Abstract
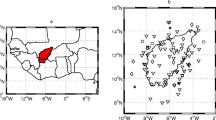
The main purpose of this study is to map the spatio-temporal variation of hydrological drought severities in the Euphrates Basin by using Kriging, Radial Based Function (RBF), Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW), Local Polynomial Interpolation (LPI), and Global Polynomial Interpolation (GPI) methods and to determine the distribution of hydrological drought trends. For this purpose, 18 streamflow observation stations and grid-based ERA5 reanalysis data were employed in and around the Euphrates Basin. The standardized runoff index (SRI) was calculated on monthly, 3-month, and 12-month time scales to determine hydrological droughts. Hydrological drought trends were determined by Mann Kendall (MK) and Modified Mann Kendall (MMK) tests. According to SRI, spatial-temporal distributions of droughts were mapped by Kriging, RBF, IDW, GPI, and LPI methods in the Geographical Information Systems environment. The LPI and Kriging method was selected as the most effective methods to predict hydrological droughts based on the cross-validation error. As a result of the trend analysis, the predominance of decreasing SRI trends in May (61.1%), June (72.2%), July (55.6%), August (61.1%) indicates that the basin is at risk of hydrological drought, especially in summer. According to the maps of spatial droughts, the widespread distribution of droughts in the basin indicated that the basin was greatly affected by hydrological droughts. For this reason, it has been emphasized that transboundary water effective management between riparian countries, planning of water structures, and effective implementation of the drought management plan is of great importance.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Adhikary PP, Dash C (2017) Comparison of deterministic and stochastic methods to predict spatial variation of groundwater depth. Appl Water Sci 7(1):339–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0249-8
Aguilar FJ, Agüera F, Aguilar MA, Carvajal F (2005) Effects of terrain morphology, sampling density, and interpolation methods on grid DEM accuracy. Photogrammetric Eng Remote Sens 71(7):805–816. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.71.7.805
Ahani H, Kherad M, Kousari MR, Rezaeian-Zadeh M, Karampour MA, Ejraee F, Kamali S (2012) An investigation of trends in precipitation volume for the last three decades in different regions of Fars province, Iran. Theoret Appl Climatol 109:361–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0572-z
Aksoy H, Cetin M, Eris E, Burgan HI, Cavus Y, Yildirim I, Sivapalan M (2021) Critical drought intensity-duration-frequency curves based on standardized precipitation index. Hydrol Sci J 66(8):1337–1358. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2021.1934473
Alhumaima AS, Abdullaev SM (2018) Preliminary Assessment of hydrothermal risks in the Euphrates-Tigris basin: Droughts in Iraq. Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Вычислительная математика и информатика 7(4)
Ali G, Sajjad M, Kanwal S, **ao T, Khalid S, Shoaib F, Gul HN (2021) Spatial–temporal characterization of rainfall in Pakistan during the past half-century (1961–2020). Sci Rep 11(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86412-x
Amini MA, Torkan G, Eslamian S, Zareian MJ, Adamowski JF (2019) Analysis of deterministic and geostatistical interpolation techniques for map** meteorological variables at large watershed scales. Acta Geophys 67(1):191–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0226-y
Apaydin H, Sonmez FK, Yildirim YE (2004) Spatial interpolation techniques for climate data in the GAP region in Turkey. Climate Res 28(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr028031
Ayantobo OO, Li Y, Song S, Yao N (2017) Spatial comparability of drought characteristics and related return periods in mainland China over 1961–2013. J Hydrol 550:549–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.05.019
Aydın O, Çiçek İ (2015) Geostatistical interpolation of precipitation in Turkey. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, pp 195–195
Ayugi B, Eresanya EO, Onyango AO, Ogou FK, Okoro EC, Okoye CO, Ongoma V (2022) Review of Meteorological Drought in Africa: Historical Trends, Impacts, Mitigation Measures, and Prospects. Pure appl Geophys 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-022-02988-z
Bagheri F (2016) Map** drought hazard using SPI index and gis (a case study: Fars province, Iran). Int J Environ Geoinform 3:22–28. https://doi.org/10.30897/ijegeo.304419
Bajjali W (2017) ArcGIS for environmental and water issues. Springer, Berlin
Childs C (2004) Interpolating surfaces in ArcGIS spatial analyst ArcUser. July-September 3235:32–35
Dikici M (2020) Drought analysis with different indices for the Asi Basin (Turkey). Sci Rep 10(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77827-z
Duhan D, Pandey A (2013) Statistical analysis of long term spatial and temporal trends of precipitation during 1901–2002 at Madhya Pradesh, India. Atmos Res 122:136–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.10.010
Erxleben J, Elder K, Davis R (2002) Comparison of spatial interpolation methods for estimating snow distribution in the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Hydrol Process 16:3627–3649. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1239
Farmer WH (2016) Ordinary kriging as a tool to estimate historical daily streamflow records. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20:2721. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-2721-2016
