Abstract
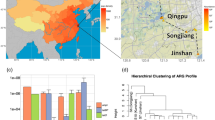
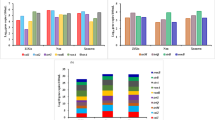
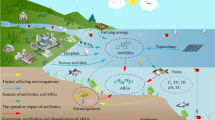
The massive use of antibiotics has led to the escalation of microbial resistance in aquatic environment, resulting in an increasing concern regarding antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), posing a serious threat to ecological safety and human health. In this study, surface water samples were collected at eight sampling sites along the Yangtze River Estuary. The seasonal and spatial distribution patterns of 10 antibiotics and target genes in two major classes (sulfonamides and tetracyclines) were analyzed. The findings indicated a high prevalence of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes along the Yangtze River Estuary. Kruskal–Wallis analysis revealed significant seasonal variations in the abundance of all target genes. The accumulation of antibiotic resistance genes in the coastal area of the Yangtze River Estuary can be attributed to the influence of urban instream runoff and the discharge of effluents from wastewater treatment plants. ANISOM analysis indicated significant seasonal differences in the microbial community structure. VPA showed that environmental factors contribute the most to ARG variation. PLS-PM demonstrate that environmental factors and microbial communities pose direct effect to ARG variation. Analysis of driving factors influencing ARGs in this study may shed new insights into the mechanism of the maintenance and propagation of ARGs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ali AM, Ronning HT, Alarif W, Kallenborn R, Al-Lihaibi SS (2017) Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in effluent-dominated Saudi Arabian coastal waters of the red sea. Chemosphere 175:505–513
Ashbolt NJ, Amezquita A, Backhaus T et al (2013) Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA) for environmental development and transfer of antibiotic resistance. Environ Health Perspect 121(9):993–1001
Berg J, Thorsen MK, Holm PE, Jensen J, Nybroe O, Brandt KK (2010) Cu exposure under field conditions coselects for antibiotic resistance as determined by a novel cultivation-independent bacterial community tolerance assay. Environ Sci Technol 44(22):8724
Boreen AL, Arnold WA, Mcneill K (2004) Photochemical fate of sulfa drugs in the aquatic environment: sulfa drugs containing five-membered heterocyclic groups. Environ Sci Technol 38(14):3933–3940
Chen H, Liu S, Xu XR, Liu SS, Zhou GJ, Sun KF, Zhao JL, Ying GG (2015) Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar Pollut Bull 90:181–187
Chen J, Su Z, Dai T, Huang B, Mu Q, Zhang Y, Wen D (2019) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of the East China Sea bays. J Environ Sci 81:156–167
Darby EM, Trampari E, Siasat P, Gaya MS, Alav L, Webber MA, Blair JMA (2022) Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance revisited. Nat Rev Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-022-00820-y
de Bentzmann S, Plesiat P (2011) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa opportunistic pathogen and human infections. Environ. Microbiol 13(7):1655–1665
Du J, Zhao HX, Liu SS, **e HJ, Wang Y, Chen JW (2017) Antibiotics in the coastal water of the South Yellow Sea in China: occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Sci Total Environ 595:521–527
Freedman Z, Zak DR (2014) Atmospheric N deposition increases bacterial laccase-like multicopper oxidases: implications for organic matter decay. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:4460–4468
Gomez-Smith CK, LaPara TM, Hozalski RM (2015) Sulfate reducing bacteria and Mycobacteria dominate the biofilm communities in a chloraminated drinking water distribution system. Environ Sci Technol 49(14):8432–8440
Guo JH, Li J, Chen H, Bond PL, Yuan ZG (2017) Metagenomic analysis reveals wastewater treatment plants as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements. Water Res 123:468–478
Guo XP, **g L, Fan Y, Jie Y, Yin DQ (2014) Prevalence of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in drinking water treatment plants in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci Total Environ 493:626–631
Guo XP, Lu DP, Niu ZS, Feng JN, Chen YR, Tou FY, Liu M, Yang Y (2018a) Bacterial community structure in response to environmental impacts in the intertidal sediments along the Yangtze Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 126:141–149
