Abstract
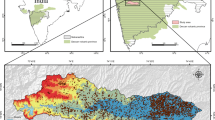
During the last three decades, remotely sensed data (both satellite images and aerial photographs) have been increasingly used in groundwater exploration and management exercises. An integrated approach has been adopted in the present study to delineate groundwater recharge potential zones using RS and GIS techniques. IRS-1C satellite imageries and Survey of India toposheets are used to prepare various thematic layers viz. geology, soil, land-use, slope, lineament and drainage. These layers were then transformed in to raster data using feature to raster converter tool in ArcGIS 9.3 software. The raster maps of these factors are allocated a fixed score and weight computed from Influencing Factor (IF) technique. The weights of factors contributing to the groundwater recharge are derived using aerial photos, geology maps, a land use database, and field verification. Subjective weights are assigned to the respective thematic layers and overlaid in GIS platform for the identification of potential groundwater recharge zones within the study area. Then these potential zones were categories as ‘high’, ‘moderate’, ‘low’, ‘poor’. The resulted map shows that 19 % of the area has highest recharge potential, mainly confined to buried pediplain, agriculture land-use and river terraces (considerable amount of precipitated water percolates into subsurface), 28 % of the area has moderate groundwater recharge potentiality and rest of the area has low to poor recharge potentiality. The residual hills and linear ridges with steep slopes are not suitable for artificial recharge sites. Finally, 13 % of total average annual precipitated water (840 mm) percolates downward and ultimately contributes to recharge the aquifers in the Kovilpatti Municipality area. The paper is an attempt to suggest for maintaining the proper balance between the groundwater quantity and its exploitation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adham MI, Jahan CS, Mazumder QH, Hossain MMA, Al-mamunul H (2010) Study on groundwater recharge potentiality of Barind Tract, Rajshahi district, Bangladesh using GIS and remote sensing technique. J Geol Soc India 75:432–438
Antony Ravindran A, Selvam S (2014) Coastal disaster damage and neotectonic subsidence study using 2D ERI technique in Dhanushkodi, Rameshwaram island, Tamilnadu, India. Middle-East J Sci Res 19(8):1117–1122
Bagyaraj M, Ramkumar T, Venkatramanan S, Gurugnanam B (2012) Application of remote sensing and GIS analysis for identifying groundwater potential zone in parts of Kodaikanal Taluk, South India. Front Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s11707-012-0347-6
Balasubramanaian A, Thirugnana RS, Chellaswamy R, Radhakrishnan V (1993) Numerical modeling for prediction and control of saltwater enchroment in the coastal aquifers of Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu (21), Tech. Report.
Chenini I, Benmammou A, Elmay M (2010) Groundwater recharge zone map** using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis: a case study in central Tunisia (Maknassy Basin). International Journal of Water Resources Management 24:921–939
Greenbaum D (1985) Review of remote sensing applications to groundwater exploration in basement and regolith. Br Geol Surv Rep OD 85:36
Gumma MK, Pavelic P (2012) Map** of groundwater potential zones across Ghana using remote sensing, geographic information systems, and spatial modeling. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2810-y
Gustavsson M, Kolstrup E, Seijmonsbergen AC (2006) A new symbol and GIS based detailed geomorphological map** system: renewal of a scientific discipline for understanding landscape development. Geomorphology 77:90–111
Jasrotia AS, Kumar R, Saraf AK (2007) Delineation of groundwater recharge sites using integrated remote sensing and GIS in Jammu district, India. Int J Remote Sens 28:5019–5036
Kamal ASMM, Midorikawa S (2004) GIS-based geomorphological map** using remote sensing data and supplementary geoinformation: a case study of the Dhaka city area Bangladesh. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 6:111–125
Khawlie M (1986) Land-use planning for the development of the disrupted urbancenter: Beirut Lebanon. International Journal of Dev Technology 4:267–281
Koch M, Mather PM (1997) Lineament map** for groundwater resource assessment: a comparison of digital synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery and stereoscopic large format camera (LFC) photographs in the Red Sea hills, Sudan. Int J Remote Sens 18:1465–1482
Kumar PKD, Gopinath G, Seralathan P (2007) Application of remote sensing and GIS for the demarcation of groundwater potential zones of a river basin in Kerala, southwest coast of India. Int J Remote Sens 28:5583–5601
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3(2):189–196
Murthy KSR (2000) Groundwater potential in a semiarid region of Andhra Pradesh: a geographical information system approach. Int J Remote Sens 21:1867–1884
Nag SK (2005) Application of lineament density and hydrogeomorphology to delineate groundwater potential zones of Baghmundi block in Purulia district, West Bengal. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 33:522–529
Rodell M, Velicogna I, Famiglietti JS (2009) Satellite- based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 460:999–1003
Saraf AK, Choudhary ER (1998) Integrated remote sensing and GIS for ground water exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. Int J Remote Sens 19:1825–1841
Selvam S (2012) Use of remote sensing and GIS techniques for land use and land cover map** of Tuticorin coast, Tamilnadu. Univers J Environ Res Technol 2(4):233–241
Selvam S (2015a) Irrigational feasibility of groundwater and evaluation of hydrochemistry facies in the SIPCOT industrial area, south Tamilnadu, India: a GIS approach. Water Qual Expo Health 7:265–284. doi:10.1007/s12403-014-0146-2
