Abstract
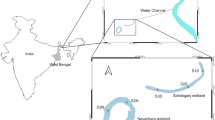
The river Ganga has several floodplain wetlands that support its ecology and ecosystem. Phytoplankton is an important component of the aquatic ecosystem, which plays an important role as a bioindicator for the assessment of aquatic health. The present study was conducted between 2018 and 2019 to understand the seasonal variation in the phytoplankton diversity of the Charaganga wetland and, parallelly, in the river Ganga in Nabadweep, India. The study explains how riverine connectivity affects the structure of the algal community in the wetland ecosystem. In the study, it has been observed that in the wetland, maximum mean phytoplankton density was noticed during pre-monsoon, i.e., 4079 unit l−1 followed by post-monsoon 3812 unit l−1 and monsoon 550 unit l−1, respectively. In the river system, the phytoplankton density varied from 78 unit l−1 to 653 unit l−1 seasonally, i.e., highest during monsoon and lowest during pre-monsoon. In both the ecosystems, i.e., wetland and river, the supreme influential group was Cyanophyceae followed by diatoms. One-way ANOVA showed a significant variation (p > 0.05) of three algal groups of phytoplankton (Bacillariophyceae, Coscinodiscophyceae, Chlorophyceae) in the river, while in the wetland, no significant variation (p > 0.05) was found among the other algal groups. The observed higher Shannon and Margalef’s species richness value in the wetland was observed than in the river defines the significance and importance of the wetland ecosystem, which may support the growth and conservation of various aquatic organisms as well. The study highlighted that the influencing abiotic factors like water temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, and nutrients have affected the phytoplankton community in both the water bodies, i.e., wetland and river. We concluded that river connectivity is required to restore the biotic flora of the wetland ecosystem.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Experimental data will be provided by the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alam, R., Ahmed, Z., Seefat, S. M., & Nahin, K. T. K. (2021). Assessment of surface water quality around a landfill using multivariate statistical method, Sylhet, Bangladesh. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 15, 100422.
APHA. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, (23).
Arumugam, S., Sigamani, S., Samikannu, M., & Perumal, M. (2016). Assemblages of phytoplankton diversity in different zonation of Muthupet mangroves. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 3, 234–241.
Balzer, M. J., Hitchcock, J. N., Hadwen, W. L., Kobayashi, T., Westhorpe, D. P., Boys, C., & Mitrovic, S. M. (2023). Experimental additions of allochthonous dissolved organic matter reveal multiple trophic pathways to stimulate planktonic food webs. Freshwater Biology, 68(5), 821–836.
Bellinger, E. G., & Sigee, D. C. (2015). Freshwater algae: Identification, enumeration and use as bioindicators. John Wiley & Sons.
Bera, A., Dutta, T. K., Bhattacharya, M., Patra, B. C., & Kumar Sar, U. (2022). Anthropogenic stress on river health: With special reference to Kangsabati River, West Bengal, India. In River Health and Ecology in South Asia (pp. 39–61). Springer.
Bera, K. (2014). Geo-informatics approach to demarcate ground water potential zone in semi-arid region of Kansai-Tangai interfluves area. International Multidisciplinary e-Journal, 3(9), 1–9.
Bijoy Nandan, S., Jayachandran, P. R., & Sreedevi, O. K. (2014). Spatio-temporal pattern of primary production in a tropical coastal Wetland (Kodungallur-Azhikode Estuary), South West Coast of India. Journal of Coastal Development, 17, 392.
Boyd, C. E., & Tucker, C. S. (1998). Ecology of aquaculture ponds. In Pond aquaculture water quality management (pp. 8–86). Springer.
Cardoso, S. J., Roland, F., Loverde-Oliveira, S. M., & de MoraesHuszar, V. L. (2012). Phytoplankton abundance, biomass and diversity within and between Pantanal wetland habitats. Limnologica, 42(3), 235–241.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes 1. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(2), 361–369.
Carlson, R. E., & Simpson, J. (1996). A coordinator’s guide to volunteer lake monitoring methods. North American Lake Management Society, 96, 305.
