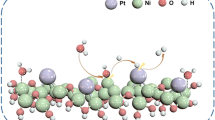
Abstract
Single-atomic Fe-N4 is the well-acknowledged active site in iron-nitrogen-carbon (Fe-N-C) material for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The adjusting of the electronic distribution of Fe-N4 is promising for further enhancing the performance of the Fe-N-C catalyst. Herein, a phosphorus (P)-doped Fe-N-C catalyst with penta-coordinated single atom sites (FeNPC) is reported for efficient oxygen reduction. Fe K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) verifies the coordination environment of single Fe atom, while density functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal that the penta-coordination and neighboring doped P atoms can simultaneously change the electronic distribution of Fe-N4 and its adsorption strength of key intermediates, reducing the reaction-free energy of the potential-limiting step. Electrochemical tests validate the remarkable intrinsic ORR activity of FeNPC in alkaline media (a half-wave potential (E1/2) of 0.904 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) and limited current density (JL) of 6.23 mA·cm−2) and an enhanced ORR performance in neutral (E1/2 = 0.751 V, JL = 5.27 mA·cm−2) and acidic media (E1/2 = 0.735 V, JL = 5.82 mA·cm−2) with excellent stability, highlighting the benefits of optimizing the local environment of single-atomic Fe-N4.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ager, J. W.; Lapkin, A. A. Chemical storage of renewable energy. Science 2018, 360, 707–708.
Chong, L.; Wen, J. G.; Kubal, J.; Sen, F. G.; Zou, J. X.; Greeley, J.; Chan, M.; Barkholtz, H.; Ding, W. J.; Liu, D. J. Ultralow-loading platinum-cobalt fuel cell catalysts derived from imidazolate frameworks. Science 2018, 362, 1276–1281.
Fu, J.; Liang, R. L.; Liu, G. H.; Yu, A. P.; Bai, Z. Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z. W. Recent progress in electrically rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805230.
Shui, J. L.; Wang, M.; Du, F.; Dai, L. M. N-doped carbon nanomaterials are durable catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in acidic fuel cells. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400129.
Yang, X. D.; Zheng, Y. P.; Yang, J.; Shi, W.; Zhong, J. H.; Zhang, C. K.; Zhang, X.; Hong, Y. H.; Peng, X. X.; Zhou, Z. Y. et al. Modeling Fe/N/C catalysts in monolayer graphene. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 139–145.
Bu, L. Z.; Zhang, N.; Guo, S. J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Yao, J. L.; Wu, T.; Lu, G.; Ma, J. Y.; Su, D. et al. Biaxially strained PtPb/Pt core/shell nanoplate boosts oxygen reduction catalysis. Science 2016, 354, 1410–1414.
Wang, Y.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. A fundamental comprehension and recent progress in advanced Pt-based ORR nanocatalysts. SmartMat 2021, 2, 56–75.
Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. B.; Wang, D. S. Design concept for electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1730–1752.
Ji, S. F.; Chen, Y. J.; Wang, X. L.; Zhang, Z. D.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Chemical synthesis of single atomic site catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11900–11955.
Mun, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Han, J. W.; Lee, J. Versatile strategy for tuning ORR activity of a single Fe-N4 site by controlling electron-withdrawing/donating properties of a carbon plane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6254–6262.
Dong, J. C.; Zhang, X. G.; Briega-Martos, V.; **, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, Z. L.; Wu, D. Y.; Feliu, J. M.; Williams, C. T. et al. In situ Raman spectroscopic evidence for oxygen reduction reaction intermediates at platinum single-crystal surfaces. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 60–67.
Shang, L.; Yu, H. J.; Huang, X.; Bian, T.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. F.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C. H.; Zhang, T. R. Well-dispersed ZIF-derived Co, N-Co-doped carbon nanoframes through mesoporous-silica-protected calcination as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1668–1674.
Tobisu, M.; Yamakawa, K.; Shimasaki, T.; Chatani, N. Nickel-catalyzed reductive cleavage of aryl—oxygen bonds in alkoxy- and pivaloxyarenes using hydrosilanes as a mild reducing agent. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2946–2948.
Li, L. B.; Huang, B. Y.; Tang, X. N.; Hong, Y. S.; Zhai, W. J.; Hu, T.; Yuan, K.; Chen, Y. W. Recent developments of microenvironment engineering of single-atom catalysts for oxygen reduction toward desired activity and selectivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103857.
Kumar, K.; Gairola, P.; Lions, M.; Ranjbar-Sahraie, N.; Mermoux, M.; Dubau, L.; Zitolo, A.; Jaouen, F.; Maillard, F. Physical and chemical considerations for improving catalytic activity and stability of non-precious-metal oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 11264–11276.
