Abstract
Cell death, including apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death, is frequently observed in liver disease. Upon activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, mitochondria release not only apoptogenic cytochrome c but also mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) into the cytosol. The impact of DNase II, a lysosomal acid DNase that degrades mtDNA, on hepatocyte death remains unclear. Administration of ABT-737, a Bcl-xL inhibitor, upregulated DNase II activity in murine hepatocyte cell line BNL CL.2 cells and induced apoptosis. In cells treated with DNase II siRNA, ABT-737 led to accumulation of mtDNA in the cytosol and increased expression of interferon (IFN)-β and induction of propidium iodide (PI)-positive cells, in addition to apoptosis. Induced PI-positive cells were suppressed by RIP1 inhibitor, Necrostatin-1, but not by pan-caspase inhibitor, ZVAD-FMK, suggesting non-apoptotic cell death. Both the increase in IFN-β and the induction of non-apoptotic cell death were abolished by administering a TLR9 antagonist, ODN2088, or by the removal of mtDNA from cells with ethidium bromide. Hepatocyte-specific Mcl-1 knockout mice developed hepatocyte apoptosis accompanied by upregulated DNase II activity in their livers. Further knockout of DNase II induced IFN-β expression and RIP1-dependent non-apoptotic hepatocyte death, both of which were suppressed by the administration of ODN2088. Mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD), an obesity-associated fatty liver model, showed increased expression of IFN-β with suppression of DNase II activity in their livers and developed not only hepatocyte apoptosis but also non-apoptotic hepatocyte death. Hepatocyte-specific knockout of DNase II exacerbated HFD-induced non-apoptotic hepatocyte death and liver fibrosis. In conclusion, without DNase II, apoptotic stimulation on hepatocytes induces TLR9-dependent IFN-β production and RIP1-dependent non-apoptotic cell death originating from mtDNA. In fatty livers, DNase II activity is suppressed in contrast to simple inactivation of Bcl-xL or Mcl-1, and both apoptotic and non-apoptotic hepatocyte death can develop, leading to the progression of liver fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
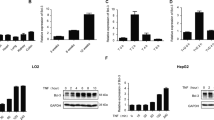
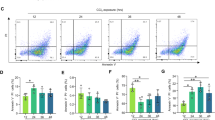
Hepatocyte death is observed in various types of liver diseases, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), alcoholic liver disease and viral hepatitis [1]. Mitochondria play a pivotal role in the cell signaling that leads to hepatocyte death, including apoptosis [2, 3], necrosis [4, 5] and necroptosis [28]. Hepatocyte apoptosis in L-Mcl-1 KO mice is decreased by disrupting Bak, a mitochondrial protein, indicating that the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway is activated in the L-Mcl-1 KO mouse liver [29]. DNase II activity in L-Mcl-1-KO mouse livers was significantly higher than that in WT control littermate livers (Fig. 4a). To examine the impact of DNase II on hepatocytes in mice, we generated hepatocyte-specific DNase II-KO mice (Dnase2aflox/flox Alb-Cre, L-DNase II-KO). DNase II mRNA expression levels and activity were suppressed in livers from L-DNase II-KO mice (Sup.Fig.11A, Sup.Fig.11B). There were no significant differences between the L-DNase II-KO and WT mice in regard to their hematoxylin and eosin (HE)-stained liver sections, serum alanine transaminase (ALT) levels, serum caspase-3/7 activity and the number of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling (TUNEL)-positive or PI-positive cells in their liver sections (Sup.Fig.11C-11H). We then crossed L-DNase II-KO mice with L-Mcl-1-KO mice and generated hepatocyte-specific Mcl-1/DNase II-KO (L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO) mice. The DNase II activity in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers was significantly suppressed compared with that in WT control or L-Mcl-1-KO littermate livers (Fig. 4a). Mcl-1 protein expression was reduced in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers similar to that in L-Mcl-1-KO mice (Fig. 4b). The L-Mcl-1-KO and L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice exhibited no significant differences in their serum caspase-3/7 activity or number of TUNEL-positive hepatocytes (Fig. 4c, d). In contrast, the number of PI-positive cells in livers from L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice was significantly greater than that in livers from L-Mcl-1-KO mice (Fig. 4e). The serum ALT levels and IL-1α levels of L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice were significantly higher than those of L-Mcl-1-KO mice (Fig. 4c). In addition, the amount of mtDNA isolated from the cytosolic fraction of L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers was also significantly higher than that from L-Mcl-1-KO mouse livers (Fig. 4f).
