Abstract
Carbon dots (CDs) as luminescent zero-dimensional carbon nanomaterials have good aqueous dissolution, photostability, high quantum yield, and tunability of emission color. It has great application potential in many fields, including bioimaging, labeling of biological species, drug delivery, and sensing in biomedical. However, controlling the fluorescence emission of carbon dots remains a formidable challenge. Herein, we designed and exploited a photo-controlled fluorescent switching based on photochromic diarylethene (DT) and CDs for bioimaging. It could be modulated reversibly between “ON” and “OFF” under UV/vis light exposure. The fluorescent modulation efficiency was as high as 95.3%. The fluorescent switching could be used to the bioimaging in HeLa cells with low cell toxicity. Therefore, this fluorescent switching could be a promising candidate in many potential application areas, especially in bioimaging.
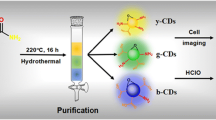
Graphical abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supplementary files.
References
Pirsaheb, M., Asadi, A., Sillanpää, M., & Farhadian, N. (2018). Application of carbon quantum dots to increase the activity of conventional photocatalysts: A systematic review. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 271, 857–871.
Xu, X., Ray, R., Gu, Y., Ploehn, H. J., Gearheart, L., Raker, K., & Scrivens, W. A. (2004). Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126, 12736–12737.
Gao, G., Jiang, Y.-W., Yang, J., & Wu, F.-G. (2017). Mitochondria-targetable carbon quantum dots for differentiating cancerous cells from normal cells. Nanoscale, 9, 18368–18378.
Jalili, R., & Amjadi, M. (2018). Bio-inspired molecularly imprinted polymer–green emitting carbon dot composite for selective and sensitive detection of 3-nitrotyrosine as a biomarker. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 255, 1072–1078.
Ren, X., Lu, P., Feng, R., Zhang, T., Zhang, Y., Wu, D., & Wei, Q. (2018). An ITO-based point-of-care colorimetric immunosensor for ochratoxin A detection. Talanta, 188, 593–599.
Paudyal, S., Vallejo, F. A., Cilingir, E. K., Zhou, Y., Mintz, K. J., Pressman, Y., Gu, J., Vanni, S., Graham, R. M., & Leblanc, R. M. (2022). DFMO carbon dots for treatment of neuroblastoma and bioimaging. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 5, 3300–3309.
Zhao, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, P., Yan, Z., Zhou, Y., Du, Y., Qu, C., Song, Y., Zhou, D., Qu, S., & Yang, R. (2021). Cell-based fluorescent microsphere incorporated with carbon dots as a sensitive immunosensor for the rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157 in milk. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 179, 113057.
He, H., Liu, X., Li, S., Wang, X., Wang, Q., Li, J., Wang, J., Ren, H., Ge, B., Wang, S., Zhang, X., & Huang, F. (2017). High-density super-resolution localization imaging with blinking carbon dots. Analytical Chemistry, 89, 11831–11838.
Liu, X., Chen, S. Y., Chen, Q., Yao, X., Gelleri, M., Ritz, S., Kumar, S., Cremer, C., Landfester, K., Mullen, K., Parekh, S. H., Narita, A., & Bonn, M. (2020). Nanographenes: Ultrastable, switchable, and bright probes for super-resolution microscopy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition English, 59, 496–502.
Yi, Y., Liu, L., Wu, Y., & Zhu, G. (2021). Fluorescent and colorimetric dual-signal enantiomers recognition via enzyme catalysis: The case of glucose enantiomers using nitrogen-doped silicon quantum dots/silver probe coupled with beta-D-glucose oxidase. Analytical Sciences, 37, 275–281.
Kou, X., Jiang, S., Park, S. J., & Meng, L. Y. (2020). A review: Recent advances in preparations and applications of heteroatom-doped carbon quantum dots. Dalton Transactions, 49, 6915–6938.
Jiang, G., Jia, Y., Cui, S., & Pu, S. (2020). Photo-modulated reversible switching of fluorescence from ZnO quantum dots with a photochromic diarylethene. ChemistrySelect, 5, 13919–13924.
Wen, P., Xu, Y., Li, S., Sun, Z., Panmai, M., **ang, J., Tie, S., & Lan, S. (2021). Two-dimensional closely-packed gold nanoislands: A platform for optical data storage and carbon dot generation. Applied Surface Science, 555, 149586.
Yang, C., Li, T., Yang, Q., Guo, Y., & Tao, T. (2022). One-step hydrothermal synthesis of fluorescent silicon nanoparticles for sensing sulfide ions and cell imaging. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 273, 121048.
Peng, H.-S., & Chiu, D. T. (2015). Soft fluorescent nanomaterials for biological and biomedical imaging. Chemical Society Reviews, 44, 4699–4722.