Zhang, H. G.; Chung, H. T.; Cullen, D. A.; Wagner, S.; Kramm, U. I.; More, K. L.; Zelenay, P.; Wu, G. High-performance fuel cell cathodes exclusively containing atomically dispersed iron active sites. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2548–2558.
Shao, M. H.; Chang, Q. W.; Dodelet, J. P.; Chenitz, R. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3594–3657.
Cui, T. T.; Wang, Y. P.; Ye, T.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z. Q.; Li, J.; Lei, Y. P.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Engineering dual single-atom sites on 2D ultrathin N-doped carbon nanosheets attaining ultra-low-temperature zinc-air battery. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115219.
Han, A.; Wang, X. J.; Tang, K.; Zhang, Z. D.; Ye, C. L.; Kong, K. J.; Hu, H. B.; Zheng, L. R.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, C. X. et al. An adjacent atomic platinum site enables single-atom iron with high oxygen reduction reaction performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19262–19271.
Zhang, N.; Zhou, T. P.; Chen, M. L.; Feng, H.; Yuan, R. L.; Zhong, C. A.; Yan, W. S.; Tian, Y. C.; Wu, X. J.; Chu, W. S. et al. High-purity pyrrole-type FeN4 sites as a superior oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 111–118.
Chen, Y. J.; Ji, S. F.; Zhao, S.; Chen, W. X.; Dong, J. C.; Cheong, W. C.; Shen, R. A.; Wen, X. D.; Zheng, L. R.; Rykov, A. I. et al. Enhanced oxygen reduction with single-atomic-site iron catalysts for a zinc-air battery and hydrogen-air fuel cell. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5422.
Jiang, R.; Li, L.; Sheng, T.; Hu, G. F.; Chen, Y. G.; Wang, L. Y. Edge-site engineering of atomically dispersed Fe-N4 by selective C—N bond cleavage for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction activities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11594–11598.
Zhang, H. G.; Hwang, S.; Wang, M. Y.; Feng, Z. X.; Karakalos, S.; Luo, L. L.; Qiao, Z.; **e, X. H.; Wang, C. M.; Su, D. et al. Single atomic iron catalysts for oxygen reduction in acidic media: Particle size control and thermal activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14143–14149.
Wang, D. N.; Wu, Y. L.; Li, Z. G.; Pan, H.; Wang, Y. Q.; Yang, M. S.; Zhang, G. X. N-doped carbon nanoflower-supported Fe-N4 motifs for high-efficiency reduction of oxygen in both alkaline and acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130401.
Wu, Y. L.; Liang, G. F.; Chen, D.; Li, Z. L.; Xu, J. C.; Huang, G. J.; Yang, M. Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; **e, F. Y. et al. Fe-N4 doped carbon nanotube cathode catalyst for PEM fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48923–48933.
Yang, Z. K.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M. Z.; Li, Z. J.; Chen, W. X.; Wei, W. C.; Yuan, T. W.; Qu, Y. T.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C. M. et al. Boosting oxygen reduction catalysis with Fe-N4 sites decorated porous carbons toward fuel cells. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2158–2163.
Shang, H. S.; Sun, W. M.; Sui, R.; Pei, J. J.; Zheng, L. R.; Dong, J. C.; Jiang, Z. L.; Zhou, D. N.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Chen, W. X. et al. Engineering isolated Mn—N2C2 atomic interface sites for efficient bifunctional oxygen reduction and evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 5443–5450.
Wu, G.; Zelenay, P. Nanostructured nonprecious metal catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1878–1889.
Xu, J.; Lai, S. H.; Qi, D. F.; Hu, M.; Peng, X. Y.; Liu, Y. F.; Liu, W.; Hu, G. Z.; Xu, H.; Li, F. et al. Atomic Fe-Zn dual-metal sites for high-efficiency pH-universal oxygen reduction catalysis. Nano Res. 2020, 14, 1374–1381.
Zagal, J. H.; Koper, M. T. M. Reactivity descriptors for the activity of molecular MN4 catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14510–14521.
Peng, L. S.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y. Q.; Qian, F. R.; Wang, Q.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Shang, L.; Zhang, T. R.; Waterhouse, G. I. N. Mesopore-rich Fe-N-C catalyst with FeN4-O-NC single-atom sites delivers remarkable oxygen reduction reaction performance in alkaline media. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202544.
Li, R. Z.; Wang, D. S. Understanding the structure—performance relationship of active sites at atomic scale. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6888–6923.
Li, L. B.; Huang, S. H.; Cao, R.; Yuan, K.; Lu, C. B.; Huang, B. Y.; Tang, X. N.; Hu, T.; Zhuang, X. D.; Chen, Y. W. Optimizing microenvironment of asymmetric N, S-coordinated single-atom Fe via axial fifth coordination toward efficient oxygen electroreduction. Small 2022, 18, 2105387.
