Summary
It is well recognized that organized management of heart failure patients, including care by heart failure specialists, improves outcomes of these patients. In response to this, the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology proposed a basic framework of a heart failure curriculum, which became a blueprint for training programs across Europe. The present curriculum for heart failure was well coordinated with the version issued by the German Society for Cardiology in order to achieve good comparability. Training in this Austrian curriculum takes two years, during which the predominant activity focuses on the care of patients with heart failure. The first year includes general (basic) training, while in the second year special modules (advanced chronic and acute heart failure with specific treatment, device treatment, interventional heart failure treatment, outpatient care or rehabilitation, heart failure diagnostics) must be chosen that impart in-depth knowledge, experience and/or skills. Of the five offered modules two must be completed for 6 months each. At least one specialist in internal medicine and cardiology with the additional qualification of heart failure must act as a supervisor at the training center. A certified Heart Failure Unit or a comparable structure should be available at the training center and integrated into the clinical routine of the cardiology department. Applications for recognition of curricular achievements in order to obtain the additional qualification “heart failure specialist” shall be evaluated by a dedicated committee of the nucleus of the Heart Failure Working Group of the Austrian Cardiological Society. The candidate will receive recognition of the additional qualification in heart failure, issued by the Austrian Cardiological Society.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Preamble
As a result of the enormous advances made in theoretical knowledge and methodologies, cardiology has become increasingly specialized in various areas. The board of the Austrian Cardiological Society (ÖKG) is aware of this development and has commissioned the Working Groups for Heart Failure, Interventional Cardiology, Cardiac Imaging and Rhythmology to draw up curricula for obtaining additional qualifications within cardiology. These curricula are intended to facilitate a further deepening of cardiological knowledge and technical skills within the discipline. On the one hand, they build on the contents of the training in internal medicine and cardiology, while on the other hand they go beyond the theoretical knowledge and technical skills required by the training regulations for cardiology. For these curricula the term additional qualification was chosen in order to distinguish the additional qualification under the umbrella of the scientific societies from the requirement for specializations that are laid down in the Physicians Act (ÄrzteG § 49). Specializations are regulated in the Framework Specialization Ordinance 2015 and in the Specialization Ordinance 2017 of the Austrian Medical Association. An internationally comparable format is explicitly required for a curriculum. The present curriculum for heart failure was therefore coordinated with the version issued by the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Cardiological Society (ECS) [1] and in particular with the versions brought out by the German Society for Cardiology [2] and the Swiss Society for Cardiology [3].
1. Introduction
Acute and chronic heart failure are disease patterns that are playing an increasingly important role in cardiology and medicine as a whole. The clinical syndrome “heart failure” has become the most frequent cause for hospital admission in Austria [4]. At the same time, the spectrum of diagnostic and therapeutic options for heart failure has expanded dramatically over the last two decades. In addition, heart failure, which is increasingly understood as a systemic disease, [5] requires a high degree of interdisciplinarity and expertise in neighboring disciplines (e. g. heart surgery, nephrology). Accordingly, the knowledge, experience and skills of the attending physicians required for state of the art treatment have considerably increased. This development has already been taken into account in many clinics by setting up specialized outpatient clinics and in some cases even heart failure units (HFU) [6].
This curriculum is therefore intended to define a framework within which interested colleagues can acquire in-depth knowledge, practical experience and skills in the field of heart failure and obtain certification as such. In future, every cardiologist should have sufficient knowledge of the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure. Patients with advanced heart failure or rare cardiomyopathies in particular, benefit from treatment by colleagues who have been trained in depth and in a structured manner within the framework of a curriculum. In the interest of future Europewide compatibility, the basic structure of this curriculum is based on a proposal made by the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology [1] and the curriculum on heart failure drawn up by the German Society of Cardiology [2]. Other international initiatives, e. g. the Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA), were also discussed and considered in partial aspects [7].
2. Aim
The aim of specialization within the curriculum of heart failure is to train physicians in the etiology, pathophysiology, diagnostics and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure in all stages, namely beyond the standard of general cardiologists. In this process, comprehensive knowledge is acquired in diagnostics, drug-conservative and interventional, electrophysiological, “device” treatment and intensive care of heart failure. The curriculum is certified by the ÖKG Heart Failure Working Group on the basis of defined knowledge, practical experience and skills, thus ensuring the quality of this specialization. This concerns both the candidates to be trained and the training centers.
