Abstract
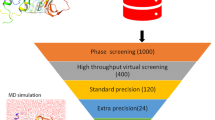
Vascular endothelial growth factor is an angiogenic that promotes the development and metastasis of tumors (VEGF). The epidermal growth factor receptor, or EGFR, controls the division, growth, and death of cells via several signaling pathways. It has been found that most of the tyrosine kinase EGFR/VEGFR-2 inhibited by drugs that the FDA has approved are so far. The main objective of the present study was to identify an efficacious and selective dual inhibitor of VEGFR-2/EGFR for the treatment of cancer. Out of the 400 ligands tested against the kinases, 12 compounds demonstrated the best docking scores through molecular docking for the two kinases. Of these, only compound SCHEMBL2435814 inhibited the kinases with the highest score values when compared to a reference, vandetanib, as a dual inhibitor of EGFR/VEGFR-2 kinases through interaction with the identified active sites pocket. Following drug-likeness score toxicity and pharmacokinetic testing, the two compounds, SCHEMBL2435814 and vandetanib, were analyzed to determine how the two kinases interacted with each other. The results of calculations of π-cation interactions, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic interactions demonstrated a strong interaction between the two kinases and SCHEMBL2435814. Eventually, molecular dynamic modeling was used to assess the stability of complexes. This demonstrated many characteristics, including RMSF, RMSD, SASA, RG, and H-bond analysis, which demonstrated that SCHEMBL2435814 with the two kinases was more stable than vandetanib over a 100ns simulation period. By suppressing EGFR/VEGFR-2, chemical SCHEMBL2435814 may be able to postpone the signaling pathway of proteins that are essential to the advancement of cancer.
Graphical Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data is available and attached.
References
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Weiderpass, E., & Soerjomataram, I. (2021). The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer, 127(16), 3029–3030. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.33587
Al-Warhi, T., Almahli, H., Maklad, R. M., Elsayed, Z. M., El Hassab, M. A., Alotaibi, O. J., ..., El-Ashrey, M. K. (2023). 1-Benzyl-5-bromo-3-hydrazonoindolin-2-ones as novel anticancer agents: Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling insights. Molecules, 28(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073203
Al-Warhi, T., Elbadawi, M. M., Bonardi, A., Nocentini, A., Al-Karmalawy, A. A., Aljaeed, N., ..., Eldehna, W. M. (2022). Design and synthesis of benzothiazole-based SLC-0111 analogues as new inhibitors for the cancer-associated carbonic anhydrase isoforms IX and XII. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 37(1), 2635–2643. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2022.2124409
Elbadawi, M. M., Eldehna, W. M., Abd El-Hafeez, A. A., Somaa, W. R., Albohy, A., Al-Rashood, S. T., ..., Abe, M. (2022). 2-Arylquinolines as novel anticancer agents with dual EGFR/FAK kinase inhibitory activity: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modelling insights. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 37(1), 349–372. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2021.2015344
Sabt, A., Eldehna, W. M., Al-Warhi, T., Alotaibi, O. J., Elaasser, M. M., Suliman, H., & Abdel-Aziz, H. A. (2020). Discovery of 3,6-disubstituted pyridazines as a novel class of anticancer agents targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 2: Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico insights. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 35(1), 1616–1630. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1806259
Eliwa, E. M., Frese, M., Halawa, A. H., Soltan, M. M., Ponomareva, L. V., Thorson, J. S., ..., Sewald, N. (2021). Metal-free domino amination-Knoevenagel condensation approach to access new coumarins as potent nanomolar inhibitors of VEGFR-2 and EGFR. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 14(4), 578–599. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2021.1981462
Amin, K. M., Barsoum, F. F., Awadallah, F. M., & Mohamed, N. E. (2016). Identification of new potent phthalazine derivatives with VEGFR-2 and EGFR kinase inhibitory activity. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 123, 191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.07.049
Boraei, A. T. A., Ashour, H. K., El Tamany, E. S. H., Abdelmoaty, N., El-Falouji, A. I., & Gomaa, M. S. (2019). Design and synthesis of new phthalazine-based derivatives as potential EGFR inhibitors for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioorganic Chemistry, 85, 293–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.12.039
