Abstract
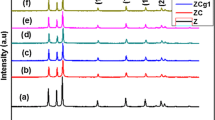
We have synthesized Yttrium and Cobalt-co-doped ZnO nanorods (NRs) by co-precipitation method and studied the effect of Yttrium and Cobalt co-do** on the structure, dielectric, and magnetic responses. X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy suggested a decrease in lattice parameters and an increase in the particle size of all Co-ZnO nanorods. It was observed that high co-do** decreased the dielectric properties and increased the electrical conductivity due to the generation of free charge carriers through the substitution of Yttrium and Cobalt ions in the host ZnO. It was also discovered that co-doped ZnO Nanorods experienced a considerable transformation that was defined by the shift from ZnO’s diamagnetic behavior to room-temperature ferromagnetism (RTFM) behavior. In the ZnO lattice samples, room-temperature ferromagnetism (RTFM) has been mostly created by vacancies and zinc interstitials due to the do** of transition metals. However, with changes in dopant concentration only from 1 to 4% and then 5%, remanent magnetization (Mr) first increased from 0.038 emu/g to 0.118emu/g and then decreased drastically to 0.0346emu/g. It was found that the increasing O2 vacancies are highly associated with the improved magnetic and electric characteristics of the sample of Zn0.91Y0.05Co0.04O. It was discovered that Zn0.91Y0.05Co0.04O nanotubes have higher electrical conductivity and magnetic properties than pure ZnO. This strong dielectric and ferromagnetism response implies that the charge carriers’ hop** is responsible for this transport, which is commonly referred to as a high-frequency devices and diluted magnetic semiconductors supporting spintronic applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The paper is not submitted priorly or simultaneously to anywhere and no part is presented or published. All the data are included and no separate repository or representation of data.
References
Y. Hao, S. Lou, S. Zhou, Y. Wang, X. Chen, G. Zhu et al., Novel magnetic behavior of Mn-doped ZnO hierarchical hollow spheres. J. Nanopart. Res. 14(1), 1–9 (2012)
G.A. Prinz, Magnetoelectronics Sci. 282(5394), 1660–1663 (1998)
R. Khan, K. Althubeiti, A.M. Afzal, N. Rahman, S. Fashu, W. Zhang et al., Structure and magnetic properties of (Co, Ce) co-doped ZnO-based diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 24394–24400 (2021)
P. Li, S. Wang, J. Li, Y. Wei, Structural and optical properties of co-doped ZnO nanocrystallites prepared by a one-step solution route. J. Lumin. 132(1), 220–225 (2012)
R. Khan, V. Tirth, A. Ali, K. Irshad, N. Rahman, A. Algahtani et al., Effect of Sn-do** on the structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles for spintronics applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(16), 21631–21642 (2021)
X. Wang, L. Zhu, L. Zhang, J. Jiang, Z. Yang, Z. Ye et al., Properties of Ni doped and Ni–Ga co-doped ZnO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 509(7), 3282–3285 (2011)
J. Fu, X. Ren, S. Yan, Y. Gong, Y. Tan, K. Liang et al., Synthesis and structural characterization of ZnO doped with Co. J. Alloys Compd. 558, 212–221 (2013)
Y.-M. Hao, S.-Y. Lou, S.-M. Zhou, R.-J. Yuan, G.-Y. Zhu, N. Li, Structural, optical, and magnetic studies of manganese-doped zinc oxide hierarchical microspheres by self-assembly of nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 1–9 (2012)
A. Stroppa, X. Duan, M. Peressi, Structural and magnetic properties of Mn-doped GaAs (1 1 0) surface. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 126(2–3), 217–221 (2006)
Y. Chang, D. Wang, X. Luo, X. Xu, X. Chen, L. Li et al., Synthesis, optical, and magnetic properties of diluted magnetic semiconductor zn 1 – x mn x O nanowires via vapor phase growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(19), 4020–4022 (2003)
Y. Ohno, D. Young, F. Beschoten Ba, Matsukura, H. Ohno, D. Awschalom, Electrical spin injection in a ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructure. Nature. 402(6763), 790–792 (1999)
Q. Wang, Q. Sun, P. Jena, Ab initio study of electronic and magnetic properties of the C-codoped Ga 1 – x mn x N (10 1¯ 0) surface. Phys. Rev. B 75(3), 035322 (2007)
C.F. Klingshirn, C.F. Klingshirn, Optical properties of bound and localized excitons and of defect states. Semicond. Opt. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28362-8_14
X. Xu, C. Cao, Structure and ferromagnetic properties of co-doped ZnO powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(14), 2216–2219 (2009)
T. Dietl, A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater. 9(12), 965–974 (2010)
L. Sun, F. Yan, H. Zhang, J. Wang, G. Wang, Y. Zeng et al., Room-temperature ferromagnetism and in-plane magnetic anisotropy characteristics of nonpolar GaN: mn films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(16), 7451–7454 (2009)