Deficiency in hepatocyte DNase II in L-Mcl-1-KO mice increased non-apoptotic hepatocyte death but not hepatocyte apoptosis. We mated Mcl-1flox/flox Dnase2aflox/+ Alb-Cre mice and Mcl-1flox/flox Dnase2aflox/+ mice and generated L-Mcl-1-KO mice, L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice and control littermates (Mcl-1flox/flox Dnase2aany/any). The littermates were analyzed at 6 to 8 weeks of age; n ≥ 8 per group unless otherwise indicated. a DNase II activity in whole livers was measured using the SRED method. Representative figures and graphs of the quantitative results; n = 3 per group. b Expression of Mcl-1 and β-actin proteins assessed by western blotting analysis of liver lysates. c Serum caspase-3/7 activity, serum ALT levels and serum IL-1α levels. d HE and TUNEL staining of liver sections. Representative images and the quantitative results of TUNEL-positive cell counts. e Confocal micrographs of PI-injected mouse livers. Representative images and the quantitative results of PI-positive cell counts; n = 4–6 per group. Scale bar 100 μm. f The amount of mtDNA in cytosolic fractions was quantified via quantitative real-time PCR for COX I; n = 6 per group (left graph). Ifnb1 and Isg15 mRNA expression levels; n = 8 per group (middle and right graphs). Data are shown as the mean + SD. *P < 0.05 based on one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test
Non-apoptotic hepatocyte death in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice depends on TLR9/IFN-β signaling and RIP1
To investigate the mechanisms underlying the induction of non-apoptotic hepatocyte death in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice, we examined the TLR9/IFN-β signaling pathway based on our in vitro results. The mRNA expression levels of IFN-β and ISG15, but not IL-1β, were elevated in the livers of L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice compared with the levels in livers of L-Mcl-1-KO mice (Fig. 4f, Sup.Fig.5B). We performed a complementary DNA microarray analysis using total RNA from the livers of L-Mcl-1-KO and L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice. According to the pathway analysis, IFN-β is one of the top upstream regulators (Sup.Table1), which supported the involvement of TLR9/IFN-β signaling in the induction of non-apoptotic hepatocyte death in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice. The administration of ODN2088, a TLR9 antagonist, decreased the serum ALT levels in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice but not in L-Mcl-1-KO mice (Fig. 5a). After the administration of ODN2088, the number of PI-positive hepatocytes was also decreased (Fig. 5b), and the increased mRNA expression of IFN-β in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers was attenuated (Fig. 5c). The administration of Necrostatin-1 also attenuated the serum ALT levels and the number of PI-positive hepatocytes in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice but not in L-Mcl-1 KO mice (Fig. 5d, e).
Hepatocyte non-apoptotic cell death in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice is induced by TLR9/IFN-β signaling and is dependent on RIP1. L-Mcl-1-KO mice, L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice and control littermates (Mcl-1flox/flox Dnase2aany/any) at 6 to 8 weeks of age were intraperitoneally treated with ODN2088, Nec-1 or vehicle. Schematic of the experimental procedure for the continuous collection of blood samples and serum ALT levels at the indicated times (a, d); n = 20 per group. Confocal micrographs of PI-injected L-Mcl-1-KO and L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers. Representative images and their quantitative analysis; n = 4–6 per group. Scale bar 100 μm (b, e). Ifnb1 mRNA expression levels; n = 7–8 per group (c). N.S. not significant. *P < 0.05 based on paired Student’s t-test for (a, d) and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test for (b, c, e)
HFD decreases DNase II activity and increases non-apoptotic hepatocyte death
Research has shown that WT mice fed the HFD exhibit increased hepatocyte apoptosis in a time-dependent manner [30]. We examined DNase II activity in livers from WT mice fed the HFD for 8 months and found it was reduced compared with the activity in livers from WT mice fed a normal diet (ND) (Fig. 6a). Compared with mice fed the ND, WT mice fed the HFD for 8 months exhibited an increased number of TUNEL-positive cells as well as cleaved caspase-3-positive cells in liver sections (Fig. 6b), indicating increased hepatocyte apoptosis. Importantly, WT mice fed the HFD showed a significantly increased number of PI-positive cells (Fig. 6c) and significantly increased IFN-β expression (Fig. 6d). To examine the role of DNase II in the livers of HFD models, we fed WT mice and L-DNase II-KO mice the ND or HFD and analyzed the phenotypes of WT mice and L-DNase II-KO mice fed the HFD for 8 months (Fig. 6a). The number of TUNEL-positive cells or cleaved caspase-3-positive cells in the liver sections did not change with the disruption of DNase II in hepatocytes (Fig. 6b). In contrast, the number of PI-positive cells and the mRNA expression levels of IFN-β in the liver significantly increased (Fig. 6c, d). The serum ALT levels were significantly higher in the L-DNase II-KO mice than in the WT mice (Fig. 6e). Liver fibrosis was exacerbated in the L-DNase II-KO mice compared with that in the WT mice, as evidenced by Sirius Red staining and the mRNA expression levels of Col1a2 in the liver (Fig. 6b, d). These results indicate that hepatocyte DNase II regulates the development of non-apoptotic hepatocyte death and the progression of fibrosis in the liver of HFD models. Taken together, these results suggest that the decrease in DNase II activity observed in HFD models is involved in the development and progression of steatohepatitis.
