Abstract
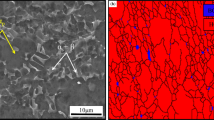
In the present work, the impact behavior of unmodified A356 alloys with the addition of Ni or V in as-cast and T6 heat-treated conditions was assessed. Charpy V-notched specimens obtained from sand and permanent mold casting showed low total absorbed energy average values (W t < 2 J). SEM analysis of fracture profiles and surfaces indicated a Si-driven crack propagation with a predominant transgranular fracture mode. Occasionally, intergranular contributions to fracture were detected in the permanent mold cast alloys due to the locally finer microstructure. Concurrent mechanisms related to the chemical composition, solidification conditions and heat treatment were found to control the impact properties of the alloys. While the trace element Ni exerted only minor effects on the impact toughness of the A356 alloy, V had a strong influence: (i) V-containing sand cast alloys absorbed slightly higher impact energies compared to the corresponding A356 base alloys; (ii) in the permanent mold cast alloys, V in solid solution led to a considerable loss of ductility, which in turn decreased the total absorbed energy.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Apelian, S. Shivkumar, and G. Sigworth, Fundamental Aspects of Heat Treatment of Cast Al-Si-Mg Alloys, AFS Trans., 1989, 97, p 727–742
E. Sjölander and S. Seifeddine, The Heat Treatment of Al-Si-Cu-Mg Casting Alloys, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2010, 210(10), p 1249–1259
K.T. Kashyap, S. Murali, K.S. Raman, and K.S.S. Murthy, Casting and Heat Treatment Variables of Al-7Si-Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1993, 9(3), p 189–204
L. Pedersen and L. Arnberg, The Effect of Solution Heat Treatment and Quenching Rates on Mechanical Properties and Microstructures in AlSiMg Foundry Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32(3), p 525–532
M. Zhu, Z. Jian, G. Yang, and Y. Zhou, Effects of T6 Heat Treatment on the Microstructure, Tensile Properties, and Fracture Behavior of the Modified A356 Alloys, Mater. Des., 2012, 36, p 243–249
D.L. Zhang, L.H. Zheng, and D.H. StJohn, Effect of a Short Solution Treatment Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Modified Al-7wt.%Si-0.3wt.%Mg alloy, J. Light Met., 2002, 2(1), p 27–36
J.A. Taylor, D.H. St John, L. Zheng, G.A. Edwards, J. Barresi, and M.J. Couper, Solution Treatment Effects in Al-Si-Mg Casting Alloys: Part I. Intermetallic Phases, Alum. Trans., 2001, 4–5, p 95–110
S. Murali, K.S. Raman, and K.S.S. Murthy, Effect of Magnesium, Iron (Impurity) and Solidification Rates on the Fracture Toughness of Al-7Si-0.3 Mg Casting Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1992, 151(1), p 1–10
Z. Ma, F.H. Samuel, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, and S. Valtierra, Effect of Fe Content and Cooling Rate on the Impact Toughness of Cast 319 and 356 Aluminum Alloys, AFS Trans., 2003, 111, p 255–266
S. Shivkumar, L. Wang, and C. Keller, Impact Properties of A356-T6 Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1994, 3(1), p 83–90
M. Merlin, G. Timelli, F. Bonollo, and G.L. Garagnani, Impact Behaviour of A356 Alloy for Low-Pressure Die Casting Automotive Wheels, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209(2), p 1060–1073
D. Casari, M. Merlin, and G.L. Garagnani, A Comparative Study on the Effects of Three Commercial Ti-B-Based Grain Refiners on the Impact Properties of A356 Cast Aluminium Alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 2013, 48(12), p 4365–4377
O. Elsebaie, A.M. Samuel, and F.H. Samuel, Effects of Sr-Modification, Iron-Based Intermetallics and Aging Treatment on the Impact Toughness of 356 Al-Si-Mg Alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 2011, 46(9), p 3027–3045
G. Jha, S. Ningileri, X. Li, and R. Bowers, The Challenge of Effectively Utilizing Trace Elements, Impurities in a Varying Raw Materials Market, Light Met., 2013, 2013, p 929–934
J. Grandfield, L. Sweet, C. Davidson, J. Mitchell, A. Beer, S. Zhu, X. Chen, and M. Easton, An Initial Assessment of the Effects of Increased Ni and V Content in A356 and AA6063 Alloys, Light Metals, 2013, 2013, p 39–45
D. Casari, T.H. Ludwig, M. Merlin, L. Arnberg, and G.L. Garagnani, The Effect of Ni and V Trace Elements on the Mechanical Properties of A356 Aluminium Foundry Alloy in As-Cast and T6 Heat Treated Conditions, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 610, p 414–426