Zhang, H. Q., Gong, F. H., Li, C. G., Zhang, C., Wang, Y. J., Xu, Y. G., & Sun, L. P. (2016). Design and discovery of 4-anilinoquinazoline-acylamino derivatives as EGFR and VEGFR-2 dual TK inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 109, 371–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.12.032
Dank, M., Zaluski, J., Barone, C., Valvere, V., Yalcin, S., Peschel, C., ..., Bugat, R. (2008). Randomized phase III study comparing irinotecan combined with 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid to cisplatin combined with 5-fluorouracil in chemotherapy naive patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction. Annals of Oncology, 19(8), 1450–1457. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdn166
Falchook, G. S., & Kurzrock, R. (2015). VEGF and dual-EGFR inhibition in colorectal cancer. Cell Cycle, 14(8), 1129–1130. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2015.1022071
Gaber, A. A., Bayoumi, A. H., El-Morsy, A. M., Sherbiny, F. F., Mehany, A. B. M., & Eissa, I. H. (2018). Design, synthesis and anticancer evaluation of 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives as potent EGFR(WT) and EGFR(T790M) inhibitors and apoptosis inducers. Bioorganic Chemistry, 80, 375–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.06.017
Sigismund, S., Avanzato, D., & Lanzetti, L. (2018). Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Molecular Oncology, 12(1), 3–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12155
Tabernero, J. (2007). The role of VEGF and EGFR inhibition: Implications for combining anti-VEGF and anti-EGFR agents. Molecular Cancer Research, 5(3), 203–220. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-06-0404
Folkman, J., & D’Amore, P. A. (1996). Blood vessel formation: What is its molecular basis? Cell, 87(7), 1153–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81810-3
Olsson, A.-K., Dimberg, A., Kreuger, J., & Claesson-Welsh, L. (2006). VEGF receptor signalling ? in control of vascular function. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 7(5), 359–371. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1911
Ezelarab, H. A. A., Ali, T. F. S., Abbas, S. H., Sayed, A. M., Beshr, E. A. M., & Hassan, H. A. (2023). New antiproliferative 3-substituted oxindoles inhibiting EGFR/VEGFR-2 and tubulin polymerization. Molecular Diversity. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10603-z
Shibuya, M. (2011). Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) signaling in angiogenesis: A crucial target for anti- and pro-angiogenic therapies. Genes & Cancer, 2(12), 1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911423031
Ghosh, S., Sullivan, C. A. W., Zerkowski, M. P., Molinaro, A. M., Rimm, D. L., Camp, R. L., & Chung, G. G. (2008). High levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors (VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, neuropilin-1) are associated with worse outcome in breast cancer. Human Pathology, 39(12), 1835–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2008.06.004
Modi, S. J., & Kulkarni, V. M. (2019). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR-2)/KDR inhibitors: Medicinal chemistry perspective. Medicine in Drug Discovery, 2, 100009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medidd.2019.100009
Dhuguru, J., & Skouta, R. (2020). Role of indole scaffolds as pharmacophores in the development of anti-lung cancer agents. Molecules, 25(7). Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071615
Wan, Y., Li, Y., Yan, C., Yan, M., & Tang, Z. (2019). Indole: A privileged scaffold for the design of anti-cancer agents. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 183, 111691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111691
Holmes, K., Roberts, O. L., Thomas, A. M., & Cross, M. J. (2007). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: Structure, function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition. Cellular Signalling, 19(10), 2003–2012.
Alanazi, M. M., Mahdy, H. A., Alsaif, N. A., Obaidullah, A. J., Alkahtani, H. M., Al-Mehizia, A. A., ..., Eissa, I. H. (2021). New bis ([1, 2, 4] triazolo)[4, 3-a: 3′, 4′-c] quinoxaline derivatives as VEGFR-2 inhibitors and apoptosis inducers: Design, synthesis, in silico studies, and anticancer evaluation. Bioorganic Chemistry, 112, 104949.
Eissa, I. H., Ibrahim, M. K., Metwaly, A. M., Belal, A., Mehany, A. B., Abdelhady, A. A., ..., Mahdy, H. A. (2021). Design, molecular docking, in vitro, and in vivo studies of new quinazolin-4 (3H)-ones as VEGFR-2 inhibitors with potential activity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioorganic Chemistry, 107, 104532.
