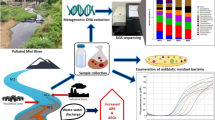
Abstract
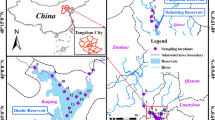
Wanfeng Lake, a highland lake in the upper part of the Pearl River Basin, China, has long been disturbed by aquaculture and human activities, resulting in the accumulation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), which pose a major threat to humans and animals. In this study, 20 antibiotics, 9 ARGs, 2 mobile genetic elements (intl1 and intl2), and microbial community structure were investigated in Wanfeng Lake. The results of the study showed that the total concentration of antibiotics in surface water was 372.72 ng/L, with ofloxacin (OFX) having the highest concentration (169.48 ng/L), posing a high ecological risk to aquatic organisms. The total concentration of antibiotics in sediments was 235.86 ng/g, with flumequine (FLU) having the highest concentration (122.54 ng/g). This indicates that the main type of antibiotics in Wanfeng Lake are quinolones. QPCR analysis results of the relative abundance of ARGs in both surface water and sediments showed that sulfonamide resistance genes > macrolide resistance genes > tetracycline resistance genes > quinolone resistance genes, indicating that sulfonamide resistance genes were the dominant type. The metagenomic results showed that the predominant microorganisms in the sediment under the phylum level were Planctomycetes, Proteobacteria, Euryarchaeota, and Chloroflexi. Pearson’s correlation analysis showed a significantly positive correlation between antibiotics and environmental factors with ARGs in Wanfeng Lake and a significant positive correlation between antibiotics and ARGs with microorganisms in sediments. This suggests that there is a potential pressure of antibiotics on ARGs, while microorganisms provide the driving force for the evolution and spread of ARGs. This study provides a basis for further research on the occurrence and spread of antibiotics and ARGs in Wanfeng Lake.
Graphical Abstract
A total of 14 antibiotics were detected in surface water and sediments. OFX poses a high ecological risk in all points of surface water. Antibiotics and ARGs were significantly positively correlated in Wanfeng Lake. Antibiotics and ARGs in sediments were positively correlated with microorganisms








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that [the/all other] data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Bai Y, Ruan XH, Li RF, Zhang YP, Wang ZZ (2021) Metagenomics-based antibiotic resistance genes diversity and prevalence risk revealed by pathogenic bacterial host in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Geochem Health 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01021-x
Benjamin B, Chao X, Huson H (2015). Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3176
Chakraborty J, Sapkale V, Shah M, Rajput V, Mehetre G, Agawane S, Kamble S, Dharne M (2020) Metagenome sequencing to unveil microbial community composition and prevalence of antibiotic and metal resistance genes in hypersaline and hyperalkaline Lonar Lake, India. Ecol Indic 110:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105827
Chen CQ, Zheng L, Zhou JL, Zhao H (2017) Persistence and risk of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in major mariculture sites in Southeast China. Sci Total Environ 580:1175–1184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.075
Chen HY, **g LJ, Yao ZP, Meng FS, Teng YG (2019) Prevalence, source and risk of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of Lake Tai (China) deciphered by metagenomic assembly: a comparison with other global lakes. Environ Int 127:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.048
Chen JM, Sun RX, Pan CG, Sun Y, Mai BX, Li QX (2020a) Antibiotics and food safety in aquaculture. J Agric Food Chem 68(43):11908–11919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03996
Chen Y, Hu C, Qu JH, Yang M (2008) Photodegradation of tetracycline and formation of reactive oxygen species in aqueous tetracycline solution under simulated sunlight irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A-Chem 197(1):81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.12.007
Chen Y, Shen W, Wang B, Zhao X, Su L, Kong M, Li H, Zhang S, Li J (2020b) Occurrence and fate of antibiotics, antimicrobial resistance determinants and potential human pathogens in a wastewater treatment plant and their effects on receiving waters in Nan**g, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111371
Cheng J, Tang X, Liu C (2020) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in various rural environmental media. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(23). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09287-x
Chenxi F, Huijun D, Qianqian Z, Yaqiong S, Yuguang W, Yao W, Boming W, Jiaxuan G, Min Q (2022) Comparative analysis of antibiotic resistance genes on a pig farm and its neighboring fish ponds in a lakeside district. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex : 1987) 303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119180
