Abstract
Background
Morbidity and mortality rates of Digestive System Cancers (DSC) continue to pose human lives and health. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-like protein 3 (NFE2L3) is aberrantly expressed in DSC. This study aimed to explore the clinical value and underlying mechanisms of NFE2L3 as a novel biomarker in DSC.
Methods
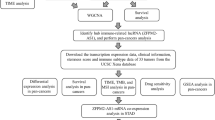
We utilized data from databases and clinical gastric cancer specimens to validate the aberrant expression level of NFE2L3 and further assessed the clinical value of NFE2L3. To investigate the potential molecular mechanism of NFE2L3, we analyzed the correlation of NFE2L3 with immune molecular mechanisms, constructed PPI network, performed GO analysis and KEGG analysis, and finally explored the biological function of NFE2L3 in gastric cancer cells.
Results
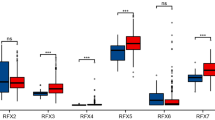
NFE2L3 expression is up-regulated in DSC and has both prognostic and diagnostic value. NFE2L3 correlates with various immune mechanisms, PPI network suggests proteins interacting with NFE2L3, GSEA analysis suggests potential molecular mechanisms for NFE2L3 to play a role in cancer promotion, and in vitro cellular experiments also confirmed the effect of NFE2L3 on the biological function of gastric cancer cells.
Conclusion
Our study confirms the aberrant expression and molecular mechanisms of NFE2L3 in DSC, indicating that NFE2L3 could serve as a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of DSC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Globally, tumors continue to pose a threat to human life and health. In 2021, statistics from the American Cancer Society showed that there were 338,090 new cases and 169,280 deaths were estimated for digestive tract tumors in the United States (Siegel et al. 2021). DSC mainly include cholangiocarcinoma (CHOL), colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), esophageal carcinoma (ESCA), liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD), rectum adenocarcinoma (READ), and stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD), continue to be major types of cancer threatening human health and survival. DSC are affected by several risk factors, including lifestyle habits, tobacco use, alcoholism, physical activity, and gender (** the progression of DSC. Relevant studies have indicated that cancers harbor high TMB means the potential to generate many neoantigens, making tumors more immunogenic for ICIs (Bravaccini et al. 2021; Chan et al. 2019). Expect MSI, the TMB also demonstrated the significance of the DSC. A higher TMB is normally related to an adverse outcome in advanced tumors.
According to our results, we revealed that NFE2L3 was closely correlated with immunity. It is expected to become novel immunotherapeutic target for DSC in future. Further studies should continue to investigate the mechanisms of NFE2L3 in immunotherapy.
Our findings indicated a significant positive correlation between NFE2L3 and immune or molecular subtypes. Cellular and immune subtypes are the main factors responsible for tumor heterogeneity. Treatment elicits varied responses from tumors, owing to the genetic diversity within the tumor. The combination of immune and molecular subtypes for precisely targeted tumor therapy will also greatly enhance the current status of immunotherapeutic efficacy. Therefore, we believe that NFE2L3 plays a vital role in DSC immunotherapy. Therapeutic cancer vaccines remain a valid immunotherapy option and hold significant implications for the clinical advancement of cancer patients (Pe'er et al. 2021; Baharom et al. 2022). Over the past few years, there has been a significant amount of research conducted on vaccines and therapeutics specifically designed for the innate and adaptive immune systems in the field of cancer treatment (Peng et al. 2022; Ratnam et al. 2019). Thus, the important functions of immune cells in tumor-specific immunity against immune cells can be understood. Our findings showed that compared with non-responders, patients who generated antibody responses to therapy exhibited prolonged DFS. We have reason to believe that NFE2L3 to be a potential target for immunotherapy in future.
A multitude of studies have indicated that patients with immune cell infiltration tumors exhibit a more favorable response to ICI than patients with non-immunological tumors. Recent research has revealed that NFE2L3 plays a pivotal role in cancer development (Wang et al. 2018; Zhang et al. 2019), but the precise mechanisms have yet to be elucidated. The findings of this research indicated that DSCs experienced immune cell infiltration. The immune cell infiltration encompasses a wide range of cell types, such as Tregs, T cells, dendritic cells, NK cells, T follicular helper cells, macrophages, mast cells, and monocytes. In STAD, we observed a strong correlation between NFE2L3 expression and immune cells abundance. The research revealing the correlation of immune cell infiltration with NFE2L3 may open unique avenues for precise cancer therapeutics against cancers.