Guo XP, Liu X, Niu ZS, Lu DP, Zhao S, Sun XL, Wu JY, Chen YR, Tou FY, Hou L, Liu M, Yang Y (2018b) Seasonal and spatial distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments along the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ Pollut 242:576–584
Guo XP, Yang Y, Lu DP, Niu ZS, Feng JN, Chen YR, Tou FY, Garner E, Xu J, Liu M, Hochella MF Jr (2018c) Biofilms as a sink for antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the Yangtze Estuary. Water Res 129:277–286
Hawkey PM, Jones AM (2009) The changing epidemiology of resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother 64(4):3–10
He LY, Liu YS, Su HC, Zhao JL, Liu SS, Chen J, Liu WR, Ying GG (2014) Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in representative broiler feedlots environments: identification of indicator ARGs and correlations with environmental variables. Environ Sci Technol 48(22):13120–13129
Hu J, Shi J, Chang H, Li D, Yang M, Kamagata Y (2008) Phenoty** and genoty** of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from a natural river basin. Environ Sci Technol 42:3415–3420
Hu S, Liu X, Peng Y (2003) Assessment of antibiotic prescription in hospitalized patients at a Chinese university hospital. J Infect 46:161–163
Huang YH, Liu Y, Du PP, Zeng LJ, Mo CH, Li YW, Lü HX, Cai QY (2019) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes in water and sediments of urban rivers with black-odor water in Guangzhou, south China. Sci Total Environ 670:170–180
Jiang L, Hu X, Xu T, Zhang H, Sheng D, Yin D (2013) Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and their relationship with antibiotics in the Huangpu River and the drinking water sources, Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 458:267–272
Jiang L, Hu XL, Yin DQ, Zhang HC, Yu ZY (2011) Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 82:822–828
Jiao N, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Gardner WD, Mishonov AV, Richardson MJ, Hong N, Pan D, Yan XH, Jo YH, Chen CTA, Wang P, Chen X, Huang B, Deng H, Shi Y, Yang D (2007) Ecological anomalies in the East China Sea: impacts of the three gorges dam? Water Res 41(6):1287–1293
Ke YC, Sun WJ, **g ZB, Zhao ZN, **e SG (2023) Seasonal variations of microbial community and antibiotic resistome in a suburb drinking water distribution system in a northern Chinese city. J Environ Sci 127:714–725
Kheiri R, Akhtari L (2016) Antimicrobial resistance and integron gene cassette arrays in commensal Escherichia coli, from human and animal sources in IRI. Gut Pathogens 8(1):40
Larsson DGJ, Flach CF (2022) Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat Rev Microbiol 20:257–269
Li H, Li S, Tang W, Yang Y, Zhao J, **a S, Zhang W, Wang H (2018) Influence of secondary water supply systems on microbial community structure and opportunistic pathogen gene markers. Water Res 136:160–168
Li P, Wu Y, He Y, Zhang B, Huang Y, Yuan Q, Chen Y (2020) Occurrence and fate of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in a reservoir with ecological purification facilities for drinking water sources. Sci Total Environ 707:135276
Li TJ, Yu XY, Li M, Rong LL, **ao XY, Zou XM (2023) Ecological insight into antibiotic resistome of ion-adsorption rare earth mining soils from south China by metagenomic analysis. Sci Total Environ 872:162265
Liu SG, Xu QH, Lou S, Tu JB, Yin WJ, Li X, ** YC, Radnaeva LD, Nikitina E, Makhinov AN, Araruna JT, Fedorova IV (2023) Spatiotemporal distributions of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes and microbial communities in the coastal areas of the Yangtze River Estuary. Ecotox Environ Safe 259:115025
Lu J, Zhang YX, Wu J, Wang JH, Zhang C, Lin YC (2019) Occurrence and spatial distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea areas, China. Environ Pollut 252(Part A):450–460
Lu Z, Na G, Hui G, Wang L, Bao C, Yao Z (2015) Fate of sulfonamide resistance genes in estuary environment and effect of anthropogenic activities. Sci Total Environ 527–528:429–438
Luo X, Zhang WL, Yuan LX, Man XU, Lei HE, Jiang YF, Zhong WZ, Zhang Y (2019) Correlation between resistance genes and microbial community in polluted rivers. China Environ Sci 39(6):2606–2613
Luo Y, Mao D, Rysz M, Zhou Q, Alvarez P (2010a) Trends in antibiotic resistance genes occurrence in the Haihe River. China Environ Sci Technol 44(19):7220–7225. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100233w
Luo Y, Mao D, Rysz M, Zhou Q, Zhang H, Xu L, Alvarez PJJ (2010b) Trends in antibiotic resistance genes occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ Sci Technol 44:7220–7225