Chan, F., Pace, M. L., Howarth, R. W., & Marino, R. M. (2004). Bloom formation in heterocystic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria: The dependence on colony size and zooplankton grazing. Limnology and Oceanography, 49(6), 2171–2178.
Chaparro, G., O’Farrell, I., & Hein, T. (2019). Multi-scale analysis of functional plankton diversity in floodplain wetlands: Effects of river regulation. Science of the Total Environment, 667, 338–347.
Chaurasia, M., & Pandey, G. C. (2007). Study of physico-chemical characteristics of some water ponds of Ayodhya-Faizabad. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 27(11), 1019.
Cox, E. J., & Cox, E. J. (1996). Identification of freshwater diatoms from live material (Vol. 158). Chapman & Hall.
Desikachary, T. V. (1959). Cyanophyta. Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
Desta, H., Lemma, B., & Fetene, A. (2012). Aspects of climate change and its associated impacts on wetland ecosystem functions: A review. Journal of American Science, 8(10), 582–596.
Dixit, R. B., Patel, A. K., Toppo, K., & Nayaka, S. (2017). Emergence of toxic cyanobacterial species in the Ganga River, India, due to excessive nutrient loading. Ecological Indicators, 72, 420–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.08.038
Dupuis, A. P., & Hann, B. J. (2009). Climate change, diapause termination and zooplankton population dynamics: An experimental and modelling approach. Freshwater Biology, 54(2), 221–235.
Ernst, B., Neser, S., O’Brien, E., Hoeger, S. J., & Dietrich, D. R. (2006). Determination of the filamentous cyanobacteria Planktothrix rubescens in environmental water samples using an image processing system. Harmful Algae, 5(3), 281–289.
Frank, S. J. D., Gopi, G. V., Lakshminarayanan, N., & Pandav, B. (2022). Factors influencing occurrence and species richness of heronries in the wetlands of Tamil Nadu, India. Wetlands, 42(1), 1–10.
Gao, J., Shen, L., Nie, Z., Zhu, H., Cao, L., Du, J., & Xu, G. (2022). Microbial and planktonic community characteristics of Eriocheir sinensis culture ponds experiencing harmful algal blooms. Fishes, 7(4), 180.
Ghosh, D., & Biswas, J. K. (2015). Impact of jute retting on phytoplankton diversity and aquatic health: Biomonitoring in a tropical oxbow lake. Journal of. Ecological Engineering, 16(5), https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/60449
Ghosh, D., & Biswas, J. K. (2018). Impact of jute retting on physicochemical profile of Chhariganga oxbow lake in Nadia district, West Bengal, India. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 3(1), 36–44.
Gogoi, P., Das, S. K., Sarkar, S. D., Chanu, T. N., Manna, R. K., Sengupta, A., et al. (2021a). Environmental factors driving phytoplankton assemblage pattern and diversity: Insights from Sundarban eco-region, India. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 21(2), 354–367.
Gogoi, P., Kumari, S., Sarkar, U. K., Lianthuamluaia, L., Puthiyottil, M., Bhattacharjya, B. K., & Das, B. K. (2021b). Dynamics of phytoplankton community in seasonally open and closed wetlands in the Teesta–Torsa basin, India, and management implications for sustainable utilization. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193, 1–25.
Gogoi, P., Sinha, A., Sarkar, S. D., Chanu, T. N., Yadav, A. K., Koushlesh, S. K., et al. (2019). Seasonal influence of physicochemical parameters on phytoplankton diversity and assemblage pattern in Kailash Khal, a tropical wetland, Sundarbans, India. Applied Water Science, 9(7), 1–13.
Guiry, M. D., & Guiry, G. M. (2014). AlgaeBase. National University of Ireland.
Hammer, D. A., & Bastian, R. K. (2020). Wetlands ecosystems: Natural water purifiers? In Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment (pp. 5–19). CRC Press.
Haque, M., Jewel, M., Sayed, A., Akhi, M., Atique, U., Paul, A. K., et al. (2021). Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton community and functional groups in a tropical river. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(11), 1–16.
Harris, L., & Gurel, E. (1986). Price and volume effects associated with changes in the S&P 500 list: New evidence for the existence of price pressures. The Journal of Finance, 41(4), 815–829.
