Abstract
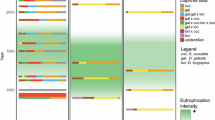
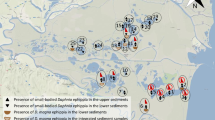
The genotype composition of a Daphnia population complex during a summer period in Lake Maarsseveen (The Netherlands) was determined by allozyme analysis. The depth distribution, diel vertical migration and several parameters of the total population were measured. Young-of-the-year (0+) perch (Perca fluviatilis) were caught and species and allozyme types of Daphnia in the perch gut were also analysed. During May 1997, the densities of D. hyalina, D. galeata, the back-cross D. g × h — hyalina and the multilocus allozyme genotypes of the hybrid D. g × h decreased, except one multilocus genotype (MMMF). Total population size decreased and the ratio of females with eggs to those without eggs decreased as well. Food limitation during this clear-water phase in the lake is considered responsible. All genotypes, except MMMF, gradually descended in the water column. This drift is thought to be a reaction to the abundantly present 0+ perch or to the kairomones of this fish, although predation on the daphnids was still absent. In June, diel vertical migration started, except again part of the MMMF subpopulation. The other part migrated over a short distance compared with the other taxa and allozyme types. Within two weeks, the upper 5 m of the epilimnion was devoid of Daphnia, and guts of perch were predominantly filled with MMMF. The daphnids in the gut and the lake did not differ in allozyme type composition. By the end of July, population density had increased again. The size and composition of the Daphnia population complex continuously changed during the study period, as did the depth distribution of the components. Different genotypes within the population complex seem to have developed different strategies to cope with starvation and predation and the state at a particular moment can be understood only if past and present factors are considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boersma M., Spaak P. and De Meester L. 1998. Predator-mediated plasticity in morphology, life history and behavior in Daphnia: the uncoupling of responses. Am. Nat. 152: 237–248.
De Meester L. 1993. Genotype, fish-mediated chemicals, and phototactic behavior in Daphnia magna. Ecology 74: 1467–1474.
De Meester L. and Cousyn C. 1997. The change in phototactic behaviour of a Daphnia magna clone in the presence of fish kairomones: the effect of exposure time. Hydrobiologia 360: 169–175.
De Meester L., Dawidowicz P., Van Gool E. and Loose C.J. 1998. Ecology and evolution of predator-induced behavior of zooplankton: depth selection and diel vertical migration in Daphnia. In: Harvell C.D. and Tollrian R. (eds), Consequences of Inducible Defences for Population Biology, Princeton University Press, New York.
De Meester L. and Weider L.J. 1999. Depth selection behavior, fish kairomones, and the life histories of Daphnia hyalina x galeata hybrid clones. Limnol. Oceanogr. 44: 1428–1258.
DeMott W.R. 1989. The role of competition in zooplankton succession.. In: Sommer U. (ed.), Plankton Ecology: Succession in Plankton Communities. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, p. 195–252.
Duncan A., Guisande C. and Lampert W. 1993. Further trade-offs in Daphnia vertical migration strategies. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 39: 99–108.
Duncan A., Kubecka J. and Quilliam B. 1999. An accoustic study of fish in Lake Maarsseveen June 1998. Virginia water. Report Royal Holloway Institute for Environmental Research, Surrey, UK.
Flik B.J.G. and Ringelberg J. 1993. Influence of food availability on the initiation of diel vertical migration (DVM) in lake Maarsseveen. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 39: 57–65.
Flik B.J.G., Aanen D.K. and Ringelberg J. 1997. The extent of predation by juvenile perch during diel vertical migration of Daphnia. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 49: 51–58.
Flik B.J.G. and Vijverberg J. 2003. Contrasting migration behaviour of Daphnia pulicaria and D. galeata x hyalina in avoidance of predation of 0+ perch (Perca fluviatilis). Hydrobiologia 491: 289–299.
Forward R.B. Jr. and Rittschof D. 1993. Activation of photoresponses of brine shrimp nauplii involved in diel vertical migration by chemical cues from fish. J. Plankton res. 15: 693–701.
Geller W. 1986. Diurnal vertical migration of zooplankton in a temperature great Lake (L. Constance): a starvation avoidance mechanism. Arch. Hydrobiol./Suppl. 74: 1–60.
Gliwicz Z.M. 1986. Predation and the evolution of vertical migration in zooplankton. Nature 320: 746–748.
Hall D.J., Werner E.E., Giliam J.F., Mittelbach G.G., Howard D. and Doner C.G. 1979. Diel foraging behavior and prey selection in the Golden Shiner (Notemigonus crysoleucas). J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 36: 1029–1039.
Hebert P.D. and Beaton M. 1989. Methodologies for Allozyme analysis Using Cellulose Acetate Electrophoresis. Helena Laboratories, Beaumont, Texas, pp. 1–31.
King C.E.and Miracle M.R. 1995. Diel vertical migration by Daphnia longispina in a Spanish lake: genetic sources of distributional variation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40: 226–231.
Lampert W. 1989. The adaptive significance of diel vertical migration of zooplankton. Functional Ecology 3: 21–27.
Lampert W., Fleckner W., Hai H. and Taylor B.E. 1986. Phytoplankton control by grazing zooplankton: A study on the spring clear-water phase. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31: 478–490.
Larsson P. and Dodson S. 1993. Chemical communication in planktonic animals. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 129: 129–155.
