Abstract
Objective
To study Ermiaosan in the treatment of UC by using network pharmacology and molecular docking, and to provide references for experiments and clinical application for treating UC with dampness-heat syndrome.
Methods
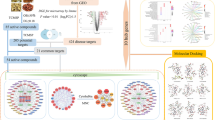
The main active chemical components of Ermiaosan were screened out through TCMSP, the targets of components were obtained from TCMSP, the SwissTargetPrediction, TTD and the DrugBank database, and these targets genes were retrieved by UniProt database, the disease genes were obtained from TTD and Genecard database. String tool was used to constructed the PPI network, to built these components and their corresponding targets, Cytoscape software was applied to merge the networks and screen out the core network. And Bioinformatic analysis was performed using the OECloud tools to explore the enrichment analyses of GO and KEGG. Molecular docking was applied to check the affinity between the components and selected targets.
Results
Forty-six main active components were predicted from Ermiaosan, and 408 intersection genes were screened from drug-disease genes. The enrichment included PI3K–Akt, TNF and HIF-1 signaling pathway, and the networks analysis showed that Ermiaosan acted on seven key targets AKT1, TNF, IL6,TP53, VEGFA, IL1B and CTNNB1 to play roles in treating UC. Molecular docking showed that top 3 chemical components could bind stably with these targets.
Conclusion
Ermiaosan can relieve dampness-heat syndrome of UC, the possible potential mechanism might be related to the targets AKT1, TNF, IL6,TP53, VEGFA, IL1B and CTNNB1 linked with TNF, PI3K-Akt, and HIF-1 signaling pathway, it will provide meaningful references for further study in experiments and clinical investigations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a common non-specific chronic protracting and relapsing inflammatory disease, which relates the large intestine mucosa and submucosa, and its most important clinical manifestations are characterized by diarrhoea, abdominal pain, mucus pus, and blood in the stool [1, 2]. And with its recurrent ymptoms, long-time treatment and significant morbidity [3, 4]. the effective treatment of UC is becoming more and more important.
At present, the precise cause of UC is unclear, and it may related to genetics, environment, leucocyte recruitment, disruption of colon barrier function and mucosal immune response [5]. The clinical treatment is mainly focus on medicine therapy, interleukin antagonist, immunosuppressive agents, corticosteroids and salicylates. Through previous studies, with various side effects in the treatment, it is necessary to explore more safe and effective ways to treat UC [6].
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has developed for thousands of years, it is one of the greatest treasures of Chinese culture, and it is the crystallization of medical wisdom and experience of the Chinese nation which accumulated from large numbers of theories and rich clinical experience [7]. According to the theory of TCM, UC belongs to the category of dysentery, diarrhoea, and hematochezia, etc. TCM symptoms of UC include mainly types of dampness-heat in large intestine, excessive heat-toxin, dampness stagnancy due to spleen deficiency, Yang deficiency of spleen and kidney, cold-heat complicated symptom and so on, and the chief symptom of UC is dampness-heat in large intestine [8]. On the one hand, when evil heat attacks blood vessels, it will cause abnormal blood circulation, then it lead to force the blood to act recklessly, therefore, the patients with UC of dampness-heat symptom characterized by bloody stool. On the other hand, “Su Wen” has recorded that “Predominant dampness causing diarrhea”, and “Yizong Bidu” said “No diarrhea without dampness”. The dampness is heavy, turbid, sticky and stagnant, and it tends to move downward, so the intestinal symptoms of UC patients occurs repeatedly with protracted process [2.
3.2 Network of intersection targets
3.2.1 PPI network of targets
To get further understanding about the interaction of these 408 overlap** targets, the STRING tool was applied to construct PPI network of the relationships of herb compounds-disease-tergets for these targets. We set the confidence score > 0.7, the analysis of PPI network shown that there were 408 nodes and the number of edges was 9421, the average node degree was 46.2, and the average local clustering coefficient was 0.534 ( As shown in Fig. 3).
