Abstract
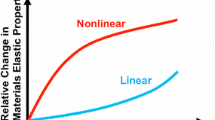
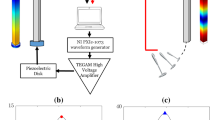
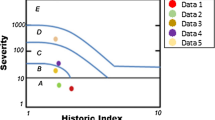
Nonlinear acoustic methods demonstrate high sensitivity for concrete damage evaluation. Among these methods, nonlinear resonance acoustic methods have been widely used in laboratory tests on small scale test samples. In this study, a nonlinear impact-echo (IE) method for concrete damage evaluation was introduced, in which the IE frequency shift was measured at different impact force levels. The nonlinear IE test and the nonlinear impact resonance acoustic spectroscopy (NIRAS) test share similarities in the experimental setup and analysis method. However, the nonlinear IE test excites a local thickness resonance mode of a member instead of the global resonance vibration. Therefore, the analyzed mode is unaffected by member boundary conditions and is applicable to large concrete structural members. To identify the fundamental IE frequencies, multiple impacts were applied along the members. Once the fundamental IE frequencies were determined, the effectiveness of the nonlinear IE method was evaluated by testing seven concrete beam specimens with varying levels of alkali-silica reaction (ASR) damage. The nonlinear IE test demonstrates high sensitivity to concrete damage and allows for quantitative assessment of the damage state of concrete without a baseline measurement.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author J.Z. upon reasonable request.
References
Van Den Abeele, K.E.A., Carmeliet, J., Ten Cate, J.A., Johnson, P.A.: Nonlinear elastic wave spectroscopy (NEWS) techniques to discern material damage, Part II: single-mode nonlinear resonance acoustic spectroscopy. J. Res. Nondestruct. Eval. 12(1), 31–42 (2000)
Breazeale, M., Thompson, D.: Finite-amplitude ultrasonic waves in aluminum. Appl. Phys. Lett. 3(5), 77–78 (1963)
Eiras, J., Kundu, T., Bonilla, M., Payá, J.: Nondestructive monitoring of ageing of alkali resistant glass fiber reinforced cement (GRC). J. Nondestruct. Eval. 32, 300–314 (2013)
Zhang, Y., Tournat, V., Abraham, O., Durand, O., Letourneur, S., Le Duff, A., et al.: Nonlinear mixing of ultrasonic coda waves with lower frequency-swept pump waves for a global detection of defects in multiple scattering media. J. Appl. Phys. 113(6), 064905 (2013)
Chen, J., Jayapalan, A.R., Kim, J.Y., Kurtis, K.E., Jacobs, L.J.: Rapid evaluation of alkali-silica reactivity of aggregates using a nonlinear resonance spectroscopy technique. Cem. Concr. Res. 40(6), 914–923 (2010)
ASTM: ASTM Standard C215 Standard Test Method for Fundamental Transverse, Longitudinal, and Torsional Resonant Frequencies of Concrete Specimens. ASTM, West Conshohocken (2019)
Leśnicki, K.J., Kim, J.Y., Kurtis, K.E., Jacobs, L.J.: Characterization of ASR damage in concrete using nonlinear impact resonance acoustic spectroscopy technique. NDT E Int. 44(8), 721–727 (2011)
Renaud, G., Callé, S., Defontaine, M.: Remote dynamic acoustoelastic testing: elastic and dissipative acoustic nonlinearities measured under hydrostatic tension and compression. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94(1), 011905 (2009)
Renaud, G., Talmant, M., Callé, S., Defontaine, M., Laugier, P.: Nonlinear elastodynamics in micro-inhomogeneous solids observed by head-wave based dynamic acoustoelastic testing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 130(6), 3583–3589 (2011)
Shokouhi, P., Rivière, J., Lake, C.R., Le Bas, P.Y., Ulrich, T.: Dynamic acousto-elastic testing of concrete with a coda-wave probe: comparison with standard linear and nonlinear ultrasonic techniques. Ultrasonics 81, 59–65 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Larose, E., Moreau, L., d’Ozouville, G.: Three-dimensional in situ imaging of cracks in concrete using diffuse ultrasound. Struct. Health Monit. 17(2), 279–284 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921717690938
Basu, S., Thirumalaiselvi, A., Sasmal, S., Kundu, T.: Nonlinear ultrasonics-based technique for monitoring damage progression in reinforced concrete structures. Ultrasonics 115, 106472 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2021.106472
ASTM: ASTM Standard C1383. Standard Test Method for Measuring the P-Wave Speed and the Thickness of Concrete Plates Using the Impact-Echo Method. ASTM, West Conshohocken (2015)
Lin, Y., Sansalone, M.: Transient response of thick circular and square bars subjected to transverse elastic impact. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 91(2), 885–893 (1992)
