, F., St-Arnaud, M., and Hijri, M., In-depth characterization of plant growth promotion potentials of selected alkanes-degrading plant growth-promoting bacterial isolates, Front. Microbiol., 2022, vol. 13, p. 863702. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.863702
Kanwal, M., Ullah, H., Gulzar, A., Sadiq, T., Gul, Z., Ullah, M., Sarfraz, M., Aslam, M.A., Khan, N.N., Batool, T., Maqsood, S., and Nawaz, A., Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons and the factors effecting rate of biodegradation, Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res., 2022, vol. 16, p. 6 https://doi.org/10.34297/ajbsr.2022.16.002182
Da Silva Correa, H., Blum, C.T., Galvão, F., and Maraho, L.T., Effects of oil contamination on plant growth and development: a review, Environ. Sci Pollut. Res., 2022, vol. 29, p. 43501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19939-9
Arellano, P., Tansey, K., Balzter, H., and Tellkamp, M., Plant family-specific impacts of petroleum pollution on biodiversity and leaf chlorophyll content in the amazon rainforest of Ecuador, PLoS ONE, 2017, vol. 12, p. e0169867. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169867
Lumactud, R., Shen, S.Y., Lau, M., and Fulthorpe, R., Bacterial endophytes isolated from plants in natural oil seep soils with chronic hydrocarbon contamination, Front. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 7, p. 755. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00755
Pawlik, M., Płociniczak, T., Thijs, S., Pintelon, I., Vangronsveld, J., and Piotrowska-Seget, Z., Comparison of two inoculation methods of endophytic bacteria to enhance phytodegradation efficacy of an aged petroleum hydrocarbons polluted soil, Agronomy, 2020, vol. 10, p. 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081196
Hwang, H.H., Chien, P.R., Huang, F.C., Yeh, P.H., Hung, S.H.W., Deng, W.L., and Huang, C.C., A plant endophytic bacterium Priestia megaterium strain BP-R2 isolated from the halophyte Bolboschoenus planiculmis enhances plant growth under salt and drought stresses, Microorganisms, 2022, vol. 10, p. 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102047
Ha-Tran, D.M., Nguyen, T.T.M., Hung, S.H., Huang, E., and Huang, C.C., Roles of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in stimulating salinity stress defense in plants: A review, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, vol. 2, p. 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063154
Mohammadipanah, F. and Zamanzadeh, M., Bacterial mechanisms promoting the tolerance to drought stress in plants, in: Secondary metabolites of plant growth promoting rhizomicroorganisms, Singh, H., , Eds., Springer: Singapore, 2019, p. 185. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-5862-3_10
Fadiji, A.E. and Babalola, O.O., Elucidating mechanisms of endophytes used in plant protection and other bioactivities with multifunctional prospects, Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 2020, vol. 8, p. 467. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00467
Zakharchenko, M.V., Lyushin, M.M., and Mustafina, E.A., Metal compounds in oils from Orenburg deposits, Neftegazokhim., 2016, vol. 1, p. 61.
Workshop On Microbiology, Netrusova, A.I., Ed., Moscow: Academy, 2005.
Veselova, S.V., Burkhanova, G.F., Nuzhnaya, T.V., and Maksimov, I.V., Roles of ethylene and cytokinins in development of defense responses in Triticum aestivum plants infected with Septoria nodorum, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2016, vol. 63, p. 609.https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443716050150
Bradford, M.M., A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem., 1972, vol. 72, p. 248. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Costa, H., Gallego, S.M., and Tomaro, M.L., Effect of UV-B radiation on antioxidant defense system in sunflower cotyledons, Plant Sci., 2002, vol. 162, p. 939.
Shikhaleeva, G.N., Budnyak, A.K., Shikhaleev, I.I., and Ivashchenko, O.L., Modified method for the determination of proline in plant objects, Bull. Kharkiv Nat. Univ. Ser. Biol., 2014, vol. 21, p. 168.
Kuramshina, Z.M., Khairullin, R.M., and Smirnova, Yu.V., Varietal responsiveness of Triticum aestivum L. to inoculation with cells of endophytic strains of Bacillus subtilis, Rus. Agric. Sci., 2019, vol. 6, p. 3. https://doi.org/10.31857/S2500-2627201963-6
Kuramshina, Z.M. and Khairullin, R.M., Endophytic strains of Bacillus subtilis promote drought resistance of plants, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2023, vol. 70 (45), p. 259. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443722603172
Kuramshina, Z.M. and Khairullin, R.M., Improving salt stress tolerance of Triticum aestivum L. with endophytic strains of Bacillus subtilis, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2023, vol. 70 (53), p. 293. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443722603068
Ziółkowska, A. and Wyszkowski, M., Toxicity of petroleum substances to microorganisms and plants, Ecol. Chem. Eng. S., 2010, vol. 17, p. 73.
