Abstract
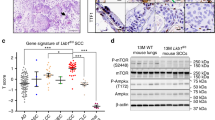
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1), encoded by TNFRSF1A, is a critical transducer of inflammatory pathways, but its physiological role in human cancer is not completely understood. Here, we observed high expression of TNFR1 in many human lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCCs) samples and in spontaneous lung SCCs derived from kinase-dead Ikkα knock-in (KA/KA) mice. Knocking out Tnfrf1a in KA/KA mice blocked lung SCC formation. When injected via tail vein, KALLU+ lung SCC cells that highly expressed TNFR1/TNF, Sox2, c-Myc, Twist1, Bcl2, and UBCH10, generated dedifferentiated spindle cell carcinomas with epithelial–mesenchymal transition markers in mouse lungs. In contrast, KALLU+ cells with silenced TNFR1 and KALLU- cells that expressed low levels of TNFR1 generated well-differentiated lung SCCs and were less tumorigenic and metastatic. We identified a downstream effector of TNFR1: oncogenic UBCH10, an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme with targets including Twist1, c-Myc, and Sox2, which enhanced SCC cell dedifferentiation. Furthermore, Tg-K5.TNFR1;KA/KA mice, which expressed transgenic TNFR1 in keratin 5-positve epithelial cells, developed more poorly differentiated and metastatic lung SCCs than those found in KA/KA mice. These findings demonstrate that an overexpressed TNFR1–UBCH10 axis advances lung carcinogenesis and metastasis through a dedifferentiation mechanism. Constituents in this pathway may contribute to the development of differentiation-related therapies for lung SCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Lung cancer confers the highest cancer mortality rate worldwide. Two major types of lung cancer, lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and lung adenocarcinoma (ADC), are non-small cell lung cancer with distinct histological features and different genomic alterations [1, 2]. SCC is derived from keratin 5 (KRT5 or K5)-positive basal cells of the pseudostratified airway epithelium in the upper and central lungs, and ADC from the epithelial cells of alveoli [Transgenic mice A mouse TNFR1 full-length cDNA fragment (1,365 bp) in the CMV-Myc Flag TNFR1 vector (MR226545, OriGene, Rockville, MD) was purified after being digested with KpnI and PmeI. This TNFR1 cDNA fragment was subcloned into the BK5 vector [46] that was digested using the enzyme XhoI. Sequencing was used to confirm the insertion of the TNFR1 cDNA fragment (1,365 bp) into the BK5 vector. The construct was linearized with KpnI digestion. The Transgenic Mouse Model Laboratory, Leidos Biomedical Research, Inc., Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research (Frederick, MD), generated the transgenic mice from an FVB background and confirmed the transgenic mice by Southern blotting with a TNFR1 cDNA probe. PCR primers for genoty** the transgenic mice were: 5´-TCA GGG GTG TTG TTT AGA ATG G-3´ and 5´-CAA TAA GAA TAT TTC CAC GCC A-3´ were used to genotype the transgenic mice. Antibodies used in this study included IKKα (IMG-136A) from IMAGENEX; Lamin B (sc-6216), cytokeratin 5 (K5, sc-17090), p50 (sc-1109), c-myc (sc-764), and IgG (sc-2025) from Santa Cruz Biotechnology; p65 (8242), c-Rel (12707), and E-cadherin (24E10) from Cell Signaling Technology; Sox2 (245610) from R&D Systems; Twist1 (T-6451) and β-actin (A-5441) from Sigma-Aldrich; TNFR1 (ab111119 and ab19139) and histone H3 (acetyl K27, ab4729) from Abcam; UBCH10 (NBP2-20782) from Novus Biologicals; K5 (PRB-160P) from Babco; α-Tublin (ab4074) and histone H3 (acetyl K27, ab4729) from Abcam. The Histology and Tissue Core Facility at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research routinely prepared paraffin sections of mouse organs and performed hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemical staining for TNFR1, K5, E-cadherin, loricrin, and involucrin. Cell lysates (15 µg) or protein extracts from the tissues (20 µg) were separated on acrylamide gels and proteins detected using immunoblotting with specific antibodies, as previously described [48] and were expressed as a fold change in mRNA expression relative to control values. Mouse lung tumor cells (1 × 105 /per well) were seeded into 6 well-plates in DMEM with 5% bovine calf serum. The numbers of the treated cells were counted 2 days after the cells were transfected with a control vector or HA-IKKα plasmid. Data represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. For the MTT assay to examine cell proliferation, the cells were plated in 96-well culture plate (2000 cells/200 µL/well) and incubated in a CO2 incubator; 20 µL of MTT (5 mg/mL, Sigma-Aldrich, M5655) was added to each well of a