Abstract
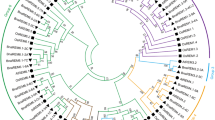
Ionotropic glutamate receptors are ligand-gated nonselective cation channels that mediate neurotransmission in the central nervous system of animals. Plants possess homologous proteins called glutamate receptor-like channels (GLRs) which are involved in vital physiological processes including seed germination, long-distance signaling, chemotaxis, Ca2+ signaling etc. Till now, a comprehensive genome-wide analysis of the GLR gene family members in different economically important species of Brassica is missing. Considering the origin of allotetraploid Brassica napus from the hybridization between the diploid Brassica oleracea and Brassica rapa, we have identified 11, 27 and 65 GLR genes in B. oleracea, B. rapa and B. napus, respectively showing an expansion of this gene family in B. napus. Chromosomal locations revealed several tandemly duplicated GLR genes in all the three species. Moreover, the gene family expanded in B. napus after allopolyploidization. The phylogenetic analysis showed that the 103 GLRs are classified into three main groups. The exon-intron structures of these genes are not very conserved and showed wide variation in intron numbers. However, protein sequences are much conserved as shown by the presence of ten short amino acid sequence motifs. Predicted cis-acting elements in 1 kb promoters of GLR genes are mainly involved in light, stress and hormone responses. RNA-seq analysis showed that in B. oleracea and B. rapa, some GLRs are more tissue specific than others. In B. napus, some GLRs are downregulated under cold stress, while others are upregulated. In summary, this bioinformatic study of the GLR gene family of the three Brassica species provides evidence for the expansion of this gene family in B. napus and also provided useful information for in-depth studies of their biological functions in Brassica.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Details of genes are given in Table 1. Details of RNA-Seq data obtained and analyzed for this study are mentioned in the manuscript and can be accessed through NCBI GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/).
References
Allender CJ, King GJ (2010) Origins of the amphiploid species Brassica napus L. investigated by chloroplast and nuclear molecular markers. BMC Plant Biol 10:54
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA et al (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp335
Beilstein MA, Nagalingum NS, Clements MD et al (2010) Dated molecular phylogenies indicate a miocene origin for Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:18724–18728. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909766107
Bortoli SD, Teardo E, Szabò I et al (2016) Evolutionary insight into the ionotropic glutamate receptor superfamily of photosynthetic organisms. Biophys Chem 218:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2016.07.004
Bowers JE, Chapman BA, Rong J, Paterson AH (2003) Unravelling angiosperm genome evolution by phylogenetic analysis of chromosomal duplication events. Nature 422:433–438
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y et al (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202
Cho D, Kim SA, Murata Y et al (2009) De-regulated expression of the plant glutamate receptor homolog AtGLR3.1 impairs long‐term Ca2+‐programmed stomatal closure. Plant J 58:437–449. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03789.x
Dai X, Zhao PX (2011) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W155–159. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr319
Dai X, Zhuang Z, Zhao PX (2011) Computational analysis of miRNA targets in plants: current status and challenges. Brief Bioinform 12:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbq065
Dai X, Zhuang Z, Zhao PX (2018) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic Acids Res 46:W49–W54. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky316
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A et al (2019) The pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D427–D432
Friedt W, Tu J, Fu T (2018) Academic and economic importance of Brassica napus Rapeseed. In: Liu S, Snowdon R, Chalhoub B (eds) The Brassica napus Genome. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–20
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R et al (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1178–D1186
Grenzi M, Bonza MC, Alfieri A, Costa A (2021) Structural insights into long-distance signal transduction pathways mediated by plant glutamate receptor-like channels. New Phytol 229:1261–1267. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17034
Grenzi M, Bonza MC, Costa A (2022) Signaling by plant glutamate receptor-like channels: what else! Curr Opin Plant Biol 68:102253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102253
Halkier BA, Gershenzon J (2006) Biology and biochemistry of glucosinolates. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:303–333
He X, Ni X, **e P (2019) Comparative transcriptome analyses revealed conserved and novel responses to Cold and freezing stress in Brassica napus L. G3: Genes Genomes Genet 9:2723–2737. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.119.400229
He X, Kang Y, Li W et al (2020) Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the TIFY gene family in the response to multiple stresses in Brassica napus L. BMC Genomics 21:736. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07128-2
Hu B, ** J, Guo A-Y et al (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296–1297
Jiao Y, Wickett NJ, Ayyampalayam S et al (2011) Ancestral polyploidy in seed plants and angiosperms. Nature 473:97–100
Kersey PJ, Allen JE, Christensen M et al (2014) Ensembl Genomes 2013: scaling up access to genome-wide data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D546–D552. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt979
Kinsella RJ, Kähäri A, Haider S et al (2011) Ensembl BioMarts: a hub for data retrieval across taxonomic space. Database 2011:bar030. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bar030
Kopsell DA, Kopsell DE (2006) Accumulation and bioavailability of dietary carotenoids in vegetable crops. Trends Plant Sci 11:499–507
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M et al (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G et al (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327
Li Y, Song Q, Zhang Y et al (2020) Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression patterns analysis of the SBP-box gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Sci Rep 10:17250
Liu S, Liu Y, Yang X et al (2014) The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat Commun 5:3930
Lohani N, Golicz AA, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2019) Genome-wide analysis of the hsf gene family in Brassica oleracea and a comparative analysis of the hsf gene family in B. oleracea, B. rapa and B. napus. Funct Integr Genomics 19:515–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0649-1
