Abstract
G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) play pivotal roles in desensitizing GPCR signaling but little is known about how GRKs recognize and phosphorylate GPCRs due to the technical difficulties in detecting the highly dynamic GPCR/GRK interaction. By combining a genetic approach with multiple biochemical assays, we identified the key determinants for the assembly of the prototypical GPCR rhodopsin with its kinase GRK1. Our work reveals that the regulatory G-protein signaling homology (RH) domain of GRKs is the primary binding site to GPCRs and an active conformation of the GRK1 kinase domain is required for efficient interaction with rhodopsin. In addition, we provide a mechanistic solution for the longstanding puzzle about the gain-of-function Q41L mutation in GRK5. This mutation is in the RH domain and increases the capacity of the GRK mutant to interact with and to desensitize GPCRs. Finally we present the principal architecture of a rhodopsin/GRK complex through negative stain electron microscopy reconstruction. Together, these data define the key components for the rhodopsin/GRK1 interaction and provide a framework for understanding GRK-mediated desensitization of GPCRs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprise the largest receptor family in humans 1. Its members play fundamental roles in a broad spectrum of physiological processes and are involved in a plethora of diseases, including metabolic syndrome, neurodegenerative diseases, immune disorders and cancers2, 3. Extracellular signals activate GPCRs through ligand binding to induce a conformational change that favors the binding of heterotrimeric G proteins to initiate GPCR signaling4, 5. In many cases, the activated receptors need to be deactivated in a timely manner to maintain cellular homeostasis. G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) deactivate GPCR signaling by phosphorylating the intracellular loops and/or the C-tail of the receptor. The receptor is then recognized by arrestins, which block G-protein access and induce the internalization of the receptor-arrestin complex to shut down the signal transduction6,7. Since GRKs play pivotal roles in the desensitization of GPCR signaling, mutations of GRKs are associated with a variety of diseases, such as heart failure, Parkinson's disease and diabetes8,9. While most GRK mutations have detrimental effects, a gain-of-function mutation that is commonly found in African Americans, GRK5 Q41L, is of particular interest as it has a well-established protective effect against heart failure by enhancing β-adrenergic receptor desensitization10. However, how this mutation affects GRK5 activity remains unknown.
GRKs belong to the AGC family of serine/threonine kinases7. The GRK family can be further divided into three subfamilies based on sequence homology: the rhodopsin kinase subfamily (GRK1 and GRK7), the β-adrenergic receptor kinase subfamily (GRK2 and GRK3) and the GRK4 subfamily (GRK4, GRK5 and GRK6). All GRK family members share a common structural architecture, in which the kinase domain is inserted into a loop between the first 9 and the 10 α-helix of a regulatory G-protein signaling homology (RH) domain, followed by a variable carboxyl terminus. The RH core domain of GRKs contains ∼130 amino acids that form a bundle of nine helices (α1-α9), which is conserved in all regulatory G-protein signaling (RGS) proteins11. The kinase domain of GRKs contains a large C-terminal lobe and a small N-terminal lobe, closely related to those of other members of the AGC protein kinase family. Although the C-terminal domains of GRKs are least conserved, a common feature of the C-terminal domain is membrane binding12.
Similar to heterotrimeric G proteins and arrestins, GRKs recognize active GPCRs. The molecular mechanism of how these key regulators recognize the active receptors is a major focus of the GPCR field. Crystal structures of the β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR)-bound Gs13, active rhodopsin (Rho) bound to a C-terminal Gα peptide14 and visual Rho-bound arrestin15 revealed that G protein and arrestin use similar but distinct strategies to interact with activated receptors. For instance, both Gs and arrestin recognize the outward movement of the cytoplasmic ends of the GPCR transmembrane (TM) helices. However, while G proteins mainly utilize the ligand-induced extension of TM5 and TM6 of β2AR for binding, visual arrestin (arrestin1) uses multiple discrete small patches, including TM7 and cytoplasmic helix 8 to interact with the activated Rho. Compared to GPCR/G-protein and GPCR/arrestin interactions, GPCR/GRK interactions are much weaker and much more dynamic, properties which have made the direct crystallization of a GPCR/GRK complex currently unattainable. Most knowledge on the receptor/GRK interaction is based on indirect assays, such as GPCR phosphorylation assays, and on molecular modeling based on limited structural information for GRKs and receptors.