Conde-Cid M, Núñez-Delgado A, Fernández-Sanjurjo MJ, Álvarez-Rodríguez E, Fernández-Calviño D, Arias-Estévez M (2020) Tetracycline and sulfonamide antibiotics in soils: presence, fate and environmental risks. Processes 8(11):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111479
Danner MC, Robertson A, Behrends V, Reiss J (2019) Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: occurrence and effects. Sci Total Environ 664:793–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.406
Ding HJ, Wu YX, Zhang WH, Zhong JY, Lou Q, Yang P, Fang YY (2017) Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 184:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.148
Du CL, Yang F, Li XG, Liao HQ, Li ZH, Gao JY, Zhang LY (2022) Metagenomic analysis of microbial community structure and distribution of resistance genes in Daihai Lake, China. Environ Pollut 302:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119065
Dunivin TK, Shade A (2018) Community structure explains antibiotic resistance gene dynamics over a temperature gradient in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94(3):9. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiy016
Engemann CA, Keen PL, Knapp CW, Hall KJ, Graham DW (2008) Fate of tetracycline resistance genes in aquatic systems: migration from the water column to peripheral biofilms. Environ Sci Technol 42(14):5131–5136. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800238e
Feng Y, Zhang WJ, Liu YW, Xue JM, Zhang SQ, Li ZJ (2018) A Simple, sensitive, and reliable method for the simultaneous determination of multiple antibiotics in vegetables through SPE-HPLC-MS/MS. Molecules 23(8):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081953
Gillings MR, Gaze WH, Pruden A, Smalla K, Tiedje JM, Zhu YG (2015) Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J 9(6):1269–1279. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.226
Guo XC, Song RR, Lu SY, Liu XH, Chen JM, Wan ZF, Bi B (2022) Multi-media occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in East Dongting Lake. Front Environ Sci 10:12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.866332
Han QF, Zhao S, Zhang XR, Wang XL, Song C, Wang SG (2020) Distribution, combined pollution and risk assessment of antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding the Yellow Sea, North China. Environ Int 138:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105551
Hossain A, HabibullahAlMamun M, Nagano I, Masunaga S, Kitazawa D, Matsuda H (2022) Antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: risks, current concern, and future thinking. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17825-4
Huang L, Xu YB, Xu JX, Ling JY, Chen JL, Zhou JL, Zheng L, Du QP (2017) Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in duck and fish production ponds with integrated or non-integrated mode. Chemosphere 168:1107–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.096
Huang W, Chen X, Wang K, Chen JY, Zheng BH, Jiang X (2019) Comparison among the microbial communities in the lake, lake wetland, and estuary sediments of a plain river network. Microbiologyopen 8(2):13. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.644
Jednacak T, Mikulandra I, Novak P (2020) Advanced methods for studying structure and interactions of macrolide antibiotics. Int J Mol Sci 21(20):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207799
Ji XL, Shen QH, Liu F, Ma J, Xu G, Wang YL, Wu MH (2012) Antibiotic resistance gene abundances associated with antibiotics and heavy metals in animal manures and agricultural soils adjacent to feedlots in Shanghai; China. J Hazard Mater 235:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.07.040
Jia J, Guan YJ, Cheng MQ, Chen H, He JF, Wang S, Wang ZZ (2018) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in Ba River, China. Sci Total Environ 642:1136–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.149
Kerrigan J, Sandberg KD, Engstorm DR, LaPara TM, Arnold WA (2018) Sedimentary record of antibiotic accumulation in Minnesota Lakes. Sci Total Environ 621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.130
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36(6):1202–1211. https://doi.org/10.1021/es011055j
Kong M, **ng LQ, Yan RM, Li J, Zhang YM, Li AM, Zhang T (2022) Spatiotemporal variations and ecological risks of typical antibiotics in rivers inflowing into Taihu Lake, China. J Environ Manag 309:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114699
Kummerer K (2009) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment - a review - Part I. Chemosphere 75(4):417–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.086
Lau CHF, Tien YC, Stedtfeld RD, Topp E (2020) Impacts of multi-year field exposure of agricultural soil to macrolide antibiotics on the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes and selected mobile genetic elements. Sci Total Environ 727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138520
Lei XN, Lu JJ, Liu ZL, Tong YB, Li SM (2015) Concentration and distribution of antibiotics in water-sediment system of Bosten Lake, **njiang. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(3):1670–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2994-5
