Abstract
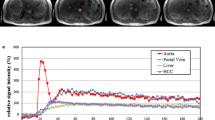
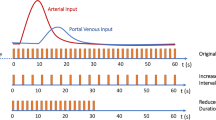
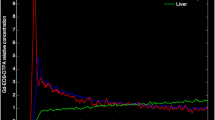
The purpose of this study was to compare measurements of hepatic tissue blood flow (TBF) calculated by xenon and perfusion CT. Seven patients with normal liver and eight with chronic liver disease underwent both xenon and perfusion CT. During xenon CT examinations, serial abdominal CT scans were obtained every minute before and during 4 min of nonradioactive 25% (v/v) xenon gas inhalation and 5 min of administration of oxygen-rich air. Hepatic arterial and portal venous TBF were measured separately with a special imaging system using the Kety-Schmidt expression based on the Fick principle (AZ-7000W; Anzai Medical Co.). The hepatic arterial fraction (HAF) was calculated as follows: [hepatic arterial TBF/(hepatic arterial TBF + portal venous TBF)]. During perfusion CT examinations, total hepatic TBF and HAF were also calculated from the enhanced CT cine image data on a workstation using a commercially available software package based on a deconvolution algorithm (CT Perfusion 3 GE Healthcare, USA). Total hepatic TBF measured by xenon and perfusion CT was 82.9±15 and 82.8±18 ml/min/100 g, respectively. The measured values by the two techniques showed a significant correlation (R 2= 0.657, P < 0.05). HAF measured by xenon and perfusion CT was 26.6±11 and 21.8±13%, respectively. The measured values by the two techniques also showed a significant correlation (R 2= 0.869, P < 0.05). We conclude that there was a good correlation between hepatic TBF quantified by xenon CT and perfusion CT.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leen E, Goldberg JA, Anderson JR, Robertson J, Moule B, Cook TG, Mcardle CS (1993) Hepatic perfusion changes in patients with liver metastases: comparison with those patients with cirrhosis. Gut 34:554–557
Tsushima Y, Blomley MJ, Kusano S, Endo K (1999) The portal component of hepatic perfusion measured by dynamic CT: an indicator of hepatic parenchymal damage. Dig Dis Sci 44:1632–1638
Lautt WW (1985) Mechanism and role of intrinsic regulation of hepatic arterial blood flow: hepatic arterial buffer response. Am J Physiol 249:G549–G556
Kleber G, Steudel N, Behrmann C, Zipprich A, Hubner G, Lotterer E, Fleig WE (1999) Hepatic arterial flow volume and reserve in patients with cirrhosis: use of intra-arterial Doppler and adenosine infusion. Gastroenterology 116:906–914
Johnson DJ, Muhlbacher F, Wilmore DW (1985) Measurement of hepatic blood flow. J Surg Res 39:470–481
Zeeh J, Lange H, Bosch J, Pohl S, Loesgen H, Eggers R, Navasa M, Chesta J, Bircher J (1988) Steady-state extrarenal sorbitol clearance as a measure of hepatic plasma flow. Gastroenterology 95:749–759
Miles KA, Hayball MP, Dixon AK (1993) Functional images of hepatic perfusion obtained with dynamic CT. Radiology 188:405–411
Ziegler SI, Haberkorn U, Byrne H, Tong C, Kaja S, Richolt JA, Byrne H, Tong C, Schosser R, Krieter H, Kaja S, Richolt JA, Lammertsma AA, Price P (1996) Measurement of liver blood flow using oxygen-15 labelled water and dynamic positron emission tomography: limitations of model description. Eur J Nucl Med 23:169–177
Taourel P, Blanc P, Dauzat M, Chabre M, Pradel J, Gallix B, Larrey D, Bruel JM (1998) Doppler study of mesenteric, hepatic, and portal circulation in alcoholic cirrhosis: relationship between quantitative Doppler measurements and the severity of portal hypertension and hepatic failure. Hepatology 28:932–936
Reichen J (1995) Assessment of hepatic function with xenobiotics. Semin Liver Dis 15:189–201
Gur D, Good WF, Herbert DL, Yonas H, Wozney P, Van Thiel DH, Wolfson SK Jr (1985) Blood flow map** in the human liver by the xenon/CT method. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:447–450
Sase S, Monden M, Oka H, Dono K, Fukuta T, Shibata I (2002) Hepatic blood flow measurements with arterial and portal blood flow map** in human liver by means of xenon CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:243–249
Bader TR, Herneth AM, Blaicher W, Steininger R, Mühlbacher F, Lechner G, Grabenwoger F (1998) Hepatic perfusion after liver transplantation: noninvasive measurement with dynamic single-section CT. Radiology 209:129–134
Van Beers BE, Leconte I, Materne R, Smith AM, Jamart J, Horsmans Y (2001) Hepatic perfusion parameters in chronic liver disease: dynamic CT measurements correlated with disease severity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:667–673
Lee TY (2002) Functional CT: physiological models. Trends Biotechnol 20:S3–S10
Blomley MJ, Lim AK, Harvey CJ, Patel N, Eckersley RJ, Basilico R, Heckemann R, Urbank A, Cosgrove DO, Taylor-Robinson SD (2003) Liver microbubble transit time compared with histology and Child-Pugh score in diffuse liver disease: A cross sectional study. Gut 52:1188–1193
World Medical Association (2000) Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 284:3043–3045
Kalender WA, Polacin A, Eidloth H, Kashiwagi S, Yamashita T, Nakano S (1991) Brain perfusion studies by xenon-enhanced CT using washin/washout study protocols. J Comput Assist Tomogr 15:816–822
Kety S (1951) The theory and applications of the exchange of inert gas at the lungs and tissue. Pharmacol Rev 3:1–41
Fick A (1870) Uber die Messung des Blutquantums in den Herzventrikeln Verhandl dphys-med Ges zu Wurzburg 2:16–28
Sase S (1996) Correction method for end-tidal xenon concentration in CBF measurements with xenon-enhanced CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:688–692
Meyer JS, Hayman LA, Yamamoto M, Sakai F, Nakajima S (1980) Local cerebral blood flow measured by CT after stable xenon inhalation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 135:239–251
Frackowiak RS, Lenzi GL, Jones T, Heather JD (1980) Quantitative measurement of regional cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in man using 15O and positron emission tomography: theory, procedure, and normal values. J Comput Assist Tomogr 4:727–736
Brasch RC, Weinmann HJ, Wesbey GE (1984) Contrast-enhanced NMR imaging: animal studies using gadolinium-DTPA complex. AJR Am J Roentgenol 142:625–630
Winkler SS, Holden JE, Sackett JF, Flemming DC, Alexander SC (1977) Xenon and krypton as radiographic inhalation contrast media with computerized tomography: preliminary note. Invest Radiol 12:19–20
Miles KA (1991) Measurement of tissue perfusion by dynamic computed tomography. Br J Radiol 64:409–412
Latchaw RE, Yonas H, Pentheny SL, Gur D (1987) Adverse reactions to xenon-enhanced CT cerebral blood flow determination. Radiology 163:251–254
Okumura M, Toyoshima N, Katada K, Sasaki M (2003) Performance evolution for image filters used for CT images. Radiological Society of North America. 89th Scientific assembly and annual meeting program: 720
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashimoto, K., Murakami, T., Dono, K. et al. Quantitative Tissue Blood Flow Measurement of the Liver Parenchyma: Comparison Between Xenon CT and Perfusion CT. Dig Dis Sci 52, 943–949 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9327-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9327-6