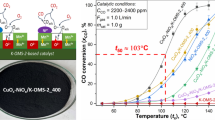
Abstract
The catalytic behaviours of pure K-OMS-2 and Ag-doped K-OMS-2 catalysts (5% Ag do**) synthesized using the hydrothermal method are the focus of investigation in this study. To characterize the catalytic performance of these synthesized catalysts, a combination of analytical techniques, including X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, and Soot Temperature Programmed Reduction (Soot TPR), were employed. The analysis of the prepared samples via XRD revealed a nanocrystalline tetragonal structure, with crystal sizes measuring approximately 22.4 nm. Further examination of the samples using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) unveiled nanorods with dimensions of 213 nm in length and 32 nm in width for K-OMS-2. In comparison, Ag-doped K-OMS-2 displayed nanorods with dimensions of 290 nm in length and 26 nm in width. Notably, the incorporation of Ag+ ions into the K-OMS-2 framework led to an increase in the intensities of the 771 and 527 cm−1 bands when compared to the pure K-OMS-2. This increase can be attributed to the replacement of K+ ions with Ag+ ions in the structure. Furthermore, the introduction of Ag+ ions into the K-OMS-2 framework significantly influenced its catalytic activity for soot oxidation, as evidenced by the augmentation of surface-adsorbed and lattice oxygen radicals, as observed in the results of Soot TPR. The doped sample exhibited substantially enhanced catalytic activity for soot oxidation, as indicated by its low T50 of 370 °C. In addition, the incorporation of the dopant was found to enhance the thermal stability of the catalyst.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Diesel engines have become the predominant choice for global commercial transportation, primarily due to their high thermal efficiency, substantial power output, and low fuel consumption. In addition, they play a pivotal role in agriculture, industrial applications, and energy production [1]. Diesel engines produce approximately 80 times more particulate matter than gasoline engines [2]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), individuals in underdeveloped and develo** countries are exposed to air pollution levels that surpass WHO’s recommended limits [3]. Consequently, the pursuit of carbon neutrality has emerged as a worldwide imperative.
Diesel particulate filters (DPF) are the most efficient technique for controlling particulate matter emissions. Constant soot removal is crucial to prevent DPF clogging due to soot accumulation [4]. The usage of a catalyst for soot oxidation is a promising method to prevent filter clogging. The efficiency of soot oxidation is greatly influenced by the degree of interaction between the soot and the catalyst, making it necessary to consider the contact conditions in this solid–solid interaction [5]. Furthermore, the resilience of the catalyst and its activity for soot oxidation in the exhaust environment is crucial, as it is subjected to temperature fluctuations and thermal degradation (due to the formation of localized hotspots), leading to a decline in catalyst activity [6]. Chemical deactivation poses a further threat to the catalyst’s long-term activity. While using noble metals as catalysts, such as Pt, has shown promising results in reducing the oxidation temperature and soot accumulation in DPF, scarcity and high costs of other platinum-group metals necessitate the exploration of alternative solutions [7].
Ceria-based catalysts [8, 9], noble metals [10,11,12,13,14,15], perovskites [16, 17], alkali-based catalysts [18, 19], and 3 DOM [20] catalysts have been extensively researched, but there is still a need to explore more materials to meet regulatory standards. Among the metal oxides, manganese-based oxides are promising candidates for various oxidative reactions (e.g., CO and VOCs) due to multivalent oxidation states. Octahedral molecular sieves, a type of manganese oxide called K-OMS-2, form a 2 × 2 structure in their most stable state [21, 22]. This structure consists of MnO6 octahedrons stacked to form a square-like tunnel structure with sides measuring 4.6 Å. The potassium atom in the centre helps balance the charge and stabilize the structure. K-OMS-2 exhibits high mobility due to weak interactions with the framework. Various oxidation states of MnOx contribute to its excellent redox properties [23].
Studies report that K-OMS-2 can be tuned by substituting K or Mn ions with single or multiple valence state ions to improve catalytic efficiency and oxygen vacancies [24, 25]. Ag-doped catalysts have been extensively researched for catalytic oxidation reactions (e.g., methanol, ethanol, toluene, CO, and formaldehyde) [26,27,28,29]. Yu et al. [30] investigated that adding Ag produced more surface oxygen vacancies and lattice defects, contributing to excellent catalytic oxidation of methanol. Furthermore, Liu et al. [31] have reported that Ag can enhance the regeneration and generation of active oxygen species with enhanced mobility, thus exhibiting improved catalytic performance with long-term stability. To our knowledge, Ag-doped K-OMS-2 for soot oxidation has not been reported.
This study aims to demonstrate and explain the soot oxidation activity of Ag/K-OMS-2. The hydrothermal synthesis method is employed to prepare K-OMS-2 and silver-doped K-OMS-2. Characterization methods such as XRD, FESEM, FTIR, Raman, and Soot TPR are utilized. A TGA instrument is used to analyze soot catalytic activity. Calculation of the soot oxidation activation energy provides a better understanding of the catalytic performance of the synthesized catalyst.