Co-expression analysis can be employed as a means to identify disease-associated genes and gene functions in tumors. Chemokines combine with the cell surface chemokine receptors to perform biological functions, such as the chemotaxis, leukocyte migration, and inflammatory activities (Charo and Ransohoff 2006; Arimont et al. 2017). The causative role of chemokines is variable, and they play an important role in many diseases, such as cancer, viral infections, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases. Researchers have found that chemokines affect anti-tumorigenic activity by regulating tumor angiogenesis and infiltration of immune cells (Lacalle et al. 2017). The results of our study showed a strong correlation between NFE2L3 and immune-related genes or chemokine receptors. In COAD, LIHC, and STAD, there was a close correlation between NFE2L3 expression and the chemokine receptors, such as C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1 (CX3CR1), plexin B2 (PLXNB2), atypical chemokine receptor 1 (ACKR1), and formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2). Anja Schmall found that the tumor-associated crosstalk between macrophages and cancer cells via the CCR2 and CX3CR1 signaling pathways directed the lung cancer growth and metastasis (Schmall et al. 2015). Circ_0013958 plays an oncogenic role in ovarian cancer by regulating the miR-637/PLXNB2 axis (Liang et al. 2021). Immune-related genes, such as PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA4, have been successfully used in tumor immunotherapy and have been shown to have a significant effect on B cell lymphomas, HCC, and non-small cell lung cancer (Xu-Monette and Zhou 2018; Kamada et al. 2019), (Thommen et al. 2018). This study revealed novel immune-related genes that are co-expressed with NFE2L3 in DSC, including TIGIT, IDO1, ADORA2A, and CD70, which can be used as immune therapy, checkpoints, and biomarkers (Zhai et al. 2018; Chauvin and Zarour 2020). Therefore, combining immune-related genes or chemokine receptors with NFE2L3 may enhance the efficacy of DSC diagnosis and immunotherapy.
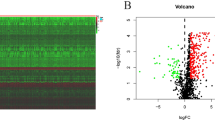
We conducted GO enrichment and KEGG analysis on the NFE2L3 binding proteins, we found that the Hedgehog signaling pathway is the primary target of protein catabolic processes and cell differentiation. Hedgehog signaling pathway activated tumors by driving EMT, and the inhibitor of Hedgehog signaling pathway exhibited remarkable clinical outcomes in various types of cancer Zhang et al. (2009). Nevertheless, the investigation into the differential regulation of target genes by NFE2L3 remains to be investigated.
NFE2L3 is involved in the regulation of various biological and cellular processes, such as cell cycle, cell differentiation, or inflammatory processes. We performed GSEA and found that NFE2L3 was significantly associated with epigenetics, methylation modification, cell cycle regulation, calcium signaling pathway and steroid hormone biosynthesis. Consequently, the distinct manifestation of NFE2L3 assumes a crucial function in DSC through various biological functions and signaling pathways, ultimately impacting the process of tumorigenesis. Nevertheless, a comprehensive understanding of the findings would require further experimental validation.
To validate the bioinformatics findings, in vivo experiments conducted on gastric cancer cells demonstrated the role of NFE2L3 as an oncogene, facilitating the proliferation and movement of gastric cancer cells. NFE2L3 enhances tumor cell migration ability by affecting the EMT through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (Ren et al. 2020; Zeng and Ju 2018). These findings and our hypothesis are validated experimental results. More in vitro research is needed to gain a better understanding of how things work in future.
The outcomes of these bioinformatics analyses lay the groundwork for future comprehensive investigations into the mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis and evolution. NFE2L3 was found to be aberrantly expressed in DSC, and significantly correlated with the diagnosis and prognosis of DSC patients. In addition, in vivo results suggest that NFE2L3 may act as an oncogene roles in gastric cancer through promoting the gastric cancer cells growth and migration.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we identified a specific role of NFE2L3 in DSC. The results of our study indicated that NFE2L3 was differentially expressed in cancers and closely related to clinical features. Therefore, it has the potential prognostic and diagnostic values for DSC. In addition, NFE2L3 was closely related to immune filtration, immune subtype, and molecular subtype and co-expressed with numerous genes and chemokines. These findings suggest that NFE2L3 has the potential to emerge as a novel therapeutic target for DSC. Additional experimental studies are required to verify these findings.
Data availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Additional files.
