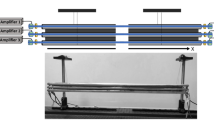
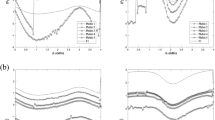
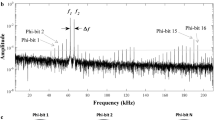
Abstract
It is shown that multiple logical phi-bit large-scale unitary operations analogous to quantum circuits can be realized by design. Logical phi-bits are nonlinear acoustic analogues of qubits which arise when elastic waveguides are coupled and driven at multiple frequencies in the presence of non-linearities. The contribution presents an approach that maps both the state of multiple phi-bits in their supporting nonlinear acoustic metastructure and their representations as complex state vectors in exponentially scaling Hilbert spaces. Upon physically actuating \(\pi \) changes in phi-bit phases and by engineering appropriate multiple phi-bits representations, one can realize a scalable phi-bit-based quantum Fourier transform.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Akhavan, O., Rezskhani, A.T., Golshani, M.: Quantum dense coding by spatial state entanglement. Phys. Lett. A 313, 261 (2003)
Feix, A., Araújo, M., Brukner, Č: Quantum superposition of the order of parties as a communication resource. Phys. Rev. A 92, 052326 (2015)
Gilyén, A., Su, Y., Low, G.H., Wiebe, N.: Quantum singular value transformation and beyond: exponential improvements for quantum matrix arithmetics. In: Proceedings of the 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on the Theory of Computing (STOC ’19), June 23–26, 2019, Phoenix, AZ, USA. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 12 pages (2019)
Alimirzaei, F., Kieslich, C.A.: Machine learning models for predicting membranolytic anticancer peptides. In: Kokossis, A., Georgiadis, M.C., Pistikopoulos, E.N. (eds.) Proceedings of the 33rd European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering (ESCAPE33), June 18–21, 2023, Athens, Greece, p. 2691
Barenco, A., Bennett, C.H., Cleve, R., DiVincenzo, D.P., Margolus, N., Shor, P., Sleator, T., Smolin, J.A., Weinfurter, H.: Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 52, 3457 (1995)
Ezeamaku, U.L., Ezekannagha, C., Eze, O.I., Odimegwu, N., Nwakaudu, A., Okafor, A., Ekuma, I., Onukwuli, O.D.: The impact of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) treatment on the tensile strength of pineapple leaf fiber reinforced with tapioca-based bio resin. Arab Gulf J. Sci. Res. 41, 416 (2023)
Bhattacharjee, S., Satpathi, U., Sinha, S.: Quantum Langevin dynamics of a charged particle in a magnetic field: response function, position-velocity and velocity autocorrelation functions. Pramana-J. Phys. 96, 53 (2022)
Al-Raeei, Marwan: Applying fractional quantum mechanics to systems with electrical screening effects. Chaos Solitons Fractals 150, 111209 (2021)
Coppersmith, D.: An approximate Fourier transform useful in quantum factoring. Technical Report RC19642, IBM (1994). ar**v:quant-ph/0201067
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. IEEE Computer Society Press, p. 124 (1994)
Mannone, M., Rocchesso, D.: Sing and measure: sound as voice as quanta. In: Miranda, E.R. (ed.) Quantum Computer Music, p. 297. Springer, Cham (2022)
Arif Hasan, M., Calderin, L., Lata, T., Lucas, P., Runge, K., Deymier, P.A.: The sound of Bell states. Commun. Phys. 2, 106 (2019)
Hasan, M.A., Runge, K., Deymier, P.A.: Experimental classical entanglement in a 16 acoustic qubit-analogue. Sci. Rep. 11, 24248 (2021)
Deymier, P.A., Runge, K., Hasan, M.A., Lata, T.D., Levine, J.A., Cutillas, P.: Realizing acoustic qubit analogues with nonlinearity tunable phi-bits in externally driven coupled acoustic waveguides. Sci. Rep. 13, 635 (2023)
Deymier, P.A., Runge, K., Hasan, M.A., Levine, J.A., Cutillas, P.: Setting the stage for materials simulation using acoustic metamaterials digital quantum analogue computing platforms. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 30, 084003 (2022)
Runge, K., Hasan, M.A., Levine, J.A., Deymier, P.A.: Demonstration of a two-bit controlled-NOT quantum-like gate using classical acoustic qubit-analogues. Sci. Rep. 12, 14066 (2022)
Deymier, P.A., Runge, K., Cutillas, P., Hasan, M.A., Lata, T.D., Levine, J.A.: Scalable exponentially complex representations of logical phi-bit states and experimental demonstration of an operable three phi-bit gate using an acoustic metastructure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 122, 141701 (2023)
Runge, K., Deymier, P.A., Hasan, M.A., Lata, T.D., Levine, J.A.: Scalability of a multiple phi-bit unitary transformation. J. Appl. Phys. (in review)
Deymier, P.A., Runge, K., Hasan, M.A., Lata, T.D., Levine, J.A.: Tuning logical phi-bit state vectors in an externally driven nonlinear array of acoustic waveguides via drivers’ phase. Quantum Rep. 5(2), 325 (2023)
Sylvester, J.: Sur l’equation en matrices px=xq. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 99(67–71), 115–116 (1884)
Pachuau, J.L., Roy, A., Saha, A.K.: Integer numeric multiplication using quantum Fourier transform. Quantum Stud. Math. Found. 9, 155–164 (2022)
Kurgalin, S., Borzunov, S.: Concise Guide to Quantum Computing. Springer, Dordrecht (2021)
Trivedi, D., Saharia, A., Choure, K., Tiwari, M., Maddila, R.K., Singh, G.: Three-qubit implementation of quantum Fourier transform for Shor’s algorithm. In: Optical and Wireless Technologies: Proceedings of OWT 2020, pp. 115–121. Springer, Singapore (2022)
Giorda, P., Iorio, A., Sen, S., Vitiello, G.: Searching for a semiclassical Shor’s algorithm. In: Quantum Computing and Quantum Bits in Mesoscopic Systems, pp. 123–131. Springer, Boston (2004)
de Boutray, H., Jaffali, H., Holweck, F., Giorgetti, A., Masson, P.A.: Mermin polynomials for non-locality and entanglement detection in Grover’s algorithm and Quantum Fourier Transform. Quantum Inf. Process. 20, 1–29 (2021)
Acampora, G., Schiattarella, R.: Deep neural networks for quantum circuit map**. Neural Comput. Appl. 33, 13723 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The development of the acoustic metastructure and experimental setup was supported in part by a grant from the W.M. Keck foundation. P.A.D and J.A.L acknowledge partial support from NSF Grant # 2204400. M.A.H. acknowledges partial support from NSF Grant # 2204382 and thanks Wayne State University startup funds for additional support. This work was also partially supported by the Science and Technology Center New Frontiers of Sound (NewFoS) through NSF grant # 2242925.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PAD wrote the main manuscript text with contributions from all authors. PAD developed the theoretical models. MAH and TDL conducted the experiments and acquired the data. PAD, KR, MAH, TDL, and JAL contributed equally to the analysis and interpretation of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deymier, P.A., Runge, K., Hasan, M.A. et al. Practical implementation of a scalable discrete Fourier transform using logical phi-bits: nonlinear acoustic qubit analogues. Quantum Stud.: Math. Found. 11, 217–229 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40509-023-00312-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40509-023-00312-5