3.2.2 Result of cytoscape network of targets and the hub genes
We used Cytoscape3.8.2 software to visualise the combined score of the STRING database of Ermiaosan and ulcerative colitis ( As shown in Fig. 4), and then we set the node size and color to map the degree value and score value to construct drug-target interaction of the drug and disease, it contained 411 nodes and the number of edges was 951, the average node degree was 92.6, with the methods Degree greater than fourfold above the average was set to select core genes by cytoHubba plugin, these top 7 targets were the key targets of Ermiaosan against ulcerative colitis, the darker the color, the higher the correlation. ( As shown in Fig. 5 and Table 3).
3.3 The results of enrichment analysis
The multiple potential mechanisms of Ermiaosan against ulcerative colitis through Bioinformatic analysis which was performed using the OECloud tools at https://cloud.oebiotech.cn., with the default option was P value < 0.05. And the results of top 10 main items of each categories of GO terms were: protein phosphorylation, positive regulation of cell proliferation, positive regulation of angiogenesis, inflammatory response, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of apoptotic process and so on ( As shown in Fig. 6a), and then top 20 important GO enrichment analysis items were selected (As shown in Fig. 6b, Table 4). As for KEGG enrichment analysis, the top 20 key pathways were identified (As shown in Fig. 7, Table 5), and the main pathways included PI3K–Akt, TNF and HIF-1 signaling pathway, the detail targets of regulation roles of these pathways are shown in Fig. 8a–f. The maps of KEGG pathway showed that the related targets of regulation roles were AKT, TNF, IL6, P53, VEGF, IL1B and so on.
a KEGG pathway annotations of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway of Ermiaosan in the regulation of ulcerative colitis. Red rectangles represent the targets of regulation roles. b KEGG pathway annotations of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway of Ermiaosan in the regulation of ulcerative colitis. Green rectangles represent the targets of potential roles. c KEGG pathway annotations of TNF signaling pathway of Ermiaosan in the regulation of ulcerative colitis. Red rectangles represent the targets of regulation roles. d KEGG pathway annotations of TNF signaling pathway of Ermiaosan in the regulation of ulcerative colitis. Green rectangles represent the targets of potential roles. e KEGG pathway annotations of HIF-1 signaling pathway of Ermiaosan in the regulation of ulcerative colitis.Red rectangles represent the targets of regulation roles. f KEGG pathway annotations of HIF-1 signaling pathway of Ermiaosan in the regulation of ulcerative colitis.Green rectangles represent the targets of potential roles.
3.4 The results of molecular docking verification
The top three main active compounds dihydroniloticin, quercetin, and beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt had a tight linkage with ulcerative colitis verified through molecular docking, Among all docking of protein–ligands, the results showed that these 3 compounds had a strong affinity with the selected top 7 key targets, except for CTNNB1(PDB ID:6o9c), the binding energy with quercetin and beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt were -4.29 kcal/mol and -4.89 kcal/mol, the rest target proteins are all less than -5 kcal/mol, all the detail information of binding energy with these 3 compounds of top 7 key targets are shown in Table 4, and the docking conformations of these targets of regulation roles AKT1, TNF, IL6,TP53, VEGFA, IL1B and CTNNB1 are shown in Fig. 9a–u.
a Dihydroniloticin with AKT1. b Dihydroniloticin with TNF. c Dihydroniloticin with IL6. d Dihydroniloticin with TP53. e Dihydroniloticin with VEGFA. f. Dihydroniloticin with IL1B. g Dihydroniloticin with CTNNB1. h Quercetin with AKT1. i Quercetin with TNF. j Quercetin with IL6. k Quercetin with TP53. l Quercetin with VEGFA. m Quercetin with IL1B. n Quercetin with CTNNB1. o Beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt with AKT1. p Beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt with TNF. q Beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt with IL6. r Beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt with TP53. s Beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt with VEGFA. t Beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt with IL1B. u Beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt with CTNNB1
4 Discussion
The incidence of UC is increasing year by year around the world, and it is listed as one of the most challenge and refractory diseases by World Health Organization [45, 46]. Pharmacotherapy is still the main measure in the treatment of UC, and the therapeutic goal is to control intestinal inflammation and improve immune disorders [47].
