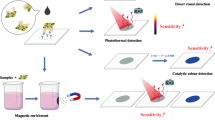
Abstract
Herein, a novel core-shell material Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) was synthesized for develo** a novel LFIA by a two-step solvothermal method with good magnetic properties and high specific surface area. It was used as both magnetic separation and label agents in LFIA for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes. The enrichment of target bacteria can be achieved quickly and easily by direct adsorption of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) on the bacteria and by the action of an applied magnetic field. It was beneficial in separation and concentration of target bacteria from food samples. The Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe)-bacterial was then detected by the anti-Listeria monocytogenes antibody on the T line under the capillary action of the LFIA strip, resulting in the formation of a visible orange band. Under the optimal conditions, there was a good linear relationship between the intensity of the T line and the quantity of Listeria monocytogenes in the range of 105-108 CFU mL− 1, with a visual detection limit of 3.3 × 106 CFU mL− 1. The strip showed strong specificity for L. monocytogenes, and the detection could be finished in 45 min, without the needing of pre-treatment. Thus, the proposed Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe)-based strip was simple prepared, label-free, low cost, rapid and convenience.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
X.Cui, Q.R.**ong, Y.H.**ong, Establishing of a method combined immunomagnetic separation with colloidal gold lateral flow assay and its application in rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 41(12), 1812–1816 (2013). https://doi.org/10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.210608
X.Y. Huang, T. Huang, X.J. Li, Flower-like gold nanoparticles-based immunochromatographic test strip for rapid simultaneous detection of fumonisin B-1 and deoxynivalenol in chinese traditional medicine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 177, 112895 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112895
Y. Li, Y.F. Zhou, X.R.Chen, Comparison of three sample addition methods in competitive and sandwich colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay. Anal. Chim. Acta 1094, 90–98 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.079
A. Thongprachum, P. Khamrin, N.Chaimongkol, Evaluation of an immunochromatography method for rapid detection of noroviruses in clinical specimens in thailand. J. Med. Virol. 82(12), 2106–2109 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.21916
X.Q. Gong, B. Zhang, J.F. Piao, High sensitive and multiple detection of acute myocardial infarction biomarkers based on a dual-readout immunochromatography test strip. Nanomedicine 14(4), 1257–1266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2018.02.013
T. Peng, X.Y. Pei, Y.J. Zheng, Performance of fluorescence microspheres-based immunochromatography in simultaneous monitoring of five quinoxalines. Food Agric. Immunol. 28(6), 1544–1554 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2017.1354357
X.Y. Pei, Q. Wang, X.M. Li, Provision of ultrasensitive quantitative gold immunochromatography for rapid monitoring of olaquindox in animal feed and water samples. Food Anal. Methods 9(7), 1919–1927 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0360-y
Y.Y. Zeng, D.M. Liang, P.M. Zheng, A simple and rapid immunochromatography test based on readily available filter paper modified with chitosan to screen for 13 sulfonamides in milk. J. Dairy. Sci. 104(1), 126–133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-18987
A. Ashuo, W.J. Zou, J.J. Fu, High throughput detection of antibiotic residues in milk by time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatography based on QR code. Assessment 37(9), 1481–1490 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2020.1778192
Y.M. Tian, T. Bu, M. Zhang, Metal-polydopamine framework based lateralflow assay for high sensitive detection of tetracycline in food samples. Food Chem. 339, 127854 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127854
R. Li, T. Bu, Y.J. Zhao, Polydopamine coated zirconium metal-organic frameworks-based immunochromatographic assay for highly sensitive detection of deoxynivalenol. Anal. Chim. Acta 1131, 109–117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.07.052
B. Shen, Y.F. Zheng, X.Y. Zhang, Clinical evaluation of a rapid colloidal gold immunochromatography assay for SARS-Cov-2 IgM/IgG. Am. J. Transl Res. 12(4), 1348–1354 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medntd.2021.100084
J.Y. Wang, M.H. Chen, Z.C.Sheng, Development of colloidal gold immunochromatographic signal-amplifying system for ultrasensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk, Rsc Adv. 2015, 5(76), 62300–62305. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra13279g
Y. Wang, R.G. Deng, G.P. Zhang, Rapid and sensitive detection of the food allergen glycinin in powdered milk using a lateral flow colloidal gold immunoassay strip test. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(8), 2172–2178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5052128
Y.R. **n, R.L. Yang, Y. Qu, Novel, Highly sensitive, and specific assay to monitor acute myocardial infarction (ami) by the determination of cardiac troponin i (ctni) and heart-type fatty acid binding protein (h-fabp) by a colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic test strip. Anal. Lett. 54(8), 1329–1350 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2020.1802594