Z. Li, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, C. Ravindran, H.W. Doty, and S. Valtierra, Parameters Controlling the Performance of AA319-Type Alloys Part II. Impact Properties and Fractography, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 367(1–2), p 111–122
N.D. Alexopoulos and A. Stylianos, Impact Mechanical Behaviour of Al-7Si-Mg (A357) Cast Aluminum Alloy. The Effect of Artificial Aging, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(16–20), p 6303–6312
N.D. Alexopoulus, A. Stylianos, and J. Campbell, Dynamic fracture toughness of Al-7Si-Mg (A357) aluminum alloy, Mech. Mater., 2013, 58, p 55–68
T.H. Ludwig, P.L. Schaffer, and L. Arnberg, Influence of Some Trace Elements on Solidification Path and Microstructure of Al-Si Foundry Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, 44(8), p 3783–3796
J.A. Taylor, D.H. St John, J. Barresi, and M.J. Couper, Influence of Mg Content on the Microstructure and Solid Solution Chemistry of Al-7%Si-Mg Casting Alloys During Solution Treatment, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2000, 331–337, p 277–282
Q.G. Wang, Microstructural Effects on the Tensile and Fracture Behavior of Aluminum Casting Alloys A356/357, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34(12), p 2887–2899
Y. Harada, S. Tamura, and S. Kumai, Effects of High-Temperature Solutionizing on Microstructure and Tear Toughness of A356 Cast Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Trans., 2011, 52(5), p 848–855
Q.G. Wang and C.H. Cáceres, The Fracture Mode in Al-Si-Mg Casting Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 241(1–2), p 72–82
E. Ogris, A. Wahlen, H. Luchinger, and P.J. Uggowitzer, On the Silicon Spheroidization in Al-Si Alloys, J. Light Met., 2002, 2(4), p 263–269
C.H. Cáceres, C.J. Davidson, and J.R. Griffiths, The Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of an Al-Si-Mg Casting Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, 197(2), p 171–179
W.H. Hunt, Jr., J.R. Brockenbrough, and P.E. Magnusen, An Al-Si-Mg Composite Model System: Microstructural Effects on Deformation and Damage Evolution, Scripta Metall. Mater., 1991, 25(1), p 15–20
ASM International, ASM Handbook Vol. 8—Mechanical Testing and Evaluation, 1st ed., ASM International, Materials Park, 2000, p 1357
T. Kobayashi and M. Niinomi, Fracture Toughness and Fatigue Characteristics of Aluminum Casting Alloy, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1991, 41, p 398–405
N.A. Belov, D.G. Eskin, and A.A. Aksenov, Multicomponent Phase Diagrams: Applications for Commercial Aluminum Alloys, 1st ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2005, p 379–380
F. Paray, B. Kulunk, and J.E. Gruzleski, Impact Properties of Al-Si Foundry Alloys, Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 2000, 13, p 17–37
S.S. Sreeja Kumari, R.M. Pillai, T.P.D. Rajan, and B.C. Pai, Effects of Individual and Combined Additions of Be, Mn, Ca and Sr on the Solidification Behaviour, Structure and Mechanical Properties of Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.8Fe Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 460–461, p 561–573
G.E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, Chap. 6, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988
D. Lados, D. Apelian, and L. Wang, Solution Treatment Effects on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-(1 to 13 Pct)Si-Mg Cast Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, 42(1), p 171–180
Acknowledgments
This research activity was supported by the “Bando Giovani Ricercatori – Fondi 5x1000 anno 2010 e Fondi Unicredit 2013” of the University of Ferrara. In addition, the authors gratefully acknowledge Hydro Aluminium AS (Norway) for financial support. Thanks are also due to Hermann Hovland from Sør-Norge Aluminium AS (Norway) for the generous supply of master alloys and to Arne Nordmark and Kurt Sandaunet from SINTEF Materials and Chemistry (Norway) for their help during the manufacturing of castings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casari, D., Ludwig, T.H., Merlin, M. et al. Impact Behavior of A356 Foundry Alloys in the Presence of Trace Elements Ni and V. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 894–908 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1355-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1355-3