The combination of dampness and heat is the basic pathological factor of UC based on the theory of TCM, on the one hand, the main pathogenesis of recurrent bloody purulent stool is that the blood stasis caused by dampness-heat, and then blood stasis-heat impairs collaterals [48], thus the symptom of abdominal pain due to the blockage of blood vesselson. On the other hand, while intestinal mucosa steeped by dampness-heat, then the colon mucosa appears hyperemia and edema, and subsequently, after a long period of time, the rottenness of blood and muscle could result in ulcer or erosion on the colon mucosa [49].
Another physician who was also listed as one of the "Four Great Masters of ** and Yuan Dynasties" named Li Dongyuan, he used Ermiaosan as the main prescription to treat diarrhea caused by dampness-heat, the good curative effect provides a reference for the treatment of diarrhea in later generations [50]. The flexible application of traditional Chinese medicine in the dialectic-al treatment of UC has gained well clinical effects [51].
In the prescription of Ermiaosan, Cang Zhu could invigorate Spleen and eliminate dampness, then the dampness can't be generated without source(in TCM, the dampness comes from the dysfunction of spleen in transportation), and the heat can not be attached as the dampness is removed. As for Huang Bo, with its cold and bitter nature, it can restrain the warm and dry nature of Cang Zhu. When these two medicines are used together, one is warm and the other is cold, the combination use of them can clear away dampness, remove heat and thus dispel all symptoms [52].
Recent studies have found out that while Cang Zhu or Huang Bo used alone, there is no strong efficacy, but only when they are used together can the maximum pharmacodynamics be achieved, some components of the two medicinal materials interact with each other to make the effect more predominant [53].
Network pharmacology and molecular docking methods were useful tools that used to explore the possible pharmacological mechanisms of Ermiaosan against UC in our study, which showed that 46 compounds and 408 target genes were related to UC. The results of GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses indicates that the effects of Ermiaosan against UC may be due to the active compounds of Ermiaosan, especially for dihydroniloticin, quercetin and beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt which could influence the regulation of the PI3K–Akt, TNF and HIF-1 signaling pathway. They may also be related to protein phosphorylation, positive regulation of cell proliferation, positive regulation of angiogenesis, inflammatory response, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of apoptotic process and so on. According to the results of PPI analysis and Cytoscape Hub, AKT1, TNF, IL6, TP53, VEGFA, IL1B and CTNNB1 were selected as key targets, and they reflect a strong affinity with dihydroniloticin, quercetin and beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt as the results of the molecular docking method.
The previous study shows IL-1β,VEGF, tumor necrosis factor-αand IL-6 are expressed at higher levels in the patients with UC [54, 55]. Modern medical research verified that Ermiaosan can inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors and regulate immunity [56], And has an impact on the gastrointestinal tract [57]. And currently, animal experiment study indicates that quercetinin could play a prophylactic effect in terms of disease activity and bowel length in UC model of mice [58]. Scholars in recent years had proved that Ermiaosan can inhibit IL-1β, IL6, IL8, TNF- α, VEGF and other inflammatory factors, thus it can reduce the occurrence and development of inflammation, and promote neovascularization [59,60,61,62,63].
When ulcerative colitis occurs, more inflammatory mediators are involved in the lesion, and during the active phase of the inflammatory lesion, the expression of active inflammatory factors is more pronounced. The increased expression of VEGF in lesions can directly stimulate the division and proliferation of vascular endothelial cells, increase the gap between endothelial cells, increase vascular permeability, and exude fibrinogen, which can provide support for vascular structures and promote angiogenesis [64],
There are literature studies reporting that angiogenesis plays an important role in its pathological mechanism and mucosal repair. VEGF is currently considered the strongest and most specific proangiogenic factor, which can promote tissue repair and induce capillary regeneration [65]. And the viewpoint of preventing blood from overflowing out of the veins and alleviating intestinal bleeding is coincidental with TCM.
PPI network analysis shows that AKT1, TNF, IL6, TP53, VEGFA, IL1B and CTNNB1 may be important targets of Ermiaosan in the treatment of ulcerative colitis, and combined with the results of GO enrichment analysis, these targets involve in protein phosphorylation, positive regulation of cell proliferation, positive regulation of angiogenesis, inflammatory response, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of apoptotic process.