HFD feeding reduces hepatocyte DNase II activity and increases hepatocyte non-apoptotic cell death. a C57BL/6J mice, L-DNase II-KO mice and their WT littermates were fed the HFD or ND for 8 months. DNase II activity in liver homogenates from C57BL/6J mice was measured using the SRED method; n = 5 per group (left panel). Representative image and quantitative analysis. The DNase II activity in liver homogenates from L-DNase II-KO mice and their WT littermates was measured using the SRED method; n = 5 per group (right panel). Representative image and quantitative analysis. b–e L-DNase II-KO mice and WT littermates fed the HFD or ND for 8 months were analyzed. HE staining, TUNEL staining, immunohistochemical staining of cleaved caspase-3 and Sirius Red staining of liver sections; n ≥ 6 per group (b). Representative images of stained sections and their quantitative analysis. Confocal micrographs of PI-injected mouse liver sections; n = 3–6 per group. Scale bar 100 μm (c). Representative images and their quantitative analysis. Ifnb1 and Col1a2 mRNA expression levels; n ≥ 6 per group (d). Serum ALT levels; n ≥ 6 per group (e). ✝P < 0.05 vs the other groups and *P < 0.05 based on one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test. ND normal diet, HFD high-fat diet
Discussion
Chronic liver diseases include various types of cell death such as apoptosis and necrotic cell death [22]. NASH is characterized by both hepatocyte apoptosis [14, 15] and necrosis [18, 19]. In general, each different mode of cell death is considered to be induced by different stimuli. Here, we show that DNase II activity is elevated upon activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and that suppression of DNase II activity upon activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway induces RIP1-dependent non-apoptotic hepatocyte death through the TLR9/IFN-β pathway. These findings suggest that apoptotic stimuli have the ability to induce RIP1-dependent cell death with necrotic phenotype and reveal a potential link between apoptosis and necrosis under the suppression of DNase II activity. In livers from the HFD-fed mice in the present study, DNase II activity was suppressed. This reduced DNase II activity may contribute to the induction of hepatocyte necrosis in NASH and could affect the exacerbation of NASH.
The liver is a mitochondrion-rich organ, and mitochondria contain many DAMPs, including mtDNA, formyl peptides, cytochrome c and adenosine triphosphate [31]. mtDNA is released into the cytosol upon activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway [9, 10]. DNA in the cytosol can be directly uptaken to lysosomes by SID1 transmembrane family member 2 (SIDT2) [32]. In the present study, apoptogenic insults via the simple inactivation of Bcl-xL by ABT-737 increased the amount of cytosolic mtDNA, which further accumulated in DNase II-knockdown cells. Cytosolic DNA is recognized by cytosolic receptors, including TLRs and cyclic-GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), and induces type I IFN [33, 34]. mtDNA contains unmethylated CpG motifs [23], and CpG DNA is recognized by TLR9 [33]. In the present study, the non-apoptotic hepatocyte death induced in DNase II activity-reduced cells upon activation of the mitochondrial pathway was dependent on mtDNA, and it was attenuated by treatment with the TLR9 antagonist ODN2088. Thus, recognition of mtDNA by TLR9 is involved in the mechanism underlying non-apoptotic cell death induction. Activation of the TLR9/IFN-β pathway is required, but not sufficient for the execution of this type of cell death, because TLR9 agonist efficiently induced IFN-β in hepatocytes but did not decrease cell viability. Further study is needed to clarify whether mtDNA recognized via TLR9 comes from its own cells or neighboring cells.
Compatible with in vitro results, the amount of cytosolic mtDNA in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers increased compared with that in L-Mcl-1 KO mouse livers. The non-apoptotic hepatocyte death observed in L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers was attenuated by treatment with the TLR9 antagonist ODN2088. Garcia-Martinez et al. [35] reported high levels of hepatocyte mtDNA in plasma from mice and patients with NASH. However, the impact of intracellular mtDNA in NASH remains to be elucidated. In the present study, suppressed DNase II activity and non-apoptotic hepatocyte death with increased expression of IFN-β were observed in HFD-fed WT mice. Further reduction in DNase II activity exacerbated non-apoptotic hepatocyte death and promoted fibrosis in HFD-fed mouse livers. Taken together, these results suggest that undegraded intracellular mtDNA is involved in non-apoptotic hepatocyte death, which contributes to the progression of NASH.
