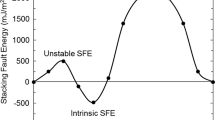
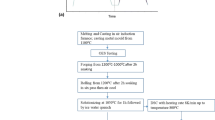
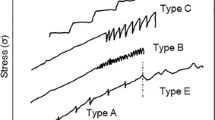
Abstract
The manganese concentration of steels which rely on transformation-induced plasticity is generally less than 2 wt pct. Recent work has highlighted the potential for strong and ductile alloys containing some 6 wt pct of manganese, but with aluminum additions in order to permit heat treatments which are amenable to rapid production. However, large concentrations of aluminum also cause difficulties during continuous casting. Alloy design calculations have been carried out in an effort to balance these conflicting requirements, while maintaining the amount of retained austenite and transformation kinetics. The results indicate that it is possible by adjusting the carbon and manganese concentrations to reduce the aluminum concentration, without compromising the mechanical properties or transformation kinetics. The deformation-induced transformation of retained austenite is explained quantitatively, for a range of alloys, in terms of a driving force which takes into account the very fine state of the retained austenite.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Following,[18] \({\Updelta}{\sigma}\) (kg/mm2)=\(\frac{{\Updelta}H}{3}(0.1)^n, \) n is strain hardening coefficient
References
Miller RL (1972) . Metall. Trans. 3:90–912
Suh D.W., Park S.J., Lee T.H., Oh C.S., Kim S.J (2010) . Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41A:397–408
H. Aaronson, P.G. Domian, G.M. Pound: TMS-AIME, 1966, vol.236, pp.781–96.
Abdelaziz S., Megahed G., El-Mahallawi I., Ahmed H (2009) . Ironmak. Steelmak. 36:432–41
Sundman B., Jansson B., Andersson J (1985) . CALPHAD 9:153–90
Bratberg: TCFE6-TCS Steels/Fe-Alloys Database, Version 6.2: Tech. Rep.: Thermo-Calc Software AB, Stockholm, Sweden, 2011.
C.F. Jatczak: SAE Technical Paper Series 800426: Tech. Rep., SAE, 1980.
ASTM E8M3 Standard Test Method for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials.
Yi H., Lee K.Y., Bhadeshia H (2011) . Mater. Sci. Technol. 27:525–29
Brofman P., Ansell G (1983) .Metall. Mater. Trans. A 14A:1929–1931
Yang H.S., Bhadeshia H.K.D.H (2009) . Scripta Mater. 60:493–95
W. Gerberich, G. Thomas, E. Parker, and V. Zackay: Metastable Austenite: Decomposition and Strength, in Second International Conference on Strength of Metals and Alloys, ASM International, Ohio, 1970, pp.984–99.
Bhadeshia H.K.D.H (2002) . ISIJ International 42:1059–60
Jang J.M., Kim S.J., Kang N.H., Cho K.M., Suh D.W (2009) . Met. Mater. Int. 15:909–16
Sherif M., Garcia Mateo M., Sourmail T., Bhadeshia H (2004) . Mater. Sci. Technol. 20:319–22
Ion J., Anisdahl L (1997) . J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 65:261–67
Furnemont Q., Kempf M., Jacques P., Goken M., Delannay F (2002) . Mater. Sci. Eng. A328:26–32
Cahoon J., Broughton W., Kutzak A (1971) . Metall. Trans. 2:1979–83
Tomota Y., Kuroki K., Mori T., Tamura I (1976) . Mater. Sci. Eng. 24:85–94
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for support from the POSCO Steel Innovation Programme, and to the World Class University Programme of the National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, project number R32-2008-000-10147-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 25, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suh, D.W., Ryu, J.H., Joo, M.S. et al. Medium-Alloy Manganese-Rich Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 44, 286–293 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1402-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1402-3