single plate and the cells incubated for 4 h at 37 °C. Medium was removed, and the formazan crystals formed by the cells were dissolved using 200 µL of DMSO for 30 min. The absorbance was read at 570 nm. All siRNAs were purchased from OriGene (Trilencer-27 siRNA), including Tnfrsf1a (mouse, TG517049), Ube2c (mouse, SR404321), TNFRSF1A (human: SR304883, SR517049; mouse: SR414807), Tnf (mouse, SR406508), and HPRT (positive-control siRNA duplex, SR30003). Transfection with Lipofectamine RNAiMAX was performed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The target protein expression was analyzed 48 h after transduction. Ube2c cDNA plasmid (MR223758L4V), which encodes UBCH10, was purchased from OriGene Biotechnology Research (Rockville). Cells were crosslinked with 1% formaldehyde and were lysed and sonicated on ice to generate DNA fragments with an average length of 200–800 bp. After preclearing, 1% of each sample was saved as an input fraction. Immunoprecipitation was performed using antibodies specifically recognizing IKKα (M-280, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), p65 and c-Rel. DNA was eluted and purified from complexes, followed by PCR amplification of the target promoters or genomic loci using primers for mouse Ube2c (p-500: 5'-CGG TCC TTG GAC CCT TTA AT-3' and 5'-TGC TAG GTC CTC CCC AGT AA-3'; p-1000: 5'-CGC TGT CTT CAG ACA CTC CA-3' and 5'-GAG ATG GCT CAG CGG TTA AG-3'; p-1500: 5'-ATA CAC CCT GGC TGA CCT TG-3' and 5'-GAA GGT GGT AAC AGG CAG GA-3'), human UBE2C (p-500: 5'-GTG GGC AAA AGG TGA GTG AT-3' and 5'-GAG CTC CTG GTG TGT TCT CC-3'; p-1000: 5'-GAT TAC GGA CGT GAG CCA CT-3' and 5'-GCG AGG GGA AAA ACT AAA GG-3'; p-1500: 5'-TAA GAC CAA CCT GGG AGC AC-3' and 5'-TGG GAG CAA TAA AAG CCA AC-3'), and mouse Tnfrsf1a (p-500: 5'-TGG CGT GAG TGA CTT TAG GT-3' and 5'-CCA CCC CAA GAA CCA ACA AG-3'). Also, the immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-H3K27ac antibody (ab4729, Abcam) in KALLU- and KALLU- cells. Then, DNA was eluted and purified from complexes, followed by PCR amplification of mouse Tnfr1 promoters with its primer including forward: 5'-TGG CGT GAG TGA CTT TAG GT-3' and Reverse: 5'-CCA CCC CAA GAA CCA ACA AG-3'. Approximately 2 × 105 mouse lung SCC cells KALLU+ cells (with or without si-RNA treatment) and KALLU- cells were injected subcutaneously into athymic NCr-nu/nu mice. Following the cell injection, the tumor growth was monitored with caliper measurements. At day 18 after cell injection, animals were euthanized when tumors reached the maximum size allowed by the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the National Institutes of Health for all animal experiments. To study metastasis, the tumors derived from nude mice were digested with 0.05% trypsin solution at 37 °C for 20 min to make a single cell solution. Isolated cells were cultured for 7 days and then subcutaneously injected into nude mice. At day 18 after cell injection, animals were euthanized and the metastases in the liver and lungs were examined. OncoLnc and Kaplan–Meier plotter were used to analyze the correlation between gene expression and patient survival rates. OncoLnc contains the survival data of 8,647 patients representing 21 cancer types, along with RNA-seq expression data of numerous genes performed by TCGA. The association of survival with a single gene was directly performed on the OncoLnc database [49]. For double gene analysis, raw data for each gene, including patient ID, survival days, status, and gene expression levels, were downloaded from OncoLnc and combined to compare the survival rate between double-high and double-low gene expression groups. The Kaplan–Meier plotter can be used to evaluate the effect of 54,675 genes on patient survival using 10,461 cancer samples. The “Use multiple gene” function was applied to analyze the correlation between double gene expression and patient survival [50]. The log-rank p-value and hazard ratio with 95% confidence intervals were determined.Antibodies
Histopathology, immunoblot analysis, and immunohistochemical and immunofluorescent staining
Cell proliferation assay
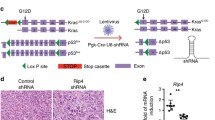
siRNA transfection and cDNA transfection
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay
Subcutaneous injection for tumor growth and metastasis studies
Analyses for cancer patient survival
Data availability
The data supporting the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012;489:519–25.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014;511:543–50.
**ao Z, Jiang Q, Willette-Brown J, ** S, Zhu F, Burkett S, et al. The pivotal role of IKKalpha in the development of spontaneous lung squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:527–40.