In this study, our results showed that DNase II activity in the liver was compromised in mice fed the HFD despite the clear activation of hepatocyte apoptosis. This finding is clearly different in that pure activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by inactivation of Bcl-xL or Mcl-1 increased DNase II activity. The underlying mechanism by which DNase II activity is suppressed in fatty livers remains unclear. We previously reported that HFD induces impairment of autophagy [30], and Inami et al. [36] reported that lipid accumulation reduces lysosomal acidity, suggesting inhibition of autophagic flux. In addition, DNase II activity is exerted in acidic environments because DNase II is an acid DNase [12]. Therefore, the dysregulation of lysosomal acidification in fatty livers might contribute to reduced DNase II activity. Further experiments are needed to clarify the mechanism underlying the reduction in DNase II activity.
In the present study, we showed that mtDNA released from mitochondria activates IFN-β in DNase II activity-reduced cells, leading to induction of non-apoptotic cell death. While ABT-737-mediated mtDNA release was dependent on Bak and Bax, neither the IFN-β activation nor non-apoptotic cell death induction was blocked by a pan-caspase inhibitor, suggesting that ABT-737-induced IFN-β production and non-apoptotic cell death in DNase II activity-reduced cells was dependent on Bak/Bax activation but independent of caspase activity. On the other hand, study reported that mtDNA released into the cytoplasm of apoptotic cells is not capable of inducing IFN production when caspases are active [9, 10]. In the present study, we did not find any difference in caspase activity between control cells and DNase II activity-reduced cells and, therefore IFN production and resultant non-apoptotic cell death seems to occur even if caspases are active. In the previous reports, they used hematopoietic cells or mouse embryonic fibroblasts, but not hepatocytes, in their experiments [9, 10]. The difference of cell types may cause the difference of caspase dependency in IFN-β production. Another possibility is that levels of caspase activity are diverse in cells and that cells with low caspase activity might be more prone to IFN production in our experiments. In condition of full Bak/Bax activation with both ABT-737 and A-1210477, a Mcl-1 inhibitor, there was no difference in IFN-β production or cell viability between DNase II activity-reduced cells and unreduced cells, suggesting that mtDNA/IFN-β-induced non-apoptotic cell death is only apparent under conditions of limited apoptosis which may admit diversity of caspase activity. However, in the condition of limited apoptosis which might be more significant in pathological conditions, mtDNA released from mitochondria has to be degraded by DNase II to avoid further destruction of cells via non-apoptotic cell death. Additionally, cells with minority MOMP [37], where minority of mitochondria develop MOMP and fail to induce apoptosis, might be involved in activation of IFN-β or induction of non-apoptotic cell death in DNase II activity-reduced cells. Further analysis at single cell level will be needed for clarifying detail mechanisms by which non-apoptotic death is induced in DNase II activity-reduced cells upon activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.
In conclusion, a lack of DNase II in hepatocytes induces RIP1-dependent non-apoptotic cell death with necrotic phenotype through the mtDNA-driven activation of TLR9/IFN-β signaling pathway upon activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Our results describe the mechanism of a potential relationship between hepatocyte apoptosis and necrosis and have implications for understanding the progression of chronic liver disease. Reduced DNase II activity might induce mtDNA-driven non-apoptotic cell death, especially in the pathogenesis of NASH, and could be one of the potential mechanisms involved in its progression.
Materials and methods
Cells and reagents
The murine hepatocyte cell line, BNL CL.2s cell, was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 °C under 5% CO2. ABT-737 was kindly provided by AbbVie (North Chicago, IL, USA). In some experiments, the cells were pretreated with a TLR9 agonist, ODN2395, or a TLR9 antagonist, ODN2088 (InvivoGen, San Diego, CA, USA), at 1 μM, the RIP1 inhibitor, Necrostatin-1 (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA, USA), at 30 μM or ZVAD-FMK (Calbiochem) at 50 μM, for the indicated time and were then reacted with specific media for further investigation as indicated. All in vitro experiments were repeated at least two or three times.
