Abstract
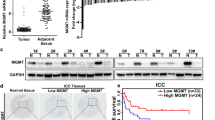
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation has recently been found involving in regulatory mechanism of the tumor progression. Our aim was to explore the biological function and clinical significance of the m6A methyltransferase METTL3 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). In this study, we revealed that METTL3 was upregulated and predicted poor prognosis of patients with ICC. Multivariate regression analysis demonstrated that METTL3 expression was an independent predictor for overall survival in patients with ICC. Moreover, METTL3 knockdown inhibited ICC progression, while METTL3 overexpression showed the opposite effect. METTL3 inhibitor STM2457 also showed anti-tumor effect in ICC. Mechanistically, METTL3 transcription was driven by H3K4me3 activation. Upregulation of METTL3 mediated m6A modification of IFIT2 mRNA and accelerated IFIT2 mRNA decay in a YTHDF2-dependent manner, which promoted the development of ICC and lead to poorer prognosis. In summary, our findings revealed that H3K4me3 activation-driven METTL3 transcription promotes ICC progression by YTHDF2-mediated IFIT2 mRNA degradation, suggesting that METTL3 may serve as a potential target for human ICC therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is the second most common primary malignant liver cancer, which accounts for ~10% of all such cancers [1, 2]. The prognosis of patients with ICC is poor. Nearly 70% of patients with ICC are already unresectable at the time of diagnosis. Even in patients undergoing curative surgical treatment, the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate is ~30%, and the 5-year recurrence rate is up to 70% [3]. Therefore, effective systemic therapy during the course of the disease is required for the ICC. The combination of gemcitabine and cisplatin is the current first-line therapy for patients with unresectable ICC, but its efficacy remains very limited [4, 31].
RIP-seq or RIP-qPCR
HuCC-T1 and HCCC-9810 Cells were seeded in a 150-mm dish at a density of 1 × 106 cells/ml. The cells were harvested in lysis buffer. The anti-YTHDF2 antibody was used for immunoprecipitated in a dilution of 1:100. The RNA of input and immunoprecipitated samples were isolated with the TRIzol reagent and subjected to sequencing using Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform supplied by Novogene or qPCR analysis. For qPCR analysis, a flank region with no signal was used as a negative control.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis of the data was carried out in SPSS 22.0 software and GraphPad Prism 9 software. The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and compared by t test, Wilcoxon test, or Chi square test. DFS and OS were measured by Kaplan–Meier method, and the differences between groups were evaluated by log rank test. The independent predictive factors were determined by the cox proportional hazard model. All the statistical analyses, p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
References
Razumilava N, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet.2014;383:2168–79.
Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma - evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:95–111.
Mavros MN, Economopoulos KP, Alexiou VG, Pawlik TM. Treatment and prognosis for patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2014;149:565–74.
Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, Cunningham D, Anthoney A, Maraveyas A, et al. Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1273–81.
Shroff RT, Javle MM, **ao L, Kaseb AO, Varadhachary GR, Wolff RA, et al. Gemcitabine, cisplatin, and nab-Paclitaxel for the treatment of advanced biliary tract cancers: a phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:824–30.
Wardell CP, Fujita M, Yamada T, Simbolo M, Fassan M, Karlic R, et al. Genomic characterization of biliary tract cancers identifies driver genes and predisposing mutations. J Hepatol. 2018;68:959–69.
Nepal C, O’Rourke CJ, Oliveira D, Taranta A, Shema S, Gautam P, et al. Genomic perturbations reveal distinct regulatory networks in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology.2018;68:949–63.
Jusakul A, Cutcutache I, Yong CH, Lim JQ, Huang MN, Padmanabhan N, et al. Whole-genome and epigenomic landscapes of etiologically distinct subtypes of cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:1116–35.
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell.2012;149:1635–46.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature.2014;505:117–20.
He L, Li H, Wu A, Peng Y, Shu G, Yin G. Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:176.
Deng X, Su R, Weng H, Huang H, Li Z, Chen J. RNA N(6)-methyladenosine modification in cancers: current status and perspectives. Cell Res. 2018;28:507–17.