3. Training implementation—duration and structure of the curriculum
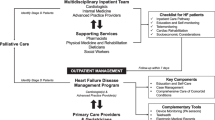
Training in the curriculum “heart failure” takes 24 months (2 years), during which the predominant activity focuses on the care of patients with heart failure. According to the proposal made by the Heart Failure Association of the ESC, the first year should include general (basic) training, while in the second year special modules must be chosen that impart in-depth knowledge, experience and/or skills (Fig. 1). Of the five offered modules two must be completed for 6 months each:
Curriculum modules:
-
Advanced chronic and acute heart failure with specialized treatment options
-
Device treatment for heart failure
-
Interventional heart failure treatment
-
Outpatient care or rehabilitation
-
Specific diagnostics for heart failure
Modular structure of the curriculum heart failure. CRT-D cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator, CRT-P cardiac resynchronization therapy pacemaker, CT computer tomography, Echo echocardiography, HF heart failure, ICD implanted cardioverter defibrillator, MRI magnetic resonance imaging, PM pace maker
The possibility to choose special modules takes into account the fact that there is no uniform heart failure specialist, as patients are treated at different stages of the disease or in different situations (e. g. outpatient versus inpatient). Some treatment modalities (e. g. interventions for valve diseases) also require expertise that not every heart failure specialist can or must master. At the same time, basic training and proof of having attended pertinent training courses ensure that all heart failure specialists have a comparably high level of knowledge and basic skills. The modules should be completed semester by semester and within 5 years.
4. Training contents (detailed list in Appendix)
1st year—Basic training
The main aim of the first year of the curriculum is to gain in-depth clinical experience in the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure patients. The candidate should document at least 80 cases using a logbook (e. g. in the form of hospital discharge letters, copies of the patient file). In addition to documentation of the (differential) diagnostic procedure and the systematic recording of comorbidities, the indication for multimodal treatment of heart failure should be mastered (life style interventions, pharmacotherapy, device treatment, interventional treatment, assist procedures, heart transplantation). Each person completing the first year of the curriculum should also have acquired the knowledge and skills to care for patients with acute heart failure and have documented this in at least 20 cases using the logbook. A total of at least 100 patients with acute or chronic heart failure should be diagnosed.
2nd year—in-depth training
For specialization in the field of heart failure, the candidate must have completed at least two of the following modules (total training period 12 months Fig. 1). Within the framework of these modules, the candidate should in particular deal with heart failure patients. The required theoretical knowledge must be demonstrated by having completed relevant advanced training courses (see Section 8 “Evaluation and quality control”).
Module advanced chronic and acute heart failure with specialized treatment options
In this module, special examination methods, including spiroergometry, biomarkers, myocardial biopsy, as well as a well-founded assessment of hemodynamics, including measurement of pulmonary arterial pressure and resistance, and reversibility testing are to be learned. Furthermore, the indications and differentiated use of pharmacological therapies, mechanical aquaphoretic therapies (ultrafiltration, peritoneal dialysis), as well as ventricular assist devices will be introduced. The selection of patients for heart and heart/lung transplantation and the care of patients before and possibly after heart transplantation will also be taught and learnt.
Module device treatment for heart failure
The device treatment module includes implantation and aftercare of implantable cardiac aggregates, e.g. cardiovascular implantable electronic devices (CIEDS), such as antibradycardia pacemakers, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), cardiac resynchronization therapies defibrillator (CRT-D), and cardiac resynchronization therapies pacemaker (CRT-P) systems.
Module interventional heart failure treatment
In this module, the candidate is assigned to the department’s cardiac catheterization laboratory and deals with interventional examinations and therapies in heart failure patients.
Module outpatient care (I) or rehabilitation (II)
In this module, the candidate is either (I) trained in the outpatient care of heart failure patients or (II) taught in the rehabilitation of heart failure patients (patient training, treatment optimization, medical training therapy, psychological care).
Module specific diagnostics for heart failure
In this module the candidate will receive in-depth training in specific diagnostics related to cardiac imaging (echocardiography, MRI, CT and scintigraphy) and genetic analysis in heart failure patients.
5. Candidate requirements
Basic training in internal medicine and cardiology of at least 3 years is required before commencing the curriculum. Moreover, basic echocardiographic knowledge and at least 6 months of intensive care experience are required. Credit may be given for equivalent knowledge, experience and skills in cardiology for a maximum period of 12 months. If all prerequisites are fulfilled, the candidate can be recognized as holding a specialisation in heart failure at the earliest 12 months after completion of training as a specialist in cardiology.
6. Requirements for the training center
At least one specialist in internal medicine and cardiology with the additional qualification of heart failure must act as a supervisor at the training center. The supervisor should have 5 years of experience in the care of heart failure patients (see below). Following the position paper heart failure unit (HFU) of the German Society of Cardiology [6] (see below), a certified HFU or a comparable structure should be available at the training center and integrated into the clinical routine of the cardiology department.
General training
The general training (1st year, 12 months) can be completed at an HFU specialty clinic or a supraregional HFU center.
