Abstract
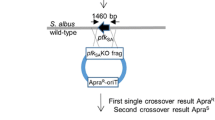
Amplification of biosynthetic gene clusters is important to increase secondary metabolite production. However, the copy number of amplified gene clusters is difficult to control precisely. In this study, the tandem amplification of a 70 kb bleomycin biosynthetic gene cluster was precisely regulated through the combined strategy of a ZouA-dependent DNA amplification system and double-reporter-guided recombinant selection in Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003. The production of bleomycin in the recombinant strain containing six copies of the bleomycin gene cluster was 9.59-fold higher than that in the wild-type strain. The combined strategy used in this study is powerful and applicable for precisely regulating the amplification of gene clusters and improving the corresponding secondary metabolite production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askenazi, M., Driggers, E.M., Holtzman, D.A., Norman, T.C., Iverson, S., Zimmer, D.P., Boers, M.E., Blomquist, P.R., Martinez, E.J., Monreal, A. W., et al. (2003). Integrating transcriptional and metabolite profiles to direct the engineering of lovastatin-producing fungal strains. Nat Biotechnol 21, 150–156.
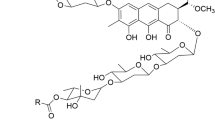
Boger, D.L., and Cai, H. (1999). Bleomycin: Synthetic and mechanistic studies. Angew Chem Int Ed 38, 448–476.
Calcutt, M.J., and Schmidt, F.J. (1994). Gene organization in the bleomycin-resistance region of the producer organism Streptomyces verticillus. Gene 151, 17–21.
Chen, H., Cui, J., Wang, P., Wang, X., and Wen, J. (2020). Enhancement of bleomycin production in Streptomyces verticillus through global metabolic regulation of N-acetylglucosamine and assisted metabolic profiling analysis. Microb Cell Fact 19, 32–48.
Chen, H., Wang, J., Cui, J., Wang, C., Liang, S., Liu, H., and Wen, J. (2019). Negative regulation of bleomycins biosynthesis by ArsR/SmtB family repressor BlmR in Streptomyces verticillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 6629–6644.
Chen, J., and Stubbe, J.A. (2005). Bleomycins: towards better therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer 5, 102–112.
Demain, A.L. (2006). From natural products discovery to commercialization: a success story. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 486–495.
Della Latta, V., Cecchettini, A., Del Ry, S., and Morales, M.A. (2015). Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: From biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol Res 97, 122–130.
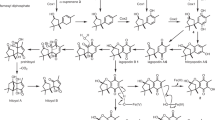
Du, L., Sánchez, C., Chen, M., Edwards, D.J., and Shen, B. (2000). The biosynthetic gene cluster for the antitumor drug bleomycin from Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 supporting functional interactions between nonribosomal peptide synthetases and a polyketide synthase. Chem Biol 7, 623–642.
Fierro, F., Barredo, J.L., Diez, B., Gutierrez, S., Fernandez, F.J., and Martin, J.F. (1995). The penicillin gene cluster is amplified in tandem repeats linked by conserved hexanucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92, 6200–6204.
Galm, U., Wang, L., Wendt-Pienkowski, E., Yang, R., Liu, W., Tao, M., Coughlin, J.M., and Shen, B. (2008). In vivo manipulation of the bleomycin biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 revealing new insights into its biosynthetic pathway. J Biol Chem 283, 28236–28245.
Gibson, D.G., Benders, G.A., Andrews-Pfannkoch, C., Denisova, E.A., Baden-Tillson, H., Zaveri, J., Stockwell, T.B., Brownley, A., Thomas, D.W., Algire, M.A., et al. (2008). Complete chemical synthesis, assembly, and cloning of a Mycoplasma genitalium genome. Science 319, 1215–1220.
Gibson, D.G., Young, L., Chuang, R.Y., Venter, J.C., Hutchison Iii, C.A., and Smith, H.O. (2009). Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6, 343–345.
Guan, H., Li, Y., Zheng, J., Liu, N., Zhang, J., and Tan, H. (2019). Important role of a LAL regulator StaR in the staurosporine biosynthesis and high-production of Streptomyces fradiae CGMCC 4.576. Sci China Life Sci 62, 1638–1654.
Gust, B., Challis, G.L., Fowler, K., Kieser, T., and Chater, K.F. (2003). PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 1541–1546.
He, Y., Lan, Y., Liu, Y., Yu, H., Han, Z., Li, X., and Zhang, L. (2016). **yangmycin and bleomycin share the same cytotoxicity pathway. Molecules 21, 862.
Kieser, T., Bibb, M.J., Buttner, M.J., Chater, K.F., and Hopwood, D.A. (2000). Practical Streptomyces Genetics. Norwich: John Innes Foundation.
Lee, H.N., Huang, J., Im, J.H., Kim, S.H., Noh, J.H., Cohen, S.N., and Kim, E.S. (2010). Putative TetR family transcriptional regulator SCO1712 encodes an antibiotic downregulator in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 76, 3039–3043.
