Abstract
Aims
Advixa is a monoclonal antibody manufactured as a biosimilar to adalimumab (Humira, Abbvie Inc.). The key objectives of this study were to use a healthy population group to assess pharmacokinetics (PK) and safety similarity between Advixa and Humira in healthy participants and to quantify the effects on adalimumab PK and safety to assess the impact of treatment with Advixa.
Methods
A group of healthy participants selected by screening aged between 18 and 45 years. According to the randomization table, each participant was given Adalimumab (Advixa or Humira) in the inpatient facilities in a hospital and observed for 72 h. Several blood samples were collected from the participants at different time points up to day 64 to measure their Pharmacokinetics and biosimilarity. The study was registered at clinicaltrial.gov retrospectively.
Results
The serum concentration–time profiles for PK and safety were compared in this randomized, double-blinded study between Humira and Advixa. A review of the data for biosimilarity confirmed that these products are similar to each other regarding healthy participants. 90% confidence interval of the relative mean Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUCo-inf of the Advixa and Humira were found within the acceptance criteria. No differences in safety profiles were observed in these studies.
Conclusion
PK and safety are similar between Advixa and Humira in participants with healthy status demonstrated in this clinical trial (NCT05172817; Registration Date/Initial Release Date: 28/09/2021). Adalimumab PK was also similar to treatment with Humira and Advixa.
Highlights
-
The serum concentration–time profiles for PK and safety were compared in this randomized, double-blinded study between Humira and Advixa.
-
A review of the data for biosimilarity confirmed that these products are similar to each other regarding healthy participants.
-
90% confidence interval of the relative mean Cmax, AUC0-t and AUC0-inf of the Advixa and Humira were found within the acceptance criteria.
-
No differences in safety profiles were observed in these studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by pathological angiogenesis and increased angiogenic factor production, which leads to increased percolation of endothelial cells, that promotes synovitis followed by bone and cartilaginous damages, resulting in, progressive changes and destruction in joints [1]. At this time, in the year 2022, RA patients make up 1% of the world’s population [2]. Chemical medicines such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, antirheumatic pharmaceuticals, and glucocorticoids were once the basis of RA treatment [3]. Because of their high specificity, biological antibodies have been widely used in the therapeutic treatment of a wide range of diseases in recent years, including malignancies, blood diseases, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases [4,5,6].
TNF- α (tumor necrosis factor-α) is substantially expressed in RA patients in the early stages [2]. TNF-α is a strong proinflammatory cytokine that causes local inflammation and lesion development by inducing numerous cytokines, increasing cell adhesion molecule expression, and activating blood neutrophils [2]. As a result, TNF- α can be employed as a therapeutic target for RA.
Adalimumab has an excellent specificity and affinity for TNF- α considered as first human immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) as well as comparable terminal half-life (t1/2) (2 weeks) [7, 8]. The binding of TNF- α to its receptors is part of the inflammatory response associated with some autoimmune illnesses. Adalimumab works by neutralizing TNF’s activity and thereby preventing the cytokine’s interaction with the p55 and p75 cell surface receptors [8].
In 2002 and 2003, US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency approved Humira (adalimumab; Abbvie Ltd.) for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) respectively.
Now it is used to treat RA, psoriatic arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, adult Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis, pediatric Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis which are immune-mediated diseases. There is a wide range of study that shows similar safety, tolerability profile with the and immunosuppressive effects of the anti-TNF class, with infection, injection site reactions, headache, and rash being the most commonly reported adverse events (AEs) in adalimumab recipients [8]. Infection was the most common adverse effect, as predicted with an immunosuppressive drug, according to a global clinical database analysis of 23,458 patients, but the overall malignancy rates were average for the general population [9].
