Abstract
Purpose
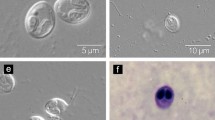
We describe two new species of Myxobolus (Myxobolidae) found parasitizing Mugil curema from two locations in Brazil: Myxobolus curemae n. sp. from gill arch and rays and Myxobolus maceioensis n. sp. from gill lamellae.
Methods
We based the descriptions on myxospore morphology, histology, and small-subunit ribosomal DNA sequences.
Results
Myxospores of the two new species had similar morphology and morphometry but differed in spore body width and length, and ssrDNA sequences differed by 10.5%. These data supported the diagnosis of the parasites as distinct and novel species. The phylogenetic analysis showed a subclade formed by species that parasitize Mugiliformes, with M. maceioensis n. sp. as a sister species of Myxobolus episquamalis and Myxobolus bizerti, while there is a group of six species that are sister related to M. curemae n. sp. Our analysis was consistent with previous studies suggesting that orders of the hosts are strongly correlated with phylogenetic signals in the Myxobolidae.
Conclusions
Myxobolus curemae n. sp. and M. maceioensis n. sp. are new species identified parasitizing M. curema.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used in this study are included in the manuscript.
References
Kent ML, Andree KB, Bartholomew JL et al (2001) Recent advances in our knowledge of the Myxozoa. J Eukaryot Microbiol 48:395–413. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2001.tb00173.x
Lom J, Dyková I (2006) Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitol 53:1–36. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2006.001
Fiala I, Bartoŝová P (2010) History of myxozoan character evolution on the basis of rDNA and EF-2 data. BMC Evol Biol 10:5–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-228
Eiras JC, Molnár K, Lu YS (2005) Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). Syst Parasitol 61:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-004-6343-9
Eiras JC, Zhang J, Molnár K (2014) Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea, Myxobolidae) described between 2005 and 2013. Syst Parasitol 88:11–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-014-9484-5
Eiras JC, Cruz CF, Saraiva A, Adriano EA (2021) Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria, Myxozoa, Myxosporea) described between 2014 and 2020. Folia Parasitol 68:012. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2021.012
Ibañez Aguirre AL (1993) Coexistence of Mugil cephalus and M. curema in a coastal lagoon in the Gulf of Mexico. J Fish Biol 42:959–961. https://doi.org/10.1006/jfbi.1993.1101
Trape S, Durand JD, Vigliola L, Panfili J (2017) Recruitment success and growth variability of mugilids in a West African estuary impacted by climate change. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 198:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2017.08.037
Mai ACG, dos Santos ML, Lemos VM, Vieira JP (2018) Discrimination of habitat use between two sympatric species of mullets, Mugil curema and Mugil liza (Mugiliformes: Mugilidae) in the rio Tramandaí Estuary, determined by otolith chemistry. Neotrop Ichthyol 16:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/1982-0224-20170045
Marin EBJ, Quintero A, Bussière D, Dodson JJ (2003) Reproduction and recruitment of white mullet (Mugil curema) to a tropical lagoon (Margarita Island, Venezuela) as revealed by otolith microstructure. Fish Bull 101:809–821
Heras S, González Castro M, Roldán MI (2006) Mugil curema in Argentinean waters: combined morphological and molecular approach. Aquaculture 261:473–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.07.003
Avigliano E, Ibañez A, Fabré N et al (2020) White mullet Mugil curema population structure from Mexico and Brazil revealed by otolith chemistry. J Fish Biol 97:1187–1200. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.14500
Albieri RJ, Araújo FG, Uehara W (2010) Differences in reproductive strategies between two co-occurring mullets Mugil curema Valenciennes 1836 and Mugil liza Valenciennes 1836 (Mugilidae) in a tropical bay. Trop Zool 23:51–62
Lima ARB, Torres RA, Jacobina UP et al (2019) Genomic damage in Mugil curema (Actinopterygii: Mugilidae ) reveals the effects of intense urbanization on estuaries in northeastern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 138:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.037
Yurakhno VM, Ovcharenko MO (2014) Study of Myxosporea (Myxozoa), infecting worldwide mullets with description of a new species. Parasitol Res 113:3661–3674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4031-5
Ovcharenko M (2015) Microparasites of worldwide mullets. Ann Parasitol 61:229–239. https://doi.org/10.17420/ap6104.12
Rocha S, Azevedo C, Oliveira E et al (2019) Phylogeny and comprehensive revision of mugiliform-infecting myxobolids (Myxozoa, Myxobolidae), with the morphological and molecular redescription of the cryptic species Myxobolus exiguus. Parasitology 146:479–496. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182018001671
Sharon G, Ucko M, Tamir B, Diamant A (2019) Co-existence of Myxobolus spp. (Myxozoa) in gray mullet (Mugil cephalus) juveniles from the Mediterranean Sea. Parasitol Res 118:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6151-9
Faye N, Kpatcha TK, Fall M, Toguebaye BS (1997) Heart infections due to myxosporean (Myxozoa) parasites in marine and estuarine fishes from Senegal. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 17:115–117
Faye N, Kpatcha TK, Debakate C, Fall M, Toguebaye BS (1999) Gill infections due to myxosporean (Myxozoa) parasites in fishes from Senegal with description of Myxobolus hani sp. n. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 19:14–16
Lom J, Arthur JR (1989) A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. J Fish Dis 12:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1989.tb00287.x
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A et al (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP et al (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msn083
Rambaut A (2012) FigTree v1.4. Molecular evolution, phylogenetics and epidemiology. http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/. Accessed 19 Dec 2021