Rho is a prototypical GPCR. It is responsible for visual signal transduction in rod cells, and has been extensively studied as a model for understanding GPCR signaling16,17. GRK1 phosphorylates light-activated Rho and initiates a series of events that lead to rapid quenching of the receptor signaling18. We had previously used the combination of a genetic approach with multiple biochemical assays to study the Rho/arrestin interaction15. To gain insight into GRK1-mediated Rho desensitization, we have used a similar strategy to dissect the Rho/GRK1 interaction. We discovered that the interaction of GRK1 with Rho is mainly mediated by the RH domain of GRK1 and requires an active conformation of the kinase domain. We also uncovered the mechanism by which the Q41L mutation of GRK5 enhances the desensitization of GPCR signaling and present an overall architecture of the Rho/GRK complex assembly through single-particle reconstruction from negative stain electron microscopy (EM) images.
Results
Establishment of an effective method to detect the transient interaction between rhodopsin and GRK1
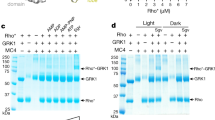
The transient and dynamic nature of the GPCR/GRK interaction makes it difficult to use conventional methods such as co-IP and pull-down assays to gain insight into its molecular and structural basis. In vivo fluorescence or luminescence-based proximity assays (e.g., FRET or BRET) have been developed for detecting GPCR/GRK interactions19, yet their sensitivity is usually not sufficient to detect the weak association between the two components due to low signal-to-noise ratios20. The lack of an efficient method to detect this weak and transient interaction has become a hurdle for studying the GPCR/GRK interaction. A genetic approach called the Tango assay has been developed to detect GPCR/arrestin interactions in vivo21. This method converts a transient interaction into a stable and amplifiable reporter signal to record the activation of a receptor without interference from endogenous signaling pathways. We have successfully used this method to detect the interaction between Rho and visual arrestin, and to validate the crystal structure we determined for the Rho/arrestin complex15. To overcome the difficulty in detecting the weak Rho/GRK1 interaction, we therefore adopted the Tango assay. Specifically, we fused human GRK1 to the N-terminus of tobacco etch virus (TEV) protease, and human Rho via an optimized TEV protease cleavage site to a modified transcriptional activator tTA from the Tet-ON 3G system that is highly sensitive and more robust than the conventional tTA (see Materials and Methods for details) (Figure 1A). An interaction between Rho and GRK1 brings the TEV protease in the direct vicinity of the cleavage site to cut and release tTA, which allows tTA to enter the nucleus to activate reporter gene transcription. We first tested whether this method can detect the active conformation of Rho. While Rho is a light-activated GPCR, mutational studies showed that the light-activated conformation of Rho can be mimicked by certain mutations, e.g., the E113Q/M257Y mutation22. In addition, the introduced cysteine residues of a Rho N2C/N282C mutant protein from a disulfide bond that increases Rho's stability without affecting its activityFull size image
Because the interaction of GRKs with GPCRs requires the active conformation of the receptor, typified by an opening of the receptor TM core at the cytoplasmic side, we then focused on the highly specific interaction of GRK1 with the Rho core (residues 1-321), which includes cytoplasmic helix 8 but lacks the Rho C-tail (Figure 2B). In this context, the N-terminal GRK1 fragment (residues 1-183) retained about 70% of the receptor interaction signal relative to FL GRK1, while all C-terminal fragments lacking the RH core domain, including the kinase and C-terminal RH extension domains in combination with or without the GRK1 C-tail, showed no receptor interaction activity (Figure 2B). These data can be more clearly viewed when all domain activity was plotted as percentile activity of FL GRK1 (Supplementary information, Figure S1). A western blot of all GRK1 constructs showed that all GRK1 fragments were expressed; however, the expression levels varied from fragment to fragment (Supplementary information, Figure S2A, left panel). In particular, fragments mainly encompassing the kinase domain (184-468, 184-513 and 184-563) showed a much lower expression level than FL and other fragments. To rule out the possibility that the lack of interaction of the kinase domain fragments is due to the low expression levels, we titrated the expression levels of all constructs to a similar level by changing the amount of DNA in the transfection (Supplementary information, Figure S2A, right panel). To investigate the correlation of the Tango activity and the amount of transfected DNA, we carried out a dose-response curve of the amount of transfected DNA with the Tango activity for both GRK1 and Rho. The data showed that for both GRK1 and Rho, between 1 and 30 ng per well, the Tango signal linearly correlated with the amount of transfected DNA (Supplementary information, Figure S2B). In our Tango assay, we transfected DNA at ∼10 ng per well, which is in the middle part of the linear dose response. Thus, the titration allowed us to adjust DNA amounts to yield similar protein expression levels. Having established these transfection conditions, we used DNA ratios that resulted in approximately equal protein levels for all constructs (deletions/wild type) in the Tango assay to reevaluate the domain map** results. The data show that, similar to the results obtained with equal amounts of DNA transfected (Figure 2B), the receptor interaction is mainly mediated by the RH domain (Supplementary information, Figure S2C). To avoid potential interference of protein expression levels on Tango assay activities, we also titrated the expression levels of the GRK1 point mutant construct to a similar level and transfected DNA at the corresponding ratios. A western blot of all key GRK mutant fragments and additional truncations used in this study is shown in Supplementary information, Figure S3. These results suggest that the observed lack of interaction was therefore not due to low expression levels of the deletion constructs and further support that the RH domain of GRK1 is the major binding interface with Rho.