Selvam S (2015b) A preliminary investigation of lithogenic and anthropogenic influence over fluoride ion chemistry in the groundwater of the southern coastal city, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 187:106. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4326-8
Selvam S, Sivasubramanian P (2012) Groundwater potential zone identification using geoelectrical survey: a case study from Medak district, Andhra Pradesh, India. International Journal of Geomatics Geoscience 3:55–62
Selvam S, Iruthaya Jeba Dhana Mala R, Muthukakshmi V (2013a) A hydrochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality index in Thoothukudi district, Tamilnadu, south India. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Applications 2(3):25–37
Selvam S, Manimaran G, Sivasubramanian P (2013b) Hydrochemical characteristics and GIS-based assessment of groundwater quality in the coastal aquifers of Tuticorin corporation, Tamilnadu, India. Appl Water Sci 3:145–159
Selvam S, Manimaran G, Sivasubramanian P (2013c) Cumulative effects of septic system disposal and evolution of nitrate contamination impact on coastal groundwater in Tuticorin, south Tamilnadu, India. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 4(4):1207–1218
Selvam S, Manimaran G, Sivasubramanian P, Balasubramanian N, Seshunarayana T (2014a) GIS-based evaluation of water quality index of groundwater resources around Tuticorin coastal city, south India. Environ Earth Sci 71:2847–2867
Selvam S, Antony Ravindaran A, Rajamanickam M, Sridharan M (2014b) Microbial contamination in the sediments and groundwater of Tuticorin corporation, south India using GIS. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(4):337–340
Selvam S, Manimaran G, Sivasubramanian P, Seshunarayana T (2014c) Geoenvironmental resource assessment using remote sensing and GIS: a case study from southern coastal region. Res J Recent Sci 3(1):108–115
Selvam S, Magesh NS, Sivasubramanian P, Prince Soundranayagam J, Manimaran G, Seshunarayana T (2014d) Deciphering of groundwater potential zones in Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J Geol Soci India 84:597–608
Selvam S, Magesh NS, Chidambaram S, Rajamanickam M, Sashikkumar MC (2015a) A GIS based identification of groundwater recharge potential zones using RS and IF technique: a case study in Ottapidaram taluk, Tuticorin district Tamil Nadu. Environ Earth Sci 73:3785–3799
Selvam S, Venkatramanan S, Singaraja C (2015b) A GIS-based assessment of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination in Tuticorin corporation, Tamilnadu India. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-015-1968-3
Shaban A (2003) Studying the hydrogeology of Occidental Lebanon: utilization of remote sensing. Etude de phydrogeologie du Liban occidental: utilization of de la deledection. These de doctorates, University Bordeaux 1, 202p.
Shaban A, Khawlie M, Bou Kheir R, Abdallah C (2001) Assessment of road instability along a typical mountainous road using GIS and aerial photos, Lebanon- eastern Mediterranean. Bull Eng Geol Environ 60:93–101
Shaban A, Khawlie M, Abdallah C (2006) Use of remote sensing and GIS to determine recharge potential zone: the case of Occidental Lebanon. Hydrogeol J 14:433–443
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Srinivasamoorthy K, Anandhan P, Selvam S (2015a) A study on assessment of credible sources of heavy metal pollution vulnerability in groundwater of Thoothukudi districts, Tamilnadu India. Water Qual Expo Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-015-0162-x
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Jacob N, Selvam S, Johnsonbabu G, Anandhan P (2015b) Radon levels in groundwater in the Tuticorin district of Tamil Nadu South India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-015-4312-1
Singh AK, Parkash B, Choudhury PR (2007) Integrated use of SRM, Landsat ETM + data and 3D perspective views to identify the tectonic geomorphology of Dehradun valley, India. Int J Remote Sens 28:2430–2414
Singh CK, Shashtri S, Singh A, Mukherjee S (2011) Quantitative modeling of groundwater in Satluj River basin of Rupnagar district of Punjab using remote sensing and geographic information system. Environ Earth Sci 62:871–881
Soundaranayagam JP, Sivasubramanian P, Chandrasekar N, Durairaj KSP (2011) An analysis of land use pattern in the industrial development city using high resolution satellite imagery. J Geor Sci 21:79–88
Srivastava PK, Bhattacharya AK (2006) Groundwater assessment through an integrated approach using remote sensing, using remote sensing, GIS and resistivity techniques: a case study froma hard rock terrain. Int J Remote Sens 27:4599–4620
UN (1967) Hydrogeologic map of Lebanon. Carte hydrogelogique du Liban au 1/100000me, UN, Beyrouth, Liban.
Venkatramanan S, Chung SY, Ramkumar T, Selvam S (2015) Environmental monitoring and assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments at Coleroon River Estuary in Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–16. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4709-x
Yeh HF, Lee CH, Hsu KC, Chang PH (2009) GIS for the assessment of the groundwater recharge potential zone. Environ Geol 58:185–195
Acknowledgments
Dr.S.Selvam gratefully acknowledges the financial support by University Grant Commission, Government of India, New Delhi through project No.F MRP-5614/15(SERO/UGC). Authors are also grateful to Shri A.P.C.V.Chockalingam, Secretary and Dr.C.Veerabahu, Principal, V.O.C College, Tuticorin for his support to carry out this study. The Editor-in-Chief Dr. Hassan A. Babaie and the anonymous reviewers had suggested their constructive comments to improve the paper. The authors are also thankful to them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. A. Babaie
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvam, S., Dar, F.A., Magesh, N.S. et al. Application of remote sensing and GIS for delineating groundwater recharge potential zones of Kovilpatti Municipality, Tamil Nadu using IF technique. Earth Sci Inform 9, 137–150 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-015-0242-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-015-0242-2