The potential structural differences in the active component that come from the biological manufacturing process need further equivalence studies, including efficacy tests in humans before biosimilar pharmaceuticals can be marketed [10]. Through a series of strictly regulated preclinical, clinical, and safety studies, A biosimilar medicinal product must compare to the authorized biological drug in terms of physicochemical, nonclinical, and clinical efficacy (known as the reference medicinal product, RMP [EU] or reference product, RP [US]) [12, 13]
Advixa is a recombinant human IgG1 mAb that is directed against human TNF- α and is developed by Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Bangladesh. It is a potential biosimilar of adalimumab and is s made in Chinese hamster ovary cells that have the same amino acid sequence as the US-licensed adalimumab reference product Humira. To confirm Advixa's basic composition, post-translational modifications, and high order structure, a comprehensive biochemical analysis was applied In comparison to US-RP. Relevant mAb production parameters, including purity, as well as product variants, were included in the similarity assessment. Advixa has the same strength as the Humira dosage formed (40 mg adalimumab per 0.4 mL deliverable solution).
A study on the administration of Advixa to healthy human participants was carried out for the first time in Bangladesh. Advixa was compared to the US-licensed Humira in terms of pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability. This analysis is the first step in the clinical development procedure for marketing authorization of this biosimilar product.
2 Methods
The ethical approval was taken from National Health Service Ethics Review Committee (NHERC) to conduct the trial and was carried with the Declaration of Helsinki and the principles of the International Conference on Harmonization which requires Good Clinical Practice.
2.1 Study population
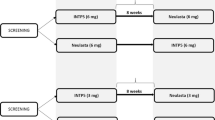
The study was carried out in Mirpur in Dhaka. The study recruited 41 healthy men and women, and the sample size was calculated with the power of 80%. Participants had to weigh between 40.0 and 95 kg and have a BMI of 18.5–29.9 kg m−2 to be eligible for the study. The study protocol required that all the vital signs of participants must be within normal limits, and evaluated by physical examination. Laboratory tests including blood and urinary parameter along with a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) as well as a radio imaging of the chest must be within the normal range or declared clinically non-significant. Female participants must be tested negative for pregnancy (screened and confirmed by serum and urinary β-human Chorionic Gonadotropin/ β-hCG). We excluded participants having a history of malignancy, such as lymphoma, leukemia, or skin cancer. Study participants with a positive surface antigen test for hepatitis B, antibody test for hepatitis C, and/or IgG and/or IgM for core antibody test and positive antibody test for human immunodeficiency virus at screening were excluded from the study. Participants with a positive laboratory test for drug abuse by urine examination and a positive breath alcohol test were not enrolled. Smokers who smokes more than 10 cigarettes per day or refused to refrain from smoking or using any other product that contains nicotine throughout the trial's hospital stay were excluded. Other significant exclusion criteria were history and/or current presence of atopic allergy; any present or previous local fungal infections; active or latent tuberculosis; known or suspected hypersensitivity to any drugs; history of invasive systemic fungal infections; any infection that requires hospitalization and/or anti-infectives or antibiotics within 6 months prior to trial drug administration.
The participants were completely aware of the trial's goal and were given a concept of pharmacological effects as well as the potential adverse effects of the study drug. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. In addition, each participant received a wage loss for taking part in the study.
The study was conducted by ideSHi from June 2021 to October 2021. All the participants were screened, recruited, and data was collected from the field site situated at Mirpur, Dhaka. After enrollment, the participants were admitted to Universal Medical College and Hospital, Dhaka, which provided the in house clinical facilities for the study 12 h before dosing.
After investigational medicinal product (IMP) administration, each participant stayed for 2 days following dosing. An interim safety analysis was undertaken with data accumulated at that point after 5 participants per arm had been examined for a minimum of 2 days.
Participants were randomly assigned to groups before receiving the IMP. The randomization chart was prepared by following coded randomization. Single subcutaneous dose of 40 mg adalimumab; Advixa or Humira® was injected around 3 cm away from the navel or mid-thigh by trained nurses at the in-house clinical setting. Participants were required to remain in a relaxed state after receiving the medication and were not allowed to engage in intense activities. Blood samples were taken at each time point, and safety checks were performed as per the protocol.