G. Husnain, F. Tao, S.-D. Yao, Structural and magnetic properties of co + implanted n-GaN dilute magnetic semiconductors. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 405(9), 2340–2343 (2010)
Z. Lu, H.-S. Hsu, Y. Tzeng, J.-C.-A. Huang, Carrier-mediated ferromagnetism in single crystalline (Co, Ga)-codoped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94(15), 152507 (2009)
N.G. Szwacki, J. Majewski, T. Dietl, Aggregation and magnetism of Cr, Mn, and Fe cations in GaN. Phys. Rev. B 83(18), 184417 (2011)
V. Gandhi, R. Ganesan, H.H. Abdulrahman Syedahamed, M. Thaiyan, Effect of cobalt do** on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation method. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(18), 9715–9725 (2014)
T. Oshio, K. Masuko, A. Ashida, T. Yoshimura, N. Fujimura, Effect of Mn do** on the electric and dielectric properties of ZnO epitaxial films. J. Appl. Phys. 103(9), 093717 (2008)
J.-J. Xu, Y.-N. Lu, F.-F. Tao, P.-F. Liang, P.-A. Zhang, ZnO nanoparticles modified by carbon quantum dots for the photocatalytic removal of synthetic pigment pollutants. ACS omega 8(8), 7845–7857 (2023)
A. Jr Franco, H. Pessoni, P. Ribeiro, F. Machado, Magnetic properties of co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 347–350 (2017)
J. Beltrán, C. Barrero, A. Punnoose, Understanding the role of iron in the magnetism of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(23), 15284–15296 (2015)
R. Ebrahimifard, M.R. Golobostanfard, H. Abdizadeh, Sol–gel derived Al and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films: an optoelectronic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 290, 252–259 (2014)
A. Goktas, F. Aslan, B. Yeşilata, Ä. Boz, Physical properties of solution processable n-type Fe and Al co-doped ZnO nanostructured thin films: role of Al do** levels and annealing. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process. 75, 221–233 (2018)
S. Goktas, A. Goktas, A comparative study on recent progress in efficient ZnO based nanocomposite and heterojunction photocatalysts: a review. J. Alloys Compd. 863, 158734 (2021)
D. Akcan, S. Ozharar, E. Ozugurlu, L. Arda, The effects of Co/Cu co-doped ZnO thin films: an optical study. J. Alloys Compd. 797, 253–261 (2019)
M.P. Ahmad, A.V. Rao, K.S. Babu, G.N. Rao, Particle size effect on the dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 224, 79–84 (2019)
R. Khan, M.-U. Rahman, S. Fashu, Effect of annealing temperature on the dielectric and magnetic response of (Co, Zn) co-doped SnO 2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 2673–2679 (2017)
R. Khan, Y. Zaman, Effect of annealing on structural, dielectric, transport and magnetic properties of (Zn, Co) co-doped SnO 2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 4003–4010 (2016)
R. Khan, S. Fashu, M.-U. Rahman, Effects of Ni co-do** concentrations on dielectric and magnetic properties of (Co, Ni) co-doped SnO 2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 7725–7730 (2016)
M. Mansournia, S. Rafizadeh, S.M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and light harvesting applications of zinc oxide nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 5839–5846 (2015)
A. Sukumaran, N. Sivanantham, E. Vinoth, N. Gopalakrishnan, Investigation of ferromagnetism and dual donor defects in Y-doped ZnO thin films. Phys. Scr. 97(10), 105804 (2022)
F. Aslan, F. Arslan, A. Tumbul, A. Goktas, Synthesis and characterization of solution processed p-SnS and n-SnS2 thin films: effect of starting chemicals. Opt. Mater 127, 112270 (2022)
T. Sapanathan, R.N. Raoelison, E. Padayodi, N. Buiron, M. Rachik, Depiction of interfacial characteristic changes during impact welding using computational methods: comparison between Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian and Eulerian simulations. Mater. Design. 102, 303–312 (2016)
M. Mansournia, S. Rafizadeh, S.M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, An ammonia vapor-based approach to ZnO nanostructures and their study as photocatalyst material. Ceram. Int. 42(1), 907–916 (2016)
B. Poornaprakash, S. Ramu, K. Subramanyam, Y. Kim, M. Kumar, M.S.P. Reddy, Robust ferromagnetism of ZnO:(ni + er) diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles for spintronic applications. Ceram. Int. 47(13), 18557–18564 (2021)
E. Pavoni, E. Mohebbi, D. Mencarelli, P. Stipa, E. Laudadio, L. Pierantoni, The effect of Y do** on monoclinic, orthorhombic, and cubic polymorphs of HfO2: a first principles study. Nanomaterials 12(23), 4324 (2022)
T.M. Hammad, J.K. Salem, R.G. Harrison, Synthesis, characterization, and optical properties of Y-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Nano. 4(04), 225–232 (2009)
I. Atribak, A. Bueno-López, A. García-García, Role of yttrium loading in the physico-chemical properties and soot combustion activity of ceria and ceria–zirconia catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 300(1–2), 103–110 (2009)
