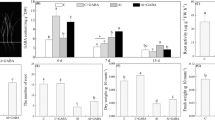
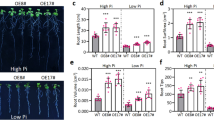
Abstract
Auxin (IAA) and paclobutrazol (PBZ) play important role in resisting abiotic stress for plants. However, the effects of combination of these regulators in plants under salinity remained obscure. In the current study, the role of 50 ppm IAA and 10 ppm PBZ on mitigating salt stress (200 and 300 mM NaCl) was investigated in soybean (Glycine max L. cv. Planet). We identified that IAA or PBZ and IAA + PBZ improved the physiological parameters that were damaged by salinity but PBZ performed best as observed by scanning election microscopy (SEM). However, IAA was more succesful to induce some antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbat peroxidase, peroxidase), although both of them reduced or did not affect GSH- related enzymes (dehydroascorbate reductase, monodehydroascorbate reductase, glutathione-s-transfease, glutathione reductase, glutathione peroxidase). Besides this, combination of IAA and PBZ treatment showed the lowest MDA with inhibited salt stress induced oxidative damage. Additionally, PBZ was more effective against as IAA to reduce the pectin methyl esterase (PME) and phenylalanine ammonium lipase (PAL) enzyme activities as well as decreased arabinose content, while they were increased with salinity. IAA or PBZ increased lignin content and led to reduced loosening in roots, while IAA performed best. Overall, this study firstly presents that these regulators (50 ppm IAA; 10 ppm PBZ) could be used together to increase salt tolerance in soybean plants via regulating physiological and biochemical metabolism, antioxidant defense system and cell wall modified parameters.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Latef AAH, Akter A, Tahjib-Ul-Arif M (2021a) Foliar application of auxin or cytokinin can confer salinity stress tolerance in Vicia faba L. Agronomy 11:790. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040790
Abdel Latef AAH, Tahjib-Ul-Arif M, Rhaman MS (2021b) Exogenous auxin-mediated salt stress alleviation in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Agronomy 11:547. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030547
Agami RA (2014) Applications of ascorbic acid or proline increase resistance to salt stress in barley seedlings. Biol Plant 58:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0392-y
Agha MS, Abbas MA, Sofy MR, Haroun SA, Mowafy AM (2021) Dual inoculation of bradyrhizobium and enterobacter alleviates the adverse effect of salinity on Glycine max seedling. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj-Napoca 49:12461–12461. https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha49312461
Alnusairi GS, Mazrou YS, Qari SH, Elkelish AA, Soliman MH, Eweis M, Abdelaal K, El-Samad GA, Ibrahim MFM, ElNahhas N (2021) Exogenous nitric oxide reinforces photosynthetic efficiency, osmolyte, mineral uptake, antioxidant, expression of stress-responsive genes and ameliorates the effects of salinity stress in wheat. Plants 10:1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081693
Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2002) The use of the electrolyte leakage method for assessing cell membrane stability as a water stress tolerance test in durum wheat. Plant Growth Regul 36:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014732714549
Bañón S, González A, Cano EA, Franco JA, Fernández JA (2002) Growth, development and colour response of potted Dianthus caryophyllus cv. mondriaan to paclobutrazol treatment. Sci Hortic 94:371–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(02)00005-5
Bashri G, Prasad SM (2016) Exogenous IAA differentially affects growth, oxidative stress and antioxidants system in Cd stressed Trigonella foenum-graecum L. seedlings: toxicity alleviation by up-regulation of ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.06.015
Bawa G, Feng L, Chen G, Chen H, Hu Y, Pu T, Wang X (2020) Gibberellins and auxin regulate soybean hypocotyl elongation under low light and high-temperature interaction. Physiol Plant 170:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13158
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Bergmeyer HU (1970) Measurement of catalase activity. Biochem Z 327:255
Bhatt D, Nath M, Sharma M, Bhatt MD, Bisht DS, Butani NV (2020) Role of growth regulators and phytohormones in overcoming environmental stress. In: Roychoudhury A, Tripathi DK (eds) Protective chemical agents in the amelioration of plant abiotic stress: biochemical and molecular perspectives. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 254–279. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119552154.ch11
Bosch M, Cheung AY, Hepler PK (2005) Pectin methylesterase, a regulator of pollen tube growth. Plant Physiol 138:1334–1346. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.059865
