Abstract
In order to verify how environmental regulation affects the improvement of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency, this study first measures the balanced panel data of industrial carbon emission efficiency of 282 cities in China from 2003 to 2019, and evaluates the direct and regulating impact of environmental regulation on China’s urban industrial carbon emission efficiency. Meanwhile, in order to investigate the potential heterogeneity and asymmetry, the panel quantile regression method is used. The empirical results show that (1) during the period 2003–2016, China’s overall industrial carbon emission efficiency showed a upward trend, with a decreasing spatial pattern from the east-central-west-northeast region. At the urban scale in China, environmental regulation has a significant direct effect on industrial carbon emission efficiency, which is lagged and heterogeneous. At the low quantiles, a one-period lag in environmental regulation has a negative effect on the improvement of industrial carbon emission efficiency. At the middle and high quantiles, a one-period lag in environmental regulation has a positive effect on the improvement of industrial carbon emission efficiency. Environmental regulation has a moderating effect on industrial carbon efficiency. With increasing industrial emission efficiency, the positive moderating effect of environmental regulation on the relationship between technological progress and industrial carbon emission efficiency shows a pattern of diminishing marginal benefits. The main contribution of this study is the systematic analysis of the potential heterogeneity and asymmetry of the direct and moderating effects of environmental regulation on the industrial carbon emission efficiency at the city scale in China by using panel quantile regression method.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during this study are available in the China Urban Statistical Yearbook, the China Energy Statistical Yearbook, from 2004 to 2017, and the China Industrial Enterprises Database and Patent Database Matching Data from 2003 to 2013.
References
Bassett KG Jr (1978) Regression quantiles. Econometrica 46:33–50
Bin X (2022) How to efficiently reduce the carbon intensity of the heavy industry in China? Using quantile regression approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19
Bin X, Chaoxia Y (2022) The impact of clean energy development on economic growth in China: from the perspectives of environmental regulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Cai H, Liu Q (2009) Competition and corporate tax avoidance: evidence from Chinese industrial firms. Econ J 119
Chen L, Xu L (2017) Dynamic tracks of industrial carbon emissions from energy consumption in Guangdong, China. J Environ Account Manag 5
Chen L, Xu L, Yang Z (2019) Inequality of industrial carbon emissions of the urban agglomeration and its peripheral cities: a case in the Pearl River Delta, China. Renew Sustain Energy Revi 109
Cheng Z, Liu J, Li L, Gu X (2020) The effect of environmental regulation on capacity utilization in China’s manufacturing industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:14807–14817
Conrad K, Wastl D (1996) The impact of environmental regulation on productivity in German industries. Empir Econ 20
Dasgupta S, Laplante B, Wang H, Wheeler D (2003) Confronting the environmental Kuznets curve. J Econ Perspect 16
Du W, Li M (2019) Influence of environmental regulation on promoting the low-carbon transformation of China’s foreign trade: based on the dual margin of export enterprise. J Clean Prod 244:118687
Eguchi S, Chen ME (2022) CO 2 Reduction potential from efficiency improvements in China's coal-fired thermal power generation: a combined approach of metafrontier DEA and LMDI
Feng T, Du H, Lin Z, Zuo J (2020) Spatial spillover effects of environmental regulations on air pollution: evidence from urban agglomerations in China. J Environ Manag 272
Feng W, **aoyu S, M. RD, Min W (2019) Changing trends of the elasticity of China's carbon emission intensity to industry structure and energy efficiency. Energy Econ 86
Galvao AF (2011) Quantile regression for dynamic panel data with fixed effects. J Econom 164
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1992) Environmental impacts of a north american free trade agreement. cepr discussion papers 8, 223–250
Guang-Qin LI, Liu L (2018) Environmental regulation,fiscal decentralization and green economic efficiency in China. East China Econ Manag
Guangming Y, Fan Z, Fengtai Z, Dalai M, Lei G, Ye C, Yao L, Qing Y (2021) Spatiotemporal changes in efficiency and influencing factors of China's industrial carbon emissions. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28
Guihuan Y, Liming J, Chongqing X (2022) How environmental regulation affects industrial green total factor productivity in China: the role of internal and external channels. Sustainability 14
Guo R, Yuan Y (2020) Different types of environmental regulations and heterogeneous influence on energy efficiency in the industrial sector: evidence from Chinese provincial data. Energy Policy 145
Hamamoto M (2006) Environmental regulation and the productivity of Japanese manufacturing industries. Resour Energy Econ 28:299–312
Hansen LP (1982) Large sample properties of generalized method of moments estimators. Econometrica 50