Prior to dosing (-15 min) and at 4, 12, 24, 36, 48, 72 ± 2, 96 ± 2,120 ± 2, 144 ± 2, 168 ± 2, 192 ± 2, 360 ± 2, 528 ± 2, 696 ± 2, 864 ± 2, 1032 ± 2, 1200 ± 2, 1536 ± 2 h blood samples were collected for pharmacokinetic analysis (19-time points).
All blood samples were collected in Serum Separator tubes. The samples were kept upright for 30 min at room temperature followed by centrifugation for 10 min at 2000 RCF (2 ℃ − 8 ℃). Serum samples were stored at or below − 70 ℃ after aliquoting into duplicate microcentrifuge tubes.
2.2 PK assessments and endpoints
The concentrations of Advixa and Humira in the blood were measured by the ELISA method. Bound analyte, and 3,3ʹ,5,5ʹ-tetramethylbenzidine for colorimetric readout. were identified by using a TNF-coated plate, a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-human IgG antibody. A plate reader was used to measure colorimetric intensity at 450 nm (detection) and 630 nm (reference) wavelengths.
Cmax, terminal half-life (t1/2), AUC from time 0 extrapolated to infinity [AUC (0)], and AUC from time 0 to the last quantifiable concentration [AUC (0, tlast)] were the primary PK endpoints.
2.3 Safety evaluation
During the trial, all adverse events (AEs) reported by the participants during the study period were well documented. Any clinically significant aberration was reported as an AE when compared to the baseline. A safety check was done for subjects who completed the 1536-h follow-up visit or withdrew from the trial early. When adverse events (AEs) occurred during the trial, the individual was tracked until the AE was resolved or stabilized. All adverse events were listed, including chest discomfort, pain, restlessness, headache, low blood pressure, swelling at the site of blood collection, vertigo, abdominal cramp, increased frequency of loose stool, upper abdominal burning sensation, itching at the site of IP administration, vomiting, burning sensation to the other thigh. The adverse events (AEs) associated with the study medication were summarized.
2.4 Statistical analysis
As the study was a parallel and double blinded study, so all the assessors along with the participants were blinded in all the stages of the assessment. A one-way ANOVA model with treatment as a fixed effect was used to investigate AUC (0), AUC (0, tlast), and the (Cmax). The PK parameters were log-transformed for analysis, and the difference in mean parameters between the two groups was calculated, then equivalency was assessed by re-expressing on the original ratio scale. For each comparison, PK equivalence was declared if the 90 percent CI for the test: reference ratio fell entirely within the 70–145 percent equivalence margin. Bioequivalence was established if all three PK metrics met the PK equivalence criterion. Other PK metrics, serum drug concentrations, and safety/tolerance data were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
3 Results
3.1 Demographics and baseline characteristics of the subjects
The study medication was given to 41 healthy subjects who were randomly selected. During the trial, 1 subject who received Humira® willingly discontinued and did not attend the follow-up visits (Fig. 1). Table 1 displays the demographic information for the 41 subjects. Subjects' basic information with Advixa was as follows: The typical age was 28.25 ± 9.53 years with an average weight of 53.07 ± 1.507 kg and an average height of 156.3 ± 7.526 cm, resulting in an average BMI of 21.65 ± 2.58 kg/m2. The basic information of subjects with Humira® was as follows: the average age was 27.29 ± 9.128 years, the average weight was 54.59 ± 1.92 kg, the average height was 156.7 ± 8.386 cm and the average BMI was 22.11 kg/m2. There was no statistically significant difference in demographic characteristics between the two groups. The inclusion criteria were met by all subjects who participated in the study.
At 19 different time intervals, the individuals' blood was drawn. ELISA was used to determine the drug concentration in the plasma. Figure 2a depicts the plasma drug concentration curve after data processing, while Fig. 2b depicts the curve after logarithmic adjustment (b).
