Abstract
Objective
Numerous epidemiological and experimental studies have indicated that ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure can lead to myocardial injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. The effects of procyanidin (PC) on PM2.5-induced cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are still unknown. The purpose of this study was to explore the protective effect of PC supplementation on PM2.5-induced oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats.
Method
Rats were treated by gavage with three different PC concentrations (50, 100 and 200 mg/kg) for 21 days prior to exposure to 10 mg/kg PM2.5 suspension liquid by intratracheal instillation every other day for three times. We determined myocardial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities in the myocardium were measured. The expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins, including p-Akt/Akt, Bcl-2, caspase-3 and Bax, were determined. In addition, histopathological examination was used to evaluate cardiac injury.
Results
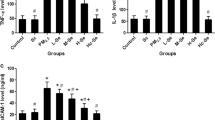
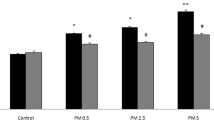
PM2.5 exposure noticeably elevated the contents of MDA and ROS and decreased the activities of GSH-Px and SOD. PM2.5 exposure inhibited Bcl-2 expression and up-regulated caspase-3 and Bax expression in the myocardium of rats. The anti-apoptosis–related index p-Akt/Akt was reduced. Moreover, pretreatment with PC could attenuate these PM2.5-induced changes. However, remarkable differences in the protective effect of different PC doses did not exist.
Conclusions
The results indicated that PC supplementation could effectively attenuate the oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by PM2.5 in rat myocardial tissue.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Al-Saad S, Donnem T, Al-Shibli K, Persson M, Bremnes RM, Busund LT (2009) Diverse prognostic roles of Akt isoforms, PTEN and PI3K in tumor epithelial cells and stromal compartment in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 29:4175–83
Azimzadeh O, Sievert W, Sarioglu H, Merl-Pham J, Yentrapalli R, Bakshi MV, Janik D, Ueffing M, Atkinson MJ, Multhoff G, Tapio S (2015) Integrative proteomics and targeted transcriptomics analyses in cardiac endothelial cells unravel mechanisms of long-term radiation-induced vascular dysfunction. J Proteome Res 14:1203–19
Bo L, Jiang S, **e Y, Kan H, Song W, Zhao J (2016) Effect of vitamin E and omega-3 fatty acids on protecting ambient PM2.5-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells. PLoS One 11:e0152216
Burt S (2004) Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods–a review. Int J Food Microbiol 94:223–53
Chen DM, Cai X, Kwik-Uribe CL, Zeng R, Zhu XZ (2006) Inhibitory effects of procyanidin B(2) dimer on lipid-laden macrophage formation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 48:54–70
Chen Y, Wang L, Liu T, Qiu Z, Qiu Y, Liu D (2021) Inhibitory effects of Panax ginseng glycoproteins in models of doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in vivo and in vitro. Food Funct 12:10862–74
Crobeddu B, Aragao-Santiago L, Bui LC, Boland S, BaezaSquiban A (2017) Oxidative potential of particulate matter 2.5 as predictive indicator of cellular stress. Environ Pollut 230:125–33
Del Re DP, Amgalan D, Linkermann A, Liu Q, Kitsis RN (2019) Fundamental Mechanisms of Regulated Cell Death and Implications for Heart Disease. Physiol Rev 99:1765–817
Du X, Jiang S, Bo L, Liu J, Zeng X, **e Y, He Q, Ye X, Song W, Zhao J (2017) Combined effects of vitamin E and omega-3 fatty acids on protecting ambient PM2.5-induced cardiovascular injury in rats. Chemosphere 173:14–21
Fang J, Tang Y, Cheng X, Wang L, Cai C, Zhang X, Liu S, Li P (2019) Exenatide alleviates adriamycin-induced heart dysfunction in mice: modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Chem Biol Interact 304:186–93
Fukai T, Ushio-Fukai M (2011) Superoxide dismutases: role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1583–606
Galiana-Simal A, Olivares-Alvaro E, Klett-Mingo M, Ruiz-Roso MB, Ballesteros S, de Las Heras N, Fuller PJ, Lahera V, Martin-Fernandez B (2016) Proanthocyanidins block aldosterone-dependent up-regulation of cardiac gamma ENaC and Nedd4–2 inactivation via SGK1. J Nutr Biochem 37:13–19
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE, Didelot C, Kroemer G (2006) Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 13:1423–33
Gorr MW, Velten M, Nelin TD, Youtz DJ, Sun Q, Wold LE (2014) Early life exposure to air pollution induces adult cardiac dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 307:H1353-60
Huang RJ, Zhang Y, Bozzetti C, Ho KF, Cao JJ, Han Y, Daellenbach KR, Slowik JG, Platt SM, Canonaco F, Zotter P, Wolf R, Pieber SM, Bruns EA, Crippa M, Ciarelli G, Piazzalunga A, Schwikowski M, Abbaszade G, Schnelle-Kreis J, Zimmermann R, An Z, Szidat S, Baltensperger U, El Haddad I, Prevot AS (2014) High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 514:218–22
Huang K, Shi C, Min J, Li L, Zhu T, Yu H, Deng H (2019) Study on the mechanism of curcumin regulating lung injury induced by outdoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5). Mediators Inflamm 2019:8613523
Jiang Y, Wang C, Lin Z, Niu Y, **a Y, Liu C, Chen C, Ge Y, Wang W, Yin G, Cai J, Chen B, Chen R, Kan H (2019) Alleviated systemic oxidative stress effects of combined atmospheric oxidant capacity by fish oil supplementation: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184
Karimi GK, Antoniades C, Nicholls SJ, Channon KM, Figtree GA (2015) Redox biomarkers in cardiovascular medicine. Eur Heart J 36.1576–82, 82a-b.