Bubna GA, Lima RB, Zanardo DYL, Dos Santos WD, Ferrarese MDLL, Ferrarese-Filho O (2011) Exogenous caffeic acid inhibits the growth and enhances the lignification of the roots of soybean (Glycine max). J Plant Physiol 168:1627–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.03.005
Cackett L, Cannistraci CV, Meier S, Ferrandi P, Pěnčík A, Gehring C, Novák O, Ingle RA, Donaldson L (2022) Salt-specific gene expression reveals elevated auxin levels in Arabidopsis thaliana plants grown under saline conditions. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.804716
Castillejo C, de la Fuente JI, Iannetta P, Botella MÁ, Valpuesta V (2004) Pectin esterase gene family in strawberry fruit: study of FaPE1, a ripening-specific isoform. J Exp Bot 55:909–918
Cengiz S, Kişmiroğlu C, Cebi N, Çatak J, Yaman M (2020) Determination of the most potent precursors of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in chips, crackers, and breakfast cereals by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using precolumn derivatization with 4-nitro-1, 2-phenlenediamine. Microchem J 158:105170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105170
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90:856–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13299
Chun HJ, Baek D, Cho HM, Lee SH, ** BJ, Yun DJ, Kim MC et al (2019) Lignin biosynthesis genes play critical roles in the adaptation of Arabidopsis plants to high-salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 14:1625697. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2019.1625697
Claussen W (2005) Proline as a measure of stress in tomato plants. Plant Sci 168:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.07.039
Das AK, Anik TR, Rahman MM, Keya SS, Islam MR, Rahman MA, Mostofa MG et al (2022) Ethanol treatment enhances physiological and biochemical responses to mitigate saline toxicity in soybean. Plants 11:272. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030272
Desta B, Amare G (2021) Paclobutrazol as a plant growth regulator. Chem Biol Technol 8:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-020-00199-z
Dinler BS, Antoniou C, Fotopoulos V (2014) Interplay between GST and nitric oxide in the early response of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants to salinity stress. J Plant Physiol 171:1740–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2014.07.026
Dinler BS, Gunduzer E, Tekinay T (2016) Pre-treatment of fulvic acid plays a stimulant role in protection of soybean (Glycine max L.) leaves against heat and salt stress. Acta Biol Crac Ser Bot 58:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1515/abcsb-2016-000
Dinler BS, Cetinkaya H, Sergiev I, Shopova E, Todorova D (2021) Paclobutrazol induced non-enzymatic antioxidants and polyamine levels in soybean plants grown under salinity stress. Botanica 27:149–159
Dinler BS, Cetinkaya H, Sergiev I, Shopova E, Todorova D (2022) Paclobutrazol dependent salt tolerance ıs related to CLC1 and NHX1 gene expressıon ın soybean plants. Acta Sci Pol Hortorum Cultus 21:25–38. https://doi.org/10.24326/asphc.2022.3.3
Fahad S, Hussain S, Matloob A, Khan FA, Khaliq A, Saud S, Hassan S, Shan D, Huang J et al (2015) Phytohormones and plant responses to salinity stress: a review. Plant Growth Regul 75:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-0013-y
Fletcher RA, Gilley A, Davis TD, Sankhla N (2000) Triazoles as plant growth regulators and stress protectants. Hortic Rev 24:55–138
Forghani AH, Almodares A, Ehsanpour AA (2020) The role of gibberellic acid and paclobutrazol on oxidative stress responses induced by in vitro salt stress in sweet sorghum. Russ J Plant Physiol 67:555–563. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443720030073
Foyer CH, Halliwell B (1976) The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 133:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386001
Gall HL, Philippe F, Domon JM, Gillet F, Pelloux J, Rayon C (2015) Cell wall metabolism in response to abiotic stress. Plants 4:112–166. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4010112
Gigli-Bisceglia N, Van Zelm E, Huo W, Lamers J, Testerink C (2022) Arabidopsis root responses to salinity depend on pectin modification and cell wall sensing. Develoment 149:dev200363
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42083-8
Hagerman AE, Austin PJ (1986) Continuous spectrophotometric assay for plant pectin methyl esterase. J Agric Food Chem 34:440–444. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00069a015
Hajihashemi S, Kiarostami K, Saboora A, Enteshari S (2007) Exogenously applied paclobutrazol modulates growth in salt-stressed wheat plants. Plant Growth Regul 53:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-007-9209-8