The N-terminus of GRK1 contains the αNT helix (residues 1-20), which is conserved among all members of the GRK family, and has been proposed to play a crucial role in receptor binding based on its requirement for receptor phosphorylation25. Our extensive domain map** data show that deletion of the αNT does not significantly affect receptor interaction (Figure 2B; Supplementary information, Figure S1). For instance, GRK1 (31-183) contains the RH core domain but lacks αNT, yet has a similar binding capacity as GRK1 (1-183), with both constructs retaining about 70% of the binding capacity of FL GRK1 (Figure 2A and 2B). Consistent with this result, GRK1 (31-563) differs from FL GRK1 only by the absence of the αNT-containing N-terminus, yet it retains full binding capacity relative to non-truncated GRK1 (Figure 2B; Supplementary information, Figure S1). In addition, the fragment comprising the N-terminal 30 amino acids of GRK1 (GRK1 (1-30)) did not show any interaction with the receptor (Figure 2B). Collectively, these data indicate that the very N-terminus is not needed for receptor binding. Further evidence comes from a mutation study of residues that were proposed to interact with αNT to form the so-called active conformation. The structure of GRK6 in which αNT was resolved shows that V477 of the AGC C-tail (V479 in GRK1) and R190 of the β3-strand of the kinase N-lobe of GRK6 (R194 in GRK1) form key interactions with αNT to hold αNT in a specific position believed to be the active conformation for receptor docking26. However, mutations of V479 and R194 in GRK1 did not inhibit Rho binding (Supplementary information, Figure S4A). Similarly, mutations of L4 and Y13 of GRK2 have been shown to abolish Rho phosphorylation based on a GPCR/GRK2 docking simulation study20. We therefore asked whether mutations of the corresponding residues in GRK1 (L6A and F15A, respectively) affect Rho binding. Our binding data revealed that these mutations did reduce receptor interaction but did not totally abrogate receptor binding (Figure 2C).
Since the N-terminal RH core domain contains most, but not all, of the receptor binding capacity (∼70%), we asked whether a complete RH domain (core domain plus C-terminal extension) has full receptor interaction capacity. As shown in Figure 2D, Supplementary information, Figure S1, constructs in which the RH core domain (helices α1-9) is fused with the C-terminal extension domain (helix α10 with or without the C-tail) by deletion of the kinase domain (1-183 + 508-559 and 1-183 + 508-532) have full receptor interaction capacity (≥ 100%, Figure 2D).
We then used the in vitro AlphaScreen assay to validate these observations. Similar to our observations using the Tango assay, the purified N-terminal domain of GRK1 (1-183) had about 70-80% receptor binding activity (Figure 2E). GRK1 (31-183) that has a further deletion of the very N-terminus including αNT had almost the same capacity as GRK1 (1-183). Consistently, GRK1 (31-563) had almost the same receptor binding activity as the FL protein. GRK1 (1-183 + 508-559), which had full activity in Tango assay, was difficult to express and purify. However, we could purify GRK1 (31-183 + 508-563) and show that it retained about 70% of the receptor binding capacity (Figure 2E). Together, these results indicate that the RH domain of GRK1 mediates the major interaction with Rho.
We next asked whether the RH domain-mediated receptor interaction is conserved within the GRK family. We chose GRK1, GRK2 and GRK5 to represent each subfamily, and tested their interaction with Rho, β2AR, 5-HT1B and the class B GPCR parathyroid hormone receptor (PTH1R). GRK1 and GRK2 both showed a similarly strong interaction with Rho (Supplementary information, Figure S4B). For β2AR, PTH1R and 5-HT1B, GRK2 showed the strongest interaction signal, consistent with the observation that GRK2 is the predominant kinase for desensitizing a broad spectrum of GPCRs. Since GRK2 is the native partner for most GPCRs, we focused on GRK2 for the domain analysis. Consistent with the observation for Rho/GRK1, GRK2 (1-184) comprising the RH core domain contains almost full capability for interacting with β2AR, PTH1R and 5-HT1B (Supplementary information, Figure S4C). Moreover, a further deletion of the first 27 amino acids (generating GRK2 (28-184)) does not affect the receptor interaction. One distinct feature of GRK2 is the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain at its C-terminus. The PH domain has the ability to bind to Gβγ and may help anchor GRK2 to the membrane for receptor binding. As shown in Supplementary information, Figure S4D, deletion of the C-terminal PH domain (GRK2 (1-547)) did not affect receptor binding ability. This result suggests that in addition to the PH domain, GRK2 may use additional domains for membrane binding. A sequence homology analysis suggests that a cluster of positively charged residues at the N-terminus of GRK2 may also participate in membrane binding27.