Leonard A, Zhang L, Balfour A, Garside R, Hawkey P, Aimee K, Murray O, Gaze U (2018) Exposure to and colonisation by antibiotic-resistant E. coli in UK coastal water users: environmental surveillance, exposure assessment, and epidemiological study. Environ Int 114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.11.003
Li WH, Shi YL, Gao LH, Liu JM, Cai YQ (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 89(11):1307–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.079
Li L, D Liu Q, Zhang K, Song XH, Zhou Z, Tang X (2019) Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of selected antibiotics in the freshwater lakes along the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River Basin. J Environ Manag 249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109396
Li YC, Huang C, Yang XL, Zhang X (2020) Ofloxacin laden microemulsion contact lens to treat conjunctivitis. J Biomater Sci-Polym Ed 31(12):1566–1579. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2020.1764165
Liang HB, Wang F, Mu R, Huang J, Zhao RX, Li XY, Yu K, Li B (2021) Metagenomics analysis revealing the occurrence of antibiotic resistome in salt lakes. Sci Total Environ 790:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148262
Liang XM, Guan FL, Chen BW, Luo PY, Guo CF, Wu GQ, Ye Y, Zhou QB, Fang HS (2020) Spatial and seasonal variations of antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotics in the surface waters of Poyang Lake in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 196:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110543
Liu N, ** XW, Feng CL, Wang ZJ, Wu FC, Johnson AC, **ao HX, Hollert H, Giesy JP (2020) Ecological risk assessment of fifty pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Chinese surface waters: a proposed multiple-level system. Environ Int 136:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105454
Liu XH, Lu SY, Guo W, ** BD, Wang WL (2018a) Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: a review of lakes, China. Sci Total Environ 627:1195–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.271
Liu XH, Lu SY, Meng W, Wang WL (2018b) Occurrence, source, and ecological risk of antibiotics in Dongting Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(11):11063–11073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1290-1
Lyautey E, Bonnineau C, Billard P, Loizeau J, Naffrechoux E, Tlili A, Topp E, Ferrari B, Pesce S (2021) Diversity, functions and antibiotic resistance of sediment microbial communities from Lake Geneva are driven by the spatial distribution of anthropogenic contamination. Front Microbiol 12:10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.738629
Lu LH, Liu J, Li Z, Zou X, Guo JS, Liu ZP, Yang JX, Zhou YY (2020) Antibiotic resistance gene abundances associated with heavy metals and antibiotics in the sediments of Changshou Lake in the three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Ecol Indic 113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106275
Luo Y, Mao DQ, Rysz M, Zhou DX, Zhang HJ, Xu L, Alvarez PJJ (2010) Trends in antibiotic resistance genes occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ Sci Technol 44(19):7220–7225. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100233w
Minato Y, Dawadi S, Kordus SL, Sivanandam A, Aldrich CC, Baughn AD (2018) Mutual potentiation drives synergy between trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. Nat Commun 9:7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03447-x
Ngoc H, Lan H, Long D, Nu M, Huu H, Wenshan G, Quang T,Nam H, Huiting C, Dinh D, Thi T, Karina Y (2019) Occurrence and risk assessment of multiple classes of antibiotics in urban canals and lakes in Hanoi, Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 692(C). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.092
Pan X, Lin L, Zhang WH, Dong L, Yang YY (2020) Metagenome sequencing to unveil the resistome in a deep subtropical lake on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China. Environ Pollut 263:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114470
Pearman J, Biessy L, Thomson G, Waters S, Vandergoes M, Howarth J, Rees A, Moy C, Pochon X, Wood S (2020) Local factors drive bacterial and microeukaryotic community composition in lake surface sediment collected across an altitudinal gradient. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 96(6). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiaa070
Qi Z, Le Z, Han F, Qi Y, Liu R (2022) β-lactamase genes transmission influenced by tetracycline, sulfonamide and β-lactams antibiotics contamination in the on-site farm soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113753
Ramanan L, Devi S, Martin B, Minggui W, Mark W (2016) Achieving global targets for antimicrobial resistance. Science 353(6302). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf9286
Partridge S, Tsafnat G, Coiera E, Iredell J (2005) Gene cassettes and cassette arrays in mobile resistance integrons. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33(4). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00175.x