da Silva Correa, H., Blum, C.T., Galvão, F., and Maranho, L.T., Effects of oil contamination on plant growth and development: a review, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2022, vol. 29, p. 43501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19939-9
Hidalgo, K.J., Sierra-Garcia, I.N., Dellagnezze, B.M., and de Oliveira, V.M., Metagenomic insights into the mechanisms for biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the oil supply chain, Front. Microbiol., 2020, vol. 11, p. 561506. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.561506
Pawlik, M., Cania, B., Thijs, S., Vangronsveld, J., and Piotrowska-Seget, Z., Hydrocarbon degradation potential and plant growth-promoting activity of culturable endophytic bacteria of Lotus corniculatus and Oenothera biennis from a long-term polluted site, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2017, vol. 24, p. 19640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9496-1
Antoszewski, M., Mierek-Adamska, A., and Dąbrowska, G.B., The Importance of microorganisms for sustainable agriculture-a review, Metabolites, 2022, vol. 12, p. 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111100
Mitter, E. R.K., Kataoka, R., de Freitas, J. R., and Germida, J.J., Potential use of endophytic root bacteria and host plants to degrade hydrocarbons, Int. J. Phytoremediation, 2019, vol. 21, p. 9. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1583637
Liu, Y., Morelli, M., Koskimäki, J.J., Qin, S., Zhu, Y.-H., Zhang, X.X., Editorial: Role of endophytic bacteria in improving plant stress resistance, Front. Plant Sci., 2022, vol. 13, p. 1106701. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1106701
Gkorezis, P., Daghio, M., Franzetti, A., Van Hamme, J.D., Sillen, W., and Vangronsveld, J., The interaction between plants and bacteria in the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbons: An environmental perspective, Front. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 7, p. 1836. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01836
Kuramshina, Z.M., Smirnova, Y.V., and Khairullin, R.M., Increasing Triticum aestivum tolerance to cadmium stress through endophytic strains of Bacillus subtilis, Russ. J. Plant. Physiol., 2016, vol. 63, p. 636. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443716050083
Marchut‑Mikolajczyk, O., Drożdżyński, P., Pietrzyk1, D., and Antczak, T., Biosurfactant production and hydrocarbon degradation activity of endophytic bacteria isolated from Chelidonium majus L., Microb. Cell Fact., 2018, vol. 17, p. 171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1017-5
Peele, A., Vekateswarulu, T.C. Tammineedi, J., Kanumuri, L., Ravuru, B.K., Dirisala, V.R., Kodali, V.P., Role of biosurfactants in bioremediation of oil pollution—a review, Petroleum, 2018, vol. 4, p. 241.
Cherepanova, E.A., Galyautdinov, I.V., Burkhanova, G.F., and Maksimov, I.V., Isolation and identification of lipopeptides of Bacillus subtilis 26D strain, Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol., 2021, vol. 57, p. 496. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0555109921050032
Maksimov, I.V., Singh, B.P., Cherepanova, E.A. Burkhanova, G.F., and Khairullin, R.M., Prospects and applications of lipopeptide-producing bacteria for plant protection (Review), Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2020, vol. 56, p. 15. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683820010135
Sorokan, A., Veselova, S., Benkovskaya, G., and Maksimov, I., Endophytic strain Bacillus subtilis 26D increases levels of phytohormones and repairs growth of potato plants after colorado potato beetle damage, Plants, 2021, vol. 10, p. 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050923
Nafikova, A.R., Surina, O.B., Khairullin, R.M., and Maksimov, I.V., Influence of metabolites of Bacillus subtilis strains 26D and 11VM on the growth of seedlings and calli of wheat, Agrokhimiya, 2018, vol. 5, p. 39. https://doi.org/10.7868/s000218811805006x
Le Mire, G., Siah, A., Brisset, M.-N., Gaucher, M., Deleu, M., Jijakli, M.H., Surfactin protects wheat against Zymoseptoria tritici and activates both salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-dependent defense responses, Agriculture, 2018, vol. 8, p. 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture8010011
Pršic, J. and Ongena, M., Elicitors of plant immunity triggered by beneficial bacteria, Front. Plant Sci., 2022, vol. 11, p. 594530. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.594530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS STATEMENT ON THE WELFARE OF ANIMALS
This article does not contain any studies involving humans and animals as research subjects.
Additional information
Abbreviations: PO, peroxidase; CAT, catalase.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuramshina, Z.M., Sattarova, L.R. & Maksimov, I.V. Increasing the Resistance of Wheat to Oil Pollution Using Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus subtilis. Russ J Plant Physiol 70, 124 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443723700188
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443723700188