It explains that the blood entering components of Ermiaosan can alleviate the progression of UC by regulating AKT1, TNF, IL6, TP53, VEGFA, IL1B, CTNNB1 and other target proteins mainly related to positive regulation of cell proliferation, positive regulation of angiogenesis, inflammatory response, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway, positive regulation of gene expression to reduce inflammation, regulate immunity, promote cell regeneration and angiogenesis and other processes. And this process coincides with the view of traditional Chinese medicine to eliminate dampness-heat, then fundamentally prevent it from hurting collaterals, and promote muscle production to stop bleeding, promote the dissipation of pathological products, and prevent blood from overflowing the collaterals, thus accelerating intestinal healing.
KEGG pathway analysis shows that Ermiaosan plays therapeutic role in treating UC may be related to the regulation on PI3K–Akt, TNF and HIF-1 signaling pathways. It has been reported that PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway plays a significant role in the regulation of cell activation and inflammatory response [66], and some scientific tests estabblished that the expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α can be down-regulated by inhibiting PI3K–Akt signal pathway, thus, which can play a protective, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic role in intestinal mucosa of UC rats [67]. And it can inhibit the secretion of the inflammatory factor TNF-α and IL-6 by regulating HIF-1related signal pathway, then to ameliorate the inflammatory reaction of UC [68]. Further more, in our previous research, we found out that in the pathogenesis of UC, the immune response mediated by TNF signal pathway is closely related to it, while inhibiting the expression of this pathway can effectively reduce the content of IL-1, IL-6 and so on [69].
The above results indicate that Ermiaosan may regulate PI3K–Akt, TNF and HIF-1 signaling pathways by acting on key targets such as AKT1, TNF, IL6, TP53, VEGFA, IL1B and CTNNB1 can inhibit inflammation, regulate immunity, positive regulation of cell proliferation, positive regulation of angiogenesis improve mucosal barrier and etc., so as to exert therapeutic effect in UC with dampness-heat syndrome based on active compounds of dihydroniloticin, quercetin and beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt, and they reflect a strong affinity with each other.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, the results of our study show that Ermiaosan may play therapeutic role in treating UC with dampness-heat syndrome based on active compounds of dihydroniloticin, quercetin and beta-sitosterol 3-O-glucoside_qt, and they mainly acting on seven targets AKT1, TNF, IL6, TP53, VEGFA, IL1B and CTNNB1 may be related to the regulation on PI3K–Akt, TNF and HIF-1 signaling pathways.
Data availability
All the data and materials used in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Keshteli AH, Madsen KL, Dieleman LA, et al. Diet in the pathogenesis and management of ulcerative colitis; a review of randomized controlled dietary interventions. Nutrients. 2019;11:1498.
Ren J, Yan D, Wang YC, et al. Inhibitor of differentiation-2 protein ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by inhibiting NF-κB activation in neutrophils. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 760999.
Mahadevan-Velayos U. Phosphatidylcholine in steroid refractory chronic ulcerative colitis–is it all in the mucus? Gastroenterology. 2008;135:317–9.
Zhou ZY, Chen H, Shen YK, et al. Chinese herb injections in the adjuvant treatment for ulcerative colitis: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:3166416. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3166416.
Dharmasiri S, Garrido-Martin EM, Harris RJ, et al. Human intestinal macrophages are involved in the pathology of both ulcerative colitis and crohn disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27:1641–52.
Gupta M, Mishra V, Gulati M, et al. Natural compounds as safe therapeutic options for ulcerative colitis. Inflammopharmacology. 2022;30:397–434.
Wang YF, Zhang RS, Pi M, et al. Correlation between TCM syndromes and type 2 diabetic comorbidities based on fully connected neural network prediction model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:6095476. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6095476.
Liu FY, Zhang XY. Discussion on the treatment of ulcerative colitis from dampness-heat from perspective of intestinal microecology. Gansu Sci&Technol. 2021;37:129–31.