Hui Z, Xuejun D, Lei W, Tingting J (2022) The effects of environmental regulation on chemical industry location: evidence from the region along the Yangtze River, China. Growth Chang 53
Jaffe AB, Palmer KL Environmental regulation and innovation: a panel data study. Social Science Electronic Publishing
Jianmin Y, Wei Z (2022) How heterogeneous technological progress promotes industrial structure upgrading and industrial carbon efficiency? Evidence from China's industries. Energy 247
**g**g L, Ming Z (2020) Does environmental regulation promote green technology innovation in Chinese manufacturing? Open Access Library J 07
**gyi W, Kaisi S, Jiupai N, Deti X (2021) Evaluation and factor analysis of industrial carbon emission efficiency based on “green-technology efficiency”—the case of Yangtze River Basin, China. Land 10
Kaya, Yoichi/YOKOBORI, Keiichi Environment, nergy and economy: strategies for sustainability
Kaya Y (1990) Impact of carbon dioxide emission control on GNP growth: interpretation of proposed scenarios IPCC energy and industry subgroup, response strategies working group
Kedong Y, Lu L, Haolei G (2022) Green paradox or forced emission reduction—the dual effects of environmental regulation on carbon emissions. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19
Khanh CL, Huy TT (2022) The nexus between environmental regulation and ecological footprint in OECD countries: empirical evidence using panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29
Koenker R (2004) Quantile regression for longitudinal data. J Multivar Anal 91:74–89
Li Y, Chiu Y-h, Lin T-Y (2019) Energy and environmental efficiency in different Chinese regions. Sustainability 11
Lin B, Xu B (2018) Factors affecting CO2 emissions in China’s agriculture sector: a quantile regression. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 94:15–27
Lin B, Wang M (2019) Dynamic analysis of carbon dioxide emissions in China's petroleum refining and coking industry. Sci Total Environ 671
Liu LQ, Hao YX, Zhang S, Deng YZ, **e BC (2020) Environmental efficiency of China’s thermal power enterprises: a bootstrapped directional distance function with metafrontier approach. J Energy Eng 146:04020034
Long R, Shao T, Chen H (2016) Spatial econometric analysis of China’s province-level industrial carbon productivity and its influencing factors. Appl Energy 166
Lu Y (2020) An Empirical analysis on the nonlinear relationship between economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions in China. International journal of sustainable development and planning: Encouraging the unified approach to achieve sustainability
Lu Y, Li M (2020) Industrial carbon emission efficiency in the Yangtze River economic belt and its influencing factors. Int J Des Nat Ecodyn 15
Lu Z, Qiaoyu W, Ming Z (2021) Environmental regulation and CO2 emissions: based on strategic interaction of environmental governance. Ecol Complex 45
Matthias, BUSSE (2004) Trade, Environmental regulations and the world trade organization: new empirical evidence. J World Trade
Mielnik O, Goldemberg J (1999a) Communication the evolution of the “carbonization index” in develo** countries. Energy Policy 27:307–308
Mielnik O, Goldemberg J (1999b) The evolution of the ‘carbonization index’ in develo** countries. Fuel & Energy Abstracts. J Energy Policy 27(5):307–308
Millimet DL, Roy J (2016) Empirical tests of the pollution haven hypothesis when environmental regulation is endogenous. J Appl Econom
Ouyang Q, Wang T, Deng Y, Li Z, Atif J (2021) The impact of environmental regulations on export trade at provincial level in China: evidence from panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29
Ozcan B, Ozturk I (2019) Renewable energy consumption-economic growth nexus in emerging countries: a bootstrap panel causality test. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 104
Peng J, Song Y, Tu G, Liu Y (2021) A study of the dual-target corporate environmental behavior (DTCEB) of heavily polluting enterprises under different environment regulations: green innovation vs. pollutant emissions. J Clean Prod:126602
Powell D (2016) Quantile regression with nonadditive fixed effects. Social Science Electronic Publishing
Qing X, Mengqi Q, Haoran L, **aoru H (2022) Is environmental regulation works on improving industrial resilience of China? Learning from a provincial perspective. Energy Rep 8
Qingming Y, Baorong Z (2019) Study on the changes and influencing factors of industrial carbon emission in Bei**g-Tian**-Hebei region. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 384
Qiu Z, Wang Y, Economics SO (2018) The impact of environmental regulation on industrial ecological efficiency under the constraints of administrative monopoly:based on dynamic spatial durbin model and threshold effect. Ind Econ Res
Quocviet B, Zhaohua W, Bin Z, Phong LH, Dung VK (2021) Revisiting the biomass energy-economic growth linkage of BRICS countries: A panel quantile regression with fixed effects approach, 316
Rubashkina Y, Galeotti M, Verdolini E (2015) Environmental regulation and competitiveness: empirical evidence on the Porter Hypothesis from European manufacturing sectors. Energy Policy 83:288–300
Sea-**, Chang, Jaiho, Chung, Jon, Jungbien, Moon (2013) When do wholly owned subsidiaries perform better than joint ventures? Strat Manag J