Hasanuzzaman M, Parvin K, Anee TI, Masud AAC, Nowroz F (2022) Salt stress responses and tolerance in soybean. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K (eds) Plant stress physiology-perspectives in agriculture. IntechOpen, London, pp 47–82
Herzog V, Fahimi HD (1973) A new sensitive colorimetric assay for peroxidase using 3, 3′-diaminobenzidine as hydrogen donor. Anal Biochem 55:554–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(73)90144-9
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circ Calif Agric Exp Stn 347:1–32
Hossain MA, Asada K (1984) Inactivation of ascorbate peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts on dark addition of hydrogen peroxide: its protection by ascorbate. Plant Cell Physiol 25:1285–1295
Hu X, Zhang G, Hamaker BR, Miao M (2022) The contribution of intact structure and food processing to functionality of plant cell wall-derived dietary fiber. Food Hydrocoll 127:107511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107511
Husen A, Iqbal M, Aref IM (2016) IAA-induced alteration in growth and photosynthesis of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants grown under salt stress. J Environ Biol 37:421
Iglesias MJ, Terrile MC, Bartoli CG, D’Ippólito S, Casalongué CA (2010) Auxin signaling participates in the adaptative response against oxidative stress and salinity by interacting with redox metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 74:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9667-7
Islam F, Farooq MA, Gill RA, Wang J, Yang C, Ali B, Zhou W (2017) 2, 4-D attenuates salinity-induced toxicity by mediating anatomical changes, antioxidant capacity and cation transporters in the roots of rice cultivars. Sci Rep 7:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09708-x
Islam MM, Ye W, Akter F, Rhaman MS, Matsushima D, Munemasa S, Murata Y et al (2020) Reactive carbonyl species mediate methyl jasmonate-induced stomatal closure. Plant Cell Physiol 61:1788–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcaa107
Jaleel CA, Gopi R, Manivannan P, Panneerselvam R (2007) Responses of antioxidant defense system of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. to paclobutrazol treatment under salinity. Acta Physiol Plant 29:205–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-007-0025-6
Jungklang J, Saengnil K, Uthaibutra J (2017) Effects of water-deficit stress and paclobutrazol on growth, relative water content, electrolyte leakage, proline content and some antioxidant changes in Curcuma alismatifolia Gagnep. cv. Chiang Mai Pink. Saudi J Biol Sci 24:1505–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.09.017
Kamran M, Cui W, Ahmad I, Meng X, Zhang X, Su W, Liu T et al (2018) Effect of paclobutrazol, a potential growth regulator on stalk mechanical strength, lignin accumulation and its relation with lodging resistance of maize. Plant Growth Regul 84:317–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-017-0342-8
Kaya C, Ashraf M, Dikilitas M, Tuna AL (2013) Alleviation of salt stress-induced adverse effects on maize plants by exogenous application of indoleacetic acid (IAA) and inorganic nutrients-A field trial. Aust J Crop Sci 7:249–254
Ke D, Sun G (2004) The efect of reactive oxygen species on ethylene production induced by osmotic stress in etiolated mungbean seedling. Plant Grow Regul 44(3):199–206
Khalid A, Aftab F (2020) Effect of exogenous application of IAA and GA3 on growth, protein content, and antioxidant enzymes of Solanum tuberosum L. grown in vitro under salt stress. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 56:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-019-10047-x
Khan MN, Ahmed I, Ud Din I, Noureldeen A, Darwish H, Khan M (2022) Proteomic insight into soybean response to flooding stress reveals changes in energy metabolism and cell wall modifications. PLoS ONE 7:e0264453. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264453
Kishor A, Srivastav M, Dubey AK, Singh AK, Sairam RK, Pandey RN, Dahuja A, Sharma RR (2009) Paclobutrazol minimises the effects of salt stress in mango (Mangifera indica L.). J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 84:459–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2009.11512549
Kuo J, Wang YW, Chen M, Fuh G, Lin CH (2019) The effect of paclobutrazol on soil bacterial composition across three consecutive flowering stages of mung bean. Folia Microbiol 64:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-0644-x
Kutschera U, Wang ZY (2016) Growth-limiting proteins in maize coleoptiles and the auxin-brassinosteroid hypothesis of mesocotyl elongation. Protoplasma 253:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0787-4
