Abstract
We have evaluated an in-situ ionic liquid-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction procedure for the determination of six endocrine disrupting phenols in seawaters and industrial effluents using HPLC. The optimized method requires 38 μL of the water-soluble ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, and 5 mL of seawater or industrial effluent. After appropriate work-up, a drop (~10 μL) of an ionic liquid is formed that contains the analytes of interest. It is diluted with acetonitrile and injected into the HPLC system. This procedure is accomplished without heating or cooling the solutions. The method is characterized by (a) average relative recoveries of 90.2%, (b) enrichment factors ranging from 140 to 989, and (c) precisions (expressed as relative standard deviations) of less than 11% when using a spiking level of 10 ng mL−1. The limits of detection range from 0.8 ng mL−1 for 4-cumylphenol to 4.8 ng mL−1 for bisphenol-A.

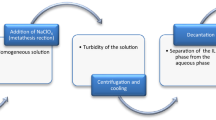
Scheme of the in situ IL-DLIME procedure to determine endocrine disrupting phenols in environmental waters.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur CL, Pawliszyn J (1990) Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal Chem 62(19):2145
Risticevic S, Niri VH, Vuckovic D, Pawliszyn J (2009) Recent developments in solid-phase microextraction. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(3):781
Lee J, Lee HK, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2008) Environmental and bioanalytical applications of hollow fiber membrane liquid-phase microextraction: a review. Anal Chim Acta 624(2):253
Xu L, Basheer C, Lee HK (2007) Developments in single-drop microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1152(1–2):184
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Milani Hosseini MR, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S (2006) Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1116(1–2):1
Herrera-Herrera AV, Asensio-Ramos M, Hernández-Borges J, Rodríguez-Delgado MA (2010) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of organic analytes. Trends Anal Chem 29(7):728
Dadfarnia S, Shabani AMH (2010) Recent development in liquid phase microextraction for determination of trace level concentration of metals—A review. Anal Chim Acta 658(2):107
**e S, **ang B, Zhang M, Deng H (2010) Determination of medroxyprogesterone in water samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with low solvent consumption. Microchim Acta 168(3–4):253
Poole CF, Poole SK (2010) Extraction of organic compounds with room temperature ionic liquids. J Chromatogr A 1217(16):2268
Sun P, Armstrong DW (2010) Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry. Anal Chim Acta 661(1):1
Aguilera-Herrador E, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M (2010) The roles of ionic liquids in sorptive microextraction techniques. Trends Anal Chem 29(7):602
Zhou Q, Bai H, **e G, **ao J (2008) Temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid phase micro-extraction. J Chromatogr A 1177(1):43
Zhou Q, Bai H, **e G, **ao J (2008) Trace determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental samples by temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-phase microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1188(2):148
Mallah MH, Shemirani F, Maragheh MG (2009) Ionic liquids for simultaneous preconcentration of some lanthanoids using dispersive liquid−liquid microextraction technique in uranium dioxide powder. Environ Sci Technol 43(6):1947
Zhang H-F, Shi Y-P (2010) Temperature-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of anthraquinones in Radix et Rhizoma Rhei samples. Talanta 82(3):1010
Zhou Q, Zhang X, **ao J (2009) Ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid-phase micro-extraction: a novel approach for the sensitive determination of aromatic amines in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1216(20):4361
Liu Y, Zhao E, Zhu W, Gao H, Zhou Z (2009) Determination of four heterocyclic insecticides by ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1216(6):885
Pena MT, Casais MC, Mejuto MC, Cela R (2009) Development of an ionic liquid based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method for the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1216(36):6356
Zhao R-S, Wang X, Zhang L-L, Wang S-S, Yuan J-P (2011) Ionic liquid/ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction, a new sample enrichment procedure for the determination of hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers in environmental water samples. Anal Methods in press. doi:10.1039/C0AY00708K.