Song NY, Zhu F, Wang Z, Willette-Brown J, ** S, Sun Z, et al. IKKalpha inactivation promotes Kras-initiated lung adenocarcinoma development through disrupting major redox regulatory pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E812–E821.
Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara K, Kozlowski P, et al. LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature 2007;448:807–10.
Xu C, Fillmore CM, Koyama S, Wu H, Zhao Y, Chen Z, et al. Loss of Lkb1 and Pten leads to lung squamous cell carcinoma with elevated PD-L1 expression. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:590–604.
Liu J, Wang T, Creighton CJ, Wu SP, Ray M, Janardhan KS, et al. JNK(1/2) represses Lkb(1)-deficiency-induced lung squamous cell carcinoma progression. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2148.
Wang X, Gray Z, Willette-Brown J, Zhu F, Shi G, Jiang Q, et al. Macrophage inducible nitric oxide synthase circulates inflammation and promotes lung carcinogenesis. Cell Death Disco. 2018;4:46.
Gray Z, Shi G, Wang X, Hu Y. Macrophage inducible nitric oxide synthase promotes the initiation of lung squamous cell carcinoma by maintaining circulated inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:642.
Park E, Zhu F, Liu B, **a X, Shen J, Bustos T, et al. Reduction in IkappaB kinase alpha expression promotes the development of skin papillomas and carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9158–68.
Liu B, Park E, Zhu F, Bustos T, Liu J, Shen J, et al. A critical role for I{kappa}B kinase {alpha} in the development of human and mouse squamous cell carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:17202–7.
Hoste E, Arwert EN, Lal R, South AP, Salas-Alanis JC, Murrell DF, et al. Innate sensing of microbial products promotes wound-induced skin cancer. Nat Commun. 2015;6:5932.
Lind MH, Rozell B, Wallin RP, van Hogerlinden M, Ljunggren HG, Toftgard R, et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-mediated signaling is required for skin cancer development induced by NF-kappaB inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:4972–7.
Arnott CH, Scott KA, Moore RJ, Robinson SC, Thompson RG, Balkwill FR. Expression of both TNF-alpha receptor subtypes is essential for optimal skin tumour development. Oncogene 2004;23:1902–10.
Park EJ, Lee JH, Yu GY, He G, Ali SR, Holzer RG, et al. Dietary and genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell 2010;140:197–208.
Nakagawa H, Umemura A, Taniguchi K, Font-Burgada J, Dhar D, Ogata H, et al. ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:331–43.
Andersen DS, Colombani J, Palmerini V, Chakrabandhu K, Boone E, Rothlisberger M, et al. The Drosophila TNF receptor Grindelwald couples loss of cell polarity and neoplastic growth. Nature 2015;522:482–6.
van Ree JH, Jeganathan KB, Malureanu L, van Deursen JM. Overexpression of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UbcH10 causes chromosome missegregation and tumor formation. J Cell Biol. 2010;188:83–100.
Hao Z, Zhang H, Cowell J. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2C: molecular biology, role in tumorigenesis, and potential as a biomarker. Tumour Biol: J Intern Soc Oncodevelop Biol Med. 2012;33:723–30.
**a X, Park E, Liu B, Willette-Brown J, Gong W, Wang J, et al. Reduction of IKK{alpha} expression promotes chronic ultraviolet B exposure-induced skin inflammation and carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:2500–8.
Zhu F, Willette-Brown J, Song NY, Lomada D, Song Y, Xue L, et al. Autoreactive T cells and chronic fungal infection drive esophageal carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe. 2017;21:478–93. e477
Zhu F, Willette-Brown J, Zhang J, Ferre EMN, Sun Z, Wu X, et al. NLRP3 inhibition ameliorates severe cutaneous autoimmune manifestations in a mouse model of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy-like disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:1404–15.
Lobito AA, Kimberley FC, Muppidi JR, Komarow H, Jackson AJ, Hull KM, et al. Abnormal disulfide-linked oligomerization results in ER retention and altered signaling by TNFR1 mutants in TNFR1-associated periodic fever syndrome (TRAPS). Blood 2006;108:1320–7.
Karathanasis C, Medler J, Fricke F, Smith S, Malkusch S, Widera D, et al. Single-molecule imaging reveals the oligomeric state of functional TNFalpha-induced plasma membrane TNFR1 clusters in cells. Sci Signal. 2020;13:13. eaax5647
Kong YH, Syed Zanaruddin SN, Lau SH, Ramanathan A, Kallarakkal TG, Vincent-Chong VK, et al. Co-Expression of TWIST1 and ZEB2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with poor survival. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0134045.
Wang H, Unternaehrer JJ. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: at the crossroads of differentiation and dedifferentiation. Dev Dyn. 2019;248:10–20.
Hao Z, Zhang H, Cowell J. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2C: molecular biology, role in tumorigenesis, and potential as a biomarker. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:723–30.
