Study population
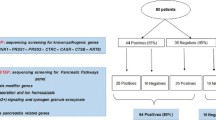
Three unrelated families of Chinese origin were included in the study (Figure 1). Patients IV-1 and III-1 from AIP1, patient II-1 from AIP2, and patient II-1 from AIP3 fulfilled the diagnostic criteria19, 20 on the basis of the histological examination of pancreatic specimens obtained during surgery. Moreover, 26 unrelated patients with type 1 AIP, 20 patients with chronic pancreatitis, and 520 unrelated healthy volunteers, were included as a control (Supplementary Figure 3).
Whole-exome sequencing (WES)
WES was performed on DNA extracted from peripheral blood obtained from patients IV-1 and III-1 of AIP1 family, patient II-1 of AIP2 family, and patient II-1 of AIP3 family and their male family members (II-2 and II-4 from AIP1, I-1 and II-2 from AIP2, and I-1 from AIP3) shown in Figure 1a. The samples were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq2500 platform (100 bp X2) after exome capture with SureSelectXT Human All Exon V5 kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). After raw data processing, reads were mapped to human genome reference hg19 using BWA (bio-bwa.sourceforge.net) with realignment around the known Indels from the 1000 Genomes Pilot study (http://www.1000genomes.org/category/pilot-study). The recalibration of the base quality scores was performed according to the recommendations of the GATK Best Practices (http://www.broadinstitute.org/gatk). Variant calling and independent filtering were performed using GATK Unified Genotyper and SAMtools mpileup.
Only variants with a mean read depth of at least × 10 and a minimum quality score of 30 were considered for further analyses. This low coverage threshold, even though it may include a certain number of false positives, was chosen to consider the largest number of possible variants. The Phred-scaled quality score of 30 corresponds to a base calling accuracy of 99.9%.
As AIP is rare in the general population, variants with a minor allele frequency >1% in 1000 Genomes (October 2014 release, all subjects) and NHLBI-ESP 6500 Exomes (all subjects) databases were excluded.
An autosomal recessive inheritance model was used for the identification of candidate genes in families. Therefore, we analyzed the exome data considering homozygous variants shared by the affected for which the parents resulted heterozygous. The candidate pathogenic variants were validated by Sanger sequencing.
Immunohistochemistry and microscopy
Pancreatic tissues from patients with AIP were used for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis. IgG, IgG4, CD3, CD20, CD138, κ, λ, and βCGRP antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). To identify the ultrastructural characteristics of AIP, pancreatic tissues were fixed with glutaraldehyde (2% v/v) in 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4), dehydrated through a gradient of ethanol, and embedded in EPON epoxy resin. Ultrathin sections of 90-nm thickness were sliced from each block, and double-strained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate and observed using transmission electron microscopy. Deposits of IgG4 were detected by direct immunofluorescence microscopy on frozen sections using 100-fold diluted fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled antibodies specific to mouse or rabbit IgG (Dako, Hamburg, Germany).
Transfection of HEK293 cells in vitro
The GV287 plasmid was linearized with AgeI to obtain a CALCB fragment of 384 bp (c.88T>C mutant or wild-type) or 640 bp (INS [c.86 G +1: +256]). The fragment was sub-cloned into pcDNA3·1(−) (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). After transfection of CALCB expression vectors or the empty control in HEK293 cells for 24 h, the cells were harvested, and total protein was extracted for Western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent analyses (ELISA).
RNA-SEQ
Transcriptome deep sequencing (RNA-seq) was performed using total RNA isolated from wild-type-, and S30P mutant-transfected cells. Three individuals from each genotypic group were randomly selected. Total RNA was extracted from frozen tissue using the SV Total RNA Isolation System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The samples were sent to DRIGEN Co., Ltd. for RNA-seq library preparation using the TruSeq SBS Kit (75 cycles) and single-end sequencing on Illumina NextSeq 500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). RNA-seq reads were quality filtered using SolexaQA packages with default parameters, as well as, for the requisite length >70 bp for both ends of each read pair. The sequencing data have been submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive. Genes that showed a significant (P<0.05) difference in transcript levels were termed as differentially expressed (DE) genes.
Analysis of CALCB expression and ERK phosphorylation
To determine the expression of exogenous βCGRP among the empty vector-, wild-type-, S30P mutant-, and IR [1] mutant-transfected HEK293 cells, Western blot analysis was carried out using antibodies specific for Flag and βCGRP. GAPDH was used to assess the loading variation and enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) for transfection efficiency and extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation (phospho-T202/204). βCGRP levels in the supernatant and cell lysate were measured by ELISA (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA).
Proteins from transfected HEK293 cells lysate were separated on 4–12% Tris-glycine gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were probed with antibodies directed against (phospho-T202/204) ERK1/2 (AP0472), total ERK (ABclonal, Wuhan, China, A1796), AKT1 (ABclonal, AP0004), (phospho-S473) AKT1 (ABclonal, AP0140), and GAPDH (ABclonal, AP5809).
Subcellular localization of βCGRP
Ubi-MCS-3FLAG-SV40-EGFP was expressed in HEK293 cells, and immunofluorescence confocal microscopy was employed to determine its subcellular localization using GM130 antibody (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA) and anti-mouse-cy3 (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, USA) for the Golgi apparatus, Flag antibody (Sigma, CA, USA) and anti-rabbit-647 (Jackson ImmunoResearch) for βCGRP, and calnexin antibody (Sigma) and anti-rabbit-647 for the ER.
Localization of trypsin/PAR2, PAR2/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and CD4/FOXP3
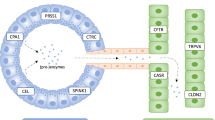
PAR2 is reported to coexpress with CGRP by a subpopulation of primary spinal afferent neurons that control neurogenic inflammation.29, 30 Moreover, trypsin activation of PAR2 induces activation of ERK1/2 in order to regulate a variety of nuclear transcription factors by phosphorylation, which contributes to the effect of trypsin on gastrointestinal smooth muscle contraction.31 In the current study, confocal immunofluorescence microscopy was undertaken to determine the correlation of trypsin (TRYP) and PAR2, PAR2 and ERK, PI3K and AKT, and ERK and VEGFR2. Trypsin was detected with a rabbit anti-human antibody (ABclonal) and labeled with a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated to Cy3. PAR2 was detected with a rabbit anti-human antibody (Wanlei, Shenyang, China) and labeled with a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated to FITC. ERK was detected with rabbit anti-human antibody (Sangon, Shanghai, China) and labeled with a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated to Cy3. AKT was detected with a mouse anti-human antibody (Sanying, Wuhan, China) and labeled with a goat anti-mouse secondary antibody conjugated to Cy3. PI3K was detected with a rabbit anti-human antibody (Wanlei) and labeled with a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated to FITC. VEGFR2 was detected with rabbit anti-human antibody (Sangon) and labeled with a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated to FITC. Nuclei were counterstained using 4', 6-diamidine-2-phenylidole dihydrochloride (DAPI).
Tregs were identified by staining with anti-CD4 and anti-Foxp3. CD4 was detected with a rabbit anti-human antibody (Sanying) and labeled with a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated to Cy3. Foxp3 was detected with a mouse anti-human antibody (Santa Cruz) and labeled with a goat anti-mouse secondary antibody conjugated to FITC. Nuclei were co-stained using DAPI.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed with SPSS version 18.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Normal variation was expressed as mean±s.d. and analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference t-test among groups.