Our observation that the very N-terminus of GRK1 is dispensable for receptor binding was unexpected, as numerous studies suggested that this region is critical for receptor binding and phosphorylation28,29. Since most predictions for receptor binding were based on the fact that deletions or mutations of αNT inhibit receptor phosphorylation, we utilized the assay described in Figure 1H to examine whether N-terminally truncated GRK1 still has the ability to stimulate the phosphorylation-dependent interaction between receptor and arrestin. All GRK1 constructs that lack the kinase domain (1-183, 31-183 and 31-183 + 508-563) failed to stimulate the Rho-arrestin interaction, indicating that this assay indeed detects GRK1 kinase activity (Figure 2F). Very interestingly, GRK1 (31-563), which contains the intact kinase domain and binds activated Rho (Figure 2B and 2E) but lacks the very N-terminus, lost the ability to stimulate the phosphorylation-dependent interaction between Rho and arrestin (Figure 2F). This is consistent with reports that this region is crucial for receptor phosphorylation. We used the direct kinase assay to validate these observations. The data show that indeed deletion of the first 30 residues (generating GRK1 (31-563)) abolished the ability of GRK1 to phosphorylate Rho; however, surprisingly, we found this deletion has no effect on its autophosphorylation activity (Figure 2G). These data suggest that while the very N-terminus of GRK1 is not needed for receptor binding, it is essential for receptor phosphorylation.
An active conformation of the kinase domain of GRK1 is needed for receptor interaction
Although the intact RH domain (the core domain fused to the C-terminal extension, 1-183 + 508-559) has full receptor interaction capacity in isolation, binding capacity may be modulated by the kinase activity in the context of the FL protein. Numerous studies have suggested that an active conformation of the kinase domain, characterized by four correctly aligned key hydrophobic residues (the “regulatory spine”), is needed for both receptor binding and phosphorylation, and conversely that receptor binding stimulates GRK kinase activity7. To test whether an active kinase domain conformation is required for Rho binding in the context of FL GRK1, we included the ATP-competitive GRK inhibitor paroxetine into our Tango assay. ATP competitive inhibitors mimic the effect of ATP in stabilizing an active kinase conformation, but block catalytic activity because they cannot be hydrolyzed30. As shown in Figure 3A, paroxetine indeed increased the interaction between receptor and GRK1, similar to the ATR ligand. Similar results were also obtained in an AlphaScreen assay, in which paroxetine increased the interaction between Rho and GRK1 in vitro. We next examined whether mutations of the critical ATP-binding residue K219 in β3 and of E238 in αC, which binds and positions K219 (nomenclature for human GRK1; shown as corresponding K216 and E235, respectively, in the bovine GRK1 structure in Figure 3B) (Figure 3B, left panel), affect the receptor binding capacity in our Tango system. Our data show that both K219A and E238A mutations almost completely eliminate the receptor binding capability of GRK1 (Figure 3B, right panel). We also tested the K219R mutant, a very conservative mutation that results in catalytic ally inactive protein, for which corresponding mutations do not affect folding in other protein kinases31. The K219R mutant also showed a complete block of receptor interaction. In contrast, K220 and D192 (shown as the corresponding K217 and D189 residues in the bovine GRK1 structure in Supplementary information, Figure S5A) form a comparably strong salt bridge within the relatively stable -sheet of the N-lobe, and their mutations only moderately affected receptor binding (Supplementary information, Figure S5A). Finally, we introduced triple P-to-A mutations into the PxxP motif (PPFKP) of the AGC C-tail in GRK1 (3PA, P470A/P471A/P474A; shown as corresponding P467, P468 and P471 in the bovine GRK1 structure in Supplementary information, Figure S5B), which have been shown to have the ability to disrupt receptor interaction and phosphorylation32. Consistent with a reported pull-down assay, the 3PA mutant shows no receptor interaction capacity (Supplementary information, Figure S5B), further indicating that an active kinase conformation is required for a stable interaction between GRK1 and Rho.