Karthikeyan K, Bai BR, Devaraj SN (2007) Efficacy of grape seed proanthocyanidins on serum and heart tissue lipids in rats subjected to isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury. Vascul Pharmacol 47:295–301
Kim R (2005) Unknotting the roles of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333:336–43
Lawrence SP, Holman GD, Koumanov F (2010) Translocation of the Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1) in cardiomyocyte responses to insulin and energy-status signalling. Biochem J 432:515–23
Li R, Kou X, Geng H, **e J, Tian J, Cai Z, Dong C (2015) Mitochondrial damage: an important mechanism of ambient PM2.5 exposure-induced acute heart injury in rats. J Hazard Mater 287:392–401
Li J, Li H, Li H, Guo W, An Z, Zeng X, Li W, Li H, Song J, Wu W (2019) Amelioration of PM2.5-induced lung toxicity in rats by nutritional supplementation with fish oil and Vitamin E. Respir Res 20:76
Liang CS, Duan FK, He KB, Ma YL (2016) Review on recent progress in observations, source identifications and countermeasures of PM2.5. Environ Int 86:150–70
Lin HH, Chen JH, Huang CC, Wang CJ (2007) Apoptotic effect of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid on human gastric carcinoma cells involving JNK/p38 MAPK signaling activation. Int J Cancer 120:2306–16
Lin Z, Chen R, Jiang Y, **a Y, Niu Y, Wang C, Liu C, Chen C, Ge Y, Wang W, Yin G, Cai J, Clement V, Xu X, Chen B, Chen H, Kan H (2019) Cardiovascular benefits of fish-oil supplementation against fine particulate air pollution in China. J Am Coll Cardiol 73:2076–85
Long MH, Zhu XM, Wang Q, Chen Y, Gan XD, Li F, Fu WL, **ng WW, Xu DQ, Xu DG (2020) PM2.5 exposure induces vascular dysfunction via NO generated by iNOS in lung of ApoE-/- mouse. Int J Biol Sci 16:49–60
LoPiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB, Dennis PA (2008) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: effective combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Updat 11:32–50
Mantena SK, Katiyar SK (2006) Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit UV-radiation-induced oxidative stress and activation of MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling in human epidermal keratinocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1603–14
Pang Y, Abeysinghe IS, He J, He X, Huhman D, Mewan KM, Sumner LW, Yun J, Dixon RA (2013) Functional characterization of proanthocyanidin pathway enzymes from tea and their application for metabolic engineering. Plant Physiol 161:1103–16
Rajagopalan S, Al-Kindi SG, Brook RD (2018) Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol 72:2054–70
Rauf A, Imran M, Abu-Izneid T, Ul HI, Patel S, Pan X, Naz S, Sanches Silva A, Saeed F, Rasul Suleria HA (2019) Proanthocyanidins: a comprehensive review. Biomed Pharmacother 116:108999
Reed J (2002) Cranberry flavonoids, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 42:301–16
Ren JY, Yin BW, Li X, Zhu SQ, Deng JL, Sun YT, Zhang ZA, Guo ZH, Pei HT, Zhang F, Li RQ, Chen FG, Ma YX (2021) Sesamin attenuates PM2.5-induced cardiovascular injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in rats. Food Funct 12:12671–82
Ren J, Liang J, Wang J, Yin B, Zhang F, Li X, Zhu S, Tian H, Cui Q, Song J, Liu G, Ling W, Ma Y (2022) Vascular benefits of vitamin C supplementation against fine particulate air pollution in healthy adults: a double-blind randomised crossover trial. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 241:113735
Sancini G, Farina F, Battaglia C, Cifola I, Mangano E, Mantecca P, Camatini M, Palestini P (2014) Health risk assessment for air pollutants: alterations in lung and cardiac gene expression in mice exposed to Milano winter fine particulate matter (PM2.5). PLoS One 9:e109685
Senoner T, Dichtl W (2019) Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases: still a therapeutic target? Nutrients 11.
