Abstract
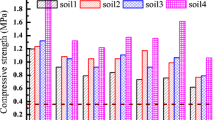
The stabilization/solidification (S/S) method is one of the most effective remediation techniques for treating contaminated soils. Several stabilizers, mostly the cementitious materials, have been used for the S/S treatment. In this paper, the feasibility of utilizing fuel fly ash (FFA) as a partial replacement of ordinary Portland cement (OPC) for the S/S treatment of marl soil contaminated with heavy metals was investigated. Two industrial waste materials, namely steel and electroplating wastes, were used to synthetically contaminate the marl soil. The stabilizers comprising of OPC and FFA were mixed with the contaminated soil at different dosages ranging from 10 to 40%, by mass, and a total of 48 S/S-treated soil mixtures were prepared. A series of experiments, including density, porosity, permeability, unconfined compressive strength (UCS), and toxicity characteristics leaching procedure (TCLP), were carried out on the soil mixtures to evaluate the efficiency of the proposed S/S treatment. Test results showed that the incorporation of FFA at higher volumes reduced the density and increased the porosity and permeability of the treated mixtures. Although FFA addition resulted in reducing the UCS values by an average of 46%, and this reduction was more significant at higher FFA percentages, the UCS values of all mixtures were more than 0.35 MPa (350 kPa), which passed the minimum requirements set by USEPA. In addition, the metal immobilization ability of the proposed treatment was confirmed by the TCLP analysis. As compared to the negative effect of the contamination of the soil by the electroplating waste, the contamination of the soil by steel waste had a higher negative effect. The results of this study would contribute in selecting an environment-friendly treatment of the contaminated soils using industrial waste materials, such as FFA, as a partial replacement of OPC. Nevertheless, the present study is an initial attempt to explore the possibility of utilizing FFA as a partial replacement of OPC in S/S treatment of marl soil contaminated with heavy metals. It is recommended to conduct another study in future including analysis of the treated soil mixtures using XRD, SEM, and FTIR techniques to better understand the stabilization/solidification mechanism and its implications on the test results.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All authors ensure that all data and materials used in preparing this article are available and comply with field standards.
References
Ahmad, S., Al-Amoudi, O. S. B., Mustafa, Y. M. H., et al. (2020). Stabilization and solidification of oil-contaminated sandy soil using portland cement and supplementary cementitious materials. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 32, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0003169
Ahmad, S., Ba-Naimoon, M. S. M., Bahraq, A. A., et al. (2022). Stabilization/solidification of petroleum oil-contaminated soil using different stabilizers to deliver a pavement subbase material. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07295-2
Ahmad, S., Khalid, H. R., Shaqraa, A. A., et al. (2023). Properties of natural pozzolan-based geopolymer concrete: Effects of natural pozzolan content, type of alkaline activator, and silicate/alkali ratio. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 27, 356–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2022.2043941
Al-Amoudi, O. S. B., Al-Homidy, A. A., Maslehuddin, M., & Saleh, T. A. (2017). Method and mechanisms of soil stabilization using electric arc furnace dust. Science and Reports, 7, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46676
Al-Amoudi, O. S. B., Khan, K., & Al-Kahtani, N. S. (2010). Stabilization of a Saudi calcareous marl soil. Construction and Building Materials, 24, 1848–1854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.04.019
Al-Malack, M. H., Abdullah, G. M., Al-Amoudi, O. S. B., & Bukhari, A. A. (2016). Stabilization of indigenous Saudi Arabian soils using fuel oil fly ash. Journal of King Saud University - Engineering Sciences, 28, 165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2014.04.005
Asavapisit, S., & Chotklang, D. (2004). Solidification of electroplating sludge using alkali-activated pulverized fuel ash as cementitious binder. Cement and Concrete Research, 34, 349–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.08.012
ASTM International. (2007). ASTM D422-63: Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils (pp. 1–8). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D0422-63R07
ASTM International. (2014). ASTM D854-14: Standard test methods for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer (pp. 1–9). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D0854-23
ASTM International. (2018). ASTM D4318–17: Standard test methods for liquid limit, plastic limit, and plasticity index of soils (pp. 1–20). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D4318-17E01
ASTM International. (2016a). ASTM D4254: Standard test methods for minimum index density and unit weight of soils and calculation of relative density (pp. 1–9). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D4254-16
ASTM International. (2016b). ASTM D2166/D2166M-16: Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil (pp. 1–6). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D2166_D2166M-16
ASTM International. (2000). ASTM D2434: Standard test method for permeability of granular soils (constant head) (pp. 1–5). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D2434-68R
ASTM International. (2017). ASTM D2487: Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (unified soil classification system) (pp. 1–10). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D2487-17
ASTM International. (2015). ASTM D3282: Standard practice for classification of soils and soil-aggregate mixtures for highway construction purposes (pp. 1–7). Conshoshocken, PA, United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D3282-09
Bakkar, A., Seleman, M.M.E.-S., Ahmed, M. M. Z., et al. (2023). Recovery of vanadium and nickel from heavy oil fly ash (HOFA): A critical review. RSC Advances, 13, 6327–6345.