Special part
Depending on the modules completed, the special training (2nd year) can be completed at a department with a special HFU clinic, a supraregional HFU center, a special HFU outpatient clinic or a rehabilitation center for cardiovascular diseases with a focus on heart failure. During this period, the candidate is predominantly assigned to the care structures corresponding to the module. To achieve specialization, the candidate must have completed at least two different modules for a total training period of 12 months, namely 6 months for each module (see Fig. 1). Within the framework of these modules, the candidate should in particular be entrusted with the treatment of heart failure patients.
Module advanced chronic and acute heart failure with specialized treatment options
This module, in which specialized treatment options, such as heart transplantation and ventricular support systems are introduced, is to be completed at a supraregional HFU center. The center should maintain an active program for heart transplantation and ventricular assist devices or at least be connected to such a center.
Module device treatment for heart failure
This module is to be completed at a department with an HFU specialty clinic or a supraregional HFU center.
Module interventional heart failure treatment
The module interventional heart failure treatment should be completed in a department with an HFU specialty clinic or a supraregional HFU center. At this center, at least 50 interventional procedures should be performed per year in heart failure patients.
Module outpatient care (I) or rehabilitation (II)
The module outpatient care (I) can be completed at a heart failure outpatient clinic of a department with a specialized HFU clinic or a supraregional HFU center or in a specialized HFU outpatient clinic. The rehabilitation module can be completed in an outpatient or inpatient rehabilitation center for cardiovascular diseases with a focus on heart failure.
Module specific diagnostics for heart failure
The module specific diagnostics for heart failure should be completed at a department with an HFU specialty clinic or a supraregional HFU center.
Regular conferences with case reviews of heart failure patients should be offered at the center. Instruments for quality assurance (e. g. morbidity and mortality conferences) should also be implemented. The candidate should regularly attend these meetings and have presented at least three cases. The requirements for an HFU in the heart failure network were drawn up on the basis of the corresponding consensus paper issued by the DGK/DGTHG [6]. The following summarizes in brief the most important criteria for the individual HFU modules of the Heart Failure Network.
HFU outpatient clinic
Staff: cardiology specialist, certified specialist assistant staff (medical assistant or nurse). Cooperation: effective cooperation with an HFU specialty clinic or HFU in the supraregional center. Diagnostics: electrocardiogram (ECG), long-term ECG, stress ECG, possibility for echocardiography and PM, ICD and CRT aftercare, possibility for testing for troponin and natriuretic peptide. Appointments to be given: acute <48 h, post-stationary <7 days.
HFU speciality clinic (additional features)
Staff at intensive care unit (ICU) or intermediate care unit (IMCU): specialist in cardiology and intensive care medicine or specialist in heart surgery and intensive care medicine, or interdisciplinary management, doctor 24/7 on site, specialist 24/7 on call, key care/patient = 1/4. Cooperation: proven cooperation with HFU in supraregional center. Structure: at least four hospital beds (IMCU or ICU), availability 24/7. Diagnostics: long-term blood pressure monitor, echocardiography (transthoracic and transesophageal), X ray, CT, hemodynamics. Treatment: ventilation (invasive and/or non-invasive), hemodialysis, cardiac catheterization laboratory with 24/7 percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) availability, ICD/CRT implantation.
Supraregional HFU center (additional features)
Staff: heart team (cardiologist and heart surgeon) 24/7, ventricular assist device (VAD)/heart transplantation (HTx) coordinator 24/7, if necessary. Structure: at least four hospital beds (IMCU or heart failure ICU) in an area separate from the general intensive care unit, cooperation with heart transplantation or VAD center, if necessary. Diagnostics: sleep apnea screening, lung function test, spiroergometry, cardiac MRI, myocardial biopsy. Treatment: percutaneous cardiac support systems (intra-aortic balloon pump, microaxial pump), extracorporeal life support systems (ECLS), transfemoral aortic valve implantation (TAVI), endovascular mitral valve reconstruction, ablation of complex ventricular tachycardia.
7. Training supervisor requirements
The following requirements apply for the training supervisor:
-
A physician specialized in internal medicine and cardiology with a concentration on heart failure must act as supervisor at the training institution. The supervisor should have 5 years of experience in the care of heart failure patients.
-
This head of the specialization program ensures that the candidates receive the necessary supervision when learning the diagnostic and therapeutic procedures dictated by the curriculum. The specialist also ensures that the candidates attend the formal learning units and courses and are involved in the department’s training and research activities.
8. Evaluation and quality control
Evaluation of the candidate with a view to their completion of the curriculum shall consist of the following components:
-
Qualification report written by the supervisor of the specialization program. The report contains details on the activities, competence and achieved independence of the candidate. In addition to information on theoretical knowledge and experience, it also contains a description of progress made in practical activities and theoretical knowledge about heart failure.
-
Documentation of the patient cases or the examinations/procedures conducted in a logbook (in hard copy or electronic form). The correctness of the logbook is confirmed in writing by the supervisor of the specialization center.