ANOVA was performed on log-transformed pharmacokinetic parameters Cmax, AUC0-t, AUC0-inf, early partial AUC, and terminal partial AUC at the α level of 0.05 for Adalimumab. As factors in the analysis of the variance model, there were sequences, and subjects nested within Sequence, period, and treatment. ANOVA and 90% confidence intervals were calculated for the ratio of geometric means of test and reference formulations using SAS system 9.4
The data in Table 2 demonstrate that there was no significant difference in plasma medication concentrations between Advixa and Humira. The average Cmax values were 7819.68 ± 3869.61 (ng/mL) and 7324.59 ± 1550.11 (ng/mL), for Advixa and Humira respectively, with a ratio of 95.56% for the modified Geometric Mean (75.20–121.44%), and the average AUC0-t values were 3,399,298.9615 ± 1,658,244.9686 and 3,004,287.9583 ± 601,639.75792 (h × ng/mL), respectively.
The findings of the equivalence determination between the test drug Advixa and reference drug Humira have been plotted in Table 3. The PK parameters were compared with the equivalence standard of 70–145%
3.2 Safety evaluation
A single dose (40 mg/0.4 ml) of Adalimumab was well tolerated. Within 17 adverse events in total, almost 29.4% were in patients randomized to Advixa and 70.6% were in patients randomized to Humira®. Complaints of increased frequency of loose stool, itching over the site of IP administration, low blood pressure, and abdominal cramps were reported mostly during the entire course of the study.
Major complaints and adverse events were increased frequency of loose stool (11.76%) where 5.88% were in the Advixa group and 5.88% were due to Humira®, abdominal cramps (11.76%) were 5.88% due to Humira® and 5.88% were in Advixa group, low blood pressure (11.76%) and itching over the site of IP administration (11.76%) were entirely in Humira® group. Some minor complaints like the burning sensation of the other thigh (5.88%), vertigo (5.88%), upper abdominal burning sensation (5.88%) were entirely in Advixa group, and chest discomfort (5.88%), headache (5.88%), swelling at the site of blood collection (5.88%), vomiting (5.88%), pain (5.88%), restlessness (5.88%) were entirely in Humira® group. Among all the adverse events, 94.12% were reported by females whereas 5.88% were reported by male participants. The reported AEs were mild in severity, unlikely related to the study medication, and were resolved. No serious or significant adverse event was reported during the entire course of the study. Laboratory values were mostly found within the provided normal range but 15% of subjects reported mild anemia where 7.5% were in the Advixa group and 7.5% were in the Humira® group. In addition, 12.5% of the participants reported increased monocyte levels where 5% were in Advixa group and 7.5% were in Humira® group.
There were no significant complaints from participants. No clinically significant findings were observed during the entire course of the study. All the vital signs were within normal limits. The values which were clinically not significant were recorded in case report forms.
4 Discussion
Adalimumab biosimilar candidate Advixa is indicated for the treatment of a variety of inflammatory diseases [11]. To evaluate biosimilarity, evaluation of the PK bioequivalence of the proposed biosimilar to the reference product (RP) is required according to current guidelines. Demonstrating the PK and safety biosimilarity between Advixa and US- and EU-approved Humira was the aim of the study. In healthy subjects. For measuring PK variables, healthy volunteers are a more sensitive population group in comparison to the patient population. Selecting more homogenous healthy subjects in these cases can provide a reliable outcome as various disease-related factors that can influence the PK characteristics of study drugs can be avoided (EMEA guideline). To access equivalence between the proposed adalimumab biosimilar and the reference product, a single-dose crossover design is considered appropriate.
Biosimilars are less expensive than their reference products (RPs) and provide an opportunity to increase patient access to disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) [12]. A number of biosimilar agents for the adalimumab reference product have been developed and evaluated in several clinical and nonclinical studies, showing similarity on the basis of structural and functional assays [13]. For several biosimilar agents such as PF-06410293, adalimumab-US, and adalimumab-EU, PK similarity was confirmed with the RP along with the structural and functional assays [14,15,16]. The present study was designed to assess the PK similarity and safety of the proposed biosimilar Advixa and US FDA-approved RP Humira in healthy Bangladeshi adult participants. This population group is considered as most sensitive to compare differences in PK and safety parameters as no immunosuppressive medications or underlying disease conditions affect the study outcome as per the ICH-GCP guidelines.