Sansalone, M.J., Streett, W.B.: Impact-Echo: Nondestructive Evaluation of Concrete and Masonry. Bullbrier Press, Ithaca (1997)
Gibson, A., Popovics, J.S.: Lamb wave basis for impact-echo method analysis. J. Eng. Mech. 131(4), 438–443 (2005)
Prada, C., Clorennec, D., Royer, D.: Local vibration of an elastic plate and zero-group velocity Lamb modes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124(1), 203–212 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.2918543
Laurent, J., Royer, D., Hussain, T., Ahmad, F., Prada, C.: Laser induced zero-group velocity resonances in transversely isotropic cylinder. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 137(6), 3325–3334 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4921608
Hayashi, T., Song, W.J., Rose, J.L.: Guided wave dispersion curves for a bar with an arbitrary cross-section, a rod and rail example. Ultrasonics 41(3), 175–183 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0041-624X(03)00097-0
Guyer, R.A., McCall, K.R., Boitnott, G.N.: Hysteresis, discrete memory, and nonlinear wave propagation in rock: a new paradigm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74(17), 3491–3494 (1995)
Van Den Abeele, K.E.A., Johnson, P.A., Sutin, A.: Nonlinear elastic wave spectroscopy (NEWS) techniques to discern material damage, Part I: nonlinear wave modulation spectroscopy (NWMS). J. Res. Nondestruct. Eval. 12(1), 17–30 (2000)
**, J., Moreno, M.G., Riviere, J., Shokouhi, P.: Impact-based nonlinear acoustic testing for characterizing distributed damage in concrete. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 36(3), 51 (2017)
Johnson, P.A., Zinszner, B., Rasolofosaon, P.N.: Resonance and elastic nonlinear phenomena in rock. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 101(B5), 11553–11564 (1996)
Payan, C., Ulrich, T.J., Le Bas, P.Y., Saleh, T., Guimaraes, M.: Quantitative linear and nonlinear resonance inspection techniques and analysis for material characterization: application to concrete thermal damage. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 136(2), 537–546 (2014)
Malone, C.: Quantitative Assessment of Alkali-Silica Reaction in Small and Large-Scale Concrete Specimens Utilizing Nonlinear Acoustic Techniques. University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln (2020)
Bjurström, H., Ryden, N.: Detecting the thickness mode frequency in a concrete plate using backward wave propagation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 139(2), 649–657 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4941250
Malone, C., Zhu, J., Hu, J., Snyder, A., Giannini, E.: Evaluation of alkali-silica reaction damage in concrete using linear and nonlinear resonance techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 303, 124538 (2021)
Rivard, P., Saint-Pierre, F.: Assessing alkali-silica reaction damage to concrete with non-destructive methods: from the lab to the field. Constr. Build. Mater. 23(2), 902–909 (2009)
Giannini, E.R., Folliard, K.J., Zhu, J., Bayrak, O., Kreitman, K., Webb, Z., et al.: Non-destructive Evaluation of In-service Concrete Structures Affected by Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR) or Delayed Ettringite Formation (DEF)—Final Report, Part I. FHWA/TX-13/0-6491-1 (2013). http://library.ctr.utexas.edu/ctr-publications/0-6491-1.pdf
Sun, H., Tang, Y., Malone, C., Zhu, J.: Long-term ultrasonic monitoring of concrete affected by alkali-silica reaction. Struct. Health Monit. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/14759217231169000
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy— Nuclear Energy University Program (NEUP) under the Contract DE-NE0008544.
Funding
U.S. Department of Energy DE-NE0008544.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ and CM conceptualized the methodology. CM collected data and performed analysis. All authors wrote, edited, and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author **ying Zhu is an Associate Editor of Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.
Consent for Publication
The publisher has the author’s permission to publish this paper and the research findings within it. Results in this paper are based on the work in the first author’s Master Thesis [25].
Code Availability
The code is available upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malone, C., Sun, H. & Zhu, J. Nonlinear Impact-Echo Test for Quantitative Evaluation of ASR Damage in Concrete. J Nondestruct Eval 42, 93 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-023-01003-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-023-01003-2