Mice
C57BL/6J mice (WT mice) were purchased from Charles River Japan (Tokyo, Japan). We crossed mice bearing the Dnase2aflox allele [38] with Alb-Cre transgenic mice expressing Cre recombinase under the control of the albumin gene promoter, generating hepatocyte-specific DNase II-KO mice (Dnase2aflox/flox Alb-Cre). We previously reported hepatocyte-specific Mcl-1-KO (L-Mcl-1-KO) mice, which spontaneously undergo continuous hepatocyte apoptosis [28]. Hepatocyte-specific Mcl-1/DNase II-KO (Mcl-1flox/flox Dnase2aflox/flox Alb-Cre) mice (L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mice) were generated by crossing L-DNase II-KO mice and L-Mcl-1-KO mice. The TLR9 antagonist ODN2088 was administered intraperitoneally (50 μg/200 μl) for 2 consecutive days, and Necrostatin-1 was administered intraperitoneally (6 mg/kg) once. In some experiments, male mice aged 6–8 weeks were fed the HFD containing 32% fat (HFD32; CLEA Japan, Tokyo, Japan) or the ND containing 5% fat (CRF-1; CLEA Japan) for 8 months. All mice were housed in a specific pathogen-free facility and treated with humane care. The animal care and use committee at Osaka University Medical School approved all of the experiments.
Measurement of DNase II activity
DNase II activity was measured with the single radial enzyme-diffusion (SRED) method, which can measure the activity of DNase II, but not DNase I, phosphodiesterase I or phosphodiesterase II [39, 40]. Equivalent amounts of cultured cells or liver homogenates, normalized based on their protein concentrations, were applied to wells with radii of 1.5 mm that were punched in a 1% (w/v) agarose gel containing 0.05 mg/ml salmon sperm DNA (Sigma-Aldrich), 5 μg/ml EtBr (Nakalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan), 0.5 M sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.7) and 10 mM EDTA. The radii of the dark circles were measured under ultraviolet light after 24–72 h of incubation at 37 °C. To determine the DNase II activity of the samples, a standard curve was constructed using porcine DNase II (Sigma-Aldrich).
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of hepatocyte death and histological analysis
Cell viability was assessed with a water-soluble tetrazolium salt (WST) assay (Nakalai Tesque) and/or by counting viable cells automatically (TC20 Cell Counter, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) after Trypan blue staining. In some experiments, BNL CL.2 cells were treated with A-1210477, an Mcl-1 inhibitor (MCE Monmouth Junction, NJ, USA). L-929 cells, murine fibroblast cell line, were pretreated with 50 µM ZVAD for 30 min and then treated with 20 ng/ml recombinant mouse tumor necrosis factor-α for 1.5 h. Mouse serum ALT levels were measured using a standard method at the Oriental Kobo Life Science Laboratory (Nagahama, Japan). Mouse serum IL-1α levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (LSBio, Seattle, WA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. For apoptosis assays, the supernatant of cultured cells or mouse serum was measured with a luminescent substrate assay for caspase-3 and caspase-7 (Caspase-Glo Assay, Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. TUNEL staining was performed using an ApopTag Kit (Millipore, Moldheim, France) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. For immunohistochemical staining, cleaved caspase-3 was labeled in paraffin-embedded liver sections using cleaved caspase-3 antibody (#9661, Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA). Bound primary antibody was detected with avidin-biotin complexes using a Vectastain ABC Kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA). TUNEL-positive cells and cleaved caspase-3-positive cells were counted in six fields per liver section at 100× magnification. CL2 cells were stained with 5 μg/ml PI for 15 min and then washed three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Live cells were analyzed with a BZ-9000 or BZ-X700 fluorescence microscope (KEYENCE, Osaka, Japan). The percentage of PI-positive cells was calculated by counting more than 200 cells on each dish. PI (5 mg/kg per mouse) (WAKO, Osaka, Japan) was injected into mice via the tail vein 1 h before killing. The mouse livers were subsequently collected and cryopreserved with a cryopreservation compound. Cryosections from the mouse livers were analyzed with an FV1000D confocal microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). PI-positive cells were counted in six fields per liver section. Liver fibrosis was evaluated with Sirius Red staining. The Sirius Red-positive area was measured with ImageJ software (National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
siRNA-mediated knockdown
siRNAs for Dnase2a (s65051, s65055), Ifnb1 (s68092, s201518), Ripk1 (s72976, s72977), Aim2 (s234106, s234107) and the appropriate negative controls were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). CL2 cells were transfected with 5 nM siRNA using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. At 72 h after transfection, CL2 cells were analyzed or treated with ABT-737 unless otherwise indicated.