Huang, Z., Pan, B., Soininen, J., Liu, X., Hou, Y., & Liu, X. (2023). Seasonal variation of phytoplankton community assembly processes in Tibetan Plateau floodplain. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1122838.
Imhoff, J. F., Sahl, H. G., Soliman, G. S. H., & Trüper, H. G. (1979). The Wadi Natrun: Chemical composition and microbial mass developments in alkaline brines of eutrophic desert lakes. Geomicrobiology Journal, 1(3), 219–234.
Issa, A. A., Abd-Alla, M. H., & Ohyama, T. (2014). Nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria: Future prospect. Advances in Biology and Ecology of Nitrogen Fixation, 2, 24–48.
Kahsay, A., Lemmens, P., Triest, L., De Meester, L., Kibret, M., Verleyen, E., et al. (2022). Plankton diversity in tropical wetlands under different hydrological conditions (Lake Tana, Ethiopia). Frontiers in Environmental Science, 189.
Kataki, S., Chatterjee, S., Vairale, M. G., Sharma, S., Dwivedi, S. K., & Gupta, D. K. (2021). Constructed wetland, an eco-technology for wastewater treatment: A review on various aspects of microbial fuel cell integration, low temperature strategies and life cycle impact of the technology. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 148, 111261.
Kumar, J., Alam, A., Sarkar, U. K., Das, B. K., Kumar, V., & Srivastava, S. K. (2020). Assessing the phytoplankton community and diversity in relation to physico-chemical parameters in a tropical reservoir of the River Ganga basin, India. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 6, 1–15.
Lackey, J. B. (1938). The manipulation and counting of river plankton and changes in some organisms due to formalin preservation. Public Health Reports (1896-1970), 2080–2093.
Lakshminarayana, J. S. S. (1965). Studies on the phytoplankton of the River Ganges, Varanasi, India, Part II “The seasonal growth and succession of the plankton algae in the River Ganges”. Hydrobiologia, 25(1), 138–165.
Li, X., Zhao, Y., Chai, F., Yu, H., Sun, X., & Liu, D. (2022). Phytoplankton community structure dynamics in relation to water environmental factors in Zhalong Wetland. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 14996.
Liu, X., Song, J., Ren, Y., Zhan, D., Liu, T., Liu, K., et al. (2023). Spatio-temporal patterns of zooplankton community in the Yellow River estuary: Effects of seasonal variability and water-sediment regulation. Marine Environmental Research, 106060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2023.106060
Lopez-Archilla, A. I., Moreira, D., López-García, P., & Guerrero, C. (2004). Phytoplankton diversity and cyanobacterial dominance in a hypereutrophic shallow lake with biologically produced alkaline pH. Extremophiles, 8(2), 109–115.
Meena, D. K., Lianthuamluaia, L., Mishal, P., Swain, H. S., Naskar, B. K., Saha, S., et al. (2019). Assemblage patterns and community structure of macro-zoobenthos and temporal dynamics of eco-physiological indices of two wetlands, in lower Gangetic plains under varying ecological regimes: A tool for wetland management. Ecological Engineering, 130, 1–10.
Mitbavkar, S., & Anil, A. C. (2008). Seasonal variations in the fouling diatom community structure from a monsoon influenced tropical estuary. Biofouling, 24(6), 415–426.
Mitsch, W. J., Bernal, B., Nahlik, A. M., Mander, Ü., Zhang, L., Anderson, C. J., Jørgensen, S. E., & Brix, H. (2013). Wetlands carbon, and climate change. Landscape Ecology, 28, 583–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-012-9758-8
Mohanty, T. R., Tiwari, N. K., Kumari, S., Ray, A., Manna, R. K., Bayen, S., et al. (2022). Variation of Aulacoseira granulata as an eco-pollution indicator in subtropical large river Ganga in India: A multivariate analytical approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18096-9
Munn, M. D., Osborne, L. L., & Wiley, M. J. (1989). Factors influencing periphyton growth in agricultural streams of central Illinois. Hydrobiologia, 174(2), 89–97.