Wang X, Yin L, Yang L, Zheng Y, Liu S, Yang J, et al. Silencing ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 2C inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. FEBS J. 2019;286:4889–909.
Liu Y, Zhao R, Chi S, Zhang W, **ao C, Zhou X, et al. UBE2C is upregulated by estrogen and promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition via p53 in endometrial cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2020;18:204–15.
Bartlett DW, Davis ME. Insights into the kinetics of siRNA-mediated gene silencing from live-cell and live-animal bioluminescent imaging. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:322–33.
Schipper JH, Frixen UH, Behrens J, Unger A, Jahnke K, Birchmeier W. E-cadherin expression in squamous cell carcinomas of head and neck: inverse correlation with tumor dedifferentiation and lymph node metastasis. Cancer Res. 1991;51:6328–37.
Dostert C, Grusdat M, Letellier E, Brenner D. The TNF family of ligands and receptors: communication modules in the immune system and beyond. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:115–60.
**a X, Liu S, **ao Z, Zhu F, Song NY, Zhou M, et al. An IKKalpha-nucleophosmin axis utilizes inflammatory signaling to promote genome integrity. Cell Rep. 2013;5:1243–55.
Kunsch C, Ruben SM, Rosen CA. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Molec Cell Biol. 1992;12:4412–21.
Beacon TH, Delcuve GP, Lopez C, Nardocci G, Kovalchuk I, van Wijnen AJ, et al. The dynamic broad epigenetic (H3K4me3, H3K27ac) domain as a mark of essential genes. Clin Epigen. 2021;13:138.
Bass AJ, Watanabe H, Mermel CH, Yu S, Perner S, Verhaak RG, et al. SOX2 is an amplified lineage-survival oncogene in lung and esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1238–42.
Vesuna F, van Diest P, Chen JH, Raman V. Twist is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367:235–41.
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 2004;117:927–39.
Gaeta ML, Johnson DR, Kluger MS, Pober JS. The death domain of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 is necessary but not sufficient for Golgi retention of the receptor and mediates receptor desensitization. Lab Invest. 2000;80:1185–94.
Jones SJ, Ledgerwood EC, Prins JB, Galbraith J, Johnson DR, Pober JS, et al. TNF recruits TRADD to the plasma membrane but not the trans-Golgi network, the principal subcellular location of TNF-R1. J Immunol. 1999;162:1042–8.
Song NY, Li X, Ma B, Willette-Brown J, Zhu F, Jiang C, et al. IKKalpha-deficient lung adenocarcinomas generate an immunosuppressive microenvironment by overproducing Treg-inducing cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119:e2120956119.
Hu Y, Baud V, Oga T, Kim KI, Yoshida K, Karin M. IKKa controls formation of the epidermis independently of NF-kB. Nature 2001;410:710–4.
Descargues P, Sil AK, Sano Y, Korchynskyi O, Han G, Owens P, et al. IKKalpha is a critical coregulator of a Smad4-independent TGFbeta-Smad2/3 signaling pathway that controls keratinocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:2487–92.
Liu B, Willette-Brown J, Liu S, Chen X, Fischer SM, Hu Y. IKKalpha represses a network of inflammation and proliferation pathways and elevates c-Myc antagonists and differentiation in a dose-dependent manner in the skin. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18:1854–64.
Grinberg-Bleyer Y, Oh H, Desrichard A, Bhatt DM, Caron R, Chan TA, et al. NF-kappaB c-Rel is crucial for the regulatory T cell immune checkpoint in cancer. Cell 2017;170:1096–108.
Matsumoto T, Jiang J, Kiguchi K, Ruffino L, Carbajal S, Beltran L, et al. Targeted expression of c-Src in epidermal basal cells leads to enhanced skin tumor promotion, malignant progression, and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4819–28.
Liu B, **a X, Zhu F, Park E, Carbajal S, Kiguchi K, et al. IKKalpha is required to maintain skin homeostasis and prevent skin cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:212–25.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8..
Anaya J. OncoLnc: linking TCGA survival data to mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs. PeerJ Computer Sci. 2016;2:e67.
Lanczky A, Nagy A, Bottai G, Munkacsy G, Szabo A, Santarpia L, et al. miRpower: a web-tool to validate survival-associated miRNAs utilizing expression data from 2178 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;160:439–46.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health (ZIA BC011212 and ZIA BC 011391) to Y.H.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Author information
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by Dr Angelo Peschiaroli
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
**ao, Z., Shi, G., **, S. et al. A TNFR1–UBCH10 axis drives lung squamous cell carcinoma dedifferentiation and metastasis through a cell-autonomous signaling loop. Cell Death Dis 13, 885 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05308-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05308-4
- Springer Nature Limited