Yankova E, Blackaby W, Albertella M, Rak J, De Braekeleer E, Tsagkogeorga G, et al. Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia. Nature.2021;593:597–601.
Lai KC, Liu CJ, Lin TJ, Mar AC, Wang HH, Chen CW, et al. Blocking TNF-α inhibits angiogenesis and growth of IFIT2-depleted metastatic oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;370:207–15.
Pidugu VK, Pidugu HB, Wu MM, Liu CJ, Lee TC. Emerging functions of human IFIT proteins in cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 2019;6:148.
Zeng C, Huang W, Li Y, Weng H. Roles of METTL3 in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:117.
Yang C, Hu Y, Zhou B, Bao Y, Li Z, Gong C, et al. The role of m(6)A modification in physiology and disease. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:960.
Cheng M, Sheng L, Gao Q, **ong Q, Zhang H, Wu M, et al. The m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes bladder cancer progression via AFF4/NF-κB/MYC signaling network. Oncogene.2019;38:3667–80.
Vu LP, Pickering BF, Cheng Y, Zaccara S, Nguyen D, Minuesa G, et al. The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells. Nat Med. 2017;23:1369–76.
Wang H, Deng Q, Lv Z, Ling Y, Hou X, Chen Z, et al. N6-methyladenosine induced miR-143-3p promotes the brain metastasis of lung cancer via regulation of VASH1. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:181.
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J, Cheng CL, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology. 2018;67:2254–70.
Cai X, Wang X, Cao C, Gao Y, Zhang S, Yang Z, et al. HBXIP-elevated methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett. 2018;415:11–9.
Wang Q, Chen C, Ding Q, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Chen J, et al. METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification of HDGF mRNA promotes gastric cancer progression and has prognostic significance. Gut.2020;69:1193–205.
Ivashkiv LB, Donlin LT. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:36–49.
Lai KC, Liu CJ, Chang KW, Lee TC. Depleting IFIT2 mediates atypical PKC signaling to enhance the migration and metastatic activity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncogene.2013;32:3686–97.
Koh SY, Moon JY, Unno T, Cho SK. Baicalein suppresses stem cell-like characteristics in radio- and chemoresistant MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells through up-regulation of IFIT2. Nutrients. 2019;11:624.
Shen H, Zhan M, Zhang Y, Huang S, Xu S, Huang X, et al. PLZF inhibits proliferation and metastasis of gallbladder cancer by regulating IFIT2. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:71.
Su W, **ao W, Chen L, Zhou Q, Zheng X, Ju J, et al. Decreased IFIT2 expression in human non-small-cell lung cancer tissues is associated with cancer progression and poor survival of the patients. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:8139–49.
Li J, **e H, Ying Y, Chen H, Yan H, He L, et al. YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:152.
Huang CS, Chu J, Zhu XX, Li JH, Huang XT, Cai JP, et al. The C/EBPbeta-LINC01133 axis promotes cell proliferation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through upregulation of CCNG1. Cancer Lett. 2018;421:63–72.
Moore MJ, Zhang C, Gantman EC, Mele A, Darnell JC, Darnell RB. Map** Argonaute and conventional RNA-binding protein interactions with RNA at single-nucleotide resolution using HITS-CLIP and CIMS analysis. Nat Protoc. 2014;9:263–93.
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge the financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772522, 82002501, 82072644, 81972651, and 31771630), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515010123, 2019A1515010096 and 2019A1515010686).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X-YY conceived the study. X-YY, Q-CX and Y-CT designed the study. Q-CX, Y-CT, Y-HS, SC and Y-QZ performed experiments and analyzed the results. Y-HS, C-SH and X-TH provided and assisted in the collection and analysis of clinical samples. X-YY and WZ supervised and guaranteed the study. X-YY, Q-CX, Y-CT and WZ wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, QC., Tien, YC., Shi, YH. et al. METTL3 promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression by regulating IFIT2 expression in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Oncogene 41, 1622–1633 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02185-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02185-1
- Springer Nature Limited