Abstract
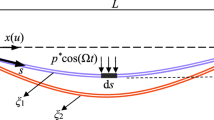
The stochastic fluctuating factors caused by wind gust can change the dynamic behavior of iced transmission lines, which has been widely concerned by scholars. The stochastic impulsive disturbance in nature is simulated as Poisson white noise in this paper. For the path integration method under Poisson white noise excitation, a function that considers the randomness of pulses occurring at each time interval is used as an approximation of the short-time transition probability density. The Chapman–Kolmogorov equation with variable substitution is numerically solved using the backward Runge–Kutta method and the linear interpolation. Thus the evolution of probability density function of the system is worked out. After that, based on the results obtained by the path integration method, three indexes are got to measure the reliability of the system through the reliability theory. The effects of pulse sparsity, wind gust intensity and security domain scope on system reliability are revealed by analyzing the reliability function, first passage probability density, and mean first passage time. The accuracy of the path integration method is verified by comparing the results with the Monte Carlo results.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availibility
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Ibrahim, R., Chang, W.: Stochastic excitation of suspended cables involving three simultaneous internal resonances using Monte Carlo simulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 168(1–4), 285–304 (1999)
Liu, Z., Ding, C., Qin, J., Lei, Y.: The nonlinear gallo** of iced transmission conductor under uniform and turbulence wind. Struct. Eng. Mech. 75(4), 465–475 (2020)
Tagata, G.: Analysis of a randomly excited non-linear stretched string. J. Sound Vib. 58(1), 95–107 (1978)
Tagata, G.: Non-linear string random vibration. J. Sound Vib. 129(3), 361–384 (1989)
Bai, Y., Xu, W., Wei, W., Zhang, Z.: Stochastic dynamics and first passage analysis of iced transmission lines via path integration method. Chaos 33(7), 073105 (2023)
Grigoriu, M.: Reliability of linear systems under Poisson white noise. Probab. Eng. Mech. 24(3), 397–406 (2009)
Grigoriu, M.: Response of dynamic systems to Poisson white noise. J. Sound Vib. 195(3), 375–389 (1996)
Köylüoǧlu, H., Nielsen, S., Iwankiewicz, R.: Reliability of non-linear oscillators subject to Poisson driven impulses. J. Sound Vib. 176(1), 19–33 (1994)
Luongo, A., Zulli, D.: Dynamic instability of inclined cables under combined wind flow and support motion. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(1), 71–87 (2012)
Lu, N., Liu, Y., Beer, M.: System reliability evaluation of in-service cable-stayed bridges subjected to cable degradation. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 11(14), 1486–1498 (2018)
Okpokparoro, S., Sriramula, S.: Reliability analysis of floating wind turbine dynamic cables under realistic environmental loads. Ocean Eng. 278, 114594 (2023)
Wei, S., Sun, Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.: Random vibration and reliability analysis of fluid-conveying pipe under white noise excitations. Appl. Math. Model. 123, 259–273 (2023)
Huang, X., Fei, Z., Li, H., Liu, X.: An online technology for measuring icing shape on conductor based on vision and force sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 66(12), 3180–3189 (2017)
Ren, Z., Xu, W., Zhang, S.: Reliability analysis of nonlinear vibro-impact systems with both randomly fluctuating restoring and dam** terms. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 82, 105087 (2019)
Han, Q., Xu, W., Yue, X., Zhang, Y.: First-passage time statistics in a bistable system subject to Poisson white noise by the generalized cell map** method[J]. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 23(1–3), 220–228 (2015)
Grigoriu, M.: Dynamic systems with Poisson white noise. Nonlinear Dyn. 36(2–4), 255–266 (2004)
Zeng, Y., Zhu, W.: Stochastic averaging of quasi-linear systems driven by Poisson white noise. Probab. Eng. Mech. 25(1), 99–107 (2010)
Jia, W., Zhu, W., Xu, Y.: Stochastic averaging of quasi-non-integrable Hamiltonian systems under combined Gaussian and Poisson white noise excitations. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 51(2), 45–53 (2013)
Yue, X., Xu, W., Jia, W., Wang, L.: Stochastic response of a \(\varphi ^6\) oscillator subjected to combined harmonic and Poisson white noise excitations. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 392(14), 2988–2998 (2013)
Di Matteo, A., Di Paola, M., Pirrotta, A.: Probabilistic characterization of nonlinear systems under Poisson white noise via complex fractional moments. Nonlinear Dyn. 77(3), 729–738 (2014)
