Abstract
Background
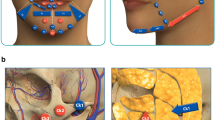
This study aimed to evaluate the use of fat grafting enriched with platelet-rich plasma through a computerized-assisted map** for esthetic restoration in progressive hemifacial atrophy (Parry-Romberg disease).
Methods
This prospective study was conducted on 53 patients presented by Parry-Romberg disease and was corrected by facial fat grafting (FFG) enriched with platelet-rich plasma (PRP). A computerized software program was used to design a detailed map to achieve clinical symmetry with fat grafting application, as the anatomical subunits direct 3-dimensional volumetric symmetric, and compartments direct isolated recipient-specific grafting. Also, volumetric asymmetry was assessed through outlines of facial contour, projection, and proportions for both sides and comparing the mirror image of unaffected side as a template.
Results
Objective ultrasound and photogrammetric measurements showed a significant improvement in facial symmetry postoperatively compared to preoperative (P < 0.05), with no significant differences between 12 and 18 months after surgery. The FACE-Q score regarding comparison before surgery and 18 months after surgery showed a statistically significant improvement in all modules (P < 0.001) with overall satisfaction concerning outcome of 82.7 ± 0.8.
Conclusion
Enriched fat grafting with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a good alternative to reconstruct soft tissue defects for patients with progressive hemifacial atrophy (Parry-Romberg disease) with a minimally invasive approach and low complications. It provides volumetric replacement, enhancement of skin texture, and improvement of hyperpigmentation with restoration of facial contour for an esthetic pleasing appearance. Isolated replacement in accordance with the anatomical facial subunits and fat compartments allows three-dimensional reconstruction and maximizes fat retention.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
01 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-022-01129-z
References
Al-Aizari NA, Azzeghaiby SN, Al-Shamiri HM, Darwish S, Tarakji B (2015) Oral manifestations of Parry-Romberg syndrome: a review of literature. Avicenna J Med 5(2):25–28. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-0770.154193
Aloua R, Kerdoud O, Kaouani A, Slimani F (2021) Lipofilling as an aesthetic restorative technique for the facial hemiatrophy of Parry-Romberg syndrome: an analysis of 27 cases. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021(79):138–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.01.006
Schultz KP, Dong E, Truong TA, Maricevich RS (2019) Parry Romberg syndrome. Clin Plast Surg 46(2):231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2018.11.007
Kumar NG, Maurya BS, Sudeep CS (2019) Parry Romberg syndrome: literature review and report of three cases. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 18(2):210–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-018-1147-7
Qiao J, Gui L, Fu X, Niu F, Liu J, Chen Y, Wang M, Chen J, You Y (2017) A novel method of mild to moderate Parry-Romberg syndrome reconstruction: computer-assisted surgery with mandibular outer cortex and fat grafting. J Craniofac Surg 28(2):359–365. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000003293
Clauser LC, Tieghi R, Consorti G (2010) Parry-Romberg syndrome: volumetric regeneration by structural fat grafting technique. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 38(8):605–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2010.02.005
Hunstad JP, Shifrin DA, Kortesis BG (2011) Successful treatment of Parry-Romberg syndrome with autologous fat grafting: 14-year follow-up and review. Ann Plast Surg 67(4):423–425. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31820b3aa8
Agostini T, Spinelli G, Marino G, Perello R (2014) Esthetic restoration in progressive hemifacial atrophy (Romberg disease): structural fat grafting versus local/free flaps. J Craniofac Surg 25(3):783–787. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000000831
Lo LJ, Yamaguchi K, Niu LS, Liao CH, Lin HH (2020) Fat grafting in patients with extensive unilateral facial deficiency: three-dimensional computer-assisted planning, implementation, and outcome assessment. Ann Plast Surg 84(1S Suppl 1):S94–S99. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002185
Picard F, Hersant B, La Padula S, Meningaud JP (2017) Platelet-rich plasma-enriched autologous fat graft in regenerative and aesthetic facial surgery: Technical note. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg 118(4):228–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jormas.2017.05.005
**ong BJ, Tan QW, Chen YJ, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Tang SL, Zhang S, Lv Q (2018) The effects of platelet-rich plasma and adipose-derived stem cells on neovascularization and fat graft survival. Aesthetic Plast Surg 42(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-1062-1
Willemsen JCN, Spiekman M, Stevens HPJ, van der Lei B, Harmsen MC (2016) Platelet-rich plasma influences expansion and paracrine function of adipose-derived stromal cells in a dose-dependent fashion. PlastReconstr Surg 137(3):554e–565e. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000479995.04255.bb
Slack GC, Tabit CJ, Allam KA, Kawamoto HK, Bradley JP (2014) Parry-Romberg reconstruction: beneficial results despite poorer fat take. Ann Plast Surg 73(3):307–310. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31827aeb0d
Cervelli V, Gentile P, Scioli MG, Grimaldi M, Casciani CU, Spagnoli LG, Orlandi A (2009) Application of platelet-rich plasma in plastic surgery: clinical and in vitro evaluation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 15(4):625–634. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEC.2008.0518
Gentile P, Di Pasquali C, Bocchini I, Floris M, Eleonora T, Fiaschetti V, Floris R, Cervelli V (2013) Breast reconstruction with autologous fat graft mixed with platelet-rich plasma. Surg Innov 20(4):370–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350612458544
Wang W, **e Y, Huang RL, Zhou J, Tanja H, Zhao P, Cheng C, Zhou S, Pu LLQ, Li Q (2017) Facial contouring by targeted restoration of facial fat compartment volume: the midface. PlastReconstr Surg 139(3):563–572. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000003160
Xue AS, Dayan E, Rohrich RJ (2020) Facial fat augmentation finesse. Plast Reconstr Surg 146(4):416e–419e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000007205
Wen L, Wang J, Li Y, Liu D (2018) Progress of midfacial fat compartments and related clinical applications. Zhongguo**u Fu Chong JianWaiKeZaZhi 32(2):248–251. https://doi.org/10.7507/1002-1892.201710088 (Chinese)
Rodby KA, Kaptein YE, Roring J, Jacobs RJ, Kang V, Quinn KP, Antony AK (2016) Evaluating autologous lipofilling for Parry-Romberg syndrome-associated defects: a systematic literature review and case report. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 53(3):339–350. https://doi.org/10.1597/14-232
Denadai R, Raposo-Amaral CA, Buzzo CL, Raposo-Amaral CE (2019) Isolated fat grafting for reconstruction of lower face volumetric asymmetry in skeletally immature patients: a clinical outcome study. Ann Plast Surg 83(5):529–537. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000001934
Kasielska-Trojan A, Zieliński T, Antoszewski B (2020) Autologous fat transfer for facial recontouring in Parry-Romberg syndrome. J CosmetDermatol 19(3):585–589. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13072
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All contributing authors have been involved with preoperative consultations, data collection, surgical procedures, follow-up assessment, and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (METC) of Menoufia Faculty of Medicine (IRB NO; 2015–147) and performed in accordance with the principles of Helsinki Declaration.
Consent to participate
The patient provided written informed consent for participation in the study and for the use of images.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Figs. 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, and 8.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Level of Evidence: Level IV, Therapeutic
The original online version of this article was revised: The original online version of this article was revised due to a retrospective Open Access cancellation.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
AboShaban, M.S., Ghareeb, F.M. Esthetic restoration of progressive hemifacial atrophy (Parry-Romberg disease) by free fat grafting using computerized-assisted map**. Oral Maxillofac Surg 28, 195–203 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-022-01115-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-022-01115-5