Mckinney CW, Loftin KA, Meyer MT, Davis JG, Pruden A (2010) tet and sul antibiotic resistance genes in livestock lagoons of various operation type, configuration, and antibiotic occurrence. Environ Sci Technol 44(16):6102–6109
Pei RT, Cha JM, Caelson KH (2007) Response of antibiotic resistance genes (ARG) to biological treatment in dairy lagoon water. Environ Sci Technol 41(14):5108–5113
Peng XZ, Zhang K, Tang CM, Huang QX, Cui JL (2011) Distribution pattern, behavior, and fate of antibacterials in urban aquatic environments in south China. J Environ Monit 13(2):446–454
Peng Y, Li L, Wu D, Yang PJ, Peng XY, Wang XM (2022) Metagenomic analysis on the responses of microbial community to ammonia stress. China Environ Sci 42(2):777–786
Pruden A, Pei R, Storteboom H, Carlson KH (2006) Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: studies in Northern Colorado. Environ Sci Technol 40(23):7445–7450
Roberts MC (2005) Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 245:195–203
Schmeller DS, Loyau A, Bao K, Brack W, Chatzinotas A, De Vleeschouwer F, Friesen J, Gandois L, Hansson SV, Haver M, Le Roux G, Shen J, Teisserenc R, Vredenburg VT (2018) People, pollution and pathogens - global change impacts in mountain freshwater ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 622–623:756–763
Sharma VK, Johnson N, Cizmas L, Mcdonald TJ, Kim H (2016) A review of the influence of treatment strategies on antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes. Chemosphere 150:702–714
Skold O (2000) Sulfonamide resistance: mechanisms and trends. Drug Resist Updat 3(3):155–160
Stalder T, Barraud O, Casellas M, Dagot C, Ploy MC (2012) Integron involvement in environmental spread of antibiotic resistance. Front Microbiol 3:199
Su JQ, Wei B, Ou-Yang WY, Huang FY, Zhao Y, Xu HJ, Zhu YG (2015) Antibiotic resistome and its association with bacterial communities during sewage sludge composting. Environ Sci Technol 49(12):7356–7363
Sunagawa S, Coelho LP, Chaffron S, Kultima JR, Labadie K, Salazar G, Djahanschiri B, Zeller G, Mende DR, Alberti A, Cornejo-Castillo FM, Costea PI, Cruaud C, d’Ovidio F, Engelen S, Ferrera I, Gasol JM, Guidi L, Hildebrand F, Kokoszka F, Lepoivre C, Lima-Mendez G, Poulain J, Poulos BT, Royo-Llonch M, Sarmento H, Vieira-Silva S, Dimier C, Picheral M, Searson S, Kandels-Lewis S, Tara Oceans coordinators, Bowler C, de Vargas C, Gorsky G, Grimsley N, Hingamp P, Iudicone D, Jaillon O, Not F, Ogata H, Pesant S, Speich S, Stemmann L, Sullivan MB, Weissenbach J, Wincker P, Karsenti E, Raes J, Acinas SG, Bork P (2015) Ocean plankton. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 348(6237)1261359
Tao Y, Dai T, Huang B, Wen D (2016) The impact of wastewater treatment effluent on microbial biomasses and diversities in coastal sediment microcosms of hangzhou bay. Mar Pollut Bull 144(1):355–363
Tenenhaus M, Vinzi VE, Chatelin Y-M, Lauro C (2005) PLS path modeling. Comput Stat Data Anal 48(1):159–205
Thiele-Bruhn S (2003) Pharmaceutical antibiotic compounds in soils - a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166(2):145–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200390023
Treeck UV, Schmidt F, Wiedemann B (1981) Molecular nature of a streptomycin and sulfonamide resistance plasmid (pBP1) prevalent in clinical Escherichia coli strains and integration of an ampicillin resistance transposon (TnA). Antimicrob Agents Chemother 19(3):371–380
Wang GG, Zhou SH, Han XK, Zhang LL, Ding SY, Li Y, Zhang DJ, Zarin K (2020a) Occurrence, distribution, and source track of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the main rivers of Chongqing City, Southwest China. J Hazard Mater 389:122110
Wang JH, Lu J, Wu J, Feng YX (2022) Seasonal distribution of antibiotic resistance genes under the influence of land-ocean interaction in a semi-enclosed bay. Chemosphere 301:134718
Wang Z, Han M, Li E, Liu X, Ning K (2020b) Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in an agriculturally disturbed lake in China: their links with microbial communities, antibiotics, and water quality. J Hazard Mater 393:122426
Wu JJ, Su YL, Deng YQ, Guo ZX, Mao C, Liu GF, Xu LW, Cheng CH, Bei L, Feng J (2019) Prevalence and distribution of antibiotic resistance in marine fish farming areas in Hainan, China. Sci Total Environ 653:605–611
Xu BJ, Luo Y, Zhou QX, Mao DQ (2010) Sources, dissemination, and ecological risks of antibiotic resistances genes (ARGs) in the environment. Environ Chem 29(2):169–178
Xu QH, Liu SG, Lou S, Radnaeva LD, Nikitina E, Nikolavich MA, Tavares AJ, ** YC, Li X (2023) Distributions of antibiotic resistance genes and microbial communities in the nearshore area of the Yangtze River Estuary. Environ Sci 44(1):158–168. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202203160