-
Documentation of on-going specialist training in the subdiscipline in the form of confirmation of attendance at accredited congresses, workshops, symposia and training/simulation courses held by the specialist societies or their members (HFA meeting, DACH-HF meeting, working group meetings with didactic contents, heart failure consensus meetings). For attendance at a meeting of the major cardiological societies (European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology) the candidate will be credited a maximum of 2 days. At least five heart failure-specific training days must be documented per training year.
9. Accreditation for training
Applications for recognition of curricular achievements in order to obtain the additional qualification “heart failure specialist” shall be evaluated by a dedicated committee of the nucleus of the Heart Failure Working Group of the Austrian Cardiological Society (two co-leaders of the working group, three dedicated members). For this purpose, the documents listed in Section 8 “Evaluation and quality control” are to be submitted. The candidate will receive recognition of the additional qualification in heart failure, issued by the ÖKG. Recognition is valid for 5 years, after which recertification must be applied for (proof of at least one heart failure-specific advanced training per year). Certification as a training institution and certification as a supervisor are granted by the abovementioned committee. The function of supervisor is in principle linked to certification of the training institution. Certification as a training center for the additional qualification is valid for 5 years, after which recertification must be applied for.
10. Transitional arrangements
Specialists in internal medicine and cardiology who have been clinically active in the field of heart failure for at least 2 of the last 5 years (including at least two of the required modules) and/or who can demonstrate special scientific expertise in heart failure can acquire the additional qualification “heart failure specialist” on application, without formally completing the curriculum. The applicant’s predominant activity in the area of heart failure as well as the required minimum numbers of the required examinations must be confirmed by the head of the particular institution. The transitional regulation is valid from 1 June 2019 until 30 May 2021.
References
McDonagh TA, Gardner RS, Lainscak M, Nielsen OW, Parissis J, Filippatos G, Anker SD. Heart failure association of the European Society of Cardiology Specialist Heart Failure curriculum. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014;16:151–62.
Frey N, Albrecht A, Bauersachs J, Hasenfuss G, Laufs U, Luchner A, Pauschinger M, Raake P, Sack S, von Scheidt W, Schulze C, Smetak N, Subin B – DGK Taskforce Curriculum Herzinsuffizienz. Curriculum Herzinsuffizienz. Kardiologe 2018;12:56–67.
Mohaci P, Maeder MT, Flammer AJ, Meyer P, Moschovitis G, Paul M, Pfister O, Suter T, Ruschitzka F, Positionspapier HR. „Herzinsuffizienz – Curriculum“ der Arbeitsgruppe Herzinsuffizienz der SGK. Cardiovasc Med. 2018;21(1):26–32.
https://www.statistik.at/web_de/statistiken/menschen_und_gesellschaft/gesundheit/stationaere_aufenthalte/spitalsentlassungen_nach_ausgewaehlten_diagnosen/index.html. Accessed: 14.04.2019.
Shah SJ, Kitzman DW, Borlaug BA, van Heerebeek L, Zile MR, Kass DA, Paulus WJ. Phenotype-specific treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a multiorgan roadmap. Circulation. 2016;134(1):73–90.
Ertl G, Angermann CE, Bekeredjian R, Beyersdorf F, Güder G, Gummert J, Katus HA, Kindermann I, Pauschinger M, Perings S, Raake PWJ, Störk S, von Scheidt W, Welz S, Böhm M. Kardiologe. 2016;10:222–35.
Francis GS, Greenberg BH, Hsu DT, et al. ACCF/AHA/ACP/HFSA/ISHL 2010 Clinical Competence Statement on Management of Patients with Advanced Herat Failure and Cardiac Transplant. Circulation. 2010;122:644–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
R. Berger: research grant, speakers fee by or consultant of Abbott, Amgen, Bayer, Biotronic, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardinal Health, Medtronic, Novartis, Orion Pharma, Servier. M. Hülsmann: research grant, speakers fee by or consultant of Abbott, Gebro, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche Diagnostics, MSD, Pint Pharma, Servier, Thermo Fisher. D. Mörtl: speakers fee and/or consultant fees from Abbott, Merck, Novartis, ResMed, Roche Diagnostics, Servier, Vifor. G. Pölzl: director of the HerzMobil Tyrol DMP; research grant, speakers fee by or consultant of Abbott, Merck, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, Servier, Vifor.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Training program schedule
1st year—Basic training
2nd year—in-depth training
Module: advanced chronic and acute heart failure with specialized treatment options
Module: device treatment for heart failure
Module: interventional heart failure treatment
Module: outpatient care (I) or rehabilitation (II)
Outpatient care (I)
Rehabilitation (II)
Module: specific diagnostics for heart failure
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, R., Hülsmann, M., Mörtl, D. et al. Curriculum heart failure. Wien Klin Wochenschr 131, 299–312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-019-1480-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-019-1480-y