El-Metwally, S. A., Abou-El-Regal, M. M., Eissa, I. H., Mehany, A. B., Mahdy, H. A., Elkady, H., ..., Elkaeed, E. B. (2021). Discovery of thieno [2, 3-d] pyrimidine-based derivatives as potent VEGFR-2 kinase inhibitors and anti-cancer agents. Bioorganic Chemistry, 112, 104947.
Hernandez-Davies, J. E., Zape, J. P., Landaw, E. M., Tan, X., Presnell, A., Griffith, D., ..., Sakamoto, K. M. (2011). The multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor linifanib (ABT-869) induces apoptosis through an Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3β-dependent pathway. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 10(6), 949–959. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-10-0904
Lang, S. A., Schachtschneider, P., Moser, C., Mori, A., Hackl, C., Gaumann, A., ..., Stoeltzing, O. (2008). Dual targeting of Raf and VEGF receptor 2 reduces growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer through direct effects on tumor cells, endothelial cells, and pericytes. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 7(11), 3509–3518. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-08-0373
**, L., Zhang, J.-Q., Liu, Z.-C., Zhang, J.-H., Yan, J.-F., **, Y., & Lin, J. (2013). Novel 5-anilinoquinazoline-8-nitro derivatives as inhibitors of VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase: Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 11(26), 4367–4378.
Ani, F. E., Ibeji, C. U., Obasi, N. L., Kelani, M. T., Ukogu, K., Tolufashe, G. F., ..., Kruger, H. G. (2021). Crystal, spectroscopic and quantum mechanics studies of Schiff bases derived from 4-nitrocinnamaldehyde. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 8151.
Oyeneyin, O., Ipinloju, N., Nathanael, O., & Akerele, D. (2021). Structural modification of ibuprofen as new NSAIDs via DFT, molecular docking and pharmacokinetics studies. International Journal of Advances in Engineering and Pure Sciences, 33(4), 614–626.
Oyeneyin, O. E., Adejoro, I. A., Obadawo, B. S., Amoko, J. S., Kayode, I. O., Akintemi, E. O., & Ipinloju, N. (2021). Investigation into the molecular properties of 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) Prop-2-en-1-one 4-phenyl Schiff base and some of its derivatives-DFT and molecular docking studies. Science Letters, 9(1), 4–11.
Oyeneyin, O. E., Obadawo, B. S., Orimoloye, S. M., Akintemi, E. O., Ipinloju, N., Asere, A. M., & Owolabi, T. O. (2021). Prediction of inhibition activity of BET bromodomain inhibitors using grid search-based extreme learning machine and molecular docking. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 18(11), 1039–1049.
Kikiowo, B., Ogunleye, A. J., Inyang, O. K., Adelakun, N. S., Omotuyi, O. I., Metibemu, D. S., ..., Ijatuyi, T. T. (2020). Flavones scaffold of Chromolaena odorata as a potential xanthine oxidase inhibitor: Induced Fit Docking and ADME studies. BioImpacts: BI, 10(4), 227.
Lionta, E., Spyrou, G., Vassilatis, D. K., & Cournia, Z. (2014). Structure-based virtual screening for drug discovery: Principles, applications and recent advances. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 14(16), 1923–1938. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026614666140929124445
Murali, M., Gowtham, H. G., Ansari, M. A., Alomary, M. N., Alghamdi, S., Almehmadi, M., ..., Amruthesh, K. N. (2022). Repositioning therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening of plant-based anti-HIV compounds as possible inhibitors against COVID-19 viral RdRp. : Current Pharmaceutical Design, 28(12), 969–980. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612828666220428120939
Anandan, S., Gowtham, H. G., Shivakumara, C. S., Thampy, A., Singh, S. B., Murali, M., ..., Glossman-Mitnik, D. (2022). Integrated approach for studying bioactive compounds from Cladosporium spp. against estrogen receptor alpha as breast cancer drug target. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 22446. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-22038-x
Murali, M., Ahmed, F., Gowtham, H. G., Aribisala, J. O., Abdulsalam, R. A., Shati, A. A., ..., Amruthesh, K. N. (2023). Exploration of CviR-mediated quorum sensing inhibitors from Cladosporium spp. against Chromobacterium violaceum through computational studies. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 15505. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-42833-4
Wishart, D. S., Feunang, Y. D., Guo, A. C., Lo, E. J., Marcu, A., Grant, J. R., ..., Wilson, M. (2017). DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(D1), D1074-D1082. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1037
Kundu, D., & Dubey, V. K. (2021). Potential alternatives to current cholinesterase inhibitors: An in silico drug repurposing approach. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 47(6), 919–930. https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2021.1952216
Schrodinger, L. (2021). he fPyMOLg molecular graphics system, version 2.5.
