Abstract
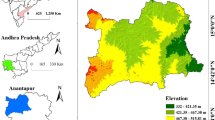
The Kabul basin is a plateau situated in the east-central part of Afghanistan, covering its capital. Groundwater has a vital role in drinking purposes and agricultural activities in the basin. Accordingly, to fulfill the drinking water and irrigation requirements and address sustainable water resources management for future development, discovering the groundwater recharge potential zones (GWRPZs) is essential. An attempt was undertaken to delineate the GWRPZs combined with the application of remote sensing (RS), geographic information system (GIS) integrated with analytical hierarchy process (AHP). Various influential variables, including geology, geomorphology, soil, lineament and drainage density, precipitation, land use and land cover, slope, elevation, and water depth, were utilized to produce different thematic maps. The raster formats of different thematic features were prepared in the ArcGIS environment. A statistical analysis was done based on the AHP methodology to determine the weights and ratings of various themes. Based on the results, eventually, five categories of the GWRPZs have been recognized. Very poor (8 km2, less than 1%), poor (187 km2, 7%), moderate (610 km2, 23%), good (1084 km2, 42%), and very good (715 km2, 27%). The validation of outcomes was done with the utilization of water level records. The kappa coefficient (0.81), and overall accuracy (88.57%) indicate a moderate to good correlation between the result outcomes and the well’s water level records. Results offer further insights. The GWRPZs map can be utilized by local authorities to develop sustainable water resources management and artificially recharge groundwater.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aawar T, Khare D, Singh L (2019) Identification of the trend in precipitation and temperature over the Kabul River sub-basin : a case study of Afghanistan. Model Earth Syst Environ 5:1377–1394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00597-9
Abijith D, Saravanan S, Singh L et al (2020) GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for identification of potential groundwater recharge zones - a case study from Ponnaniyaru watershed, Tamil Nadu, India. HydroResearch 3:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2020.02.002
Abuzied SM, Alrefaee HA (2017) Map** of groundwater prospective zones integrating remote sensing, geographic information systems and geophysical techniques in El-Qaà Plain area, Egypt. Hydrogeol J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1603-3
Achu AL, Reghunath R, Thomas J (2020a) Map** of groundwater recharge potential zones and identification of suitable site-specific recharge mechanisms in a tropical river basin. Earth Syst Environ 4:131–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-019-00138-5
Achu AL, Thomas J, Reghunath R (2020b) Multi-criteria decision analysis for delineation of groundwater potential zones in a tropical river basin using remote sensing, GIS and analytical hierarchy process (AHP). Groundw Sustain Dev 10:100365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100365
Ahmadzai H, Omuto C (2019) Afghanistan soil catalogue. FAO, Kabul
Ahsan S, Bokhari A, Ahmad B et al (2018) Future climate change projections of the Kabul River basin using a multi-model ensemble of high-resolution statistically downscaled data. Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-018-0061-y
Aich V, Akhundzadah NA, Knuerr A et al (2017) Climate change in Afghanistan deduced from reanalysis and coordinated regional climate downscaling experiment (CORDEX) - South Asia simulations. Climate. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5020038
Akinlalu AA, Adegbuyiro A, Adiat KAN et al (2017) Application of multi-criteria decision analysis in prediction of groundwater resources potential : a case of Oke-Ana, Ilesa Area Southwestern, Nigeria. NRIAG J Astron Geophys 6:184–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrjag.2017.03.001
Al-Abadi AM, Pourghasemi HR, Shahid S, Ghalib HB (2016) Spatial map** of groundwater potential using entropy weighted linear aggregate novel approach and GIS. Arab J Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2374-1
Arnous MO (2016) Groundwater potentiality map** of hard-rock terrain in arid regions using geospatial modelling : example from Wadi Feiran. Hydrogeol J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1417-8
Banks D (2002) Guidelines for sustainable use of groundwater in Afghanistan
Bohannon RG, Turner KJ (2005) Department of the interior (U.S.). In: USGS. http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2005