An active conformation of the kinase domain is needed for rhodopsin (1-321) interaction. (A) Paroxetine increases the rhodopsin/GRK1 interaction in the Tango assay (left panel) and in the AlphaScreen assay (right panel). Statistics to the DMSO control. (B) Mutations that disrupt the active conformation of the kinase domain abrogate rhodopsin/GRK1 interaction in the Tango assay. Mutations of human K219 and E238 equal bovine K216 and E235 as shown in the structure, respectively. Statistics were referred to the WT GRK1. (C) Examination of RH domain/kinase domain interface mutations on receptor interaction by Tango assay. Mutations of human T212, Y255, R461 and E521 equal bovine T209, Y252, R458 and E518 as shown in the structure, respectively. Statistics were referred to the WT GRK1. (D) HDX perturbation heat map of rhodopsin-GRK1 versus apo GRK1 overlaid on the structure of GRK1 (PDB ID: 3C4W). The colors indicate the % difference in GRK1 deuterium exchange (color code at bottom) upon complex formation with rhodopsin. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. n.s., not significant (differences relative to DMSO control (panel A) or FL GRK1 (all other panels)).
Since the kinase catalytic center is far from the RH domain, we speculated that the local conformational change caused by these mutations is transmittable to the RH domain through the interfaces that connect the kinase domain to the RH domain. There are two major interfaces between the RH domain and the kinase domain. One is the “upper” interface between the terminal subdomain (α1-3, α8-10) of the RH domain and the N-lobe of the kinase domain, and the other is the “lower” interface between the bundle subdomain (α4-7) of the RH domain and the C-lobe of the kinase domain (Figure 3C, middle panel). We then examined the effects of mutations of these interfaces. T212, Y255 and E521 (shown as corresponding to T209, Y252 and E518 in the bovine GRK1 structure in Figure 3C) on the upper surface form a hydrogen bond network that connects the α10 of the RH domain and the β-sheet bundle of the N-lobe. Mutations of these residues decreased receptor binding ability, and for the T212G mutation, in particular, almost totally abolished receptor interaction (Figure 3C, left lower panel). Similarly, F505 and F509 (shown as corresponding to F502 and F506 in the bovine GRK1 structure in Supplementary information, Figure S5C) form hydrophobic interactions with β4, β5 and αB of the N-lobe to hold the last helix of the kinase domain in position to connect with α10 of the RH domain. Mutations of those residues decreased receptor interaction (Supplementary information, Figure S5C). On the other hand, mutations of lower interface residues T97 and R461 (shown as corresponding to T97 and R458 in the bovine GRK1 structure in Figure 3C) did not affect receptor binding (Figure 3C, right panel), suggesting that a tight connection between the RH bundle domain and the C-lobe of the kinase domain is not needed for receptor binding.
We then used hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX) to probe possible conformational changes of human GRK1 upon receptor binding. We first used HDX to study the dynamics of apo GRK1. The most stable regions we observed in apo GRK1 are the lower interface between the RH domain and the C-lobe of the kinase domain, as well as α9 and α10 of the upper bundle of the RH domain (Supplementary information, Figure S6A-S6B). Since the Rho/GRK1 interaction is quite weak and dynamic, we covalently fused Rho and GRK1 through a flexible linker to stabilize the complex to allow us to study potential conformational changes of GRK1 upon receptor binding. The biggest change we observed is the destabilization of the lower connection between the RH domain and the C-lobe of the kinase domain, indicating a possible dissociation of the connection upon receptor binding (Figure 3D, Supplementary information, Figure S6C). Although the magnitudes of differences are small, these are statistically significant and detected with confidence33. We also observed stabilization of α9 of the RH domain, while α10 of the RH domain seems to become more dynamic, suggesting an exquisite conformational change in this region upon receptor binding.
Identification of key architecture elements crucial for receptor/kinase interaction
We next asked whether we can use the Tango assay to identify a surface on the RH domain that is crucial for receptor binding. We therefore performed an extensive mutational screen of the RH domain of GRK1. For easy comparison of data from different experimental batches, we normalized each mutation's activity to percent of WT GRK1 activity when ATR is present. In addition, we used a spectrum of colors, from bright blue to green, orange and magenta to visualize the severity of mutations for receptor binding, from slight (> 75% of WT), to medium (50%-75% of WT), severe (25%-50% of WT) and most severe (< 25% of WT), respectively, on the structure of GRK1 (PDB: 3C4W). This allowed us to easily identify a cluster of residues that is important for receptor binding. Our early domain map** study showed that the first 30 amino acids are dispensable for receptor interaction, while further deletion of the N-terminus to residue 41 resulted in a complete loss of receptor binding (Figure 4A), suggesting that residues between amino acids 30 and 41 (the loop between αNT and the 1 helix of the RH domain) are important for receptor binding. We therefore mutated these residues one by one. The Tango data show that while mutations of the charged residues, K33E, K34A and K38A, failed to inhibit receptor binding, mutations of the hydrophobic residues L39, L41 and P42 severely affected receptor interaction.