Zhang YN, Li XJ. Li **ujun's Experience in Differentiation and Treatment of Leukemia. Hunan J Tradit Chin Med. 2019;35:34–35+48.
Tang SP, Xu Y, Yu B. Analysis of common drugs for treating “diarrhea” and “dysentery” in Treatise on Seasonal Disease. J Hunan Univ Chin Med. 2022;42:825–9.
A retrospective study of self-designed Qingchanghewei Decoction in the treatment of ulcerative colitis with dampness-heat of large intestine syndrome. Med Diet Health. 2022;20:18–20.
Chen XL, Wen Y, Wu ZC, et al. Development of a traditional chinese medicine syndrome-specific scale for ulcerative colitis: the large intestine dampness-heat syndrome questionnaire. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:4039019.
Liu M, Xuan ZH, Ding JM, et al. Experimental study on acute toxicity of ermiao powder water extract. Acta Chin Med Pharm. 2022;50:33–6.
Fan QY, Lv ZX. 27 Cases of ulcerative colitis treated with Ermiao modified powder and Yunnan Baiyao. J Pract Tradit Chin Intern Med. 2009;23:40–1.
Huang XL. Observation on Clinical Effect of Ermiaosan for Oral Use Combined with Ulcerative Colitis No.1 Prescription in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Proceedings of Guangdong Provincial Academic Conference on Spleen-stomach Digestive Diseases of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine in 2012, Guangdong, China. 2012:163–166.
Qin SM, Huang MY, Wu HM, et al. Discussion on the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis with Dampness as the Pathogenesis. J Emerg Tradit Chin Med. 2022;31:1948–1950+1962.
Li YT, Liu JS, Feng YM, et al. Research progress on compatibility theory and pharmacology of Ermiao powder in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin Med Sci. 2022;12:52–55+67.
Meng XW, Zhang Z, Zhao DJ, et al. A review of the application of classic prescription Ermiaosan in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Shanxi Med J. 2021;50:38–9.
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (2020). Vol I (**药典2020版.一部)[M]. Bei**g. China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press, 2020:168/318.
Wu YT. Discussion on clinical application of phellodendri chinrnsis cortex based on Piwei Lun. J New Chin Med. 2019;51:65–6.
Ren XL, Hao GT, Du ZF. Progress in clinical application and pharmacological research of Cortex Phellodentri Chinensis in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. J Shanxi Coll Tradit Chin Med. 2016;17;:63–64.
Long QQ, Zhao XQ, Dai Q, et al. Demonstration research on quality standard of cortex Phellodentri chinensis. Asia-Pac Tradit Med. 2016;17:63–4.
Wang L, Du X, Zhu HL, et al. Review of pharmacological actions of effective components of cortex Phellodentri chinensis. Jiangsu J Tradit Chin Med. 2022;54:77–81.
Chen YF, Zhong XH. Pharmacological effects of cortex Phellodentri chinensis and its active ingredient extraction. Crop Res. 2015;29:564–8.
Chen J, Wu QP, Fab XY, et al. Prevention and treatment of ulcerative colitis based on the traditional Chinese medicine constitution theory. Chin J EthoMed Ethnopharm. 2022;31:27–31.
Gao CY, Cheng HQ, Liu DQ. Experience of Liu Deqing in warming three-jiao dampness-resistance syndrome with atractylodes lancea. J Pract Tradit Chin Med. 2020;36:803–4.
Chen SD. New edition of materia medica[M]. Bei**g: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press; 2008. p. 39.
Liu DX, Bai YC, Wang Y, et al. Randomized controlled, multi-centre clinical study on qinre qushi granules in treatment of acute upper respiratory tract infection(Summer-heat and Dampness Syndrome). Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol. 2020;31:1483–7.
Zhang MF, Shen YQ. Research progress on pharmacological action of Atractylodes lancea and its effective constituent in digestive system. Drug Eval Res. 2017;40:411–9.
Zhuang D, Qin J, Wang HY, et al. Research progress in the pesticide effect of Atractylodes lancea. Chin J Bioprogr Eng. 2021;19:306–13.