Baghdadi M, Shemirani F (2009) In situ solvent formation microextraction based on ionic liquids: a novel sample preparation technique for determination of inorganic species in saline solutions. Anal Chim Acta 634(2):186
Mahpishanian S, Shemirani F (2010) Preconcentration procedure using in situ solvent formation microextraction in the presence of ionic liquid for cadmium determination in saline samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 82(2):471
Vaezzadeh M, Shemirani F, Majidi B (2010) Microextraction technique based on ionic liquid for preconcentration and determination of palladium in food additive, sea water, tea and biological samples. Food Chem Toxicol 48(6):1455
Yao C, Anderson JL (2009) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using an in situ metathesis reaction to form an ionic liquid extraction phase for the preconcentration of aromatic compounds from water. Anal Bioanal Chem 395(5):1491
Yao C, Li T, Twu P, Pitner WR, Anderson JL (2011) Selective extraction of emerging contaminants from water samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using functionalized ionic liquids. J Chromatogr A 1218(12):1556
Wetherill YB, Akingbemi BT, Kanno J, McLachlan JA, Nadal A, Sonnenschei C, Watson CS, Zoelleri RT, Belcher SM (2007) In vitro molecular mechanisms of bisphenol A action. Reprod Toxicol 24(2):178
Virtanen HE, Meyts ERD, Main KM, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J (2005) Testicular dysgenesis syndrome and the development and occurrence of male reproductive disorders. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207(2):S501
Bateman HL, Patisaul HB (2008) Disrupted female reproductive physiology following neonatal exposure to phytoestrogens or estrogen specific ligands is associated with decreased GnRH activation and kisspeptin fiber density in the hypothalamus. Neurotoxicology 29(6):988
Richter CA, Birnbaum LS, Farabollini F, Newbold RR, Rubin BS, Talsness CE, Vandenbergh JG, Walser-Kuntz DR, Saal FSV (2007) In vivo effects of bisphenol A in laboratory rodent studies. Reprod Toxicol 24(2):199
López-Darias J, Pino V, Ayala JH, González V, Afonso AM (2008) Micelle mediated extractions using nonionic surfactant mixtures and HPLC-UV to determine endocrine-disrupting phenols in seawaters. Anal Bioanal Chem 391(3):735
López-Darias J, Germán-Hernández M, Pino V, Afonso AM (2010) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction versus single-drop microextraction for the determination of several endocrine-disrupting phenols from seawaters. Talanta 80(5):1611
Pino V, Anderson JL, Ayala JH, González V, Afonso AM (2008) The ionic liquid 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide as novel extracting system for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contained in sediments using focused microwave-assisted extraction. J Chromatogr A 1182(2):145
Yiantzi E, Psillakis E, Tyrovola K, Kalogerakis N (2010) Vortex-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction of octylphenol, nonylphenol and bisphenol-A. Talanta 80(5):2057
Zhao R-S, Wang X, Yuan J-P, Zhang LL (2009) Solid-phase extraction of bisphenol A, nonylphenol and 4-octylphenol from environmental water samples using microporous bamboo charcoal, and their determination by HPLC. Microchim Acta 165(3–4):443
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Gómez MJ, Malato O, Agüera A, Fernández-Alba AR (2004) Comparative study of analytical methods involving gas chromatography–mass spectrometry after derivatization and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of selected endocrine disrupting compounds in wastewaters. J Chromatogr A 1047(1):129
Gatidou G, Thomaidis NS, Stasinakis AS, Lekkas TD (2007) Simultaneous determination of the endocrine disrupting compounds nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylates, triclosan and bisphenol A in wastewater and sewage sludge by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1138(1–2):32
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Shariati S, Esrafili A, Shamsipur M (2009) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-UV detection as a very simple, rapid and sensitive method for the determination of bisphenol A in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1216(9):1511
Fattahi N, Assadi Y, Hosseini MRM, Jahromi EZ (2007) Determination of chlorophenols in water samples using simultaneous dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and derivatization followed by gas chromatography-electron-capture detection. J Chromatogr A 1157(1–2):23
Nagaraju D, Huang S-D (2007) Determination of triazine herbicides in aqueous samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with gas chromatography–ion trap mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1161(1–2):89
Yazdi AS, Razavi N, Yazdinejad SR (2008) Separation and determination of amitriptyline and nortriptyline by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography flame ionization detection. Talanta 75(5):1293
Acknowledgements
A.M.A. acknowledges funding from the Spanish Ministry of Innovation and Science (MICINN) project ref. CTQ2008-06253/BQU, and from the Canary Agency for Research and Innovation (ACIISI) reinforcement project ref. SolSubC20081000171. V.P. thanks the MICINN for the Ramón y Cajal contract with the University of La Laguna (ULL). J.L.D. thanks the ACIISI for the contract with the ULL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 67 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Darias, J., Pino, V., Ayala, J.H. et al. In-situ ionic liquid-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method to determine endocrine disrupting phenols in seawaters and industrial effluents. Microchim Acta 174, 213–222 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0636-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0636-x