2 Experimental section
2.1 Materials
Potassium permanganate (99%) and manganese sulfate monohydrate (99%) from Sigma-Aldrich, silver nitrate (99%) and nitric acid (65%) from Merck are used as procured without any additional purifications.
2.2 Preparation of K-OMS-2 catalyst
2.89 g of KMnO4 dissolved in 50 ml of double distilled water was added to a mixture containing 4.12 g of MnSO4 and 1.5 ml nitric acid, with 15 ml double distilled water dropwise and stirred continuously at room temperature for fifteen minutes. This mixture was then transferred into an autoclave (100 ml) and heated in an air oven set at 100 °C for 24 h. The precipitate obtained was washed to neutralize its pH level up to 7 using distilled water before drying it in a hot air oven set at 80 °C. The dried sample is calcined at 600 °C in a muffle furnace for 4 h.
For do** of 5% Ag into K-OMS-2, the following procedure is followed: 2.89 g of KMnO4 in 50 ml double distilled water are added dropwise to a mixture containing 4.12 g MnSO4, an appropriate amount of Ag(NO3)2 and 1.5 ml HNO3 in 15 ml of double distilled water while stirring constantly at room temperature for 15 min. The mixture is put into a 100 ml autoclave and placed inside a hot air oven set at 100 °C for 24 h. The rest of the process was carried out in the same for the undoped sample.
XRD analysis was done using Rigaku Mini Flex 600 to analyze the structure and phase purity of the samples. The wavelength of 1.54 Å was used, with angles ranging from 10° to 70°. Surface morphology was analyzed using FESEM (Carl Zeiss, Germany) with an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. An excitation wavelength of 785 nm was used to record the Raman spectra using a Compact Raman Spectrometer, Renishaw (UK). With a gas flow rate of 60 mL/min (soot TPR was performed in a nitrogen atmosphere). TGA instrument was loaded with the mixed sample (catalyst and soot), which was heated between 50 and 800 °C. It facilitates locating the oxygen radicals that are actively promoting soot oxidation.
2.3 Soot catalytic activity
TGA instrument TA 50 Discovery was used to investigate catalytic soot oxidation. In a 10:1 ratio, the catalyst and soot were combined. The temperature was ramped from ambient to 700 °C while the gas flow rate (O2 flow) was set at 60 mL/min.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 X-ray diffraction (XRD)
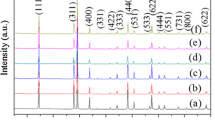
Figure 1 depicts the XRD patterns of both K-OMS-2 and silver-doped K-OMS-2 samples. The diffraction peaks at 2θ correspond to K-OMS-2. Notably, the XRD pattern of the silver-doped K-OMS-2 sample does not exhibit peaks indicative of other forms of silver. This observation has been corroborated by FTIR analysis, which confirms the complete integration of silver ions into the lattice framework (see Fig. 1b).
A reduction of the peak intensity is observed upon adding silver ions. This decrease in peak intensity can be attributed to the thorough incorporation of silver ions into the tunnel structure of K-OMS-2. However, it is essential to note that the XRD pattern also indicates the presence of the orthorhombic phase of α-Mn2O3, known as bixbyite. The formation of α-Mn2O3 has been previously explained in our earlier work [32]. Details regarding the lattice parameters are presented in Table 1.
3.2 FESEM
Figure 2 illustrates the morphology of the synthesized samples. Both samples exhibit a rod-like structure. The average rod length and width for the pure and 5% Ag-doped sample were 290 nm and 32 nm, and 213 nm and 26 nm, respectively. The elongation growth of the particles is partially inhibited, which can be attributed to the incorporation of Ag+ ions into the lattice of K-OMS-2 [33].
3.3 FTIR
Figure 3 displays the FTIR spectra of K-OMS-2 and 5-Ag/K-OMS-2. The obtained FTIR spectra exhibit slight variations from the reported peaks, which can be attributed to factors such as grain size effects, the synthesis process, and temperature influences [3. T50% of this work is compared with the literature and is tabulated in Table 2. From Fig. 6, Ti for K-OMS-2 and silver-doped K-OMS-2 are 229 and 233 °C, whereas the Ti for bare soot was significantly higher at 530 °C.
Although Ti for the Ag-doped sample is slightly higher than the undoped sample, T50% and Tmax are lower than the undoped. This observation can be explained as the silver-doped samples exhibited higher surface- and lattice-adsorbed oxygen radicals, which is observed in soot TPR results. The direct contact between soot and the catalyst enhances the exchange of surface-adsorbed oxygen radicals, which accounts for the lower T50% and Tmax observed in the Ag-doped sample. Surface-adsorbed oxygen radicals are generated by absorbing oxygen through crystal defects. These species are highly reactive and readily desorb at lower temperatures compared to lattice and bulk oxygen radicals. The redox properties of the metal ions in the catalyst facilitate the transfer of oxygen radicals from the lattice to the catalysts surface. In contrast, bulk oxygen radicals become active oxygen radicals only at much higher temperatures [50, 51].