Identification of surface mutations of GRK1 crucial for rhodopsin binding. (A) Mutational analysis of residues in the loop between αNT and α1 of the RH domain for rhodopsin interaction via Tango assay. (B) Mutational analysis of residues in the α5-α6 loop of the RH domain. M(116-120): D116R/P117A/Q118A/K120E. (C) Identification of a cluster of mutations in α9, α3 and α10 of the RH domain important for receptor interaction via Tango assay. (D) An overview of all mutations overlaid on the structure of bovine GRK1 (PDB ID: 3C4W). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. NS, not significant (differences relative to WT GRK1).
We then analyzed the lower bundle of α4, α5 and α6 of the RH domain, which has been implicated in Gα binding in the structure of the GRK2/Gαq/Gβγ complex34. While a cluster of mutations of residues of the 5-α6 loop (D116R/P117A/Q118A/K120E) shows severe inhibition of receptor binding, single mutations only mildly affected receptor binding (Figure 4B). Similarly, a cluster of alanine mutations (L102A/Q105A/K106A/Q108A) in the lower helix bundle of the RH domain, as well as two clusters of mutations of charged residues, K133E/K135E and D91A/E93A/D94A/D96A, also failed to inhibit receptor binding (Supplementary information, Figure S7). Notably, the negatively charged cluster D91/E93/D94/D96 is highly conserved among all members of the GRK family. These data demonstrate that the lower bundle subdomain (α4-6) of GRK1 is not crucial for Rho binding, while the upper portion of the RH domain is required for Rho binding.
A study of sequence conservation across all members of the GRK family and the RGS proteins found that several residues in α9 and α3 of the RH domain are crucial for phosphorylation of the Rho C-terminus35. We tested two representative mutations, α9 Q176A and W177A, in our Tango system. Both mutations, either individually or combined with other mutations, completely eliminated receptor binding (Figure 4C). On the basis of this result, we performed an extensive mutational study of this region, which showed that most mutations in this region abrogated receptor interaction. To gain an overall view of the distribution and effect of all mutations (> 80 residues) that we have screened, we plotted mutated residues color coded for the strength of binding as percent of WT activity (Supplementary information, Table S1) on the structure of GRK1 (Figure 4D). While most mutations of the RH domain residues had little effect on receptor binding, we identified a cluster of mutations on α9, α3 and α10 that strongly repressed receptor binding (Figure 4D and 4C, right panel). Interestingly, these mutations are adjacent to the P42 and L41 mutations in the loop connecting αNT with RGS α1 (Figure 4C and 4A, left panel), which together form a surface groove encompassing α9, α3, α10 and the αNT-α1 loop. Unlike this cluster, all other mutations that severely inhibited receptor binding, including mutations in the kinase domain, were distributed rather sporadically (Figure 4D), suggesting that this surface groove is crucial for receptor binding.
We then asked whether we could use a similar strategy to identify a region on the receptor side that is crucial for GRK1 interaction. We first performed a series of single mutation screens as we did in our previous study of the Rho/arrestin interaction. Surprisingly, except T70R of ICL1, most single mutations in Rho did not markedly decrease the GRK1 interaction signal and a number of single mutations, including L68R, R135G, Y306G and N310R, showed increased interaction with GRK1 (Figure 5A). Since a number of studies suggested that the intracellular loops of GPCRs may mediate the interaction with GRKs12, we introduced clusters of mutations to change the nature of the loop regions. However, these mutations did not decrease GRK1 interaction (Figure 5B). In addition, TM7 and helix 8 have been shown to play a crucial role in the recognition of arrestin. We therefore asked whether this region contributes to GRK1 interaction. While the kink mutation (308-312 GSA, M308G/M309S/N310A/K311G/Q312A) failed to repress the GRK1 interaction, a cluster of mutations on the cytoplasmic surface of helix 8 (K311A/Q312A/N315A/T319A) strongly inhibited the GRK1 interaction (Figure 5C), suggesting that helix 8 is important for this interaction.