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis
Total RNA extracted from cells and livers with an RNeasy Kit (QIAGEN) was reverse-transcribed using ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed using TaqMan Gene Expression Assays with an HT7900 Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific). The following primer probes were used: Dnase2a (Mm00438463_m1), Col1a2 (Mm01165187_m1), Ifna4 (Mm00833969_s1), Ifnb1 (Mm00439552_s1), Isg15 (Mm01705338_s1), Actb (Mm02619580_g1) and Il-1b (Mm00434228_m1). Gene expression was normalized to Actb.
Measurement of mtDNA in the cytosolic fraction
To determine the amount of mtDNA in the cytosol, 3.0 × 106 cells from the in vitro assays or 30 mg wet weight of liver tissue were homogenized with a Dounce homogenizer in 100 mM Tricine-NaOH solution, pH 7.4, containing 0.25 M sucrose, 1 mM EDTA and protease inhibitor, and the homogenates were centrifuged at 700 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. After normalization of their protein concentrations, the supernatants were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 30 min at 4 °C. The resulting supernatants and pellets were defined as the cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions, respectively [41]. The distribution of these fractions was assessed by western blotting for lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), a cytosolic fraction marker, and cytochrome c oxidase IV (COX IV), a mitochondrial fraction marker. DNA was isolated from 200 μl of the cytosolic fraction using a DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN). The amount of mtDNA was quantified via quantitative real-time PCR using primers for COX I: forward, 5’-CCCCAGATATAGCATTCCC-3’, and reverse, 5’-GTTCATCCTGTTCCTGCTCC-3’. To construct the standard curve, mitochondria were isolated from C57BL/6J mouse livers using a Mitochondrial Isolation Kit for Tissue (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and mtDNA was extracted from the isolated mitochondria using a DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN).
Depletion of mtDNA
BNL CL.2 cells were cultured with DMEM containing 200 ng/ml EtBr with 10% FBS for 4 days [27, 41]. The cells were then cultured and reacted with specific medium without EtBr for further investigations as indicated. To measure the efficiency of mtDNA depletion, total DNA was extracted by resuspending these cells in 50 mM NaOH at 95 °C for 1 h, followed by neutralization through the addition of a 10% volume of 1 M Tris HCl (pH 8.0). mtDNA and chromosomal DNA were quantified via quantitative real-time PCR using the primers for COX I described above, as well as primers for 18S ribosomal RNA: forward, 5’-TAGAGGGACAAGTGGCGTTC-3’, and reverse, 5’-CGCTGAGCCAGTCAGTGT-3’. The mtDNA copy number was normalized to the chromosomal DNA and compared with that of untreated cells to calculate the percentage of depletion. PicoGreen (Molecular Probes, Thermo Fisher Scientific) was used to detect mtDNA [42] under live cell imaging according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Western blot analysis
Cells or liver tissues were homogenized in lysis buffer (1% Nonidet P-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, PBS, pH 7.4, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1× proteinase inhibitor cocktail (Nacalai Tesque) and 1× phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Nacalai Tesque)). The supernatant was collected by centrifugation, and the protein concentration was measured using a bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Equal amounts of the protein homogenates were separated in sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. Antibodies specific for the following proteins were used for immunodetection: COX IV (#4844), LDHA (#2012), cytochrome c (#11940), RIP1 (#3493), p-RIP1 (Ser166) (#31122), RIP3 (#14401), cleaved caspase-3 (#9661) and cleaved caspase-7 (#8438) purchased from Cell Signaling Technology; Mcl-1 (600-401-394) purchased from Rockland Immunochemicals (Limerick, PA, USA); β-actin (A5316) purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; MLKL (#MABC604) purchased from EMR Millipore; and p-MLKL (ab196436) purchased from Abcam. Protein expression was measured with ImageJ software.
Flow cytometric detection of apoptosis with annexin-V
To detect apoptotic cells, cells were suspended in annexin-V binding buffer (Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA) and then stained with annexin-V and 7-AAD according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Annexin-V-positive and 7-AAD-negative cells were defined as apoptotic cells.
Microarray analysis
Gene expression in L-Mcl-1-KO and L-Mcl-1/DNase II-KO mouse livers (n = 3 per group) was analyzed using a SurePrint G3 Mouse Gene Expression Kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Genes that showed significant differential expression, defined as greater than a twofold difference, were collected and further analyzed using pathway analysis (Ingenuity, QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany).
Primary hepatocyte isolation
Primary hepatocytes were isolated by the two-step pronase-collagenase perfusion of mouse livers as described previously [43]. Primary hepatocytes were maintained in William’s Eagle medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) containing 10% fetal calf serum, 2 mM l-glutamine (Gibco), 100 nM insulin (Sigma-Aldrich) and 100 nM dexamethasone (Sigma-Aldrich). Primary hepatocytes were isolated from Baxflox/flox Bak−/− Alb-Cre mice and from Baxflox/flox Bak+/+ mice (wild-type mice). Baxflox/flox Bak−/− Alb-Cre mice have been described previously [44].
