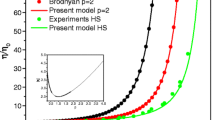
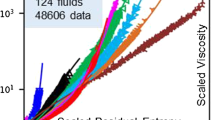
Abstract
Viscosities were measured for the ternary aqueous systems NaCl–mannitol(C6H14O6)–H2O, NaBr–mannitol–H2O, KCl–mannitol–H2O, KCl–glycine(NH2CH2COOH)–H2O, KCl–CdCl2–H2O, and their binary subsystems NaCl–H2O, KCl–H2O, NaBr–H2O, CdCl2–H2O, mannitol–H2O, and glycine–H2O at 298.15 K. A powerful new approach is presented for theoretical modeling of the viscosity of multicomponent solutions in terms of the properties of their binary solutions. In this modeling, the semi-ideal solution theory was used to associate the solvation structure formed by each ion and its first solvation shell in a binary solution with the solvation structure of the same ion and its first solvation shell in multicomponent solutions. Then, the novel mechanism proposed by Omta et al. (Science, 301:347–349, 2003) for the effect of a single electrolyte on the viscosity of water was extended to describe the influence of solute mixtures on the viscosity of water, including electrolyte mixtures, nonelectrolyte mixtures, and mixtures of electrolytes with nonelectrolytes. The established simple equation was verified by comparison with measured viscosities and viscosities reported in literature. The agreements are very impressive. This formulation provides a powerful new approach for modeling this transport property in solutions. It can stimulate further research in establishing a dynamical analogue to that formulated for the thermodynamics of multicomponent solutions. It is also very important for the study of hydration of ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra, A., Bagchi, B.: Beyond the classical transport laws of electrochemistry: New microscopic approach to ionic conductance and viscosity. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9067–9080 (2000)
Wu, Y.C., Koch, W.F., Zhong, E.C., Friedman, H.L.: The cross-square rule for transport in electrolyte mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. 92, 1692–1695 (1988)
Harned, H.S.: Some thermodynamic properties of uni-univalent halide mixtures in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57, 1865–1873 (1935)
Young, T.F., Wu, Y.C., Krawetz, A.A.: Thermal effects of the interactions between ions of like charge. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 24, 37–42 (1957)
Young, T.F., Wu, Y.C., Krawetz, A.A.: General discussion. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 24, 66–82 (1957)
Zdanovskii, A.B.: Regularities in the property variations of mixed solutions. Tr. Solyanoi Lab. Akad. Nauk SSSR 6, 5–70 (1936)
Hu, Y.F., Fan, S.S., Liang, D.Q.: The semi-ideal solution theory for mixed Ionic solutions at solid–liquid–vapor equilibrium. J. Phys. Chem. A 110, 4276–4284 (2006)
Hu, Y.F.: The thermodynamics of nonelectrolyte systems at constant activities of any number of components. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 13168–13177 (2003)
Miller, D.G.: Binary mixing approximations and relations between specific conductance, molar conductance, equivalent conductance, and ionar conductance for mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 1220–1226 (1996)
Hu, Y.F., Zhang, X.M., Li, J.G., Liang, Q.Q.: The semi-ideal solution theory. 2. Extension to conductivity of mixed electrolyte solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 15376–15381 (2008)
Omta, A.W., Kropman, M.F., Woutersen, S., Bakker, H.J.: Negligible effect of ions on the hydrogen-bond structure in liquid water. Science 301, 347–349 (2003)
Jenkins, H.D.B., Marcus, Y.: Viscosity B-coefficients of ions in solution. Chem. Rev. 95, 2695–2724 (1995)
Gurney, R.W.: Ionic Processes in Solution. McGraw-Hill, New York (1953)
Ohtaki, H., Radnai, T.: Structure and dynamics of hydrated ions. Chem. Rev. 93, 1157–1204 (1993)
Chandrasekhar, J., Spellmeier, D.C., Jorgensen, W.L.: Energy component analysis for dilute aqueous solutions of Li +, Na +, F −, and Cl − ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106, 903–910 (1984)
Batchelor, J.D., Olteanu, A., Tripathy, A., Pielak, G.J.: Impact of protein denaturants and stabilizers on water structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 1958–1961 (2004)
Gurau, M.C., Lim, S.M., Castellana, E.T., Albertorio, F., Kataoka, S., Cremer, P.S.: On the mechanism of the Hofmeister effect. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 10522–10523 (2004)
Marcus, Y.: Ionic radii in aqueous solutions. Chem. Rev. 88, 1475–1498 (1988)
Conway, B.E.: Ionic Hydration in Chemistry and Biophysics. Studies in Physical and Theoretical Chemistry, vol. 12. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1981)
Marcus, Y.: Ion Solution. Wiley, Chichester (1986)
Scatchard, G.: The speed of reaction in concentrated solutions and the mechanism of the inversion of sucrose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 43, 2387–2406 (1921)
Scatchard, G.: The hydration of sucrose in water solution as calculated from vapor-pressure measurements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 43, 2406–2418 (1921)
Stokes, R.H., Robinson, R.A.: Ionic hydration and activity in electrolyte solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 70, 1870–1878 (1948)
Robinson, R.A., Stokes, R.H.: Activity coefficients in aqueous solutions of sucrose, mannitol and their mixtures at 25°. J. Phys. Chem. 65, 1954–1958 (1961)