Nag, S. K., Das Ghosh, B., Nandy, S., Aftabuddin, M., Sarkar, U. K., & Das, B. K. (2023). Comparative assessment of carbon sequestration potential of different types of wetlands in lower Gangetic basin of West Bengal, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 154.
Naskar, M., Sarkar, S. D., Raman, R. K., Gogoi, P., Sahu, S. K., Chandra, G., & Bhor, M. (2020). Quantifying plankto-environmental interactions in a tropical river Narmada, India: An alternative model-based approach. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 20(2), 265–275.
Palit, D., & Mukherjee, A. (2010). Characterization of physico-chemical properties of water and soil in Lalbandha fresh water wetland in Birbhum District West Bengal. Ecology, Environment and Conservation Journal, 15(4), 239–245.
Palmer, C. M. (1969). A composite rating of algae tolerating organic pollution 2. Journal of phycology, 5(1), 78–82.
Parakkandi, J., Saha, A., Sarkar, U. K., Das, B. K., Puthiyottil, M., Muhammadali, S. A., et al. (2021). Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton in association with habitat parameters in a tropical reservoir, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14(10), 1–15.
Potapova, M., & Charles, D. F. (2003). Distribution of benthic diatoms in US rivers in relation to conductivity and ionic composition. Freshwater Biology, 48(8), 1311–1328.
Prants, S. V., Andreev, A. G., Budyansky, M. V., & Uleysky, M. Y. (2015). Impact of the Alaskan Stream flow on surface water dynamics, temperature, ice extent, plankton biomass, and walleye pollock stocks in the eastern Okhotsk Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 151, 47–56.
Prescott, G. W. (1982). Algae of the Western Great Lakes Area (pp. 1–977). Otto Koeltz Science Pub.
Rai, U. N., Tripathi, R. D., Singh, N. K., Upadhyay, A. K., Dwivedi, S., Shukla, M. K., et al. (2013). Constructed wetland as an ecotechnological tool for pollution treatment for conservation of Ganga river. Bioresource Technology, 148, 535–541.
Reynolds, C. S., (1995) River plankton – The paradigm regained. In: D. Harper and A. J. D. Ferguson (eds.), Ecological Basis for River Management. Wiley, New York, pp. 161–174.
Sahu, G., Satpathy, K. K., Mohanty, A. K., & Sarkar, S. K. (2012). Variations in community structure of phytoplankton in relation to physicochemical properties of coastal waters, southeast coast of India.
Sandilyan, S. (2022). Alien fish species in Indian inland wetlands: Current status and future challenges. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 30(2), 423–437.
Saravanakumar, A., Rajkumar, M., Thivakaran, G. A., & Serebiah, J. S. (2008). Abundance and seasonal variations of phytoplankton in the creek waters of western mangrove of Kachchh-Gujarat. Journal of Environmental Biology, 29(2), 271.
Sarkar, S. D., Sahoo, A. K., Gogoi, P., Raman, R. K., Munivenkatappa, M. H., Kumari, K., et al. (2019). Phytoplankton biomass in relation to flow dynamics: The case of a tropical river Mahanadi, India. Tropical Ecology, 60(4), 485–494.
Sarkar, U. K., Mishal, P., Borah, S., Karnatak, G., Chandra, G., Kumari, S., et al. (2020). Status, potential, prospects, and issues of floodplain wetland fisheries in India: Synthesis and review for sustainable management. Reviews in Fisheries Science and Aquaculture, 29(1), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2020.1779650
Sayeed, M., Hossain, M. A. R., Wahab, M., Hasan, M., Simon, K. D., & Mazumder, S. K. (2015). Water and sediment quality parameters in the Chalan Beel, the largest wetland of Bangladesh. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 33(4), 895–904.
Seeta, Y., & Reddy, P. M. (2018). Ecological studies of the River Krishna near Gadwal, Telangana with reference to water quality. G-Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(4), 37–39.
Sekerci, Y., & Petrovskii, S. (2018). Global warming can lead to depletion of oxygen by disrupting phytoplankton photosynthesis: A mathematical modelling approach. Geosciences, 8(6), 201.