Labiad MH, Giménez A, Varol H, Tüzel Y, Egea-Gilabert C, Fernández JA, Martínez-Ballesta MDC (2021) Effect of exogenously applied methyl jasmonate on yield and quality of salt-stressed hydroponically grown sea fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.). Agronomy 11:1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061083
Lawrence RA, Burk RF (1976) Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71:952–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(76)90747-6
Lichtenthaler HK, Buschmann C (1987) Chlorophyll fluorescence spectra of green bean leaves. J Plant Physiol 129:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(87)80110-4
Lin CC, Kao CH (2001) Cell wall peroxidase against ferulic acid, lignin, and NaCl-reduced root growth of rice seedlings. J Plant Physiol 158:667–671. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00245
Lin KH, Pai FH, Hwang SY, Lo HF (2006) Pre-treating paclobutrazol enhanced chilling tolerance of sweetpotato. Plant Growth Regul 49:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-006-9135-1
Lin L, Wu J, Jiang M, Wang Y (2021a) Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in environmental stresses. Int J Mol Sci 22:1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041543
Lin Y, An F, He H, Geng F, Song H, Huang Q (2021b) Structural and rheological characterization of pectin from passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa) peel extracted by high-speed shearing. Food Hydrocoll 114:106555
Liu Q, Luo L, Zheng L (2018) Lignins: biosynthesis and biological functions in plants. Int J Mol Sci 19:335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020335
Liu J, Zhang W, Long S, Zhao C (2021) Maintenance of cell wall integrity under high salinity. Int J Mol Sci 22:3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063260
Madhava Rao KV, Sresty TV (2000) Antioxidative parameters in the seedlings of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh) in response to Zn and Ni stresses. Plant Sci 157:113–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00273-9
Mandhania S, Madan S, Sawhney V (2006) Antioxidant defense mechanism under salt stress in wheat seedlings. Biol Plant 50:227–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-006-0011-7
Marshall JG, Rutledge RG, Blumwald E, Dumbroff EB (2000) Reduction in turgid water volume in jack pine, white spruce and black spruce in response to drought and paclobutrazol. Tree Physiol 20:701–707. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/20.10.701
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ 33:453–467. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02041.x
Mir AR, Siddiqui H, Alam P, Hayat S (2020) Foliar spray of Auxin/IAA modulates photosynthesis, elemental composition, ROS localization and antioxidant machinery to promote growth of Brassica juncea. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:2503–2520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00914-y
Mir AR, Alam P, Hayat S (2022) Auxin regulates growth, photosynthetic efficiency and mitigates copper induced toxicity via modulation of nutrient status, sugar metabolism and antioxidant potential in Brassica juncea. Plant Physiol Biochem 185:244–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.06.006
Moore JP, Nguema-Ona EE, Vicré-Gibouin M, Sørensen SI, Willats WG, Driouich A, Farrant JM (2013) Arabinose-rich polymers as an evolutionary strategy to plasticize resurrection plant cell walls against desiccation. Planta 237:739–754
Moreira-Vilar FC, Siqueira-Soares RDC, Finger-Teixeira A, Oliveira DMD, Ferro AP, da Rocha GJ, Ferrarese-Filho O et al (2014) The acetyl bromide method is faster, simpler and presents best recovery of lignin in different herbaceous tissues than Klason and thioglycolic acid methods. PLoS ONE 9:e110000. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110000
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Nanda AK, Melnyk CW (2018) The role of plant hormones during grafting. J Plant Res 131:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-017-0994-5
Nazarudin MA, Fauzi RM, Tsan FY (2007) Effects of paclobutrazol on the growth and anatomy of stems and leaves of Syzygium campanulatum. J Trop for Sci 19:86–91
Neumetzler L, Humphrey T, Lumba S, Snyder S, Yeats TH, Usadel B, Bonetta D et al (2012) The FRIABLE1 gene product affects cell adhesion in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 7:e42914. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042914
Ning H, Yuan J, Dong Q, Li W, Xue H, Wang Y, Li WX et al (2018) Identification of QTLs related to the vertical distribution and seed-set of pod number in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merri]. PLoS ONE 13:e0195830. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195830
Oliveira DM, Mota TR, Salatta FV, Sinzker RC, Končitíková R, Kopečný D, Dos Santos WD et al (2020) Cell wall remodeling under salt stress: Insights into changes in polysaccharides, feruloylation, lignification, and phenolic metabolism in maize. Plant Cell Environ 43:2172–2191. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13805