Larsen, A. K., Ouaret, D., El Ouadrani, K., & Petitprez, A. (2011). Targeting EGFR and VEGF(R) pathway cross-talk in tumor survival and angiogenesis. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 131(1), 80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.03.012
Trott, O., & Olson, A. J. (2010). AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 31(2), 455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Daina, A., Michielin, O., & Zoete, V. (2017). SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Salentin, S., Schreiber, S., Haupt, V. J., Adasme, M. F., & Schroeder, M. (2015). PLIP: Fully automated protein-ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(W1), W443-447. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv315
Adasme-Carreño, F., Muñoz-Gutierrez, C., Caballero, J., & Alzate-Morales, J. H. (2014). Performance of the MM/GBSA scoring using a binding site hydrogen bond network-based frame selection: The protein kinase case. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 16(27), 14047–14058. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01378F
Pronk, S., Páll, S., Schulz, R., Larsson, P., Bjelkmar, P., Apostolov, R., ..., Lindahl, E. (2013). GROMACS 4.5: A high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics, 29(7), 845–854. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt055
Ipinloju, N., Ibrahim, A., da Costa, R. A., Adigun, T. B., Olubode, S. O., Abayomi, K. J., ..., Oyeneyin, O. E. (2023). Quantum evaluation and therapeutic activity of (E)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(4-(3-oxo-3-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl) phenoxy) acetamide and its modified derivatives against EGFR and VEGFR-2 in the treatment of triple-negative cancer via in silico approach. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 29(5), 159.
Usui, T., Ban, H. S., Kawada, J., Hirokawa, T., & Nakamura, H. (2008). Discovery of indenopyrazoles as EGFR and VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors by in silico high-throughput screening. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 18(1), 285–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.10.084
Gupta, M., Lee, H. J., Barden, C. J., & Weaver, D. F. (2019). The blood-brain barrier (BBB) score. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 62(21), 9824–9836. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01220
Lipinski, C. A., Lombardo, F., Dominy, B. W., & Feeney, P. J. (2001). Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 46(1–3), 3–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-409x(00)00129-0
Bilal, M. S., Ejaz, S. A., Zargar, S., Akhtar, N., Wani, T. A., Riaz, N., ..., Alkahtani, H. M. (2022). Computational investigation of 1, 3, 4 oxadiazole derivatives as lead inhibitors of VEGFR 2 in comparison with EGFR: Density functional theory, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Biomolecules, 12(11), 1612.
Rahman, M. O., & Ahmed, S. S. (2022). Anti-angiogenic potential of bioactive phytochemicals from Helicteres isora targeting VEGFR-2 to fight cancer through molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2022.2122568
BorjianBoroujeni, M., ShahbaziDastjerdeh, M., Shokrgozar, M., Rahimi, H., & Omidinia, E. (2021). Computational driven molecular dynamics simulation of keratinocyte growth factor behavior at different pH conditions. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 23, 100514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2021.100514
Rajagopal, S., & Vishveshwara, S. (2005). Short hydrogen bonds in proteins. FEBS Journal, 272(8), 1819–1832. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04604.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.H.I. designed research; performed research; contributed analytic tools; analyzed data; and reviewed the paper. I.M. helped in designing the research, carried the experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. I.K. helped in designing the research, supervised the experiments, analyzed data, and reviewed the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not available.
Informed Consent
Not available.
Consent to Publish
Not available.
Human Ethics and Consent to Participate Statement
Our manuscript was not applied on human beings and thus requires no ethical approval.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ibraheim, M.H., Maher, I. & Khater, I. In Silico Repurposing of a Novel Inhibitor (drug) of EGFR and VEGFR-2 Kinases of Cancer by Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-024-04958-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-024-04958-8