Loose C.J., von Elert E. and Dawidowicz P. 1993. Chemical-induced diel vertical migration in Daphnia: a new bioassay for kairomones exuded by fish. Arch. Hydrobiol. 126: 329–337.
Luecke C., Vanni M.J., Magnuson J.J., Kitchell J.F. and Jacobson P.T. 1990. Seasonal regulation of Daphnia populations by planktivorous fish: implications for the spring clear-water phase. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 1718–1733.
Machacek J. 1990. The response of Daphnia to the fish-produced chemical stimuli. Annual Report 1990, Hydrobiol. Inst. Czechoslovak Acad. Sci. 31: 45–49.
Machacek J. 1993. Comparison of the response of Daphnia galeata and Daphnia obtusa to fish-produced chemical substance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 38: 1544–1550.
McAllister C.D. 1971. Some aspects of nocturnal and continuous grazing by planktonic herbivores in relation to production studies. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Technical Report No. 248, 281 pp.
Mehner T., Hülsmann S., Worischka S., Plewa M. and Benndorf J. 1998. Is the midsummer decline of Daphnia really induced by age-O fish predation? Comparison of fish consumption and Daphnia mortality and life history parameters in a biomanipulated reservoir. J. Plankton Res. 20: 1797–1811.
Müller J. and Seitz A. 1993. Habitat partitioning and differential vertical migration of some Daphnia genotypes in a lake. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 39: 167–174.
Reede T. and Ringelberg J. 1995. The influence of a fish exudate on two clones of the hybrid Daphnia galeata × hyalina. Hydrobiologia 37: 207–212.
Reede T. and Ringelberg J. 1998. Differential life history responses of several pelagic Daphnia clones differing in migratory behaviour. Aquatic Ecology 32: 245–253.
Ringelberg J. 1981. Introduction to the research area. Hydrobiol. Bulletin 15: 5–9.
Ringelberg J. 1991. Enhancement of the phototactic reaction in Daphnia hyalina by a chemical mediated by juvenile perch (Perca fluviatilis). J. Plankton Res. 13: 17–25.
Ringelberg J. and Flik B.J.G. 1994. Increased phototaxis in the field leads to enhanced diel vertical migration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 39: 1855–1864.
Ringelberg J., Flik B.J.G., Lindenaar D. and Royackers K. 1991. Diel vertical migration of Daphnia hyalina (sensu latiori) in Lake Maarsseveen: Part 1. Aspects of seasonal and daily timing. Arch. Hydrobiol. 121: 129–145.
Ringelberg J., Flik B.J.G., Aanen D.K. and Van Gool E. 1997. Amplitude of vertical migration (DVM) is a function of fish biomass, a hypothesis. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 49: 71–78.
Sokal R.R. and Rohlf F.J. 1995. Biometry, W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, pp. 887.
Spaak P. and Hoekstra J.R. 1993. Clonal structure of the Daphnia population lake Maarsseveen: its implications for diel vertical migration. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 39: 157–165.
Spaak P. and Ringelberg J. 1997. Differential behaviour and shifts in genotype composition during the beginning of a seasonal period of diel vertical migration. Hydrobiologia 360: 177–185.
Stich H.- B. and Lampert W. 1981. Predator evasion as an explanation of diurnal vertical migration. Nature 293: 396–398.
Swain W.R. and Roijackers K.M. 1986. Freshwater zooplankton sampling reconsidered: preliminary results of a high-speed sampling device for small lakes. Hydrobiol. Bulletin 19: 139–152.
Swain W.R., Lingeman R. and Heinis F. 1987. A characterization and description of the Maarsseveen Lake system. Hydrobiol. Bulletin 21: 5–16.
Tollrian R. 1995. Predator-induced morphological defenses: costs, life history shifts, and maternal effects in Daphnia pulex. Ecology 76: 6. (Abstract)
Van Gool E. and Ringelberg J. 1998. Light-induced migration behaviour of Daphnia modified by food and predator kairomones. Animal Behavior 56: 741–747.
Van Gool E. and Ringelberg J. 2002. Relationship between fish kairomone concentration in a lake and phototactic swimming in Daphnia. J. Plankton Res. 24: 713–721.
Wahl C.M., Mills E.L., McFarland W.N. and Degisi J.S. 1993. Ontogenetic changes in prey selection and visual acuity of the yellow perch, Perca flavescens. Can J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 50: 743–749.
Weider L.J. 1984. Spatial heterogeneity of Daphnia phenotypes: Vertical migration and habitat partitioning. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 225–236.
Weider L.J. and Stich H.B. 1992. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of Daphnia in Lake Constance; intra- and interspecific comparisons. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37: 1327–1334.
Weider L.J. and Pyanowska J. 1993. Plasticity of Daphnia life histories in response to chemical cues from predators. Oikos 67: 385–392.
Wolf H.G. and Mort M.A. 1986. Inter-specific hybridization underlies phenotypic variability in Daphnia populations. Oecologia (Berlin) 68: 507–511.
Zaret T.M. and Suffern J.S. 1976. Vertical migration in zooplankton as a predator avoidance mechanism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 21: 804–813.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ringelberg, J., van Gool, E. & Brehm, M. Density and depth variations of Daphnia multilocus genotypes during a summer period in Lake Maarsseveen. Aquat Ecol 38, 525–535 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-005-5667-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-005-5667-0