Chen, H., Chen, G., Meng, Z., Yang, D.: Stochastic dynamic analysis of nonlinear MDOF systems under combined Gaussian and Poisson noise excitation based on DPIM. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 176, 109163 (2022)
Bucher, C., Di Paola, M.: Efficient solution of the first passage problem by path integration for normal and Poissonian white noise. Probab. Eng. Mech. 41, 121–128 (2015)
Di Paola, M., Santoro, R.: Path integral solution for non-linear system enforced by Poisson White Noise. Probab. Eng. Mech. 23(2–3), 164–169 (2008)
Di Matteo, A., Di Paola, M., Pirrotta, A.: Path integral solution for nonlinear systems under parametric Poissonian white noise input. Probab. Eng. Mech. 44, 89–98 (2016)
Pirrotta, A., Santoro, R.: Probabilistic response of nonlinear systems under combined normal and Poisson white noise via path integral method. Probab. Eng. Mech. 26(1), 26–32 (2011)
Di Paola, M., Bucher, C.: Ideal and physical barrier problems for non-linear systems driven by normal and Poissonian white noise via path integral method. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 81, 274–282 (2016)
Koyluoglu, H., Nielsen, S., Iwankiewicz, R.: Response and reliability of Poisson-driven systems by path integration. J. Eng. Mech. 121(1), 117–130 (1995)
Ren, Z., Xu, W.: An improved path integration method for nonlinear systems under Poisson white noise excitation. Appl. Math. Comput. 373, 125036 (2020)
Peng, J., Wang, L., Wang, B., Yuan, M., Xu, W.: A new path integration method for the stochastic system under Poisson white noise excitation based on a probability map**. J. Sound Vib. 571, 118037 (2024)
Liu, X., Yang, S., Min, G., Sun, C., Liang, H., Zou, M., Wu, C., Cai, M.: Forced-self-excited system of iced transmission lines under planar harmonic excitations. Nonlinear Dyn. 110(1), 1175–1197 (2022)
Zhao, Y., Sun, C., Wang, Z., Wang, L.: Analytical solutions for resonant response of suspended cables subjected to external excitation[J]. Nonlinear Dyn. 78(2), 1017–1032 (2014)
Benedettini, F., Rega, G.: Non-linear dynamics of an elastic cable under planar excitation. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 22(6), 497–509 (1987)
Jafari, M., Hou, F., Abdelkefi, A.: Wind-induced vibration of structural cables. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(1), 351–421 (2020)
Di Paola, M., Vasta, M.: Stochastic integro-differential and differential equations of non-linear systems excited by parametric Poisson pulses. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 32(5), 855–862 (1997)
Muscolino, G., Ricciardi, G., Cacciola, P.: Monte Carlo simulation in the stochastic analysis of non-linear systems under external stationary Poisson white noise input[J]. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 38(8), 1269–1283 (2003)
Di Paola, M., Falsone, G.: Ito and Stratonovich integrals for delta-correlated processes. Probab. Eng. Mech. 8(3–4), 197–208 (1993)
Ren, Z., Xu, W., Wang, D.: Dynamic and first passage analysis of ship roll motion with inelastic impacts via path integration method. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(1), 391–402 (2019)
Jia, W., Luo, M., Ni, F., Hao, M., Zan, W.: Response and reliability of suspension system under stochastic and periodic track excitations by path integral method. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 157, 104544 (2023)
Naess, A., Moe, V.: Efficient path integration methods for nonlinear dynamic systems. Probab. Eng. Mech. 15(2), 221–231 (2000)
Zan, W., Jia, W., Xu, Y.: Reliability of dynamical systems with combined Gaussian and Poisson white noise via path integral method. Probab. Eng. Mech. 68, 103252 (2022)
**e, W., Xu, W., Cai, L.: Numerical meshfree path integration method for non-linear dynamic systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 197(1), 426–434 (2008)
Yu, J., Lin, Y.: Numerical path integration of a non-homogeneous Markov process. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 39(9), 1493–1500 (2004)
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NOs. 12372034, 12072261).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare this manuscript is original, and they have no potential conflicts of interest with respected to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Y., Xu, W. & Zhang, W. Reliability analysis of iced transmission lines under Poisson white noise excitation via path integration method. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 12019–12033 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09662-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09662-0