Previous biosimilarity and bioequivalence studies of Adalimumab have reported the geometric LS means ratios of primary study variables, AUCinf, AUClast, and Cmax at 90% CIs between the test and reference product were within the accepted range of 0.8–1.25 [17]. Another FKB327: Humira comparison study showed the Cmax was just outside the equivalence range of 0.8–1.25 in the upper 90% CI [18]. In the current study, the 90% CIs for the geometric mean ratios of all primary PK parameters were within the acceptance range of 70–145%. Assessment of Bio-equivalence of ‘Highly Variable Drugs products (HVDP)’ depends on its Inter Subject Coefficient of Variation. The HVDP are those whose subject variability for the PK parameter was larger than 30%. A widened acceptance range with valid clinical justification and a wider difference is considered clinically relevant for HVDP. Here, in the present study, for the parameters, Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-inf, the Inter-Subject CVs (%) are larger than 30% (43.07, 49.11, and 53.39 respectively). So as per the EU guidelines, the acceptance criteria can be widened to a maximum of 69.84–143.19% (for AUC0-t, and AUC0-inf) and 72.15–138.59% (for Cmax). Moreover, the Reference Scaled approach is recommended by EMEA guidelines on the investigation of bioequivalence wherein the 90% CI can be widened in proportion to the variability of the product [13]. As the subject variability observed for all PK parameters is high, the corresponding widened BE limit has been employed for a realistic assessment of the comparative performance of the test product. The comparative assessment of secondary PK parameters like Tmax, T1/2, and Kel also showed similarity of Advixa with US- and EU-approved Humira.
In this study, 25% of participants experienced AEs, where 29.4% were in Advixa group and 70.6% were in Humira® group. No deaths or SAEs or AEs leading to discontinuation occurred during the study period. More incidences of mild to moderate AEs were reported in several bioequivalence studies [15] [18].
Limitation There is no data related to immunogenicity in this part of the clinical trial. However, the immunogenicity will be assessed in the next part of the trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis patients.
5 Conclusion
A biosimilar must have similarity to the reference biologic product in terms of structural and functional assays PK, efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity to be considered as potential [18]. In conclusion, Advixa was well tolerated by the healthy participants in this study, with a safety profile as good as that of Humira. According to the EU (Doc. Ref.: CPMP/EWP/QWP/1401/98) and WHO (WHO Technical Report Series, No. 1003, 2017 Annex 6) guidance, the 90% confidence interval of the relative mean Cmax, AUC0-t and AUC0-inf of the Advixa and Humira were found within the acceptance criteria for log-transformed data. The DSMB reviewed this Phase B study (Part A) that was done on healthy participants. Part B study on the patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis is still ongoing.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Kang J, Eudy-Byrne RJ, Mondick J, Knebel W, Jayadeva G, Liesenfeld KH. Population pharmacokinetics of adalimumab biosimilar adalimumab-adbm and reference product in healthy subjects and patients with rheumatoid arthritis to assess pharmacokinetic similarity. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;86(11):2274–85.
Chen L, Huang Z, Liao Y, Yang B, Zhang J. Association between tumor necrosis factor polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis as well as systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019;52(3):1–9.
Liu C, He L, Wang J, Wang Q, Sun C, Li Y, et al. Anti-angiogenic effect of Shikonin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating PI3K/AKT and MAPKs signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;260:113039.
Kholodenko RV, Kalinovsky DV, Doronin II, Ponomarev ED, Kholodenko IV. Antibody fragments as potential biopharmaceuticals for cancer therapy: success and limitations. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(3):396–426.
Parslow AC, Parakh S, Lee FT, Gan HK, Scott AM. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Biomedicines. 2016;4(3):14.
Lombardi G, Perego S, Sansoni V, Diani M, Banfi G, Altomare G. Anti-adalimumab antibodies in psoriasis: lack of clinical utility and laboratory evidence. BMJ Open. 2016;6(12): e011941.