Rard, J.A.: Isopiestic determination of the osmotic and activity coefficients of {(1−y)H2SO4+yNa2SO4}(aq) at 298.15 K. I. Results for y=0.5 (NaHSO4) and y=0.55595, 0.70189, and 0.84920. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 21, 539–560 (1989)
Stokes, R.H., Robinson, R.A.: Interactions in aqueous nonelectrolyte solutions. I. Solute-solvent equilibria. J. Phys. Chem. 70, 2126–2131 (1966)
Robinson, R.A., Stokes, R.H.: Activity coefficients of mannitol and potassium chloride in mixed aqueous solutions at 25°. J. Phys. Chem. 66, 506–507 (1962)
Clegg, S.L., Seinfeld, J.H.: Improvement of the Zdanovskii–Stokes–Robinson model for mixtures containing solutes of different charge types. J. Phys. Chem. A 108, 1008–1017 (2004)
Clegg, S.L., Seinfeld, J.H., Edney, E.O.: Thermodynamic modelling of aqueous aerosols containing electrolytes and dissolved organic compounds. II. An extended Zdanovskii–Stokes–Robinson approach. J. Aerosol Sci. 34, 667–690 (2003)
Mikhailov, V.A.: Thermodynamics of mixed electrolyte solutions. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 42, 1414–1416 (1968)
Glasstone, S., Laidler, K.J., Eyring, H.: The Theory of Rate Process. McGraw-Hill, New York (1941)
Vogel, A.I., Bassett, J.: Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis: Including Elementary Instrumental Analysis, 5th edn. Longman, Essex (1989)
Stokes, R.H., Mills, R.: Viscosity of Electrolytes and Related Properties. Pergamon, New York (1965)
Zhang, H.L., Han, S.J.: Viscosity and density of water + sodium chloride + potassium chloride solutions at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 41, 516–520 (1996)
Isono, T.: Density, viscosity, and electrolytic conductivity of concentrated aqueous electrolyte solutions at several temperatures. Alkaline-earth chlorides, LaCl3, Na2SO4, NaNO3, NaBr, KNO3, KBr, and Cd(NO3)2. J. Chem. Eng. Date 29, 45–52 (1984)
Reilly, P.J., Stokes, R.H.: The diffusion coefficients of cadmium chloride and cadmium perchlorate in water at 25°. Aust. J. Chem. 24, 1361–1367 (1971)
Hu, Y.F., Zhang, Z.X., Zhang, Y.H., Fan, S.S., Liang, D.Q.: Viscosity and density of the nonelectrolyte system mannitol + sorbitol + sucrose + H2O and its binary and ternary subsystems at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 51, 438–442 (2006)
Mason, L.S., Kampmeyer, P.M., Robinson, A.L.: The viscosities of aqueous solutions of amino acids at 25 and 35°. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 1287–1290 (1952)
Robinson, R.A., Stokes, R.H.: Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd edn. Butterworth, London (1965)
Ellerton, H.D., Reinfelds, G., Mulcahy, D.E., Dunlop, P.J.: Activity, density, and relative viscosity data for several amino acids, lactamide, and raffinose in aqueous solution at 25°. J. Phys. Chem. 68, 398–402 (1964)
Filippov, V.K., Yakimov, M.A., Makarevskii, V.M., Luking, L.G.: A study of water activity in the ternary system KCl–CdCl2–H2O, KBr–CdBr2–H2O, and KBr–CdBr2–H2O at 25 °C. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 16, 1653–1655 (1971)
Chen, H., Sangster, J., Teng, T.T., Lenzi, F.: A general method of predicting the water activity of ternary aqueous solutions from binary data. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 51, 234–241 (1973)
Ruby, C.E., Kawai, J.: The densities, equivalent conductances and relative viscosities at 25°, of solutions of hydrochloric acid, potassium chloride and sodium chloride, and of their binary and ternary mixtures of constant chloride-ion-constituent content. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 48, 1119–1128 (1926)
Lengyel, S., Tamas, J., Giber, J., Holderith, J.: Study of viscosity of aqueous alkali halide solutions. J. Acta Chim. Hung. 40, 125–142 (1964)
Zhang, H.L., Chen, G.H., Han, S.J.: Viscosity and density of H2O + NaCl + CaCl2 and H2O + KCl + CaCl2 at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 42, 526–530 (1997)
Liu, Y.S., Shi, M.X., Cao, R., Zhang, Y.H., Hu, Y.F.: Densities and viscosities of the quaternary system mannitol–sorbitol–D-glucose–H2O and its ternary subsystems at 298.15 K. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 15, 703–709 (2007)
Pitzer, K.S.: Electrolytes. From dilute solutions to fused salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102, 2902–2906 (1980)
Clegg, S.L., Pitzer, K.S.: Thermodynamics of multicomponent, miscible, ionic solutions: Generalized equations for symmetrical electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. 96, 3513–3520 (1992)
Zhang, Y., Furyk, S., Bergbreiter, D.E., Cremer, P.S.: Specific ion effects on the water solubility of macromolecules: PNIPAM and the Hofmeister series. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 14505–14510 (2005)
Bostrom, M., Williams, D.R.M., Ninham, B.W.: Specific ion effects: Why DLVO theory fails for biology and colloid systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 168103–168106 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, YF., Zhang, XM., **, CW. et al. The Semi-ideal Solution Theory. 3. Extension to Viscosity of Multicomponent Aqueous Solutions. J Solution Chem 39, 1828–1844 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-010-9565-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-010-9565-2