Bayar, S., & Talinli, İ. (2013). Solidification/stabilization of hazardous waste sludge obtained from a chemical industry. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 15, 157–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0494-1
Brigden, K., Labunska, I., & Stringer, R. (2000). Identification of organic pollutants and heavy metal contaminants in filter ash collected from the Siderca primary and secondary steel smelter, Campana, Argentina 2000. Technical note, http://www.greenpeace.to/publications/Siderca%20report.pdf. Accessed 10.05.2023.
Chen, H., Yuan, H., Mao, L., et al. (2020). Stabilization/solidification of chromium-bearing electroplating sludge with alkali-activated slag binders. Chemosphere, 240, 124885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124885
Dehghan, H., Tabarsa, A., Latifi, N., & Bagheri, Y. (2019). Use of xanthan and guar gums in soil strengthening. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 21, 155–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1625-0
Du, Y.-J., & Jiang, N.-J. (2022). Stabilization/solidification of contaminated soils: A case study. In: Low carbon stabilization and solidification of hazardous wastes (pp. 75–92). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-824004-5.00007-4
Feng, Y. S., Du, Y. J., Reddy, K. R., & **a, W. Y. (2018). Performance of two novel binders to stabilize field soil with zinc and chloride: Mechanical properties, leachability and mechanisms assessment. Construction and Building Materials, 189, 1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.072
Feng, Y. S., Du, Y. J., Zhou, A., et al. (2021). Geoenvironmental properties of industrially contaminated site soil solidified/stabilized with a sustainable by-product-based binder. Science of the Total Environment, 765, 142778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142778
Ghais, A. (2021). Power station waste utilization in Arab Gulf countries case study: Fly ash production and economical potential. International Journal of Waste Resources, 11, 402.
Kim, G. M., Khalid, H. R., Park, S. M., & Lee, H. K. (2017). Flow property of alkali-activated slag with modified precursor. ACI Materials Journal, 114, 867–876. https://doi.org/10.14359/51700794
LaGrega, M. D., Buckingham, P. L., & Evans, J. C. (2001). Hazard waste management, 2nd edi. McGraw-Hall.
Li, G., Li, H., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Stabilization/solidification of heavy metals and PHe contaminated soil with β-cyclodextrin modified biochar (β-CD-BC) and portland cement. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031060
Liu, L., Li, W., Song, W., & Guo, M. (2018). Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: Principles and applicability. Science of the Total Environment, 633, 206–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.161
Luo, Z., Tang, C., Hao, Y., et al. (2020). Solidification/stabilization of heavy metals and its efficiency in lead–zinc tailings using different chemical agents. Environmental Technology (United Kingdom), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1845817
Malviya, R., & Chaudhary, R. (2006). Factors affecting hazardous waste solidification/stabilization: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.065
Means, J. L., Smith, L. A., Nehring, K. W., et al. (1995). The application of solidification/stabilization to waste materials. Lewis Publishers.
Meuser, H. (2012). Soil remediation and rehabilitation: Treatment of contaminated and disturbed land. Springer.
Moon, D. H., & Dermatas, D. (2006). An evaluation of lead leachability from stabilized/solidified soils under modified semi-dynamic leaching conditions. Engineering Geology, 85, 67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.09.028
Mustafa, Y. M. H., Al-Amoudi, O. S. B., Ahmad, S., et al. (2020). Utilization of portland cement with limestone powder and cement kiln dust for stabilization/solidification of oil-contaminated marl soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10590-w
Oluwatuyi, O. E., Ashaka, E. C., & Ojuri, O. O. (2019). Cement stabilization treatment of lead and naphthalene contaminated lateritic soils. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Landscape Management, 27, 41–48.