Identification of human rhodopsin (1-321) mutations that compromise the rhodopsin-GRK1 interaction in the Tango assay. (A) Screen of single mutations in different regions of rhodopsin for GRK1 interaction in the Tango assay. (B) Cluster mutations in the ICL of rhodopsin show no effect on GRK1 interaction in the Tango assay. ICL1“+”→A: H65A/K66A/K67A/R69A; ICL2“+”→A: K141A/R147A; ICL1→AAA: T62A/V63A/Q64A; ICL2→GSA: K141G/P142S/M143A/N145A/F146G/R147A/F148G/G149S; ICL3→AAA: Q236A/Q237A/Q238A. (C) A cluster of mutations in helix 8 of rhodopsin severely inhibit GRK1 interaction in the Tango assay. 308-312GSA: M308G/M309S/N310A/K311G/Q312A. Mutations are overlaid on the structure of bovine rhodopsin (PDB ID: 2X72). “WT” means rhodopsin 4M (1-321), all other mutations are based on this backbone. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. ICL, intracellular loops; NS, not significant (differences relative to “WT” rhodopsin).
Mechanism of the gain-of-function mutation Q41L of GRK5 in enhancing receptor desensitization
Heart failure is a lethal disease that is in part caused by hyper activation of β-adrenergic receptors. A genetic study discovered that Q41L, a GRK5 polymorphism commonly found in African-Americans, has a protective effect against heart failure, acting like a “genetic β-blocker” to protect against death or cardiac transplantation10. This study showed that the Q41L mutation of GRK5 augments β2AR desensitization and provided evidence of diminished downstream receptor signaling, e.g., decreased adenylyl cyclase activities. However, the exact mechanism by which the Q41L mutation enhances the desensitization of receptor signaling remains unclear. The Q41 residue resides on the helix 1 of the RH domain of GRK536 (Figure 6A, right panel). The Q41-corresponding residue in GRK1, K46 (Figure 6D, yellow sphere) is on the surface directly adjacent to the residues of the contiguous hydrophobic surface (Figure 6E, red spheres) that are required for receptor binding, suggesting the Q41L mutation of GRK5 might enhance receptor interaction by extending the hydrophobic surface (Figure 6A, right panel). Employing the Tango assay to interrogate the interaction between β2AR and GRK5, our data show that the Q41L mutation of GRK5 indeed strongly increased the interaction (Figure 6A, left panel). Since our Tango assay suggested that different GRKs may use a similar mechanism (e.g., utilize the RH domain) for receptor interaction (Supplementary information, Figure S4B and S4C), we asked whether the mutation corresponding to Q41L of GRK1, K46L has a similar effect on the Rho interaction. Therefore, we mutated K46 to the hydrophobic residues L, Y or W. All three mutations increased the interaction of GRK1 with Rho (Figure 6B), suggesting that GRKs may use this region to contact the hydrophobic core of the receptor. Since our work was focused on Rho, we employed an AlphaScreen assay to test the effects of all these mutations, including both GRK1 K46L and GRK5 Q41L, on the physical interaction of GRK1 or GRK5 with Rho. As shown in Figure 6C, the Q41L mutation clearly increased the physical interaction between GRK5 and Rho, while K46L only had a marginal effect on the GRK1- Rho interaction. We also used the direct kinase assay to examine the effect of these mutations on phosphorylation of Rho. The data showed at similar amount of loading (Figure 6E, coomassie blue stain, left panel); GRK1 (K46L) slightly increased autophosphorylation, but strongly increased (approximately three-fold relative to WT GRK1) the phosphorylation level of rho (4M) substrate (Figure 6E, middle and right panel). On the other side, compared to GRK1, GRK5 only weakly phosphorylates the Rho substrate (Figure 6F). This may be because Rho is not the native substrate of GRK5. Although not as dramatic as the K46L mutation of GRK1, we still found that the Q41L of GRK5 slightly increased the phosphorylation of Rho to about 10% above the level of the WT GRK5. We noticed that the K46L has a much stronger effect on the activity of GRK1 in the Tango assay than in the AlphaScreen assay (Figure 6B and 6C). We reasoned that this may be due to the membrane environment difference and the fact that the AlphaScreen is more sensitive to the slight change of protein concentration in vitro. On the other side, the kinase assay is highly consistent with the Tango assay where K46L has a strong effect on the phosphorylation of Rho (Figure 6B and 6E). Taken together, these data show that the GRK1 K46L mutation strongly enhances the phosphorylation of Rho, in a similar way as Q41L of GRK5 to augment the phosphorylation of β2AR37. These discoveries provide a mechanistic rationale for the gain-of-function Q41L mutation for receptor desensitization.