Zhang, J., Chai, X., He, X.-P., Kim, H.-J., Yoon, J., & Tian, H. (2019). Fluorogenic probes for disease-relevant enzymes. Chemical Society Reviews, 48, 683–722.
Witten, A., Tuggle, J., & Waag, R. C. (1988). Ultrasonic imaging with a fixed instrument configuration. Applied Physics Letters, 53, 16–18.
Hu, W., Liu, Y., Lu, Z., & Li, C. M. (2010). Poly[oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate-co-glycidyl methacrylate] Brush Substrate for Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging Protein Arrays. Advanced Functional Materials, 20, 3497–3503.
Zhang, T., Ma, N., Ali, A., Wei, Q., Wu, D., & Ren, X. (2018). Electrochemical ultrasensitive detection of cardiac troponin I using covalent organic frameworks for signal amplification. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 119, 176–181.
Zhou, X., Gao, X., Song, F., Wang, C., Chu, F., & Wu, S. (2017). A sensing approach for dopamine determination by boronic acid-functionalized molecularly imprinted graphene quantum dots composite. Applied Surface Science, 423, 810–816.
Wei, J.-R., Chen, H.-Y., Zhang, W., Pan, J.-X., Dang, F.-Q., Zhang, Z.-Q., & Zhang, J. (2017). Ratiometric fluorescence for sensitive and selective detection of mitoxantrone using a MIP@rQDs@SiO2 fluorescence probe. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 244, 31–37.
Gao, F.-X., Zhao, X.-L., He, X.-W., Li, W.-Y., & Zhang, Y.-K. (2013). A pH and temperature dual-responsive macroporous molecularly imprinted cryogel for enhanced recognition capability towards ovalbumin. Analytical Methods, 5, 6700–6708.
Jares-Erijman, E. A., & Jovin, T. M. (2003). FRET imaging. Nature Biotechnology, 21, 1387–1395.
Ye, S., Zhang, M., Guo, J., Yu, X., Song, J., Zeng, P., Qu, J., Chen, Y., & Li, H. (2022). Fluorine-nitrogen-codoped carbon dots as fluorescent switch probes for selective Fe(III) and ascorbic acid sensing in living cells. Molecules, 27, 6158.
Qi, H., Sun, X., **g, T., Li, J., & Li, J. (2022). Integration detection of mercury(ii) and GSH with a fluorescent “on-off-on” switch sensor based on nitrogen, sulfur co-doped carbon dots. RSC Advances, 12, 1989–1997.
Zheng, Y., Meana, Y., Mazza, M. M. A., Baker, J. D., Minnett, P. J., & Raymo, F. M. (2022). Fluorescence switching for temperature sensing in water. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 144, 4759–4763.
Mo, S., Tan, L., Fang, B., Wu, Z., Su, Z., Zhang, Y., & Yin, M. (2018). Mechanically controlled FRET to achieve high-contrast fluorescence switching. Science China Chemistry, 61, 1587–1593.
Zhang, X., Wei, J., Qi, H., Bai, B., Wang, H., Wang, D., & Li, M. (2022). Multicolor fluorescence switching material induced by force and acid. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 268, 120631.
Ding, H., Liu, G., Pu, S., & Zheng, C. (2014). Multi-addressable fluorescent switch based on a photochromic diarylethene with triazole-bridged methylquinoline group. Dyes and Pigments, 103, 82–88.
Ding, H., Li, B., Pu, S., Liu, G., Jia, D., & Zhou, Y. (2017). A fluorescent sensor based on a diarylethene-rhodamine derivative for sequentially detecting Cu2+ and arginine and its application in keypad lock. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 247, 26–35.
Liuye, S., Qiu, S., Cui, S., Lu, M., & Pu, S. (2021). A multi-functional chemosensor for dual channel detection of Arg and colorimetric recognition of Cu2+. Dyes and Pigments, 195, 109752.
Irie, M. (2000). Diarylethenes for memories and switches. Chemical Reviews, 100, 1685–1716.
Qu, S., Zhou, D., Li, D., Ji, W., **g, P., Han, D., Liu, L., Zeng, H., & Shen, D. (2016). Toward efficient orange emissive carbon nanodots through conjugated sp2-domain controlling and surface charges engineering. Advance Material, 28, 3516–3521.
Yuwen, Z., Mei, H., Li, H., & Pu, S. (2020). A novel diarylethene probe with high selective recognition of CN- and Mg2+ and its application. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 401, 112754.
Xu, S., & Lu, H. (2016). Mesoporous structured MIPs@CDs fluorescence sensor for highly sensitive detection of TNT. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 85, 950–956.
Qiu, S., Lu, M., Cui, S., Wang, Z., & Pu, S. (2019). A bifunctional sensor based on diarylethene for the colorimetric recognition of Cu2+ and fluorescence detection of Cd2+. RSC Advances, 9, 29141–29148.