Sharif, A. S. M., Islam, M. S., Hoque, M. N., & Bhuyan, M. S. (2017). Spatial and temporal environmental effect of lower Meghna River & its estuary on phytoplankton, Bangladesh. System, 8(9), 10–11.
Shen, J., Qin, G., Yu, R., Zhao, Y., Yang, J., An, S., et al. (2021). Urbanization has changed the distribution pattern of zooplankton species diversity and the structure of functional groups. Ecological Indicators, 120, 106944.
Singh, Y., Singh, G., Khattar, J. S., Barinova, S., Kaur, J., Kumar, S., & Singh, D. P. (2022). Assessment of water quality condition and spatiotemporal patterns in selected wetlands of Punjab, India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(2), 2493–2509.
Singha, P., & Pal, S. (2023). Wetland transformation and its impact on the livelihood of the fishing community in a flood plain river basin of India. Science of The Total Environment, 858, 159547.
Smith, G. M. (1950). Fresh-water algae of the United States.
Sridhar, R., Thangaradjou, T., Kumar, S. S., & Kannan, L. (2006). Water quality and phytoplankton characteristics in the Palk Bay, southeast coast of India. Journal of environmental biology, 27(3), 561–566.
Tas, B., & Gonulol, A. (2007). An ecologic and taxonomic study on phytoplankton of a shallow lake, Turkey. Journal of Environmental Biology, 28(2), 439.
Tiwari, N. K., das Gupta, S., Swain, H. S., Jha, D. N., Samanta, S., Manna, R. K., et al. (2022a). Water quality assessment in the ecologically stressed lower and estuarine stretches of river Ganga using multivariate statistical tool. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(7), 1–26.
Tiwari, N. K., Mohanty, T. R., Swain, H. S., Manna, R. K., Samanta, S., & Das, B. K. (2022b). Multidecadal assessment of environmental variables in the river Ganga for pollution monitoring and sustainable management. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(8), 1–33.
Varol, M., & Şen, B. (2018). Abiotic factors controlling the seasonal and spatial patterns of phytoplankton community in the Tigris River, Turkey. River Research and Applications, 34(1), 13–23.
Venkateshwarlu, M., Shahnawaz, A., & Honneshappa, K. (2011). A study on plankton dynamics of two wetland systems in Shimoga District, Karnataka (India). Current Biotica, 4(4), 461–468.
Visser, P. M., Ibelings, B. W., Bormans, M., & Huisman, J. (2016). Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Aquatic Ecology, 50(3), 423–441.
Wetzel, R. G., Likens, G. E., Wetzel, R. G., & Likens, G. E. (1991). Inorganic nutrients: nitrogen, phosphorus, and other nutrients. Limnological Analyses, 81–105.
**ao, R., Wang, Q., Zhang, M., Pan, W., & Wang, J. J. (2020). Plankton distribution patterns and the relationship with environmental gradients and hydrological connectivity of wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 20(4), 584–596.
Ye, X., Meng, Y., Xu, L., & Xu, C. (2019). Net primary productivity dynamics and associated hydrological driving factors in the floodplain wetland of China’s largest freshwater lake. Science of the Total Environment, 659, 302–313.
Zhao, W., Li, Y., Jiao, Y., Zhou, B., Vogt, R. D., Liu, H., et al. (2017). Spatial and temporal variations in environmental variables in relation to phytoplankton community structure in a eutrophic river-type reservoir. Water, 9(10), 754.
Funding
Funding for the abovementioned work is provided by the National Mission for Clean Ganga, Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Trupti Rani Mohanty: plankton analysis and MS preparation; Nitish Kumar Tiwari: field sampling, water quality analysis, statistical analysis, and MS preparation; Basanta Kumar Das: conceptualization, fund acquisition, and MS review; Himanshu Sekhar Swain: MS writing; Canciyal Jhonson: MS writing; Tanushree Banarjee: MS writing. All the author’s reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical responsibilities of authors
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Ethical approval
All the abovementioned work has been carried out as per the approval of the Institute’s ethical committee, ICAR-CIFRI.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, T.R., Tiwari, N.K., Das, B.K. et al. Riverine connectivity influences the phytoplankton ecology in the open floodplain wetland of the lower river Ganga. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1403 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11983-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11983-3