Statistical analysis
Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation otherwise indicated. Statistical significance between two groups was assessed with an unpaired or paired two-sided Student’s t-test. Multiple comparisons were performed by applying one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s honest significant difference (HSD) test using JMP Pro 12 software (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
References
Malhi H, Guicciardi ME, Gores GJ. Hepatocyte death: a clear and present danger. Physiol Rev. 2010;90:1165–94.
Takehara T, Tatsumi T, Suzuki T, Rucker EB, Hennighausen L, **ushi M, et al. Hepatocyte-specific disruption of Bcl-xL leads to continuous hepatocyte apoptosis and liver fibrotic responses. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1189–97.
Vick B, Weber A, Urbanik T, Maass T, Teufel A, Krammer PH, et al. Knockout of myeloid cell leukemia-1 induces liver damage and increases apoptosis susceptibility of murine hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2009;49:627–36.
Kon K, Kim JS, Jaeschke H, Lemasters JJ. Mitochondrial permeability transition in acetaminophen-induced necrosis and apoptosis of cultured mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2004;40:1170–9.
Masubuchi Y, Suda C, Horie T. Involvement of mitochondrial permeability transition in acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J Hepatol. 2005;42:110–6.
Ramachandran A, McGill MR, **e Y, Ni HM, Ding WX, Jaeschke H. Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 is a critical early mediator of acetaminophen-induced hepatocyte necrosis in mice. Hepatology. 2013;58:2099–108.
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:107–20.
Tait SW, Green DR. Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:621–32.
Rongvaux A, Jackson R, Harman CC, Li T, West AP, de Zoete MR, et al. Apoptotic caspases prevent the induction of type I interferons by mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 2014;159:1563–77.
White MJ, McArthur K, Metcalf D, Lane RM, Cambier JC, Herold MJ, et al. Apoptotic caspases suppress mtDNA-induced STING-mediated type I IFN production. Cell. 2014;159:1549–62.
Oka T, Hikoso S, Yamaguchi O, Taneike M, Takeda T, Tamai T, et al. Mitochondrial DNA that escapes from autophagy causes inflammation and heart failure. Nature. 2012;485:251–5.
Evans CJ, Aguilera RJ. DNase II: genes, enzymes and function. Gene. 2003;322:1–15.
Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:686–90.
Feldstein AE, Canbay A, Angulo P, Taniai M, Burgart LJ, Lindor KD, et al. Hepatocyte apoptosis and fas expression are prominent features of human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:437–43.
Malhi H, Gores GJ. Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:360–9.
Garcia-Monzon C, Martin-Perez E, Iacono OL, Fernandez-Bermejo M, Majano PL, Apolinario A, et al. Characterization of pathogenic and prognostic factors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis associated with obesity. J Hepatol. 2000;33:716–24.
Dixon JB, Bhathal PS, O’Brien PE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:91–100.
Afonso MB, Rodrigues PM, Carvalho T, Caridade M, Borralho P, Cortez-Pinto H, et al. Necroptosis is a key pathogenic event in human and experimental murine models of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;129:721–39.
Gautheron J, Vucur M, Reisinger F, Cardenas DV, Roderburg C, Koppe C, et al. A positive feedback loop between RIP3 and JNK controls non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. EMBO Mol Med. 2014;6:1062–74.
Matzinger P. The danger model: a renewed sense of self. Science. 2002;296:301–5.
Chen GY, Nunez G. Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:826–37.
Luedde T, Kaplowitz N, Schwabe RF. Cell death and cell death responses in liver disease: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:765–83.e764.
Gray MW, Burger G, Lang BF. Mitochondrial evolution. Science. 1999;283:1476–81.
Liu S, Gallo DJ, Green AM, Williams DL, Gong X, Shapiro RA, et al. Role of toll-like receptors in changes in gene expression and NF-kappa B activation in mouse hepatocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 2002;70:3433–42.
Seki E, Brenner DA. Toll-like receptors and adaptor molecules in liver disease: update. Hepatology. 2008;48:322–35.
Uematsu S, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and Type I interferons. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:15319–23.
Hashiguchi K, Zhang-Akiyama QM. Establishment of human cell lines lacking mitochondrial DNA. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;554:383–91.
Hikita H, Takehara T, Shimizu S, Kodama T, Li W, Miyagi T, et al. Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL cooperatively maintain integrity of hepatocytes in develo** and adult murine liver. Hepatology. 2009;50:1217–26.