Ding, H., Yu, S.-B., Wei, J.-S., & **ong, H.-M. (2016). Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano, 10, 484–491.
Tian, Z., Li, D., Ushakova, E. V., Maslov, V. G., Zhou, D., **g, P., Shen, D., Qu, S., & Rogach, A. L. (2018). Multilevel data encryption using thermal-treatment controlled room temperature phosphorescence of carbon dot/polyvinylalcohol composites. Advanced Science, 5, 1800795.
Dong, Y., Pang, H., Yang, H. B., Guo, C., Shao, J., Chi, Y., Li, C. M., & Yu, T. (2013). Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angewandte Chemie, 52, 7800–7804.
Eda, G., Lin, Y.-Y., Mattevi, C., Yamaguchi, H., Chen, H.-A., Chen, I.-S., Chen, C.-W., & Chhowalla, M. (2010). Blue photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene oxide. Advanced Materials, 22, 505–509.
Wang, Q., Zhang, S., Zhong, Y., Yang, X.-F., Li, Z., & Li, H. (2017). Preparation of yellow-green-emissive carbon dots and their application in constructing a fluorescent turn-on nanoprobe for imaging of selenol in living cells. Analytical Chemistry, 89, 1734–1741.
Zhao, S., Lan, M., Zhu, X., Xue, H., Ng, T.-W., Meng, X., Lee, C.-S., Wang, P., & Zhang, W. (2015). Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7, 17054–17060.
Li, Z., Li, Y., Li, J., Gao, Y., & Gu, X. (2019). Synthesis and thermal properties of ethynyl phenyl azo phenol-biphenylene resin. ACS Omega, 4, 1–8.
Cui, S., Pu, S., & Liu, G. (2014). Multi-responsive photochromism of a new diarylethene with a salicylaldehyde group. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 132, 339–344.
Wang, X., Liuye, S., Ma, X., Cui, S., & Pu, S. (2023). Construction of a solid-state fluorescent switching with carbon dots and diarylethene. Dyes and Pigments, 216, 111318.
Liao, B., Lv, H., Deng, X., He, B., & Liu, Q. (2017). Spiropyran-modified silicon quantum dots with reversibly switchable photoluminescence. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 19, 265.
Zhu, Z., Ding, H., Wang, Y., Fan, C., Tu, Y., Liu, G., & Pu, S. (2020). Rational design of a FRET-based ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor for detecting ClO− with large Stokes based on rhodamine and naphthalimide fluorophores. Tetrahedron, 76, 131291.
Liao, B., Long, P., He, B., Yi, S., Ou, B., Shen, S., & Chen, J. (2013). Reversible fluorescence modulation of spiropyran-functionalized carbon nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 1, 3716–3721.
Zhao, H., Kang, H., Fan, C., Liu, G., & Pu, S. (2020). A new multi-functional fluorescent mercuric ion sensor based on diarylethene with triazole-linked rhodamine B unit. Tetrahedron, 76, 131393.
Karpach, P. V., Scherbovich, A. A., Vasilyuk, G. T., Stsiapura, V. I., Ayt, A. O., Barachevsky, V. A., Tuktarov, A. R., & Khuzin, A. A. (2019). Maskevich, photoinduced reversible modulation of fluorescence of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in solutions with diarylethenes. Journal of Fluorescence, 29, 1311–1320.
Herder, M., Schmidt, B. M., Grubert, L., Pätzel, M., Schwarz, J., & Hecht, S. (2015). Improving the fatigue resistance of diarylethene switches. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137, 2738–2747.
Cong, S., Liu, K., Qiao, F., Song, Y., & Tan, M. (2019). Biocompatible fluorescent carbon dots derived from roast duck for in vitro cellular and in vivo C. elegans bio-imaging. Methods, 168, 76–83.
Zhou, N., Zhu, S., Maharjan, S., Hao, Z., Song, Y., Zhao, X., Jiang, Y., Yang, B., & Lu, L. (2014). Elucidating the endocytosis, intracellular trafficking, and exocytosis of carbon dots in neural cells. RSC Advances, 4, 62086–62095.
Du, F., Li, J., Hua, Y., Zhang, M., Zhou, Z., Yuan, J., Wang, J., Peng, W., Zhang, L., **a, S., Wang, D., Yang, S., Xu, W., Gong, A., & Shao, Q. (2015). Multicolor nitrogen-doped carbon dots for live cell imaging. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 11, 780–788.
Cai, Y., Wei, Z., Song, C., Tang, C., Han, W., & Dong, X. (2019). Optical nano-agents in the second near-infrared window for biomedical applications. Chemical Society Review, 48, 22–37.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22263005), and the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20212BAB203011, 20224ACB203006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Liuye, S., Ning, K. et al. A photo-controlled fluorescent switching based on carbon dots and photochromic diarylethene for bioimaging. Photochem Photobiol Sci 22, 2389–2399 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-023-00458-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-023-00458-6