Pal S, Zhao J, Khan A, Yadav NS, Batushansky A, Barak S, Rewald B, Fait A, Lazarocitch N, Rachmilevitch S (2016) Paclobutrazol induces tolerance in tomato to deficit irrigation through diversified effects on plant morphology, physiology and metabolism. Sci Rep 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39321
Pascholati SF, Nicholson RL, Butler LG (1986) Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity and anthocyanin accumulation in wounded maize mesocotyls. J Phytopathol 115:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.1986.tb00874.x
Pashang D, Weisany W, Ghajar FGK (2021) Changes in the fatty acid and morphophysiological traits of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) cultivars as response to auxin under water-deficit stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2164–2177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00512-1
Passardi F, Cosio C, Penel C, Dunand C (2005) Peroxidases have more functions than a Swiss army knife. Plant Cell Rep 24:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0972-6
Petersson SV, Johansson AI, Kowalczyk M, Makoveychuk A, Wang JY, Moritz T, Grebe M, Benfey PN, Sandberg G, Ljung K (2009) An auxin gradient and maximum in the Arabidopsis root apex shown by high-resolution cell-specific analysis of IAA distribution and synthesis. Plant Cell 21:1659–1668. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.066480
Piotrowska-Niczyporuk A, Bajguz A (2014) The effect of natural and synthetic auxins on the growth, metabolite content and antioxidant response of green alga Chlorella vulgaris (Trebouxiophyceae). Plant Growth Regul 73:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9867-7
Quamruzzaman M, Manik SN, Shabala S, Zhou M (2021) Improving performance of salt-grown crops by exogenous application of plant growth regulators. Biomolecules 11:788. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060788
Ramana GV, Padhy SP, Chaitanya KV (2012) Differential responses of four soybean (Glycine max. L) cultivars to salinity stress. Legume Res 35:185–193
Ribba T, Garrido-Vargas F, O’Brien JA (2020) Auxin-mediated responses under salt stress: from developmental regulation to biotechnological applications. J Exp Bot 71:3843–3853. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa241
Sadak MS, El-Hameid A, Asmaa R, Zaki FS, Dawood MG, El-Awadi ME (2020) Physiological and biochemical responses of soybean (Glycine max L.) to cysteine application under sea salt stress. Bull Natl Res Cent 44:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0259-7
Saeed WT (2005) Pomegranate cultivars as affected by Paclobutrazol, salt stress and change in fingerprints. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 56:581
Sahoo S, Awasthi JP, Sunkar R, Panda SK (2017) Determining glutathione levels in plants. In: Sunkar R (ed) Plant stress tolerance. Humana Press, New York, pp 273–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7136-7_16
Saini S, Kaur N, Marothia D, Singh B, Singh V, Gantet P, Pati PK (2021) Morphological analysis, protein profiling and expression analysis of auxin homeostasis genes of roots of two contrasting cultivars of rice provide inputs on mechanisms involved in rice adaptation towards salinity stress. Plants 10:1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081544
Salopek-Sondi B, Pavlović I, Smolko A, Šamec D (2017) Auxin as a mediator of abiotic stress responses. In: Pandey GK (ed) Mechanism of plant hormone signaling under stress, vol 1. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 1–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118889022.ch1
Salvador VH, Lima RB, dos Santos WD, Soares AR, Böhm PAF, Marchiosi R, Ferrarese-Filho O et al (2013) Cinnamic acid increases lignin production and inhibits soybean root growth. PLoS ONE 8:e69105. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069105
Sankar B, Karthishwaran K, Somasundaram R (2013) Leaf anatomical changes in peanut plants in relation to drought stress with or without PBZ and abscisic acid. J Phytol 5:25–29. https://doi.org/10.14719/pst.1621
Santos MP, Zandonadi DB, de Sá AFL, Costa EP, de Oliveira CJL, Perez LE, Façanha AR, Bressan-Smith R (2020) Abscisic acid-nitric oxide and auxin interaction modulates salt stress response in tomato roots. Theor Exp Plant Physiol 32:301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-020-00187-6
Sénéchal F, Graff L, Surcouf O, Marcelo P, Rayon C, Bouton S, Pelloux J et al (2014) Arabidopsis PECTIN METHYLESTERASE17 is co-expressed with and processed by SBT3. 5, a subtilisin-like serine protease. Ann Bot 114:1161–1175. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu035