References
Arimont M, Sun SL, Leurs R, Smit M, de Esch IJP, de Graaf C (2017) Structural analysis of chemokine receptor-ligand interactions. J Med Chem 60:4735–4779
Asaoka Y, Ijichi H, Koike K (2015) PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch repair deficiency. N Engl J Med 373:1979. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1510353
Baharom F, Ramirez-Valdez RA, Khalilnezhad A, Khalilnezhad S, Dillon M, Hermans D (2022) Systemic vaccination induces CD8(+) T cells and remodels the tumor microenvironment. Cell 185:4317–4332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.006
Bravaccini S, Bronte G, Ulivi P (2021) TMB in NSCLC: a broken dream? Int J Mol Sci 22:6356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126536
Bury M, Le Calvé B, Lessard F, Dal Maso T, Saliba J, Michiels C, Gerardo F, Blank V (2019a) NFE2L3 controls colon cancer cell growth through regulation of DUX4, a CDK1 inhibitor. Cell Rep 29:1469–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.09.087
Bury M, Le Calvé B, Lessard F, Dal Maso T, Saliba J, Michiels C, Ferbyre G, Blank V (2019b) NFE2L3 controls colon cancer cell growth through regulation of DUX4, a CDK1 Inhibitor. Cell Rep 29(6):1469–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.09.087
Carlino MS, Larkin J, Long GV (2021) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet 398:1002–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01206-X
Chan TA, Yarchoan M, Jaffee E, Swanton C, Quezada SA, Stenzinger A, Perters S (2019) Development of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: utility for the oncology clinic. Ann Oncol 30:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy495
Charo IF, Ransohoff RM (2006) The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N Engl J Med 354:610–621. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra052723
Chauvin JM, Zarour HM (2020) TIGIT in cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer 8:e000957. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-000957
Chen LB, Lu DW, Sun KK, Xu YM, Hu PP, Li XP (2019) Identification of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Gene 692:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.01.001
Chevillard G, Blank V (2011) NFE2L3 (NRF3): the cinderella of the cap’n’collar transcription factors. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:3337–3348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0747-x
Datta N, Chakraborty S, Basu M, Ghosh MK (2020) Tumor suppressors having oncogenic functions: the double agents cells. Cells 10:46. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010046
De Angelis GL, Bottarelli L, Azzoni C, De Angelis N, Leandro G, Di Mario F, Gaiani F, Negri F (2018). Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Acta Biomed, doi: https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v89i9-S.7960
Feng M, Zhao Z, Yang M, Ji J, Zhu D (2021) T-cell-based immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett 498:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.040
Galluzzi L, Humeau J, Buqué A, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2020) Immunostimulation with chemotherapy in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17:725–741. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-020-0413-z
Ganesh K, Stadler ZK, Cercek A, Mendelsohn RB, Shia J, Segal NH, Diaz LA Jr (2019) Immunotherapy in colorectal cancer: rationale, challenges and potential. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:361–375. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0126-x
Ju Q, Li XM, Zhang H, Yan S, Li Y, Zhao YJ (2020) NFE2L2 is a potential prognostic biomarker and is correlated with immune infiltration in brain lower grade glioma: a pan-cancer analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:3580719. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3580719
Kamada TH, Togashi YK, Tay C, Ha D, Sasaki A, Nakamura Y, Sato E, Fukuoka S, Tada Y, Tanaka A, Morikawa H, Kawazoe A, Kinoshita T, Shitara K, Skaguchi S, Nishikawa H (2019) PD-1(+) regulatory T cells amplified by PD-1 blockade promote hyperprogression of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:9999–10008. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1822001116
Lacalle RA, Blanco R, Carmona-Rodríguez L, Martín-Leal A, Mira E, Mañes S (2017) Chemokine receptor signaling and the hallmarks of cancer. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 331:181–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2016.09.011
Liang YF, Meng KY, Qiu R (2021) Circular RNA Circ_0013958 functions as a tumor promoter in ovarian cancer by regulating miR-637/PLXNB2 axis. Front Genet 12:644451. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.644451
Lin A, Zhang J, Luo P (2020) Crosstalk between the MSI status and tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer. Front Immunol 2020(11):2039. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.02039
Pe’er D, Ogawa S, Elhanani O, Keren L, Oliver TG, Wedge D (2021) Tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Cell 39:1015–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2021.07.009
Peng S, Chen S, Hu W, Mei J, Zeng XZ, Su TH, Wang W, Chen ZB, **ao H, Zhou Q, Li B, **e YB, Hu HJ, He MH, Han YY, Tang LQ, Ma YF, Li XH, Zhou XJ, Dan ZH, Liu ZL, Tan JH, Xu LX (2022) Combination neoantigen-based dendritic cell vaccination and adoptive t-cell transfer induces antitumor responses against recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res 10:728–744. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-21-0931