Fu, X. G.; Li, N.; Ren, B. H.; Jiang, G. P.; Liu, Y. R.; Hassan, F. M.; Su, D.; Zhu, J. B.; Yang, L.; Bai, Z. Y. et al. Tailoring FeN4 sites with edge enrichment for boosted oxygen reduction performance in proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803737.
Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Q.; Sun, F. F.; Chen, G. B.; Wang, J.; Peng, L. S.; Chen, W. T.; Shang, L.; Zhao, J. Q.; Sun-Waterhouse, D. et al. Molten NaCl-assisted synthesis of porous Fe-N-C electrocatalysts with a high density of catalytically accessible FeN4 active sites and outstanding oxygen reduction reaction performance. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100219.
Wang, Y.; Tang, Y. J.; Zhou, K. Self-adjusting activity induced by intrinsic reaction intermediate in Fe-N-C single-atom catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14115–14119.
Li, J. K.; Ghoshal, S.; Liang, W. T.; Sougrati, M. T.; Jaouen, F.; Halevi, B.; McKinney, S.; McCool, G.; Ma, C. R.; Yuan, X. X. et al. Structural and mechanistic basis for the high activity of Fe-N-C catalysts toward oxygen reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2418–2432.
Wang, F. T.; Zhou, Y. P.; Lin, S.; Yang, L. J.; Hu, Z.; **e, D. Q. Axial ligand effect on the stability of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts for acidic oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105128.
Chen, Z. Y.; Niu, H.; Ding, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, P. H.; Lu, Y. H.; Lu, Y. R.; Zuo, W. B.; Han, L.; Guo, Y. Z. et al. Unraveling the origin of sulfur-doped Fe-N-C single-atom catalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction activity: Effect of iron spin-state tuning. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25404–25410.
Yuan, K.; Sfaelou, S.; Qiu, M.; Lützenkirchen-Hecht, D.; Zhuang, X. D.; Chen, Y. W.; Yuan, C.; Feng, X. L.; Scherf, U. Synergetic contribution of boron and Fe—Nx species in porous carbons toward efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 252–260.
Li, Q. H.; Chen, W. X.; **ao, H.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L. R.; Zheng, X. S.; Yan, W. S.; Cheong, W. C.; Shen, R. A. et al. Fe isolated single atoms on S, N codoped carbon by copolymer pyrolysis strategy for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800588.
Qin, Q.; Jang, H.; Li, P.; Yuan, B.; Liu, X. E.; Cho, J. A tannic acid-derived N-, P-codoped carbon-supported iron-based nanocomposite as an advanced trifunctional electrocatalyst for the overall water splitting cells and zinc-air batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803312.
Chen, P. Z.; Zhou, T. P.; **ng, L. L.; Xu, K.; Tong, Y.; **e, H.; Zhang, L. D.; Yan, W. S.; Chu, W. S.; Wu, C. Z. et al. Atomically dispersed iron—nitrogen species as electrocatalysts for bifunctional oxygen evolution and reduction reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 610–614.
Yang, D. S.; Bhattacharjya, D.; Inamdar, S.; Park, J.; Yu, J. S. Phosphorus-doped ordered mesoporous carbons with different lengths as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16127–16130.
Zhao, Z. H.; Li, M. T.; Zhang, L. P.; Dai, L. M.; **a, Z. H. Design principles for heteroatom-doped carbon nanomaterials as highly efficient catalysts for fuel cells and metal-air batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6834–6840.
Gao, Y.; Kong, D. B.; Liang, J. X.; Han, D. L.; Wang, B.; Yang, Q. H.; Zhi, L. J. Inside-out dual-do** effects on tubular catalysts: Structural and chemical variation for advanced oxygen reduction performance. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 361–367.
Sun, H.; Wang, M. F.; Du, X. C.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, S. S.; Qian, T.; Yan, Y. C.; Liu, C.; Liao, M.; Zhang, Q. H. et al. Modulating the d-band center of boron doped single-atom sites to boost the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20952–20957.
**a, D. S.; Yang, X.; **e, L.; Wei, Y. P.; Jiang, W. L.; Dou, M.; Li, X. N.; Li, J.; Gan, L.; Kang, F. Y. Direct growth of carbon nanotubes doped with single atomic Fe-N4 active sites and neighboring graphitic nitrogen for efficient and stable oxygen reduction electrocatalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1906174.
Yin, H. B.; Yuan, P. F.; Lu, B. A.; **a, H. C.; Guo, K.; Yang, G. G.; Qu, G.; Xue, D. P.; Hu, Y. F.; Cheng, J. Q. et al. Phosphorus-driven electron delocalization on edge-type FeN4 active sites for oxygen reduction in acid medium. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12754–12762.