Shahzad R, Harlina PW, Ewas M, Zhenyuan P, Nie X, Gallego PP, Khan SU, Nishawy E, Khan AH, Jia H (2021) Foliar applied 24-epibrassinolide alleviates salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by suppression of ABA levels and upregulation of secondary metabolites. J Plant Interact 16:533–549. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2021.2002444
Shaki F, Maboud HE, Niknam V (2019) Effects of salicylic acid on hormonal cross talk, fatty acids profile, and ions homeostasis from salt-stressed safflower. J Plant Interact 14:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2019.1635660
Shalaby SM, Sharshir SW, Kabeel AE, Kandeal AW, Abosheiasha HF, Abdelgaied M, Yang N et al (2022) Reverse osmosis desalination systems powered by solar energy: preheating techniques and brine disposal challenges–a detailed review. Energy Convers Manag 251:114971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2021.114971
Sharma DK, Dubey AK, Srivastav M, Singh AK, Pandey RN, Dahuja A (2013) Effect of paclobutrazol and putrescine on antioxidant enzymes activity and nutrients content in salt tolerant citrus rootstock sour orange under sodium chloride stress. J Plant Nutr 36:1765–1779. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2013.807823
Sheteiwy MS, Abd Elgawad H, **ong YC, Macovei A, Brestic M, Skalicky M, El-Sawah AM (2021) Inoculation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and mycorrhiza confers tolerance to drought stress and improve seed yield and quality of soybean plant. Physiol Plant 172:2153–2169. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13454
Shi H, Chen L, Ye T, Liu X, Ding K, Chan Z (2014) Modulation of auxin content in Arabidopsis confers improved drought stress resistance. Plant Physiol Biochem 82:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.06.008
Shiraz M, Sami F, Siddiqui H, Yusuf M, Hayat S (2021) Interaction of auxin and nitric oxide improved photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant system of Brassica juncea plants under salt stress. J Plant Growth Regul 40:2379–2389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10268-0
Singh HP, Batish DR, Kaur G, Arora K, Kohli RK (2008) Nitric oxide (as sodium nitroprusside) supplementation ameliorates Cd toxicity in hydroponically grown wheat roots. Environ and Exp Bot 63:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.12.005
Smart R, Bingham GE (1974) Rapid estimates of relative water content. Plant Physiol 53:258–260. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.53.2.258
Sofy MR, Elhindi KM, Farouk S, Alotaibı MA (2020) Zinc and paclobutrazol mediated regulation of growth, upregulating antioxidant aptitude and plant productivity of pea plants under salinity. Plants 9:1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091197
Soliman M, Elkelish A, Souad T, Alhaithloul H, Farooq M (2020) Brassinosteroid seed priming with nitrogen supplementation improves salt tolerance in soybean. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00765-7
Soumya PR, Kumar P, Pal M (2017) Paclobutrazol: a novel plant growth regulator and multi-stress ameliorant. Indian J Plant Physiol 22:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-017-0316-x
Soumya V, Kiranmayi P, Kumar KS (2022) Morpho-anatomical responses of Catharanthus roseus due to combined heavy metal stress observed under scanning electron microscope. Plant Sci Today 9:623–631. https://doi.org/10.14719/pst.1621
Syahputra BSA, Sinniah UR, Ismail MR, Swamy MK (2016) Optimization of paclobutrazol concentration and application time for increased lodging resistance and yield in field-grown rice. Philipp Agric Sci 99:221–228
Takshak S, Agrawal SB (2017) Exogenous application of IAA alleviates effects of supplemental ultraviolet-B radiation in the medicinal plant Withania somnifera Dunal. Plant Biol 19:904–916. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12601
Tivendale ND, Millar AH (2022) How is auxin linked with cellular energy pathways to promote growth? New Phytol 233:2397–2404. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17946
Tyburski J, Dunajska K, Mazurek P, Piotrowska B, Tretyn A (2009) Exogenous auxin regulates H2O2 metabolism in roots of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) seedlings affecting the expression and activity of CuZn-superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase. Acta Physiol Plant 31:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-008-0225-8
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00197-1
Verhertbruggen Y, Marcus SE, Chen J, Knox JP (2013) Cell wall pectic arabinans influence the mechanical properties of Arabidopsis thaliana inflorescence stems and their response to mechanical stress. Plant Cell Physiol 54:1278–1288. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pct074