Qian JQ, Huang C, Zhu Z, He YH, Wang Y, Feng N, He SM, Li XS, Zhou LQ, Zhang CJ, Gong YQ (2022) NFE2L3 promotes tumor progression and predicts a poor prognosis of bladder cancer. Carcinogenesis 43:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgac006
Ratnam NM, Gilbert MR, Giles AJ (2019) Immunotherapy in CNS cancers: the role of immune cell trafficking. Neuro Oncol 21:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy084
Ren YG, Wang YJ, Hao S, Yang YH, **ong WD, Qiu L, Tao J, Tang A (2020) NFE2L3 promotes malignant behavior and EMT of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cancer 11:6939–6949. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.48100
Saliba J, Coutaud B, Makhani K, Epstein Roth N, Jackson J, Park JY, Gagnon N, Costa P, Jeyakumar T, Bury M, Beauchemin N (2022) Loss of NFE2L3 protects against inflammation-induced colorectal cancer through modulation of the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 41:1563–1575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02192-2
Schmall A, Al-Tamari HM, Herold S, Kampschulte M, Weigert A, Wietelmann A, Vipotnik N, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Pullamsetti SS, Savai R (2015) Macrophage and cancer cell cross-talk via CCR2 and CX3CR1 is a fundamental mechanism driving lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 191:437–447. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201406-1137OC
Sekine H, Motohashi H (2021) Roles of CNC transcription factors NRF1 and NRF2 in cancer. Cancers (basel) 13:541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030541
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Thommen DS, Koelzer VH, Herzig P, Roller A, Trefny M, Dimeloe S, Kiialainen A, Hanhar J, Schill C, Hess C, Princetrans SS, Wiese M, Lardinois D, Ho PC, Klein C, Karanikas V, Mertz KD, Schumacher TN, Zippelius A (2018) Tcriptionally and functionally distinct PD-1(+) CD8(+) T cell pool with predictive potential in non-small-cell lung cancer treated with PD-1 blockade. Nat Med 24:994–1004. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0057-z
Tomlinson I, Halford S, Aaltonen L, Hawkins N, Ward R (2002) Does MSI-low exist? J Pathol 197:6–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1071
Waku T, Katayama H, Hiraoka M, Hatanaka A, Nakamura N, Tanaka Y, Tamura N, Wantanabe A, Kobayashi A (2020) NFE2L1 and NFE2L3 Complementarily maintain basal proteasome activity in cancer cells through CPEB3-mediated translational repression. Mol Cell Biol 40:e00010–e00020. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00010-20
Wang H, Zhan M, Yang RM, Shi YH, Liu Q (2018) Wang J. Elevated expression of NFE2L3 predicts the poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients. Cell Cycle 17:2164–2174. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1520558/
Wang JX, Choi SYC, Niu X, Kang N, Xue H, Killam J, Yuzhou W (2020) Lactic Acid and an acidic tumor microenvironment suppress anticancer immunity. Int J Mol Sci 2020:21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218363
**e FF, You YL, Huang JH, Guan C, Chen ZJ, Fang M, Yao F (2021) Association between physical activity and digestive-system cancer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci 10:4–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2020.09.009
Xu-Monette ZY, Zhou JF (2018) Young KH. PD-1 expression and clinical PD-1 blockade in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 131:68–83. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-07-740993
Zeng X, Ju DW (2018) Hedgehog signaling pathway and autophagy in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 19:2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082279
Zhai L, Ladomersky E, Lenzen A, Nguyen B, Patel R, Lauing KL, Wu MJ, Wainwright DA (2018) IDO1 in cancer: a gemini of immune checkpoints. Cell Mol Immunol 15:447–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.143
Zhang YG, Kobayashi A, Yamamoto MK, Hayes JD (2009) The Nrf3 transcription factor is a membrane-bound glycoprotein targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum through its N-terminal homology box 1 sequence. J Biol Chem 284:3195–3210. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M805337200
Zhang LH, Hu DL, Tang B, Cheng Y, Jiao C, Cheng L, Tan ZR, Zhou HH (2019) NFE2L3 Inhibition Induces Cell Cycle Arrest at the G0/G1 Phase in colorectal cancer cells through downregulating CCND1 and pRb1-ser807/811. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2829798
Zhang Q, Tang D, Zha A, He JQ, Li DD, Chen YM, Cai WX, Dai J, Luan SD, Yin LH, Zhang W, Dai Y (2022) NFE2L3 as a potential functional gene regulating immune microenvironment in human kidney cancer. Biomed Res Int 2022:9085186. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9085186
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 82070594).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: Fan Li; Provision of study materials or patients: Fan Li, Zhili Wen; Collection and assembly of data: Fan Li; Data analysis: Fan Li; Manuscript writing: Fan li; Revised: Zhili Wen; Funding acquisition, Zhili Wen.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Wen, Z. Identification roles of NFE2L3 in digestive system cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 150, 150 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-024-05656-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-024-05656-y