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Naldoni J, Maia AAM, Correa LL et al (2018) New myxosporeans parasitizing Phractocephalus hemioliopterus from Brazil: morphology, ultrastructure and SSU-rDNA sequencing. Dis Aquat Organ 128:37–49. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao03210
Vieira DHMD, Rangel LF, Tagliavini VP et al (2020) Morphological and molecular analysis of Henneguya tietensis n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxosporea), parasitizing the gill filaments of Prochilodus lineatus (Valenciennes, 1837) from Brazil. Parasitol Res 120:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06918-7
Vieira DHMD, Rangel LF, Tagliavini VP et al (2020) A new species, Henneguya lacustris n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxosporea), infecting the gills of Astyanax lacustris from Brazil. Parasitol Res 119:4259–4265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06871-5
Molnár K, Cech G, Székely C (2008) Myxobolus species infecting the cartilaginous rays of the gill filaments in cyprinid fishes. Acta Parasitol 53:330–338. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-008-0054-3
Molnár K, Eszterbauer E, Marton S et al (2009) Myxobolus erythrophthalmi sp. n. and Myxobolus shaharomae sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) from the internal organs of rudd, Scardinius erythrophthalmus (L.), and bleak, Alburnus alburnus (L.). J Fish Dis 32:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2008.00976.x
Molnár K, Marton S, Székely C, Eszterbauer E (2010) Differentiation of Myxobolus spp. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) infecting roach (Rutilus rutilus) in Hungary. Parasitol Res 107:1137–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1982-z
Liu Y, Whipps CM, Gu ZM et al (2013) Myxobolus musseliusae (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) from the gills of common carp Cyprinus carpio and revision of Myxobolus dispar recorded in China. Parasitol Res 112:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3136-y
Negrelli DC, Vieira DHMD, Tagliavini VP et al (2019) Molecular and morphological analysis of Henneguya jundiai n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxosporea), a new parasite of the gills of Rhamdia quelen in Brazil. Acta Trop 197:105053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.105053
Molnár K (2002) Site preference of fish myxosporeans in the gill. Dis Aquat Organ 48:197–207. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao048197
Bahri S (2008) Abnormal forms of Myxobolus bizerti and Myxobolus mulleri (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) spores with caudal appendages. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 28:252–255
Liu Y, Whipps CM, Gu ZM et al (2010) Myxobolus turpisrotundus (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) spores with caudal appendages: investigating the validity of the genus Henneguya with morphological and molecular evidence. Parasitol Res 107:699–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1924-9
Liu Y, Lövy A, Gu Z, Fiala I (2019) Phylogeny of Myxobolidae (Myxozoa) and the evolution of myxospore appendages in the Myxobolus clade. Int J Parasitol 49:523–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2019.02.009
Liu XH, Zhang JY, Batueva MD, Voronin VN (2016) Supplemental description and molecular characterization of Myxobolus miyarii Kudo, 1919 (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) infecting intestine of Amur catfish (Silurus asotus). Parasitol Res 115:1547–1556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4889-x
Zhang JY, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel-Baki AAS (2014) The morphological and molecular characterization of Myxobolus khaliji n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) from the double bar seabream Acanthopagrus bifasciatus (Forsskål, 1775) in the Arabian Gulf. Saudi Arabia Parasitol Res 113:2177–2183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3870-4
Barta JR, Martin DS, Liberator PA et al (1997) Phylogenetic relationships among eight Eimeria species infecting domestic fowl inferred using complete small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. J Parasitol 83:262–271. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284453
Hallett SL, Diamant A (2001) Ultrastructure and small-subunit ribosomal DNA sequence of Henneguya lesteri n. sp (Myxosporea), a parasite of sand whiting Sillago analis (Sillaginidae) from the coast of Queensland, Australia. Dis Aquat Organ 46:197–212. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao046197
Kent ML, Khattra J, Hedrick RP, Devlin RH (2000) Tetracapsula renicola n. sp. (Myxozoa: Saccosporidae); the PKX myxozoan—the cause of proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fishes. J Parasitol 86:103–111. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284917
Eszterbauer E (2004) Genetic relationship among gill-infecting Myxobolus species (Myxosporea) of cyprinids: molecular evidence of importance of tissue-specificity. Dis Aquat Organ 58:35–40. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao058035
Andree KB, Szekely C, Molnár K et al (1999) Relationships among members of the genus Myxobolus (Myxozoa: Bilvalvidae) based on small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. J Parasitol 85:68–74. https://doi.org/10.2307/3285702
Funding
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) [Grant numbers 2020/05412-9 and 2019/25223-9], Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Alagoas (FAPEAL) [Grant number 60030.0000000464/2020] and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—CNPq [Grant number 309125/2017-0].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have contributed equally to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
During the present research work, all applicable international, national or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All the protocols used have been approved by Animal Ethical Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vieira, D.H.M.D., Agostinho, B.N., Negrelli, D.C. et al. Taxonomy and Systematics of Two New Species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae) Parasitizing the Gills of Mugil curema (Mugilidae) from the Brazilian Coast. Acta Parasit. 67, 1206–1216 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-022-00569-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-022-00569-7