Hikita H, Kodama T, Shimizu S, Li W, Shigekawa M, Tanaka S, et al. Bak deficiency inhibits liver carcinogenesis: a causal link between apoptosis and carcinogenesis. J Hepatol. 2012;57:92–100.
Tanaka S, Hikita H, Tatsumi T, Sakamori R, Nozaki Y, Sakane S, et al. Rubicon inhibits autophagy and accelerates hepatocyte apoptosis and lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology. 2016;64:1994–2014.
Kubes P, Mehal WZ. Sterile inflammation in the liver. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1158–72.
Aizawa S, Contu VR, Fujiwara Y, Hase K, Kikuchi H, Kabuta C, et al. Lysosomal membrane protein SIDT2 mediates the direct uptake of DNA by lysosomes. Autophagy. 2017;13:218–22.
Barbalat R, Ewald SE, Mouchess ML, Barton GM. Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2011;29:185–214.
Cai X, Chiu YH, Chen ZJ. The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing and signaling. Mol Cell. 2014;54:289–96.
Garcia-Martinez I, Santoro N, Chen Y, Hoque R, Ouyang X, Caprio S, et al. Hepatocyte mitochondrial DNA drives nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by activation of TLR9. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:859–64.
Inami Y, Yamashina S, Izumi K, Ueno T, Tanida I, Ikejima K, et al. Hepatic steatosis inhibits autophagic proteolysis via impairment of autophagosomal acidification and cathepsin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;412:618–25.
Ichim G, Lopez J, Ahmed SU, Muthalagu N, Giampazolias E, Delgado ME, et al. Limited mitochondrial permeabilization causes DNA damage and genomic instability in the absence of cell death. Mol Cell. 2015;57:860–72.
Kawane K, Ohtani M, Miwa K, Kizawa T, Kanbara Y, Yoshioka Y, et al. Chronic polyarthritis caused by mammalian DNA that escapes from degradation in macrophages. Nature. 2006;443:998–1002.
Yasuda T, Nadano D, Awazu S, Kishi K. Human urine deoxyribonuclease II (DNase II) isoenzymes: a novel immunoaffinity purification, biochemical multiplicity, genetic heterogeneity and broad distribution among tissues and body fluids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1119:185–93.
Koizumi T. Deoxyribonuclease II (DNase II) activity in mouse tissues and body fluids. Exp Anim. 1995;44:169–71.
Nakahira K, Haspel JA, Rathinam VA, Lee SJ, Dolinay T, Lam HC, et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:222–30.
Ashley N, Harris D, Poulton J. Detection of mitochondrial DNA depletion in living human cells using PicoGreen staining. Exp Cell Res. 2005;303:432–46.
Kodama T, Takehara T, Hikita H, Shimizu S, Shigekawa M, Tsunematsu H, et al. Increases in p53 expression induce CTGF synthesis by mouse and human hepatocytes and result in liver fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:3343–56.
Hikita H, Takehara T, Kodama T, Shimizu S, Hosui A, Miyagi T, et al. BH3-only protein bid participates in the Bcl-2 network in healthy liver cells. Hepatology. 2009;50:1972–80.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank AbbVie for providing ABT-737, Dr. S. Nagata (Kyoto University) for providing Dnase2a floxed mice, Dr. You-Wen He (Department of Immunology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC) for providing the Mcl-1 floxed mice and Dr. Kinya Otsu (King’s College London) and Dr. Osamu Yamaguchi (Osaka University) for technical assistance with the measurement of DNase II activity using the SRED method.
Funding
This work was partially supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (26253047 and 17H05508 to T Takehara and 17K09423 to HH) and a Grant-in-Aid for Research on Hepatitis from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by H.-U. Simon
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, Y., Hikita, H., Nozaki, Y. et al. DNase II activated by the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway regulates RIP1-dependent non-apoptotic hepatocyte death via the TLR9/IFN-β signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ 26, 470–486 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0131-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0131-6
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Identification of four mitochondria-related genes in sepsis based on RNA sequencing technology
BMC Immunology (2024)
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps aggravate neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis via TLR9 after traumatic brain injury
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Splenic monocytes mediate inflammatory response and exacerbate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in a mitochondrial cell-free DNA-TLR9-NLRP3-dependent fashion
Basic Research in Cardiology (2023)
-
RNA-seq coupling two different methods of castration reveals new insights into androgen deficiency-caused degeneration of submaxillary gland in male Sprague Dawley rats
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
Organellar homeostasis and innate immune sensing
Nature Reviews Immunology (2022)