Liu JQ, Liu J, Tong XL, et al. Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to discover the potential pharmacological mechanism of huai hua san against ulcerative colitis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:3255–76.
Qu Y, Yang XX, Li JX, et al. Network pharmacology and molecular docking study of Zhishi-baizhu herb pair in the treatment of gastric cancer. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:2311486. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2311486.
Li X, Ren J, Zhang W, et al. LTM-TCM: a comprehensive database for the linking of traditional Chinese medicine with modern medicine at molecular and phenotypic levels. Pharmacol Res. 2022;178: 106185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106185.
Yan LL, Zhang Z, Liu YF, et al. Anticancer activity of erianin: cancer-specific target prediction based on network pharmacology. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9: 862932. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.862932.
Zhou Y, Zhang YT, Lian XC, et al. Therapeutic target database update 2022: facilitating drug discovery with enriched comparative data of targeted agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D1398–407. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab953.
Yan DY, Zheng GH, Wang CC, et al. HIT 2.0: an enhanced platform for Herbal Ingredients' Targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D1238-D1243. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab1011.
Du L, **ao YJ, Xu YJ, et al. The potential bioactive components of nine TCM prescriptions against COVID-19 in lung cancer were explored based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;8: 813119. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.813119.
Hu PP, Sun N, Khan A, et al. Network pharmacology-based study on the mechanism of scutellarin against zearalenone-induced ovarian granulosa cell injury. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;227: 112865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112865.
Liu JH, Zhou SL, Li SY, et al. Eleven genes associated with progression and prognosis of endometrial cancer (EC) identified by comprehensive bioinformatics analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0859-1.
Wang Y, Zhang XY, Duan M, et al. Identification of potential biomarkers associated with acute myocardial infarction by weighted gene coexpression network analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5553811. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5553811.
Wang AZ, Li ZD, Zhuo S, et al. Mechanisms of cardiorenal protection with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM based on network pharmacology. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9: 857952. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.857952.
Alam MS, Rahaman MM, Sultana A, et al. Statistics and network-based approaches to identify molecular mechanisms that drive the progression of breast cancer. Comput Biol Med. 2022;145: 105508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105508.
Sun TL, Quan WJ, Peng S, et al. Network pharmacology-based strategy combined with molecular docking and in vitro validation study to explore the underlying mechanism of huo luo xiao ling dan in treating atherosclerosis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:1621–45. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S357483.
Yin B, Bi YM, Fan GJ, et al. Molecular mechanism of the effect of Huanglian Jiedu decoction on type 2 diabetes mellitus based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:5273914. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5273914.
Lu MQ, Zhang T, Lu Z, et al. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of complementary and alternative therapies for ulcerative colitis: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99: e21219. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000021219.
Abdelmegid AM, Abdo FK, Ahmed FE, et al. Therapeutic effect of gold nanoparticles on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice with reference to interleukin-17 expression. Sci Rep. 2019;9:10176. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46671-1.
Lu AN, Wang DL, Zhao F, et al. Mechanism of Shaoyao decoction in the treatment of ulcerative colitis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. Chin Tradit Herb Drug. 2020;51:6035–44.
Zhu L, Shen H, Zhang SS, et al. A multi-center, randomized controlled, double-blind clinical study on treatment of moderately active ulcerative colitis with intestinal dampness-heat syndrome by the methods of Qingre Qushi (clearing heat and eliminating Dampness ) and Liangxue Huayu(Cooling Blood for Removing Blood Stasis) Principles. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig. 2021;29:681–685+690.
Zhu PP, Fan H. Fan Heng’s treatment of ulcerative colitis from dampness-heat injury and blood injury. Jiangxi J Tradit Chin Med. 2022;53:24–6.
Cui JY, Xu FW, Yang ZT, et al. Discussion on LI Dongyuan’s theory of treating diarrhea. Tian** J Tradit Chin Med. 2019;36:453–5.
Zhu YM, Dong Y. Research progress of ulcerative colitis treated with traditional Chinese medicine. Henan Tradit Chin Med. 2021;41:1121–5.