Li, D., Zhang, J., Tian, Y., and Tan, H. (2019). Enhancement of salinomycin production by ribosome engineering in Streptomyces albus. Sci China Life Sci 62, 276–279.
Li, Y., Ling, H., Li, W., and Tan, H. (2005). Improvement of nikkomycin production by enhanced copy of sanU and sanV in Streptomyces ansochromogenes and characterization of a novel glutamate mutase encoded by sanU and sanV. Metab Eng 7, 165–173.
Liao, G., Li, J., Li, L., Yang, H., Tian, Y., and Tan, H. (2010). Cloning, reassembling and integration of the entire nikkomycin biosynthetic gene cluster into Streptomyces ansochromogenes lead to an improved nikkomycin production. Microb Cell Fact 9, 6–12.
Liu, G., Chater, K.F., Chandra, G., Niu, G., and Tan, H. (2013). Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77, 112–143.
Murakami, T., Burian, J., Yanai, K., Bibb, M.J., and Thompson, C.J. (2011). A system for the targeted amplification of bacterial gene clusters multiplies antibiotic yield in Streptomyces coelicolor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 16020–16025.
Olano, C., Lombó, F., Méndez, C., and Salas, J.A. (2008). Improving production of bioactive secondary metabolites in actinomycetes by metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 10, 281–292.
Pan, Y., Lu, C., Dong, H., Yu, L., Liu, G., and Tan, H. (2013). Disruption of rimP-SC, encoding a ribosome assembly cofactor, markedly enhances the production of several antibiotics in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microb Cell Fact 12, 65–80.
Peschke, U., Schmidt, H., Zhang, H.Z., and Piepersberg, W. (1995). Molecular characterization of the lincomycin-production gene cluster of Streptomyces lincolnensis 78-11. Mol Microbiol 16, 1137–1156.
Raisfeld, I.H. (1981). Role of terminal substituents in the pulmonary toxicity of bleomycins. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 57, 355–366.
Romero, J., Liras, P., and Martín, J.F. (1986). Utilization of ornithine and arginine as specific precursors of clavulanic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 52, 892–897.
Santos, C.N.S., and Stephanopoulos, G. (2008). Combinatorial engineering of microbes for optimizing cellular phenotype. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12, 168–176.
Shen, B., Du, L., Sanchez, C., Edwards, D.J., Chen, M., and Murrell, J.M. (2001). The biosynthetic gene cluster for the anticancer drug bleomycin from Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 as a model for hybrid peptide-polyketide natural product biosynthesis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 378–385.
Shen, B., Du, L., Sanchez, C., Edwards, D.J., Chen, M., and Murrell, J.M. (2002). Cloning and characterization of the bleomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003. J Nat Prod 65, 422–431.
Takita, T., Umezawa, Y., Saito, S., Morishima, H., Umezawa, H., Muraoka, Y., Suzuki, M., Otsuka, M., Kobayashi, S., and Ohno, M. (1981). Total synthesis of deglyco-bleomycin A2. Tetrahedron Lett 22, 671–674.
Tao, M., Wang, L., Wendt-Pienkowski, E., George, N.P., Galm, U., Zhang, G., Coughlin, J.M., and Shen, B. (2007). The tallysomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insights into the biosynthesis of the bleomycin family of antitumor antibiotics. Mol Biosyst 3, 60–74.
Umezawa, H., Maeda, K., Takeuchi, T., and Okami, Y. (1966). New antibiotics, bleomycin A and B. J Antibiot 19, 200–209.
**ang, S.H., Li, J., Yin, H., Zheng, J.T., Yang, X., Wang, H.B., Luo, J.L., Bai, H., and Yang, K.Q. (2009). Application of a double-reporter-guided mutant selection method to improve clavulanic acid production in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Metab Eng 11, 310–318.
Yanai, K., Murakami, T., and Bibb, M. (2006). Amplification of the entire kanamycin biosynthetic gene cluster during empirical strain improvement of Streptomyces kanamyceticus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 9661–9666.
Zhou, T.C., Kim, B.G., and Zhong, J.J. (2014). Enhanced production of validamycin A in Streptomyces hygroscopicus 5008 by engineering validamycin biosynthetic gene cluster. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 7911–7922.
Zhu, X., Kong, J., Yang, H., Huang, R., Huang, Y., Yang, D., Shen, B., and Duan, Y. (2018). Strain improvement by combined UV mutagenesis and ribosome engineering and subsequent fermentation optimization for enhanced 6′-deoxy-bleomycin Z production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 1651–1661.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC2100600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970072 and 31170088), and Biological Resources Programme, Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-BRP-009). We are grateful to Prof. Huarong Tan (Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for providing E. coli ET12567/pUZ8002, plasmids pIJ773 and pIJ778.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
11427_2021_1998_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Remarkable enhancement of bleomycin production through precise amplification of its biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces verticillus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Gao, W., Cui, Y. et al. Remarkable enhancement of bleomycin production through precise amplification of its biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces verticillus. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 1248–1256 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-1998-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-1998-8