Mechanism of the gain-of-function Q41L mutation of GRK5 in receptor desensitization. (A) The Q41L mutation strongly increases the GRK5/β2AR interaction in the Tango assay. (B) Substitution of the corresponding residue in GRK1(k46) with hydrophobic residues increases the rhodopsin interaction. (C) Q41L increases the GRK5/rhodopsin interaction in the AlphaScreen assay. (D) K46 lies on the upper surface of the RH domain of bovine GRK1 (PDB ID: 3C4W). Yellow: K46; red: mutations of α3, α9 and α10 that severely decrease rhodopsin binding; cyan: RH domain (light cyan: RH α10); light brown: αNT; green: kinase domain; blue: C-tail of the kinase domain. (E) Direct kinase assay of the K46L of GRK1. (F) Direct kinase assay of the Q41L of GRK5. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. NS, not significant (differences relative to WT GRK1).
Electron microscopy reveals the overall architecture of the rhodopsin/GRK complex
The main challenge of gaining structural insight into the GPCR/GRK interaction is the weak and dynamic association between receptor and kinase. Since Q41L of GRK5 shows an enhancement of receptor interaction both in live cells and in the context of purified recombinant proteins, we asked whether we could use the Q41L mutation of GRK5 to probe the architecture of the Rho/GRK interaction. To further overcome the weak interaction between the receptor and the kinase, we covalently fused Rho to GRK5 (Q41L) via a flexible linker to acquire structural information of Rho/GRK. We have successfully used a fusion protein strategy to gain structural insight into many weakly associated protein complexes, such as the Jaz9/MYC338, SnRK/PP2C39 and the Rho/arrestin complexes15. To test whether the receptor-fused kinase is active, we use the direct kinase assay to examine the kinase activity of the receptor-kinase chimera. Our data show that both the GRK1- and GRK5 (Q41L)-receptor fusion proteins can efficiently phosphorylate the chimera kinase itself (autophosphorylation) and the Rho substrate (Supplementary information, Figure S8A). We noticed that Rho is less efficiently phosphorylated in the context of the GRK5 chimera than the GRK1 chimera. This is consistent with our previous observation (Figure 6E and 6F) and with Rho not being the native substrate of GRK5. Single-particle cryo-EM is an emerging tool of current structural biology. Because of the dynamic nature of the GPCR protein and the size of our complex, obtaining high-resolution images of the Rho/GRK5 complex via cryo-EM is currently impractical. We therefore decided to use negative stain EM to shed light on the overall architecture of the Rho/GRK complex. We expressed and purified BRIL-Rho-GRK5 (Q41L) fusion protein as monodisperse protein in insect cells (Supplementary information, Figure S8B). EM images from negatively stained Rho/GRK5 complex in amphipols, a new class of stably binding surfactants, show that the receptor/kinase complex forms an average 14× 10 nm particle, roughly the same size as Rho and GRK5 stacked together (Figure 7A). 2D classification of 8 000 particles shows the majority of the complex contains two parts; the upper part has a conical shape that resembles Rho, while the slightly bigger lower part comprises two interconnected domains that resemble the shape of GRK5 (Figure 7B). Interestingly, we can also visualize the shape and the connection of the two domains of GRK5 from the 2D average of 1 100 particles (Figure 7C, upper panel), with the slightly smaller domain on the left resembling the RH domain and the slightly bigger on the right resembling the kinase domain of GRK5. GRK5 packs against Rho through the upper parts of both the RH domain and the kinase domain. On the basis of the outward movement of TM5/TM6 in the active conformation of Rho, it is conceivable that Rho uses the outstretched ICL3 loop to contact the RH domain of GRK5 and helix 8 or ICL1 to contact the kinase domain (Figure 7C, lower panel). However, because of the low resolution of the negative stain images, we cannot rule out the alternative orientation, in which the kinase domain packs against ICL3 and the RH domain contacts helix 8 or ICL1. A 3D reconstitution of the 2 000 2D images suggests that the upper part of the RH domain contacts the loop region of Rho (Figure 7D). Notably, this interface includes the surface required for Rho binding and Q41. It is therefore reasonable that the Q41L-mutated residue of GRK5 may directly contact ICL3 or the TM5-TM6 core. Taken together, the low-resolution EM images of the Rho/GRK5 complex reveal the main architecture of the Rho/GRK interaction in which GRK5 utilizes both the RH domain and the kinase domain to interact with the intracellular part (including both ICL3 and helix 8) of Rho.
Negative stain EM reveals the principal architecture of the rhodopsin/GRK5 complex. (A) Representative EM image of negatively stained rhodopsin-GRK5 (Q41L) fusion protein in amphipol. (B) 2D classification of negative stain images. (C) 2D average of negative stain images (upper panel) and a proposed model of the rhodopsin/GRK5complex. (D) 3D reconstitution of the 2D negative stain images of the rhodopsin/GRK5 complex overlaid with modeled rhodopsin/GRK5 complex (rhodopsin: PDB ID: 3PQR; GRK5: PDB ID: 4TND). Refined resolution was at 23 Å.