Cheng, W. Z.; Yuan, P. F.; Lv, Z. R.; Guo, Y. Y.; Qiao, Y. Y.; Xue, X. Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, W. L.; Wang, K. X.; Xu, Q. et al. Boosting defective carbon by anchoring well-defined atomically dispersed metal-N4 sites for ORR, OER, and Zn-air batteries. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2020, 260, 118198.
Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186.
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868.
Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the dam** function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465.
Mathew, K.; Sundararaman, R.; Letchworth-Weaver, K.; Arias, T. A.; Hennig, R. G. Implicit solvation model for density-functional study of nanocrystal surfaces and reaction pathways. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 084106.
Mathew, K.; Kolluru, V. S. C.; Mula, S.; Steinmann, S. N.; Hennig, R. G. Implicit self-consistent electrolyte model in plane-wave density-functional theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 234101.
Nørskov, J. K.; Rossmeisl, J.; Logadottir, A.; Lindqvist, L.; Kitchin, J. R.; Bligaard, T.; Jónsson, H. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17886–17892.
Wei, X. Q.; Luo, X.; Wang, H. J.; Gu, W. L.; Cai, W. W.; Lin, Y. H.; Zhu, C. Z. Highly-defective Fe-N-C catalysts towards pH-universal oxygen reduction reaction. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2020, 263, 118347.
Yuan, K.; Lutzenkirchen-Hecht, D.; Li, L. B.; Shuai, L.; Li, Y. Z.; Cao, R.; Qiu, M.; Zhuang, X. D.; Leung, M. K. H.; Chen, Y. W. et al. Boosting oxygen reduction of single iron active sites via geometric and electronic engineering: Nitrogen and phosphorus dual coordination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2404–2412.
Han, J. X.; Bao, H. L.; Wang, J. Q.; Zheng, L. R.; Sun, S. R.; Wang, Z. L.; Sun, C. W. 3D N-doped ordered mesoporous carbon supported single-atom Fe-N-C catalysts with superior performance for oxygen reduction reaction and zinc-air battery. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2021, 280, 119411.
Chai, G. L.; Qiu, K. P.; Qiao, M.; Titirici, M. M.; Shang, C. X.; Guo, Z. X. Active sites engineering leads to exceptional ORR and OER bifunctionality in P, N co-doped graphene frameworks. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1186–1195.
Li, C. L.; Chen, Z. Y.; Kong, A. G.; Ni, Y. Y.; Kong, F. T.; Shan, Y. K. High-rate oxygen electroreduction over metal-free graphene foams embedding P—N coupled moieties in acidic media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4145–4151.
Zhu, X. F.; Zhang, D. T.; Chen, C. J.; Zhang, Q. R.; Liu, R. S.; **a, Z. H.; Dai, L. M.; Amal, R.; Lu, X. Y. Harnessing the interplay of Fe—Ni atom pairs embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104597.
Chen, Y. F.; Li, Z. J.; Zhu, Y. B.; Sun, D. M.; Liu, X. E.; Xu, L.; Tang, Y. W. Atomic Fe dispersed on N-doped carbon hollow nanospheres for high-efficiency electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806312.
Song, L. T.; Wu, Z. Y.; Zhou, F.; Liang, H. W.; Yu, Z. Y.; Yu, S. H. Sustainable hydrothermal carbonization synthesis of iron/nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber aerogels as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Small 2016, 12, 6398–6406.
Chen, Y. J.; Ji, S. F.; Wang, Y. G.; Dong, J. C.; Chen, W. X.; Li, Z.; Shen, R. A.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Wang, D. S. et al. Isolated single iron atoms anchored on N-doped porous carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6937–6941.
Sakaushi, K.; Eckardt, M.; Lyalin, A.; Taketsugu, T.; Behm, R. J.; Uosaki, K. Microscopic electrode processes in the four-electron oxygen reduction on highly active carbon-based electrocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8162–8176.
Zhao, M. Q.; Liu, H. R.; Zhang, H. W.; Chen, W.; Sun, H. Q.; Wang, Z. H.; Zhang, B.; Song, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C. et al. A pH-universal ORR catalyst with single-atom iron sites derived from a double-layer MOF for superior flexible quasi-solid-state rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 6455–6463.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21875285, 22171288, and 22005340), the Key Research and Development Projects of Shandong Province (No. 2019JZZY010331), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2020MB017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Wei, X., Li, X. et al. Phosphorus-doped iron-nitrogen-carbon catalyst with penta-coordinated single atom sites for efficient oxygen reduction. Nano Res. 16, 1810–1819 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4939-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4939-5