Guo-feng Z, Pei-ji S, Tao P, Yuan-qing H, Tao Z, Pei-zhen W, Mei-hui P (2013) Changes of surface soil relative moisture content in Hengduan Mountains, China, during 1992–2010. Quatern Int 298:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2013.01.012
Hamed KH, Rao AR (1998) A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J Hydrol 204:182–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00125-X
Hao W, Chang X (2013) Comparison of spatial interpolation methods for precipitation in Ningxia, China. Int J Sci Res 2(8):198–184
Hao Z, Singh VP (2015) Drought characterization from a multivariate perspective: a review. J Hydrol 527:668–678
He B, Lü A, Wu J, Zhao L, Liu M (2011) Drought hazard assessment and spatial characteristics analysis in China. J Geog Sci 21:235–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-011-0841-x
Hodam S, Sarkar S, Marak AG, Bandyopadhyay A, Bhadra A (2017) Spatial interpolation of reference evapotranspiration in India: comparison of IDW and Kriging Methods. J Institution Eng (India): Ser A 98(4):511–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-017-0241-z
Huang WC, Yang FT (1998) Streamflow estimation using Kriging. Water Resour Res 34:1599–1608. https://doi.org/10.1029/98WR00555
Isaaks EH, Srivastava RM (1989) An introduction to applied geostatistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 561
Javari M (2016) Geostatistical and spatial statistical modelling of precipitation variations in Iran. J Civ Environ Eng 6:1–30. https://doi.org/10.4172/2165-784X.1000230
Jeffrey SJ, Carter JO, Moodie KB, Beswick AR (2001) Using spatial interpolation to construct a comprehensive archive of Australian climate data. Environ Model Softw 16(4):309–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(01)00008-1
Jehanzaib M, Shah SA, Yoo J, Kim TW (2020) Investigating the impacts of climate change and human activities on hydrological drought using non-stationary approaches. J Hydrol 588:125052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125052
Johnston K, Ver Hoef JM, Krivoruchko K, Lucas N (2001) Using ArcGIS geostatistical analyst, vol 380. Esri, Redlands
Katipoğlu OM, Acar R (2021) Determination of meteorological and hydrological drought maps with various ınterpolation methods in the Euphrates Basin. J Nat Hazards Environ 7(2):298–317. https://doi.org/10.21324/dacd.853893
Katipoğlu OM, Acar R, Şenocak S (2021) Spatio-temporal analysis of meteorological and hydrological droughts in the Euphrates Basin, Turkey. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 21(4):1657–1673. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2021.019
Katipoğlu OM, Acar R, Şenocak S, Şengül S (2022) Assessment of meteorological drought trends in the Euphrates Basin, Turkey. Arab J Geosci 15(6):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08482-5
Katipoğlu OM (2020) Analysis of meteorological and hydrological droughts in the Euphrates basin. Doctoral thesis. Ataturk University Institute of Sciences, Erzurum
Katipoğlu OM, Acar R (2019) Evaluation of hydrologic droughts by using standardized runoff index (SRI). ICADET 2019, 19–21 September 2019, Bayburt
Kendall MG (1948) Rank correlation methods
Keskin M, Dogru AO, Balcik FB, Goksel C, Ulugtekin N, Sozen S (2015) omparing spatial interpolation methods for map** meteorological data in Turkey. Energy Syst Manage. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16024-5_3
Kisaka MO, Mucheru-Muna M, Ngetich FK, Mugwe J, Mugendi D, Mairura F, Makokha GL (2016) Potential of deterministic and geostatistical rainfall interpolation under high rainfall variability and dry spells: case of Kenya’s Central Highlands. Theoret Appl Climatol 124:349–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1413-2
Kousari MR, Ahani H, Hakimelahi H (2013) An investigation of near surface wind speed trends in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran. Theoret Appl Climatol 114:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0811-y
Leng G, Tang Q, Rayburg S (2015) Climate change impacts on meteorological, agricultural and hydrological droughts in China. Glob Planet Change 126:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.01.003
Mann HB (1945) Non-parametric tests against trend. Econ J Econ Soc 245–259
Nalbantis I, Tsakiris G (2009) assessment of hydrological drought revisited. Water Resour Manage 23(5):881–897
Nasrollahi M, Khosravi H, Moghaddamnia A, Malekian A, Shahid S (2018) Assessment of drought risk index using drought hazard and vulnerability indices. Arab J Geosci 11:606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3971-y
Ozguler H, Yildiz D (2020) Consequences of the Droughts in the Euphrates-Tigris Basin International. J Water Manage Dipl 1(1):29–40
Paparrizos S, Maris F, Matzarakis A (2016) Map** of drought for Sperchios River basin in central Greece. Hydrol Sci J 61:881–891. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.965175
Pathak AA, Dodamani BM (2016) Comparison of two hydrological drought indices. Perspect Sci 8:626–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pisc.2016.06.039
Phillips DL, Dolph J, Marks D (1992) A comparison of geostatistical procedures for spatial analysis of precipitation in mountainous terrain. Agric For Meteorol 58(1–2):119–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1923(92)90114-J
Qi P, Zhang G, Xu YJ, Wu Y, Gao Z (2017) Spatiotemporal changes of reference evapotranspiration in the highest-latitude region of China. Water 9:493. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070493
Rahman MR, Lateh H (2016) Meteorological drought in Bangladesh: assessing, analysing and hazard map** using SPI, GIS and monthly rainfall data. Environ Earth Sci 75:1026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5829-5