Shadbegian RJ, Gray WB (2005) Pollution abatement expenditures and plant-level productivity: a production function approach. Ecol Econ 54:196–208
Shen J, Wei YD, Yang Z (2017) The impact of environmental regulations on the location of pollution-intensive industries in China. J Clean Prod 148
Sinn H-W (2008) Public policies against global warming: a supply side approach. Int Tax Public Finance 15
Sun C, Ding D, Fang X, Zhang H, Li J (2019) How do fossil energy prices affect the stock prices of new energy companies? Evidence from Divisia energy price index in China's market. Energy 169
Tang L, Xue X, Jia M, **g H, Wang T, Zhen R, Huang M, Tian J, Guo J, Li L, Bo X, Wang S (2020) Iron and steel industry emissions and contribution to the air quality in China. Atmos Environ 237
Tsutsui M (2010) An epsilon-based measure of efficiency in DEA - a third pole of technical efficiency. Eur J Oper Res
Wang Q, Zhao C (2020) Regional difference and driving factors of industrial carbon emissions performance in China. Alex Eng J
**ng Y, Kolstad CD (2002) Do lax environmental regulations attract foreign investment? Environ Resour Econ 21
Yan D, Kong Y, Ren X, Shi Y, Chiang SW (2019) The determinants of urban sustainability in Chinese resource-based cities: a panel quantile regression approach. Sci Total Environ 686:1210–1219
Yang G, Zhang F, Zhang F, Ma D, Yang Q (2021a) Spatiotemporal changes in efficiency and influencing factors of China's industrial carbon emissions. Environ Sci Pollut Res
Yang M, Yuan Y, Yang F, Patino-Echeverri D (2021b) Effects of environmental regulation on firm entry and exit and China's industrial productivity: a new perspective on the Porter Hypothesis. Environ Econ Policy Stud:1–30
Yi Y, Zhuqing Y, Shengnan Y (2022) Difference in the drivers of industrial carbon emission costs determines the diverse policies in middle-income regions: a case of northwestern China. Renewable and Sustain Energy Rev 155
Yiming H, Guanwen Y, Yanbin C (2022) Environmental regulation, financial pressure and industrial ecological efficiency of resource-based cities in China: spatiotemporal characteristics and impact mechanism. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19
Yiyi J, Kiyoshi F (2019): Revealing the impact of a projected emission trading scheme on the production technology upgrading in the cement industry in China: an LCA-RCOT model. Resour Conserv Recycl:X 4
Yu P, Yingming Z, Nian W (2021) How do corruption and energy efficiency affect the carbon emission performance of China's industrial sectors? Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28
Yu XN, Yang Z (2022) The impact of digital economy on industrial carbon emission efficiency: evidence from Chinese provincial data. Math Probl Eng 2022
Yujie X, Shuguang L, Jiayi W (2022) Impact of environmental regulation intensity on green innovation efficiency in the Yellow River Basin, China. J Clean Prod 373
Zhang J, Liu Y, Chang Y, Zhang L (2016) Industrial eco-efficiency in China: a provincial quantification using three-stage data envelopment analysis. J Clean Prod 143
Zhang W, Zhang N, Yu Y (2019) Carbon mitigation effects and potential cost savings from carbon emissions trading in China's regional industry. Technol Forecast Soc Change 141
Zhao H (2008) Empirical study impact of environmental regulation on enterprises' technological innovation——take Chinese 30 provincial large and medium-sized enterprise as an example. Soft Sci
Zhao X, Sun B (2016) The influence of Chinese environmental regulation on corporation innovation and competitiveness. J Clean Prod 112:1528–1536
Zhonghua C, Shiyu K (2022) The effect of environmental regulation on green total-factor productivity in China's industry. Environ Impact Assess Rev 94
Zhou Q, Zhang X, Shao Q, Wang X (2019) The non-linear effect of environmental regulation on haze pollution: empirical evidence for 277 Chinese cities during 2002–2010. J Environ Manag 248, 109274.1–109274.12
Zhu L, Hao Y, Lu Z-N, Wu H, Ran Q (2019) Do economic activities cause air pollution? Evidence from China’s major cities. Sustain Cities Soc 49
Zhu M, Shen L, Tam VWY, Liu Z, Shu T, Luo W (2020a) A load-carrier perspective examination on the change of ecological environment carrying capacity during urbanization process in China. Sci Total Environ 714
Zhu R, Zhao R, Sun J, **ao L, Jiao S, Chuai X, Zhang L, Yang Q (2020b) Temporospatial pattern of carbon emission efficiency of China's energy-intensive industries and its policy implications. J Clean Prod
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42071148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were carried out by Xueqin Lin and Weijia Cui. The first draft of the manuscript was completed by Xueqin Lin and Weijia Cui. Xueqin Lin and Weijia Cui wrote the manuscript, and Dai Wang commented on the previous version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bao**g Gu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
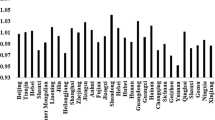
Figure 7
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Cui, W. & Wang, D. The heterogeneous effects of environmental regulation on industrial carbon emission efficiency in China using a panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 55255–55277 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26062-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26062-w