Wang FZ, Wang QB, Kwon SY, Kwak SS, Su WA (2005) Enhanced drought tolerance of transgenic rice plants expressing a pea manganese superoxide dismutase. J Plant Physiol 162:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2004.09.009
Wang Y, Li K, Li X (2009) Auxin redistribution modulates plastic development of root system architecture under salt stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 166:1637–1645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2009.04.009
Wang P, Yan B, Wan H, Fang X, Yang C (2018) The differences of cell wall in roots between two contrasting soybean cultivars exposed to cadmium at young seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut 25:29705–29714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2956-4
Waqas M, Yaning C, Iqbal H, Shareef M, ur Rehman H, Iqbal S, Mahmood S, (2019) Soil drenching of paclobutrazol: an efficient way to improve quinoa performance under salinity. Physiol Plant 165:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12820
Watson GW (2001) Soil applied paclobutrazol affects root growth, shoot growth, and water potential of American elm seedlings. J Environ Hortic 19:119–122. https://doi.org/10.24266/0738-2898-19.3.119
Webb JA, Fletcher RA (1996) Paclobutrazol protects wheat seedlings from injury due to waterlogging. Plant Growth Regul 18:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024383
Wen PF, Chen JY, Wan SB, Kong WF, Zhang P, Wang W, Huang WD et al (2008) Salicylic acid activates phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in grape berry in response to high temperature stress. Plant Growth Regul 55:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-007-9250-7
Wu HC, **n TL (2010) Heat shock-triggered Ca2+ mobilization accompanied by pectin methylesterase activity and cytosolic Ca2+ oscillation are crucial for plant thermotolerance. Plant Signal Behav 5:1252–1256. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.10.12607
Wu HC, Hsu SF, Luo DL, Chen SJ, Huang WD, Lur HS, **n TL (2010) Recovery of heat shock-triggered released apoplastic Ca2+ accompanied by pectin methylesterase activity is required for thermotolerance in soybean seedlings. J Exp Bot 61:2843–2852. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq121
**ng X, Jiang H, Zhou Q, **ng H, Jiang H, Wang S (2016) Improved drought tolerance by early IAA-and ABA-dependent H2O2 accumulation induced by α-naphthaleneacetic acid in soybean plants. Plant Growth Regul 80:303–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-016-0167-x
Xue C, Guan SC, Chen JQ, Wen CJ, Cai JF, Chen X (2020) Genome wide identification and functional characterization of strawberry pectin methylesterases related to fruit softening. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2225-9
Yan S, Che G, Ding L, Chen Z, Liu X, Wang H, Zhao W, Kang N, Zhao J, Tesfamichael K, Wang Q, Zhang X (2016) Different cucumber CsYUC genes regulate response to abiotic stresses and flower development. Sci Rep 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20760
Yan L, Riaz M, Wu X, Du C, Liu Y, Jiang C (2018) Ameliorative effects of boron on aluminum induced variations of cell wall cellulose and pectin components in trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliate (L.) Raf.) rootstock. Environ 240:764–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.022
Zhang Y, Li Y, Hassan MJ, Li Z, Peng Y (2020) Indole-3-acetic acid improves drought tolerance of white clover via activating auxin, abscisic acid and jasmonic acid related genes and inhibiting senescence genes. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.2.16687/v3
Zhao J, Lai H, Bi C, Zhao M, Liu Y, Li X, Yang D (2022) Effects of paclobutrazol application on plant architecture, lodging resistance, photosynthetic characteristics, and peanut yield at different single-seed precise sowing densities. Crop J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2022.05.012
Zheng M, Chen J, Shi Y, Li Y, Yin Y, Yang D, Li Y (2017) Manipulation of lignin metabolism by plant densities and its relationship with lodging resistance in wheat. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41805
Acknowledgements
We thank Kastamonu and Çukurova University Central Research Laboratory and Dr. Fatih BULUT for SEM images and thank METU Central Laboratory for arabinose determination.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BSD designed the research. UA, FNK, HC, BSD performed the experiments. BSD wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ayvaci, U., Koc, F.N., Cetinkaya, H. et al. Treatment with auxin and paclobutrazol mediates ROS regulation, antioxidant defence system and cell wall response in salt treated soybean. Braz. J. Bot (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-023-00922-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-023-00922-8