Oluwatuyi, O. E., & Ojuri, O. O. (2017). Environmental performance of lime–rice husk ash stabilized lateritic soil contaminated with lead or naphthalene. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 35, 2947–2964.
Oluwatuyi, O. E., Ojuri, O. O., & Khoshghalb, A. (2020). Cement-lime stabilization of crude oil contaminated kaolin clay. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 12, 160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.07.010
Park, S. M., Khalid, H. R., Seo, J. H., et al. (2018). Pressure-induced geopolymerization in alkali-activated fly ash. Sustainability, 10(3538), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103538
Pham, T. A., Kyokawa, H., Koseki, J., & Dias, D. (2022). A new index for the strength analysis and prediction of cement-mixed soils. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 27, 1512–1534. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2022.2086929
Randall, P., & Chattopadhyay, S. (2004). Advances in encapsulation technologies for the management of mercury-contaminated hazardous wastes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 114, 211–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.08.010
Shentu, J., Li, X., Han, R., et al. (2022). Effect of site hydrological conditions and soil aggregate sizes on the stabilization of heavy metals (Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) by biochar. Science of the Total Environment, 802, 149949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149949
USEPA. (1992). Method 1311.Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP). Publication SW−846: Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods. www.epa.gov/epaoswer/hazwaste/test/pdfs/1311.pdf
USEPA. (1986). Method 9100: Saturated hydraulic conductivity, saturated leachate conductivity, and intrinsic permeability. Bristol.
USEPA. (1999). Solidification/stabilization resource guide (EPA 542-B-99-002). Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Wan, X., Ding, J., Mou, C., et al. (2023). Alkali-activated red mud in stabilizing marine dredged clay with low amount of cement. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 0, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2023.2194948
Wang, F., Xu, J., Yin, H., et al. (2021). Sustainable stabilization/solidification of the Pb, Zn, and Cd contaminated soil by red mud-derived binders. Environmental Pollution, 284, 117178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117178
Wang, S., & Vipulanandan, C. (2000). Solidification/stabilization of Cr(VI) with cement. Cement and Concrete Research, 30, 385–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0008-8846(99)00265-3
Wiles, C. C. (1987). A review of solidification/stabilization technology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 14, 5–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3894(87)87002-4
Xu, D., Ji, P., Wang, L., et al. (2021a). Effect of modified fly ash on environmental safety of two soils contaminated with cadmium and lead. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 215, 112175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112175
Xu, D. M., Fu, R. B., Wang, J. X., et al. (2021b). Chemical stabilization remediation for heavy metals in contaminated soils on the latest decade: Available stabilizing materials and associated evaluation methods-A critical review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 321, 128730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128730
Ye, S., Wang, L., & Liu, T. (2022). Study of solidification and stabilization of heavy metals by passivators in heavy metal-contaminated soil. Open Chemistry, 20, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2021-0101
Yin, C. Y., Ali, W. S. W., & Lim, Y. P. (2008). Oil palm ash as partial replacement of cement for solidification/stabilization of nickel hydroxide sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150, 413–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.119
Yin, C.-Y., Bin, M. H., & Shaaban, M. G. (2006). Stabilization/solidification of lead-contaminated soil using cement and rice husk ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 1758–1764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.013
Yin, C.-Y., Shaaban, M. G., & Bin, M. H. (2007). Chemical stabilization of scrap metal yard contaminated soil using ordinary portland cement: Strength and leachability aspects. Building and Environment, 42, 794–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2005.09.013
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support provided by the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department and IRC-CBM at King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals (KFUPM), Dhahran, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Shamsad Ahmad, Ashraf A. Bahraq, and Hammad R. Khalid. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Lateef Olawale Alamutu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical responsibilities of authors
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Consent to participate
All authors agree with the content and all authors give explicit consent to submit and that they obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out, before the work is submitted to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, S., Bahraq, A.A., Khalid, H.R. et al. Stabilization/solidification of heavy metal-contaminated marl soil using a binary system of cement and fuel fly ash. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1557 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12176-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12176-8