Peak N, Knapp CW, Yang RK, Hanfelt MM, Smith MS, Aga DS, Graham DW (2007) Abundance of six tetracycline resistance genes in wastewater lagoons at cattle feedlots with different antibiotic use strategies. Environ Microbiol 9(1):143–151. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01123.x
Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Chamorro S, Marti E, Huerta B, Gros M, Sanchez-Melsio A, Borrego CM, Barcelo D, Balcazar JL (2015) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res 69:234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.11.021
Rodriguez-Verdugo A, Gaut BS, Tenaillon O (2013) Evolution of Escherichia coli rifampicin resistance in an antibiotic-free environment during thermal stress. BMC Evol Biol 13:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-50
Rytwo G, Zelkind AL (2022) Evaluation of kinetic pseudo-order in the photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin. Catalysts 12(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010024
Sandalli C, Ozgumus O, Sevim A (2013) Characterization of tetracycline resistance genes in tetracycline-resistant Enterobacteriaceae obtained from a coliform collection. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0381-z
Sanganyado E, Gwenzi W (2019) Antibiotic resistance in drinking water systems: occurrence, removal, and human health risks. Sci Total Environ 669:785–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.162
Satoru S, Phan T 2012 Distribution of quinolones, sulfonamides, tetracyclines in aquatic environment and antibiotic resistance in Indochina. Front Microbiol 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00067
Shah SQA, Cabello FC, L’Abee-Lund TM, Tomova A, Godfrey HP, Buschmann AH, Sorum H (2014) Antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial resistance genes in marine bacteria from salmon aquaculture and non-aquaculture sites. Environ Microbiol 16(5):1310–1320. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12421
Sirtori C, Aguera A, Gernjak W, Malato S (2010) Effect of water-matrix composition on Trimethoprim solar photodegradation kinetics and pathways. Water Res 44(9):2735–2744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.006
Suhartono S, Savin MC, Gbur EE (2018) Transmissible plasmids and integrons shift Escherichia coli population toward larger multiple drug resistance numbers. Microb Drug Resist 24(3):244–252. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2016.0329
Szekeres E, Chiriac CM, Baricz A, Szoke-Nagy T, Lung I, Soran ML, Rudi K, Dragos N, Coman C (2018) Investigating antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and microbial contaminants in groundwater in relation to the proximity of urban areas. Environ Pollut 236:734–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.107
Tang K, Zhao H 2023) Quinolone antibiotics: resistance and therapy. Infect Drug Resist 16. https://doi.org/10.2147/idr.s401663
Tang J, Shi TZ, Wu XW, Cao HQ, Li XD, Hua RM, Tang F, Yue YD (2015) The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in Lake Chaohu, China: seasonal variation, potential source and risk assessment. Chemosphere 122:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.032
Tong L, Qin LT, Guan C, Wilson ME, Li XJ, Cheng DD, Ma J, Liu H, Gong FJ (2020) Antibiotic resistance gene profiling in response to antibiotic usage and environmental factors in the surface water and groundwater of Honghu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(25):31995–32005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09487-5
Tuc DQ, Elodie MG, Pierre L, Fabrice A, Marie-Jeanne T, Martine B, Joelle E, Marc C (2017) Fate of antibiotics from hospital and domestic sources in a sewage network. Sci Total Environ 575:758–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.118
Vindenes T, Beaulac KR, Doron S (2016) The legislative momentum of antimicrobial stewardship: an international perspective. Curr Treat Options Infect Dis 8(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40506-016-0072-x
Wang C, Liu XH, Yang YY, Wang Z (2021a) Antibiotic and antibiotic resistance genes in freshwater aquaculture ponds in China: a meta-analysis and assessment. J Clean Prod 329:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129719
Wang PL, Wu D, You XX, Su YL, **e B (2021b) Antibiotic and metal resistance genes are closely linked with nitrogen-processing functions in municipal solid waste landfills. J Hazard Mater 403:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123689
Wang RM, Ji M, Zhai HY, Guo YJ, Liu Y (2021c) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in WWTP effluent-receiving water bodies and reclaimed wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 796:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148919
Wang YQ, Lu SY, Liu XH, Chen J, Han MZ, Wang Z, Guo W (2021d) Profiles of antibiotic resistance genes in an inland salt-lake Ebinur Lake, **njiang, China: the relationship with antibiotics, environmental factors, and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 221:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112427