C.L. Xu, H.T. Wang, C.F. Peng, Colloidal gold-based immumochromatographic assay for detection of diethylstilbestrol residues. Biome Chromatogr. 20(12), 1390–1394 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.714
X.F. Hu, G.P. Zhang, An immunochromatographic test strip to detect ochratoxin a and zearalenone simultaneously. Methods Mol. Biol. 1600, 95–105 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6958-6_9
Z.L. Wang, R. Cai, Z.P.Gao, Immunomagnetic separation: an effective pretreatment technology for isolation and enrichment in food microorganisms detection. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 19(6), 3802–3824 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12656
A.A. Mohammadi, Z. Niazi, K.Heidari, Nickel and iron-based metal-organic frameworks for removal of organic and inorganic model contaminants. Environ. Res. 212, 113164 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113164
S.Q. Li, Y.F. Chen, X.K.Pei, Water purification: Adsorption over metal-organic frameworks. Chin. J. Chem. 34(2), 175–185 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.201500761
K.Suresh, A.J.Matzger, Enhanced drug delivery by dissolution of amorphous drug encapsulated in a water unstable metal-organic framework (MOF). Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 58(47), 16790–16794 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201907652
M.R. Cai, L.Y. Qin, L.T.You, functionalization of MOF-5 with mono-substituents: effects on drug delivery behavior. Rsc Adv. 10(60), 36862–36872 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra06106a
H.Sun,X.L. Yu, X.Y.Ma, MnOx-CeO2 catalyst derived from metal-organic frameworks for toluene oxidation. Catal. Today 355, 580–586 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.05.062
N. T.Arai.H.Kanoh Kawasaki, Magnetically separable cu-carboxylate mof catalyst for the henry reaction. Synlett 10, 1549–1553 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1290935
Q.F. Sun, J.H. Cheng, R.Q. .Lin, A novel multiplex PCR method for simultaneous identification of hypervirulent Listeria monocytogenes clonal complex 87 and CC88 strains in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 366, 109558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109558
A.A.C. Cavalcanti, C.H. Limeira, I.N.D. Siqueira, The prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes in meat products in Brazil: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Res. Vet. Sci. 145, 169–176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.02.015
C. Xedzro, K. Tano-Debrah, H.Nakano, Antibacterial efficacies and time-kill kinetics of indigenous ghanaian spice extracts against Listeria monocytogenes and some other food-borne pathogenic bacteria. Microbiol. Res. 258, 126980 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2022.126980
X.Y. Wu, Q.M. Chen, C.Y. Yang, An enhanced visual detection assay for Listeria monocytogenes in food based on isothermal amplified peroxidase-mimicking catalytic beacon, Food. Control. 2022, 134, 108721. https://doi.org/1016/j.foodcont.2021.108721
J.Du, K.Liu, J.L.Liu, A novel lateral flow immunoassay strip based on a label-free magnetic Fe3O4@UiO-66-NH2 nanocomposite for rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Anal. Methods 14(24), 2423–2430 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ay00506a
J. Du, X. Chen, K.Liu, Dual recognition and highly sensitive detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food by fluorescence enhancement effect based on Fe3O4@ZIF-8-aptamer. Sens. Actuat B-Chem 360, 131654 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131654
S.Aslam,J.B. Zeng, F.Subhan, In situ one-step synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) core-shells for adsorption of methylene blue from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 505, 186–195 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.090
N. F.Chang.S.Memon Memon, Removal of emerging contaminants from water by using FeMOF composite as a sorbent. J Iran. Chem Soc 18(12), 3249–3255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02264-2
X.F. Chen, N. Ding, H.Zang, Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 1304, 241–245 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.06.053
Y.J. Chen, Z.C. **ong, L. Peng, Facile preparation of core – shell magnetic metal – organic framework nanoparticles for the selective capture of phosphopeptides. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter 7(30), 16338–16347 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03335
Z.L. Wu, Y.P. Wang, Z.K. **ong, Core-shell magnetic Fe3O4@Zn/Co-ZIFs to activate peroxymonosulfate for highly efficient degradation of carbamazepine. Appl. Catal. B 277, 119136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119136
C.F. Zhang, L.G. Qiu, F. Ke, A novel magnetic recyclable photocatalyst based on a core–shell metal–organic framework Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) for the decolorization of methylene blue dye. J. Mater. Chem. A 1(45), 14329–14334 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13030d
Q.R. Liu, C.X. Yao, J.M.Liu, An efficient method to enrich, detect and remove bisphenol A based on Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe). Microchem J. 165, 106168 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106168
D.B. Zhou, Y.B. **ao, F.Han, Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on sulfur-functionalized magnetic metal-organic frameworks for the determination of methylmercury and inorganic mercury in water and fifish samples. J. Chromatogr. A 1654, 462465 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462465