Shepard D (1968) A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM national conference, 1968. pp. 517–524. https://doi.org/10.1145/800186.810616
Shukla S, Wood AW (2008) Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL032487
Smakhtin VU, Schipper ELF (2008) Droughts: the impact of semantics and perceptions. Water Policy 10:131–143. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2008.036
Souza FAA, Samprogna Mohor G, Guzmán Arias DA, Buarque ACS, Taffarello D, Mendiondo EM (2022) Droughts in São Paulo: challenges and lessons for a water-adaptive society. Urban Water J. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2022.2047735
Staupe-Delgado R, Rubin O (2022) Challenges associated with cree** disasters in disaster risk science and practice: considering disaster onset dynamics. Int J Disaster Risk Sci 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13753-022-00391-9
Svoboda MD, Fuchs BA, Poulsen CC, Nothwehr JR (2015) The drought risk atlas: enhancing decision support for drought risk management in the United States. J Hydrol 526:274–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.006
Swain JB, Patra KC (2017) Streamflow estimation in ungauged catchments using regionalization techniques. J Hydrol 554:420–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.08.054
Tosunoglu F (2014) Investigating the relationship between atmospheric oscillations and meteorological and hydrological droughts in Turkey. Doctoral Thesis. Atatürk University, (s. 180)
Türkoğlu N, Aydın O, Duman N, Çiçek I (2016) Comparison of various spatial interpolation methods for precipitation in Turkey. J Hum Sci 13(3):5636–5658. https://doi.org/10.14687/jhs.v13i3.4173
Van Niekerk A, Joubert SJ (2011) Input variable selection for interpolating high-resolution climate surfaces for the Western Cape.Water SA37(3)
Varouchakis ΕA, Hristopulos DT (2013) Comparison of stochastic and deterministic methods for map** groundwater level spatial variability in sparsely monitored basins. Environ Monit Assess 185(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2527-y
Vicente-Serrano SM, Saz-Sánchez MA, Cuadrat JM (2003) Comparative analysis of interpolation methods in the middle Ebro Valley (Spain): application to annual precipitation and temperature. Climate Res 24(2):161–180. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr024161
Wilhite DA, Glantz MH (1985) Understanding: the drought phenomenon: the role of definitions. Water Int 10:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508068508686328
Wu J, Miao C, Tang X, Duan Q, He X (2018) A non-parametric standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrological drought on the Loess Plateau, China. Glob Planet Change 161:53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.12.006
**ao Y, Gu X, Yin S, Shao J, Cui Y, Zhang Q, Niu Y (2016) Geostatistical interpolation model selection based on ArcGIS and spatio-temporal variability analysis of groundwater level in piedmont plains, northwest China. SpringerPlus 5:425. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2073-0
Xu C, Wang J, Li Q (2018) A new method for temperature spatial interpolation based on sparse historical stations. J Clim 31(5):1757–1770. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0150.1
Yildiz D, Yildiz D, Güneş M (2019) Analysis of long-term natural streamflow trends in Upper Euphrates River Basin. Eur J Sci Technol 15:118–131. https://doi.org/10.31590/ejosat.500548
Yu Y-S, Zou S, Whittemore D (1993) Non-parametric trend analysis of water quality data of rivers in Kansas. J Hydrol 150:61–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(93)90156-4
Yue S, Pilon P, Cavadias G (2002) Power of the Mann–Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J Hydrol 259:254–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00594-7
Yıldırım A (2006) Karakaya Dams and effects of naturel environment. Dicle University Journal of Ziya Gökalp Faculty of Education 6:32–39
Yıldırımlar O (2012) Low Flow Anaysis in Firat Catchment. Master’s Thesis, Istanbul Technical University Energy Institute, Istanbul, Turkey
Zhang X, Harvey KD, Hogg W, Yuzyk TR (2001) Trends in Canadian streamflow. Water Resour Res 37:987–998. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000WR900357
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the General Directorate of Electrical Power Resources Survey and Development Administration and Copernicus Climate Change Service information for the observed monthly average streamflow data provided. In addition, the authors thank assistant professor Selim Şengül, associate professor Serkan Şenocak, the Editor, and the anonymous reviewers for their contributions to the content and development of this paper.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. O. M. Katipoğlu performed material preparation, data collection, analysis, and writing. R. Acar contributed to the editing and review of the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
We confirm that this article is original research and has not been published previously in any journal in any language.
Consent to participate
All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Consent to Publish
The authors confirm that the work described has not been published before, and it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katipoğlu, O.M., Acar, R. Space-time variations of hydrological drought severities and trends in the semi-arid Euphrates Basin, Turkey. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36, 4017–4040 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02246-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02246-7