Broshears RE, Akbari MA, Chornack MP et al (2005) Inventory of ground-water resources in the Kabul Basin, Afghanistan. USGS
Chowdhury A, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2010) Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Environ Earth Sci 1209–1222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0110-9
CIA (2020) The World Fact Book. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/af.html. Accessed 30 May 2020
City Mayors (2020) Largest cities in the world and their mayors – 1 to 150. http://www.citymayors.com/statistics/largest-cities-mayors-1.html. Accessed 1 Sep 2020
DACAAR (2011) National groundwater monitoring wells network in Afghanistan. DACAAR, Kabul
Dadgar MA, Zeaieanfirouzabadi P, Dashti M, Porhemmat R (2017) Extracting of prospective groundwater potential zones using remote sensing data, GIS, and a probabilistic approach in Bojnourd basin, NE of Iran. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2910-7
Etikala B, Golla V, Li P, Renati S (2019) Deciphering groundwater potential zones using MIF technique and GIS: a study from Tirupati area, Chittoor District, Andhra Pradesh, India. HydroResearch 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.04.001
Foody GM (2020) Explaining the unsuitability of the kappa coefficient in the assessment and comparison of the accuracy of thematic maps obtained by image classification. Remote Sens Environ 239:111630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111630
Haritash AK, Aggarwal A, Soni J et al (2018) Assessment of fluoride in groundwater and urine, and prevalence of fluorosis among school children in Haryana, India. Appl Water Sci 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0691-0
Houben G, Niard N, Tünnermeier T, Himmelsbach T (2009) Hydrogeology of the Kabul Basin (Afghanistan), part I: aquifers and hydrology. Hydrogeol J 17:665–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0377-z
Jawadi HA, Sagin J, Snow DD (2020) A detailed assessment of groundwater quality in future development. Water 1–19
Jhariya DC, Kumar T, Gobinath M et al (2016) Assessment of groundwater potential zone using remote sensing, GIS and multi criteria decision analysis techniques. J Geol Soc India 88:481–492
Kanakiya RS, Singh S, Sharma J (2014) Determining the water quality index of an urban water body Dal Lake, Kashmir, India. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 8:64–71. https://doi.org/10.9790/2402-081236471
KMARP (2017) Kabul managed aquifer recharge project preparation. In: KMARP. https://kmarp.com/home. Accessed 2 May 2020
Kolandhavel P, Ramamoorthy S (2019) Investigation of groundwater potential zones in NandiAru Sub Basin, Tamilnadu, India — an integrated geophysical and geoinformatics approach. Arab J Geosci
Kumar A, Pandey AC (2016) Geoinformatics based groundwater potential assessment in hard rock terrain of Ranchi urban environment, Jharkhand state (India) using MCDM-AHP techniques. Groundw Sustain Dev 2–3:27–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2016.05.001
Kundzewicz ZW, Döll P (2009) Will groundwater ease freshwater stress under climate change ? Hydrol Sci J. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.54.4.665
Luo D, Wen X, Zhang H et al (2020) An improved FAHP based methodology for groundwater potential zones in Longchuan River basin, Yunnan Province, China. Earth Sci Informatics 13:847–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00469-2
Machiwal D, Jha MK, Mal BC (2011) Assessment of groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of India using remote sensing, GIS and MCDM techniques. Water Resour Manag 25:1359–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9749-y
Mack TJ, Akbari MA, Ashoor MH et al (2009) Conceptual model of water resources in the Kabul Basin, Afghanistan. USGS
Mack TJ, Chornack MP, Coplen TB et al (2010) Availability of water in the Kabul Basin, Afghanistan. USGS
Mack TJ, Chornack MP, Taher MR (2013) Groundwater-level trends and implications for sustainable water use in the Kabul Basin, Afghanistan. Environ Syst Decis 33:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-013-9455-4
Mack TJ, Chornack MP, Verstraeten IM (2014) Chapter 11 sustainability of water supply at military installations, Kabul Basin, Afghanistan. pp 199–226
Maheswaran G, Geetha Selvarani A, Elangovan K (2016) Groundwater resource exploration in Salem district, Tamil Nadu using GIS and remote sensing. J Earth Syst Sci 125:311–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0659-0