Den Broeder A, Van de Putte LBA, Rau R, Schattenkirchner M, Van Riel PLCM, Sander O, et al. A single dose, placebo controlled study of the fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor-α antibody adalimumab (D2E7) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2002;29(11):2288–98.
AbbVie. HUMIRA (adalimumab) Injection, Solution for Subcutaneous use. Handbook of Therapeutic Antibodies. 2008;3. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/125057s410lbl.pdf
Burmester GR, Panaccione R, Gordon KB, McIlraith MJ, Lacerda A. SAT0130 Long-term safety of adalimumab in patients from global clinical trials in rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, and crohn’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;71(Suppl 3):514.3.
De Mora F. Biosimilar: what it is not. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80(5):949–56.
Wynne C, Altendorfer M, Sonderegger I, Gheyle L, Ellis-Pegler R, Buschke S, et al. Bioequivalence, safety and immunogenicity of BI 695501, an adalimumab biosimilar candidate, compared with the reference biologic in a randomized, double-blind, active comparator phase I clinical study (VOLTAIRE®-PK) in healthy subjects. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016;25(12):1361–70.
Huizinga TWJ, Torii Y, Muniz R. Adalimumab biosimilars in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of the evidence for biosimilarity. Rheumatol Ther. 2021;8(1):41–61.
Derzi M, Shoieb AM, Ripp SL, Finch GL, Lorello LG, O’Neil SP, et al. Comparative nonclinical assessments of the biosimilar PF-06410293 and originator adalimumab. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020;112(January):104587.
Yonemura T, Yazawa R, Haranaka M, Kawakami K, Takanuma M, Kanzo T, et al. Comparison of two biosimilarity studies of FKB327 with the adalimumab reference product: randomized phase 1 studies of single-blind, single-dose subcutaneous injection in healthy Japanese male participants. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022;23(1):1–11.
Puri A, Niewiarowski A, Arai Y, Nomura H, Baird M, Dalrymple I, et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of FKB327, a new biosimilar medicine of adalimumab/Humira, in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;83(7):1405–15.
Shin D, Lee Y, Kim H, Körnicke T, Fuhr R. A randomized phase I comparative pharmacokinetic study comparing SB5 with reference adalimumab in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2017;42(6):672–8.
Hyland E, Mant T, Vlachos P, Attkins N, Ullmann M, Roy S, et al. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics, safety, and immunogenicity of MSB11022, a biosimilar of adalimumab, with Humira®in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;82:983–93.
Isakov L, ** B, Jacobs IA. Statistical primer on biosimilar clinical development. Am J Ther. 2016;23(6):e1903–10.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the research team of Universal Medical College and Hospital for the inpatient Unit for the participants and for technical support. We also acknowledge the contribution of Inquest Biopharma Ltd for supporting the statistical analysis.
Funding
This study was funded by Incepta Pharmaceutical Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
UK, KA & MW have an equal effort in data collection, laboratory analysis, and preparation of the manuscript. UK and KA were responsible for the clinical data analysis of the study, ZK made substantial contributions to the conception of the manuscript, MH, and NS were responsible for the quality assurance of the data, IH, FA, RR, AM, HM, MK, MMR, SH, SAM, AP were involved in study designing. FQ, ZK all of them reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and informed consent
The study was approved by the National Ethical Research Committee (NERC) of the Bangladesh Medical Research Council (BMRC) with the reference number-BMRC/NREC/2019-2022/237. This study was also conducted in accordance with the principles of the ‘Declaration of Helsinki’. All the participants and their legal guardian gave their informed consent for the study as well as the publication of the study findings. The treating physician evaluated the participant’s capacity to consent by confirming that they understood the various implications associated with the publication. The Editor may evaluate any copy of the signed, written informed consent form.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All the authors of this publication have no competing interest as they had no other source of support.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kulsum, U., Azad, K., Washif, M. et al. Pharmacokinetic and safety analysis of biosimilar adalimumab in healthy volunteers in Bangladesh. Discov Appl Sci 6, 98 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-024-05725-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-024-05725-4