R. Khan, S. Fashu, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of (Al, Ni) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 4333–4339 (2017)
A. Safeen, K. Safeen, M. Shafique, Y. Iqbal, N. Ahmed, M.A.R. Khan et al., The effect of Mn and Co dual-do** on the structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of ZnO nanostructures. RSC Adv. 12(19), 11923–11932 (2022)
R. Khan, S. Fashu, Y. Zaman, Magnetic and dielectric properties of (Co, Zn) co-doped SnO 2 diluted magnetic semiconducting nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 5960–5966 (2016)
H. GENCER, A. Goktas, M. Gunes, H. Mutlu, S. ATALAY, Electrical transport and magnetoresistance properties of La 0.67 ca 0.33 MnO 3 film coated on pyrex glass substrate. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 22(05), 497–506 (2008)
X. Huang, C. Wu, H. Lu, F. Ren, Q. Xu, H. Ou et al., Electrical instability of amorphous indium-gallium-zinc oxide thin film transistors under monochromatic light illumination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(24), 243505 (2012)
S. Stojadinović, N. Tadić, R. Vasilić, Formation and characterization of ZnO films on zinc substrate by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 307, 650–657 (2016)
G. Voicu, D. Miu, C.-D. Ghitulica, S.-I. **ga, A.-I. Nicoara, C. Busuioc et al., Co doped ZnO thin films deposited by spin coating as antibacterial coating for metallic implants. Ceram. Int. 46(3), 3904–3911 (2020)
F. Mikailzade, H. Türkan, F. Önal, M. Zarbali, A. Göktaş, A. Tumbul, Structural and magnetic properties of polycrystalline Zn1 – x mn x O films synthesized on glass and p-type Si substrates using Sol–Gel technique. Appl. Phys. A 127(6), 408 (2021)
L. Chouhan, S. Srivastava, A comprehensive review on recent advancements in d0 ferromagnetic oxide materials. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process. 147, 106768 (2022)
L. Chouhan, G. Bouzerar, S. Srivastava, D 0 ferromagnetism in Li-doped ZnO compounds. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 6389–6397 (2021)
B. Dey, R. Narzary, S.K. Panda, J. Mallick, A. Mondal, S. Ravi et al., Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, band-gap reduction, and high optical transparency in p-type K-doped ZnO compounds for spintronics applications. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process. 148, 106798 (2022)
B. Dey, R. Narzary, L. Chouhan, S. Bhattacharjee, B. Parida, A. Mondal et al., Crystal structure, optical and dielectric properties of Ag: ZnO composite-like compounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07560-4
R. Narzary, B. Dey, S.N. Rout, A. Mondal, G. Bouzerar, M. Kar et al., Influence of K/Mg co-do** in tuning room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, optical and transport properties of ZnO compounds for spintronics applications. J. Alloys Compd. 934, 167874 (2023)
B. Dey, S.N. Rout, M. Kar, S. Srivastava, Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism of Ag: ZnO compounds. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 36(2), 657–663 (2023)
R. Narzary, B. Dey, L. Chouhan, S. Kumar, S. Ravi, S. Srivastava, Optical band gap tuning, zero dielectric loss and room temperature ferromagnetism in (Ag/Mg) co-doped SnO2 compounds for spintronics applications. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process. 142, 106477 (2022)
R. Narzary, B. Dey, S. Sen, B.N. Parida, A. Mondal, S. Ravi et al., Influence of Na/Mg co-do** in tuning microstructure, transport, optical, and magnetic properties of TiO2 compounds for spintronics applications. Magnetochemistry 8(11), 150 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The researchers would like to acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research, Taif University for funding this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AU, IUK, MA, KA, NR, SSA, and AK wrote this paper through their mutual discussion. AK and RK created the idea and submitted the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Hereby, we declare that the manuscript is our original work and not have been published or under editorial considerations anywhere else. The stated authors of the work have read the content and approved for submission of this manuscript to the Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics. There is no personal or financial conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, A., Khan, I.U., Aljohani, M. et al. Effect of yttrium on the structural, dielectric, and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO magnetic nanorods for potential spintronic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1252 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10664-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10664-8