Manap MA, Nampak H, Pradhan B et al (2014) Application of probabilistic-based frequency ratio model in groundwater potential map** using remote sensing data and GIS. Arab J Geosci 711–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0795-z
Martin SL, Hayes DB, Kendall AD, Hyndman DW (2017) The land-use legacy effect: towards a mechanistic understanding of time-lagged water quality responses to land use/cover. Sci Total Environ 579:1794–1803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.158
Mpofu M, Madi K, Gwavava O (2020) Groundwater for sustainable development remote sensing, geological, and geophysical investigation in the area of Ndlambe municipality, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa : implications for groundwater potential. Groundw Sustain Dev 11:100431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100431
Muniraj K, Jesudhas CJ, Chinnasamy A (2020) Delineating the groundwater potential zone in Tirunelveli Taluk, South Tamil Nadu, India, using remote sensing, geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) techniques. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect A Phys Sci 90:661–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-019-00608-5
Muralitharan J, Palanivel K (2015) Groundwater targeting using remote sensing, geographical information system and analytical hierarchy process method in hard rock aquifer system, Karur district, Tamil Nadu, India. Earth Sci Informatics 8:827–842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-015-0213-7
Noori AR, Singh SK (2021) Status of groundwater resource potential and its quality at Kabul, Afghanistan : a review. Environ Earth Sci 80:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09954-3
NSIA (2020) Estimated Population of Afghanistan 2020–21. Kabul, Afghanistan
Pell Frischmann (2012) Afghanistan resource corridor development: water strategy final Kabul River basin Report Version 4.0
Pinto D, Shrestha S, Babel MS, Ninsawat S (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in the Comoro watershed, Timor Leste using GIS, remote sensing and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) technique. Appl Water Sci 7:503–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0270-6
Qureshi AS (2002) Water resources management in Afghanistan. International Water Management Institute
Saffi MH (2007) Ground water resources at risk in Afghanistan. DACAAR
Selvam S, Dar FA, Magesh NS et al (2016) Application of remote sensing and GIS for delineating groundwater recharge potential zones of Kovilpatti Municipality, Tamil Nadu using IF technique. Earth Sci Informatics 9:137–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-015-0242-2
Siddi Raju R, Sudarsana Raju G, Rajasekhar M (2019) Identification of groundwater potential zones in Mandavi River basin, Andhra Pradesh, India using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. HydroResearch 2:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.09.001
Singh SK, Deepika NA (2017) Assessment of water quality parameters of Bhalswa Lake in New Delhi. Int J Environ Eng 9:52. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijee.2017.10008926
Taher MR, Chornack MP, Mack TJ (2013) Groundwater levels in the Kabul Basin, Afghanistan,2004–2013. USGS
Thapa R, Gupta S, Guin S, Kaur H (2017) Assessment of groundwater potential zones using multi-influencing factor (MIF) and GIS: a case study from Birbhum district, West Bengal. Appl Water Sci 7:4117–4131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0571-z
Tünnermeier T, Houben DG (2005) Hydrogeology of the Kabul Basin part I : geology, aquifer characteristics, climate and hydrography. BGR
Uhl WV, Tahiri MQ (2003) An overview of groundwater resources and challenges. Vincent W. Uhl Uhl, Baron, Rana Associates, Inc., Washington Crossing, PA, USA
Wikipedia contributors (2020a) Kabul. In: Wikipedia, Free Encycl. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Kabul&oldid=976039159. Accessed 31 Aug 2020
Wikipedia contributors (2020b) Analytic hierarchy process. In: Wikipedia, Free Encycl. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Analytic_hierarchy_process&oldid=978488631. Accessed 22 Sep 2020
Zaryab A, Noori AR, Wegerich K, Kløve B (2017) Assessment of water quality and quantity trends in Kabul aquifers with an outline for future drinking water supplies. Cent Asian J Water Res 3:3–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.K., Noori, A.R. Delineation of groundwater recharge potential zones for its sustainable development utilizing GIS approach in Kabul basin, Afghanistan. Arab J Geosci 15, 213 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09410-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09410-3