Wu Y, Yu CP, Yue M, Liu SP, Yang XY (2016) Occurrence of selected PPCPs and sulfonamide resistance genes associated with heavy metals pollution in surface sediments from Chao Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 75(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4838-0
Wu T, Zhang Y, Wang B, Chen C, Cheng Z, Li Y, Wang B, Li J (2022) Antibiotic resistance genes in Chishui River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, China: occurrence, seasonal variation and its relationships with antibiotics, heavy metals and microbial communities. Sci Total Environ 846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157472
Wang JB, Li X, Zhou ZW, Fan XY (2019) Bacterial communities, metabolic functions and resistance genes to antibiotics and metals in two saline seafood wastewater treatment systems. Biores Technol 287:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121460
Xu Y, Guo CS, Luo Y, Lv JP, Zhang Y, Lin HX, Wang L, Xu J (2016) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes in the urban rivers in Bei**g, China. Environ Pollut 213:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.054
Xu ZA, Li T, Bi J, Wang C (2018) Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of antibiotic pollution and ecological risk assessment in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci Total Environ 643:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.175
Yang YY, Liu WZ, Xu C, Wei BQ, Wang J (2017) Antibiotic resistance genes in lakes from middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China: effect of land use and sediment characteristics. Chemosphere 178:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.041
Zhang GD, Lu SY, Wang YQ, Liu XH, Liu Y, Xu JM, Zhang TT, Wang Z, Yang Y (2020a) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes and their correlations in lower Yangtze River, China. Environ Pollut 257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113365
Zhang GD, Liu XH, Lu SY, Zhang J, Wang W (2020b) Occurrence of typical antibiotics in Nansi Lake’s inflowing rivers and antibiotic source contribution to Nansi Lake based on principal component analysis-multiple linear regression model. Chemosphere 242(C). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125269
Zhang JY, Chen MX, Sui QW, Tong J, Jiang C, Lu XT, Zhang YX, Wei YS (2016) Impacts of addition of natural zeolite or a nitrification inhibitor on antibiotic resistance genes during sludge composting. Water Res 91:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.010
Zhang QQ, Ying GG, Pan CG, Liu YS, Zhao JL (2015) Comprehensive Evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ Sci Technol 49(11):6772–6782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00729
Zhao B, Xu JM, Zhang GD, Lu SY, Liu XH, Li LX, Li M (2021) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the Fuxian Lake and antibiotic source analysis based on principal component analysis-multiple linear regression model. Chemosphere 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127741
Zhi W, Maozhen H, Enhua L, ** L, Huimin W, Chao Y, Shaoyong L, Kang N (2020) Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in an agriculturally disturbed lake in China: their links with microbial communities, antibiotics, and water quality. J Hazard Mater 393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122426
Zhou L, Limbu S, Shen M, Zhai W, Qiao F, He A, Du Z, Zhang M (2018) Environmental concentrations of antibiotics impair zebrafish gut health. Environ Pollut 235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.073
Acknowledgements
This study is grateful to all reviewers for their valuable comments on the article, and to everyone who funded the research.
Funding
This research has been supported by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guizhou Province (No. (QKZYD [2022]4022), [2020]1Z051 and QKHJC-ZK[2022]YB102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuntao Zhang: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft. Jiang Li: supervision, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, project administration. Tianyu Wu: data curation and writing—reviewing. Kai Ma: sample analysis. Zhentao Cheng: methodology. Qianwen Yi: data curation. Yongheng Dai: software. Bin Wang: writing—reviewing and editing. Yu Chen: writing—reviewing and editing. Bin Wang: writing—reviewing and editing. **a Hu: investigation. Aijiang Yang: Investigation. Qi Yang: investigation. **ong Zhong: investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to publish this research (including any individual details, images or videos) in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, J., Wu, T. et al. Characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes and microbial community distribution in Wanfeng Lake, upper Pearl River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 83214–83230 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28158-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28158-9