Lysak MA, Koch MA, Pecinka A, Schubert I (2005) Chromosome triplication found across the tribe Brassiceae. Genome Res 15:516–525
Mabry ME, Turner-Hissong SD, Gallagher EY et al (2021) The evolutionary history of wild, domesticated, and feral Brassica oleracea (Brassicaceae). Mol Biol Evol 38:4419–4434. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab183
Marchler-Bauer A, Bo Y, Han L et al (2017) CDD/SPARCLE: functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D200–D203
Nagaharu U, Nagaharu N (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Naz R, Khan A, Alghamdi BS et al (2022) An insight into animal glutamate receptors Homolog of Arabidopsis thaliana and their potential applications—A. Rev Plants 11:2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11192580
O’neill CM, Bancroft I (2000) Comparative physical map** of segments of the genome of Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra that are homoeologous to sequenced regions of chromosomes 4 and 5 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 23:233–243
Park W, Li J, Song R et al (2002) CARPEL FACTORY, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 12:1484–1495. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01017-5
Park JY, Koo DH, Hong CP et al (2005) Physical map** and microsynteny of Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis genome corresponding to a 222 kbp gene-rich region of Arabidopsis chromosome 4 and partially duplicated on chromosome 5. Mol Genet Genomics 274:579–588
Patthy L (1999) Genome evolution and the evolution of exon-shuffling—a review. Gene 238:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00228-0
Price MB, Jelesko J, Okumoto S (2012) Glutamate receptor homologs in plants: functions and evolutionary origins. Front Plant Sci 3:235
Roy BC, Mukherjee A (2017) Computational analysis of the glutamate receptor gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biomol Struct Dyn 35:2454–2474
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Song X, Liu G, Duan W et al (2014) Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in chinese cabbage. Mol Genet Genomics 289:541–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0833-5
Sun R (2015) Economic/academic importance of Brassica rapa. In: Wang X, Kole C (eds) The Brassica rapa genome. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–15
Sun W, Li M, Wang J (2022) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the RCI2 Gene Family in Allotetraploid Brassica napus compared with its diploid progenitors. Int J Mol Sci 23:614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020614
Teardo E, Segalla A, Formentin E et al (2010) Characterization of a plant glutamate receptor activity. Cell Physiol Biochem 26:253–262
Teardo E, Formentin E, Segalla A et al (2011) Dual localization of plant glutamate receptor AtGLR3.4 to plastids and plasmamembrane. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA-Bioenerg 1807:359–367
Tong C, Wang X, Yu J et al (2013) Comprehensive analysis of RNA-seq data reveals the complexity of the transcriptome in Brassica rapa. BMC Genomics 14:689. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-689
Town CD, Cheung F, Maiti R et al (2006) Comparative genomics of Brassica oleracea and Arabidopsis thaliana reveal gene loss, fragmentation, and dispersal after polyploidy. Plant Cell 18:1348–1359
Wang X, Wang H, Wang J et al (2011) The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat Genet 43:1035–1039
Wang X, Wu J, Liang J et al (2015) Brassica database (BRAD) version 2.0: integrating and mining Brassicaceae species genomic resources. Database 2015:bav093
Wang T, ** X, Cao Y et al (2019) Genome-wide exploration and characterization of miR172/euAP2 genes in Brassica napus L. for likely role in flower organ development. BMC Plant Biol 19:336. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1936-2
Wang Y, Yu D, Zhao H et al (2022) A glutamate receptor-like gene is involved in ABA-mediated growth control in Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens. Plant Signal Behav 17:2145057. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2022.2145057
Wu X, Pan L, Guo X et al (2022) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of BrAGC genes in Brassica rapa reveal their potential roles in sexual reproduction and abiotic stress tolerance. Front Genet 13:1044853. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.1044853
**e L, Shang Q (2018) Genome-wide analysis of purple acid phosphatase structure and expression in ten vegetable species. BMC Genomics 19:646. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5022-1
Xu L, Dong Z, Fang L et al (2019) OrthoVenn2: a web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W52–W58. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz333
Yang Y-W, Lai K-N, Tai P-Y, Li W-H (1999) Rates of nucleotide substitution in angiosperm mitochondrial DNA sequences and dates of divergence between Brassica and other angiosperm lineages. J Mol Evol 48:597–604
Yu C-S, Chen Y-C, Lu C-H, Hwang J-K (2006) Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins 64:643–651
Yu J, Tehrim S, Zhang F et al (2014) Genome-wide comparative analysis of NBS-encoding genes between Brassica species and Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics 15:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-3
Yu B, Wu Q, Li X et al (2022) GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR-like gene OsGLR3.4 is required for plant growth and systemic wound signaling in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 233:1238–1256. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17859
Yu B, Sun Y, ** X et al (2023) Rice glutamate receptor-like channel OsGLR3.4 modulates the root tropism growth towards amino acids via plasma membrane depolarization and ROS generation. Environ Exp Bot 205:105146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.105146
Zheng Y, Luo L, Wei J et al (2018) The glutamate receptors AtGLR1.2 and AtGLR1.3 increase cold tolerance by regulating jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 506:895–900
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BCR, RG and AM conceived the idea and designed the work; BCR, AM and NS carried out the experiments. Manuscript was prepared and edited by BCR, AM and RG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable as no human/animal related work was involved.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, B.C., Shukla, N., Gachhui, R. et al. Genome-wide analysis of glutamate receptor gene family in allopolyploid Brassica napus and its diploid progenitors. Genetica 151, 293–310 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-023-00192-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-023-00192-y