Abstract
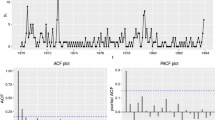
The past few decades have seen considerable interest in modeling time series of counts, with applications in many domains. Classical and Bayesian modeling have primarily focused on conditional Poisson sampling distributions at each time. There is very little research on modeling time series involving Zero-Modified (i.e., Zero Deflated or Inflated) distributions. This paper aims to fill this gap and develop models for count time series involving Zero-Modified distributions, which belong to the Power Series family and are suitable for time series exhibiting both zero-inflation and zero-deflation. A full Bayesian approach via the Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) technique enables accurate modeling and inference. The paper illustrates our approach using time series on the number of deaths from the influenza virus in the city of São Paulo, Brazil.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
the data are open to the public and are available at the links cited in the paper.
References
Andrade, B., Andrade, M., Ehlers, R.: Bayesian GARMA models for count data. Commun. Stat. Case Stud. Data Anal. Appl. 4(1), 192–205 (2015)
Balakrishna, N., Anvar, M., Abraham, B.: Zero-modified count time series with Markovian intensities. (2021). ar**v preprint ar**v:2107.01813
Benjamin, M.A., Rigby, R.A., Stasinopoulos, D.M.: Generalized autoregressive moving average models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 98, 214–223 (2003)
Box, G.E.P., Jenkins, G.M., Reinsel, G.C., et al.: Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 5th edn. Wiley, New Yark (2016)
Campbell, M.: Time series regression for counts: an investigation into the relationship between sudden infant death syndrome and environmental temperature. J. Royal Stat. Soc. Ser A (Stat. Soc.) 157(2), 191–208 (1994)
Carlin, B.P., Louis, T.A.: Bayes and Empirical Bayes methods for Data Analysis. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton - FL (2008)
CDC: Center for disease control and prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/index.html, accessed September 2020 (2020a)
CDC-H1N1: Center for disease control and prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/, accessed September 2020 (2020)
Chen, C.W.S., Lee, S.: Generalized poisson autoregressive models for time series of counts. Computat. Stat. Data Anal.sis 99, 51–67 (2016)
Chen, M., Shao, Q.: Monte Carlo estimation of Bayesian credible and HPD intervals. J. Computat. Graph. Stat. 8, 69–92 (1998)
Chib, S., Greenberg, E.: Understanding the metropolis-hastings algorithm. Am. Statist. 49(4), 327–335 (1995)
Chretien, J.P., George, D., Shaman, J., et al.: Influenza forecasting in human Populations: A sco** review. PLoS ONE 9(e94), 130 (2014)
Conceição, K.S., Andrade, M.G., Louzada, F.: Zero-modified Poisson model: bayesian approach, influence diagnostics, and an application to a Brazilian leptospirosis notification data. Biomet. J. 55, 661–678 (2013)
Conceição, K.S., Louzada, F., Andrade, M.G., et al.: Zero-modified Poisson power series distribution and its hurdle distribution version. J. Statist. Computat. Simulat. 87, 1842–1862 (2017)
Cordeiro, G.M., Andrade, M.G., de Castro, M.: Power series generalized nonlinear models. Computat. Statist. Data Anal. 53, 1155–1166 (2009)
Cox, D.: Statistical analysis of time series: some recent developments. Scand. J. Statist. 8, 93–115 (1981). (MR0623,586)
Davis, R.A., Dunsmuir, W., Wang, Y.: On autocorrelation in a Poisson regression model. Biometrika 87, 491–505 (2000)
Davis, R.A., Dunsmuir, W.T.M., Streett, S.B.: Observation-driven models for Poisson counts. Methodol. Comput. Appl. Probab. 90, 777–790 (2003)
Davis, R.A., Dunsmuir, W.T.M., Streett, S.: Maximum likelihood estimation for an observation driven model for Poisson counts. Methodol. Comput. Appl. Probab. 7, 149–159 (2005)
Davis, R.A., Holan, S.H., Lund, R., et al.: Handbook of Discrete-Valued Time Series. Chapman & Hall/CRC, New York (2016)
Dietz, E., Böhning, D.: On estimation of the poisson parameter in zero-modified poisson models. Computat. Statist. Data Anal. 34, 441–459 (2000)
Duane, S., Kennedy, A., Pendleton, B.J., et al.: Hybrid Monte Carlo. Phys. Lett. B 195(2), 216–222 (1987)
FGV-EMAp: school of applied mathematics/getúlio vargas foundation. https://emap.fgv.br/, accessed September 2020 (2020)
Fiocruz-PROCC: scientific computing program/fiocruz fundation. https://portal.fiocruz.br/en/procc-programa-de-computacao-cientifica-ingles, accessed September 2020 (2020)
Fokianos, K., Kedem, B.: Partial likelihood inference for time series following generalized linear model. J. Time Ser. Anal. 25(2), 173–197 (2004)