Q.X. Yang, Q.Q. Zhao, S.S. Ren, Fabrication of core-shell Fe3O4@MIL–100(fe) magnetic microspheres for the removal of cr(VI) in aqueous solution. J. Solid State Chem. 244, 25–30 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2016.09.010
C.M. Cheng, Y.H. Wen, X.F. Xu, Tunable synthesis of carboxyl-functionalized magnetite nanocrystal clusters with uniform size. J. Mater. Chem. 19(46), 8782–8788 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b910832g
S.Dadfarnia, A.M.H.Shabani, S.E.Moradi, Methyl red removal from water by iron based metal-organic frameworks loaded onto iron oxide nanoparticle adsorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 330, 85–93 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.12.196
J.X. Fan, D.Y. Chen, N.J. Li, Adsorption and biodegradation of dye in wastewater with Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) coreeshell bio-nanocomposites, Chemosphere. 2018, 191, 315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.042
J.B. Xu, Y.Y. **ng, Y.T. Liu, Facile in situ microwave synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) exhibiting enhanced dual enzyme mimetic activities for colorimetric glutathione sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 1179, 338825 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338825
F. Ke, L.G. Qiu, Y.P. Yuan, Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres with a designable metal–organic framework shell. J. Mater. Chem. 22(19), 9497–9500 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm31167d
M.Ahmaruzzaman J.Darabdhara, Recent developments in MOF and MOF based composite as potential adsorbents for removal of aqueous environmental contaminants. Chemosphere 304, 135261 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135261
S. H.Yang.H.Zhao Hu, High-performance Fe-doped ZIF-8 adsorbent for capturing tetracycline from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Maters 416, 126046 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126046
E. Nyarko, C. Donnelly, Differentiation of different mixed listeria strains and also acid-injured, heat-injured, and repaired cells of Listeria monocytogenes using fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Protect 78(3), 540–548 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-160
T.H. Kim, J. Park, C.J.Kim,fully integrated lab-on-a-Disc for nucleic acid analysis of food-borne pathogens. Anal. Chem. 86(8), 3841–3848 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac403971h
M. Varshney, L.J. Yang, X.L.Su, Magnetic nanoparticle-antibody conjugates for the separation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground beef. J. Food Protect 68(9), 1804–1811 (2005). https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-68.9.1804
M. Fuentes, C. Mateo, J.M. Guisan, Preparation of inert magnetic nano-particles for the directed immobilization of antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 20(7), 1380–1387 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2004.06.004
B. Jagadeesan, V.B. Schmid, B.Kupski, Detection of Listeria spp. and L. monocytogenes in pooled test portion samples of processed dairy products, Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2019, 289,30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.08.017
H.X. Che, B. Tian, L.N. Bai, Development of a test strip for rapid detection of lactoperoxidase in raw milk. J. Zhejiang Univ-Sc B 16(8), 672–679 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1400359
R. Sharma, A. Verma, N. Shinde, Adulteration of cow’s milk with buffalo’s milk detected by an on-site carbon nanoparticles-based lateral flow immunoassay. Food Chem. 351, 129311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129311
S. Ueda, M. Iwase, Y.Kuwabara, Evaluation of immunochromatography for the rapid and specific identification of Listeria monocytogenes from food. Biocontrol Sci. 18(3), 157–161 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4265/bio.18.157
S.J. Wu, J.Du,Q.S. **ang, Solvothermal synthesis of α-Fe2O3 polyhedrons and its application in an immunochromatographic strip test for the detection of foodborne pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Nanotechnology 32(8), 085502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abcb30
Q.R. Li, S. Zhang, Y.X. Cai, Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes using fluorescence immunochromatographic assay combined with immunomagnetic separation technique. Int. J Food Scie Tech 52(7), 1559–1566 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13428
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Special Project on Public Welfare of Henan Province [grant number 201300110100].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Juan Du: conceptualization, methodology and writing-review&editing; Kai Liu: investigation, data collection, formal analysis and writing-original draft; Jialei Liu: material preparation and formal analysis; Dianbo Zhao:material preparation and formal analysis; Yanhong Bai: funding acquisition, resources, project administration and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest disclosure
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Permission to reproduce material from other sources
This article does not contain material from other sources.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, J., Liu, K., Liu, J. et al. Development of a novel lateral flow immunoassay based on Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) for visual detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Measure 17, 3482–3492 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01900-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01900-0