Singh T, Sharma SD, Katiyar SK (2011) Grape proanthocyanidins induce apoptosis by loss of mitochondrial membrane potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 6:e27444
Su X, Tian J, Li B, Zhou L, Kang H, Pei Z, Zhang M, Li C, Wu M, Wang Q, Han B, Chu C, Pang Y, Ning J, Zhang B, Niu Y, Zhang R (2020) Ambient PM2.5 caused cardiac dysfunction through FoxO1-targeted cardiac hypertrophy and macrophage-activated fibrosis in mice. Chemosphere 247:125881
Sun Y, **u C, Liu W, Tao Y, Wang J, Qu YI (2016) Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract protects the retina against early diabetic injury by activating the Nrf2 pathway. Exp Ther Med 11:1253–58
Takemura G, Kanamori H, Okada H, Miyazaki N, Watanabe T, Tsujimoto A, Goto K, Maruyama R, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H (2018) Anti-apoptosis in nonmyocytes and pro-autophagy in cardiomyocytes: two strategies against postinfarction heart failure through regulation of cell death/degeneration. Heart Fail Rev 23:759–72
van der Pol A, van Gilst WH, Voors AA, van der Meer P (2019) Treating oxidative stress in heart failure: past, present and future. Eur J Heart Fail 21:425–35
Wei FX, Hu XF, Sa RN, Liu FZ, Li SY, Sun QY (2014) Antioxidant capacity and meat quality of broilers exposed to different ambient humidity and ammonia concentrations. Genet Mol Res 13:3117–27
Weichenthal SA, Godri-Pollitt K, Villeneuve PJ (2013) PM2.5, oxidant defence and cardiorespiratory health: a review. Environ Health 12:40
Wolfram R, Oguogho A, Palumbo B, Sinzinger H (2005) Enhanced oxidative stress in coronary heart disease and chronic heart failure as indicated by an increased 8-epi-PGF(2alpha). Eur J Heart Fail 7:167–72
Wu Y, Wang Y, Nabi X (2019) Protective effect of Ziziphora clinopodioides flavonoids against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HUVEC cells. Biomed Pharmacother 117:109156
**ao Y, Ding L, Gu YH (2017) Progress of acupuncture and moxibustion research on the signal transduction pathways involved in cell apoptosis in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 42:463–6
Yang L, **an D, **ong X, Lai R, Song J, Zhong J (2018) Proanthocyanidins against oxidative stress: from molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Biomed Res Int 2018:8584136
Zeng X, Liu J, Du X, Zhang J, Pan K, Shan W, **e Y, Song W, Zhao J (2018) The protective effects of selenium supplementation on ambient PM2.5-induced cardiovascular injury in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:22153–62
Zhang LM, Lv SS, Fu SR, Wang JQ, Liang LY, Li RQ, Zhang F, Ma YX (2021) Procyanidins inhibit fine particulate matter-induced vascular smooth muscle cells apoptosis via the activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 223:112586
Zhao L, Qi Y, Xu L, Tao X, Han X, Yin L, Peng J (2018) MicroRNA-140–5p aggravates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by promoting myocardial oxidative stress via targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2. Redox Biol 15:284–96
Zhu F (2018) Proanthocyanidins in cereals and pseudocereals. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59:1521–33
Funding
This paper was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81874264).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bowen Yin: conceptualisation, methodology, software, writing—original draft, formal analysis, writing—review and editing, project administration, resources. **ao Zhang: conceptualisation, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft. **gyi Ren: formal analysis, investigation, data curation. Fengge Chen: conceptualisation, methodology, resources. Hanning Zhang: methodology, software, investigation. Jufeng Liang: methodology, validation, investigation. Huanting Pei: software, investigation. Zhaohui Hu: investigation. Yan Wang: investigation. Wei Xue: investigation. **nyue Yu: investigation. Rui Zhang: investigation. Yuxia Ma: conceptualisation, methodology, investigation, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All studies were approved by the Ethics Committee of Hebei Medical University.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, B., Zhang, X., Ren, J. et al. The protective effects of procyanidin supplementation on PM2.5-induced acute cardiac injury in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 10890–10900 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22938-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22938-5