Freelanda, R.K., McCabeb, B.P.M.: Forecasting discrete valued low count time series. Int. J. Forecast. 20, 427–434 (2004)
Gelfand, A., Dey, K.: Bayesian model choice: asymptotics and exact calculations. J. Royal Statist. Soc. 56(3), 501–514 (1994)
Gelfand, A., Smith, A.: Sampling-based approaches to calculating marginal densities. J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 85, 398–409 (1990)
Gelman, A., Hwang, J., Vehtari, A.: Understanding predictive information criteria for Bayesian models. Statist. Comput. 24, 997–1016 (2014)
Geweke, J.: Evaluating the accuracy of sampling-based approaches to calculating posterior moments. J. Royal Statist. Soc. 56(3), 501–514 (1994)
Grunwald, G.K., Hyndman, R.J., Tedesco, L., et al.: Non-Gaussian conditional linear AR(1) models. Austral. New Zealand J. Statist. 42, 479–495 (2000)
GT-Influenza: Gt-influenza/info gripe/Oswaldo Cruz foundation. http://info.gripe.fiocruz.br/, accessed September 2020 (2020)
Guikema, S.D., Coffelt, J.P.: A flexible count data regression model for risk analysis. Risk Anal. 28(1), 213–223 (2008)
Harvey, A.: Forecasting, Structural Time Series Models, and the Kalman Filter. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
Huayanay, A., Bazá n, J., Cancho, V., et al.: Performance of asymmetric links and correction methods for imbalanced data in binary regression. J. Statist. Computat. Simulat. 89(9), 1694–1714 (2019)
Jung, R.C., Tremayne, A.R.: Coherent forecasting in integer time series models. Int. J. Forecast. 22, 223–238 (2006)
Kim, S., Kim, H.: A new metric of absolute percentage error for intermittent demand forecasts. Int. J. Forecast. 32, 669–679 (2016)
King, G.: Event count models for international relations: generalizations and applications. Int. Stud. Quart. 33, 123–147 (1989)
Li, W.: Time series models based on generalized linear models: some further results. Biometrics 50, 506–511 (1994)
MS-SVS: the health surveillance secretariat/ministry of health. https://www.saude.gov.br/component/tags/tag/svs, accessed September 2020 (2020)
Mullahy, J.: Specification and testing of some modified count data models. J. Econom. 33, 341–365 (1986)
Neal, R.M.: Bayesian Learning for Neural Networks. Ph.D. thesis, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Toronto, Toronto – Canada (1994)
Neal, R.M.: Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo, Chapman & Hall, New York, chap MCMC using Hamiltonian dynamics, pp. 113–162 (2011)
Nsoesie, E.O., Brownstein, J., Ramakrishnan, N., et al.: A systematic review of studies on forecasting the dynamics of influenza outbreaks. Influenza Respir Viru 8, 309–316 (2014)
R Core Team: R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, (2021). http://www.R-project.org
Samuel, T., Wanzhu, T.: Learning Hamiltonian Monte Carlo in R. Am Statist 75(4), 403–413 (2021)
Shephard, N.: Generalized Linear Autoregression. Technical report, Nuffield College, Oxford University, Tech. rep. (1995)
Silla, A., Kallberg, V.: The development of railway safety in Finland. Accid. Anal. Prevent. 45, 737–744 (2012)
SINAN: Severe acute respiratory syndrome/notifiable diseases information system. (2020). http://sinan.saude.gov.br/sinan/, accessed September 2020
Tierney, L.: Markov chains for exploring posterior distributions. Ann. Statist. 22, 1701–1728 (1994)
Watanabe, S.: A widely applicable Bayesian information criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 14(27), 867–897 (2013)
West, M., Harrison, P.: Bayesian Forecasting and Dynamic Models, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (1987)
Yi, Z.: Count data time series models and their applications. Doctoral dissertations 3024, Department: Mathematics and Statistics, Missouri University of Science and Technology, Rolla – Missouri, (2021). https://scholarsmine.mst.edu/doctoral_dissertations/3024
Zeger, S.L., Qaqish, B.: Markov regression models for time series: a quasi-likelihood approach. Biometrics 44, 1019–1031 (1988a)
Zeger, S.L., Qaqish, B.: Markov regression models for time series: of counts. Biometrika 75, 621–629 (1988b)
Acknowledgements
Marinho G. Andrade is supported by the Brazilian organization FAPESP (2019/21766-8); Katiane S. Conceição is supported by the Brazilian organization FAPESP (2019/22412-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There isn’t a conflict of interest or competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Code availability
contact the corresponding author.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Andrade, M.G., Conceição, K.S. & Ravishanker, N. Zero-modified count time series modeling with an application to influenza cases. AStA Adv Stat Anal (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10182-023-00488-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10182-023-00488-6