**ong YX, Ding G. Analysis of the significance of compatibility of Ermiaosan. Jiangxi J Tradit Chin Med. 2016;47:15–6.
Li YT, Liu JS, Feng YM, et al. Clinical application of Ermiaosan in treatment of difficult dampness-heat syndrome. J Hebei Tradit Chin Med. 2022;37:60–4.
Nakase H, Sato N, Mizuno N, et al. The influence of cytokines on the complex pathology of ulcerative colitis. Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21: 103017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2021.103017.
Yuan H, Li XX, Wang HM, et al. Effect of treatment with safflower solution on express of VEGF and bFGF in ulcerative colitis in rats. World Chin J Dig. 2012;20:3299–304.
Dai X, Ding MHZ, Zhang W, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of different elution fractions of Er-miao-san on acute inflammation induced by carrageenan in rat paw tissue. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:7958–65. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.916977.
**e L. Overview of the pharmacological action of Ermiaosan. Guangxi Tradit Chin Med. 1988;11:29.
Kottakis G, Kambouri K, Giatromanolaki A, et al. Effects of the antioxidant quercetin in an experimental model of ulcerative colitis in mice. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;59:87. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010087.
He LH, Qin QX, Wang H, et al. Effect of Ermiaosan on function of human fibroblast synovial cells induced by TNF-α. Chin J Exp Med Formul. 2020;26:11–7.
Liu J, Li Z, Hao HQ, et al. Ermiaosan aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis Rats. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2022;26:688–93.
Bae S, Jung YJ, Choi YM, et al. Effects of Er-Miao-San extracts on TNF-alpha-induced MMP-1 expression in human dermal fibroblasts. Biol Res. 2015;48:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/0717-6287-48-8.
Zhang W, Zhang QY, Xuan ZH, et al. The protective effect of different polar solvent extracts of Ermiaosan on rats with adjuvant arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:5305278. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5305278.
Yuan PF, Wang JM, Wang MJ, et al. Effect of Ermiaosan on wound healing, inflammation and neovascularization after anal fistula surgery. Res Pract Chin Med. 2021;35:82–5.
Nakase H, Sato N, Mizuno N, et al. The influence of cytokines on the complex pathology of ulcerative colitis. Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21(3): 103017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2021.103017.
Yuan H, Li XX, Wang HM, et al. Effect of treatment with safflower solution on expression of VEGF and bFGF in ulcerative colitis in rats. World Chin J Dig. 2012;20:3299–304.
Fu XX, Sun F, Wang FX, et al. Aloperine protects mice against DSS-induced colitis by PP2A-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling suppression. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:5706152. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5706152.
Yang XJ, Fu Y, Wang JJ, et al. Effect of coptidis rhizoma-magnoliae officinalis cortex on TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Chin Tradit Herb Drug. 2021;52:4587–97.
Wang XT, Wang Y, Biao YN, et al. Effect of **elitang on TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α signaling pathway in mice with ulcerative colitis. Chin J Exp Med Formul. 2023. https://doi.org/10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230239.
Qu Y, Zhang SX, Zhou L, et al. Network pharmacological study of Schizonepetae herba and Saposhnikoviae radix in treatment of ulcerative colitis. China J Chin Mater Med. 2019;44:5465–72. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190929.402.
Acknowledgements
We are really grateful for Professor Shuxin Zhang’s excellent and scientific guidance on this study, Bei**g Municipal Natural Science Foundation supported this study (7202112).
Funding
Bei**g Municipal Natural Science Foundation supported this study (7202112). The funder had no role in this study design, data collection and analysis, or decision to publish, preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YQ, SL and SZ conceived and designed this study. YQ and SL wrote this article. WW and TZ was responsible for polishing and revising the whole manuscript. LZ designed the GO and KEGG enrichment analysis and molecular docking. GN helped to search the data and reference materials about this research. All authors approved the whole final manuscript. YQ and SL contributed equally to this article, author names in bold designate shared co-first authorship.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Li, S., Wu, W. et al. Network pharmacology and molecular docking study of Ermiaosan (二妙散) in the treatment of ulcerative colitis with dampness-heat syndrome. Discov Appl Sci 6, 52 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-024-05625-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-024-05625-7