Xu T, Zhao WT, Guo XP, Zhang HZ, Yin DQ (2019) Characteristics of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in Qingcaosha Reservoir in Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ Sci Eur 32:82
Yan M, Xu C, Huang Y, Nie H, Wang J (2018) Tetracyclines, sulfonamides and quinolones and their corresponding resistance genes in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ S 631–632:840–848
Yu QL, Feng TS, Yang JW, Su WH, Zhou R, Wang YJ, Zhang H, Li H (2022) Seasonal distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the Yellow River water and tap water, and their potential transmission from water to human. Environ Pollut 292:118304.1-118304.13
Zhang J, Zhang ZF, Liu SM, Wu Y, **ong H, Chen HT (1999) Human impacts on the large world rivers: would the Changjiang (Yangtze River) be an illustration. Global Biogeochem Cycles 13(4):1099–1105
Zhang L, Gu J, Wang XJ, Sun W, Yin Y, Sun YX, Guo AY, Tuo XX (2017a) Behavior of antibiotic resistance genes during co-composting of swine manure with Chinese medicinal herbal residues. Bioresour Technol 244:252–260
Zhang L, Yan C, Wang D, Zhen Z (2022) Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of antibiotic resistance genes in constructed wetlands and associated influencing factors. Environ Pollut 303:119176
Zhang RJ, Tang JH, Li J, Cheng ZN, Chaemfa C, Liu DY, Zheng Q, Song M, Luo CL, Zhang G (2013) Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the coastal aquatic environment of the Yellow Sea, north China. Sci Total Environ 450–451:197–204
Zhang RJ, Zhang RL, Yu K, Wang YH, Huang XY, Pei JY, Wei CS, Pan ZL, Qin ZJ, Zhang G (2017b) Occurrence, sources and transport of antibiotics in the surface water of coral reef regions in the South China Sea: potential risk to coral growth. Environ Pollut 232:450–457
Zhang YP, Niu ZG, Zhang Y, Zhang K (2018) Occurrence of intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes in coastal areas of Bohai Bay (China) and the factors affecting them. Environ Pollut 236:126–136
Zheng J, Gao R, Wei Y, Chen T, Fan J, Zhou Z, Makimilua TB, Jiao Y, Chen H (2017) High-throughput profiling and analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in East Tiaoxi River, China. Environ Pollut 230:648–654
Zheng SL, Qiu XY, Chen B, Yu XG, Liu ZH, Zhong GP, Li HY, Chen M, Sun GD, Huang H, Yu WW, Freestone D (2011) Antibiotics pollution in Jiulong River Estuary: source, distribution and bacterial resistance. Chemosphere 84(11):1677–1685
Zhou L, Liu L, Chen WY, Sun JJ, Hou SW, Kuang TX, Wang WX, Huang XD (2020) Stochastic determination of the spatial variation of potentially pathogenic bacteria communities in a large subtropical river. Environ Pollut 264:114683
Zhu YG, Zhao Y, Li B, Huang CL, Zhang SY, Yu S, Chen YS, Zhang T, Gillings MR, Su JQ (2017) Continental-scale pollution of estuaries with antibiotic resistance genes. Nat Microbiol 2:16270
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42072281, 41602244, 51961145106), Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Projects (22230712900, 22ZR1464200, 20230742500), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (22120210576), Top Discipline Plan of Shanghai Universities-Class I (2022–3-YB-03), and Interdisciplinary Project in Ocean Research of Tongji University (2022–2-YB-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiuhong Xu: data curation, methodology, writing—original draft. Shuguang Liu: conceptualization, software. Sha Lou: methodology, writing—review and editing. Junbiao Tu: investigation. **n Li: investigation. Yuchen **: investigation. Wenjun Yin: investigation. Larisa Dorzhievna Radnaeva: investigation. Elena Nikitina: investigation. Aleksei Nikolavich Makhinov: methodology, writing—reviewing and editing. José Tavares Araruna: writing—reviewing and editing. Irina Viktorovna Fedorova: writing—reviewing and editing. All authors have read and approved this version of the article, and due care has been taken to ensure the integrity of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study does not involve any ethical issues.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Liu, S., Lou, S. et al. Typical antibiotic resistance genes and their association with driving factors in the coastal areas of Yangtze River Estuary. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 30440–30453 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33198-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33198-w