3.7 Activation energy for soot catalytic oxidation
Activation energy is a critical parameter for assessing the type of reaction process occurring in a system. Figure 7 presents the Osawa method’s kinetic results [57]. The activation energy was calculated using Eq. 1; the values are summarized in Table 4. The activation energy of Ag-doped K-OMS-2 is significantly lower compared to that of K-OMS-2, implying that soot undergoes oxidation more readily when the activation energy is reduced [53] (Table 4):
where ß is the heating rates, E is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, T is the measuring temperature.
3.8 Thermal aging
Thermal ageing studies measure catalysts prolonged stability and effectiveness within practical operational settings. Through subjecting catalysts to elevated temperatures over an extended duration, any changes in their catalytic activity, selectivity, and durability can be monitored [58]. The thermal stability of the catalyst is shown in Fig. 8. The aged samples showed similar activity compared to that of fresh catalysts. The T50% of Ag-doped K-OMS-2 had an increase of about ~ 21 °C compared to the fresh catalyst, and no significant changes in the crystal structure were seen in the XRD graph.
4 Conclusion
In summary, we successfully synthesized K-OMS-2 and Ag-doped K-OMS-2 through hydrothermal methods. XRD analysis revealed that the prepared samples exhibited a tetragonal phase. FESEM images displayed a nanorod-like morphology, with Ag-doped K-OMS-2 samples showing smaller-sized nanorods. This size reduction can be attributed to the inhibitory effect of Ag+ ions on nanoparticle growth. Raman and FTIR results indicated the absence of additional phases, such as silver oxides, confirming the full integration of Ag+ ions into the framework. The Soot Temperature Programmed Reduction (TPR) results showed that the Ag-doped sample exhibited higher surface-adsorbed oxygen and lattice oxygen radicals, which translates to superior catalytic activity (T50% = 370 °C). Furthermore, as calculated using the Ozawa method, the activation energy was lower for the Ag-doped sample, a crucial factor contributing to its enhanced catalytic activity.
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Y. Sun, Z. Rao, D. Zhao, B. Wang, D. Sun, X. Sun, Characterizing nonlinear dynamic features of self-sustained thermoacoustic oscillations in a premixed swirling combustor. Appl. Energy 264(February), 114698 (2020)
D. Tan, Y. Wu, J. Lv, J. Li, X. Ou, Y. Meng, G. Lan, Y. Chen, Z. Zhang, Performance optimization of a diesel engine fueled with hydrogen/biodiesel with water addition based on the response surface methodology. Energy 263(PC), 125869 (2023)
S. Chen, D. Zhao, Numerical study of non-reacting flowfields of a swirling trapped vortex ramjet combustor. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 74, 81–92 (2018)
P. Nevalainen, N. Kinnunen, M. Suvanto, Developmental study of soot-oxidation catalysts for fireplaces: the effect of binder and preparation techniques on catalyst texture and activity. Catalysts 9(11), 957 (2019)
M. Piumetti, B. van der Linden, M. Makkee, P. Miceli, D. Fino, N. Russo, S. Bensaid, Contact dynamics for a solid-solid reaction mediated by gas-phase oxygen: study on the soot oxidation over ceria-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 199, 96–107 (2016)
D. Fino, S. Bensaid, M. Piumetti, N. Russo, A Review on the Catalytic Combustion of Soot in Diesel Particulate Filters for Automotive Applications: From Powder Catalysts to Structured Reactors (Elsevier BV, 2015)
H. Huang, J. Liu, P. Sun, S. Ye, B. Liu, Effects of Mn-doped ceria oxygen-storage material on oxidation activity of diesel soot. RSC Adv. 7(12), 7406–7412 (2017)
S. Liu, X. Wu, D. Weng, R. Ran, Ceria-based catalysts for soot oxidation: a review. J. Rare Earths 33(6), 567–590 (2015)
A. Mishra, R. Prasad, Preparation and application of perovskite catalysts for diesel soot emissions control: an overview. Catal. Rev. - Sci. Eng.. Rev. - Sci. Eng. 56(1), 57–81 (2014)
H.E. Emam, N.M. Saad, A.E.M. Abdallah, H.B. Ahmed, Acacia gum versus pectin in fabrication of catalytically active palladium nanoparticles for dye discoloration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 156, 829–840 (2020)
H.E. Emam, H.B. Ahmed, Carboxymethyl cellulose macromolecules as generator of anisotropic nanogold for catalytic performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 111, 999–1009 (2018)
H.B. Ahmed, H.E. Emam, Seeded growth core-shell (Ag–Au–Pd) ternary nanostructure at room temperature for potential water treatment. Polym. Test. 89(March), 106720 (2020)
H.B. Ahmed, N. Saad, H.E. Emam, Recyclable palladium based nano-catalytic laborer encaged within bio-granules for dye degradation. Surf. Interfaces 25(March), 101175 (2021)
M.H. Wiebenga, C.H. Kim, S.J. Schmieg, S.H. Oh, D.B. Brown, D.H. Kim, J.H. Lee, C.H.F. Peden, Deactivation mechanisms of Pt/Pd-based diesel oxidation catalysts. Catal. Today 184(1), 197–204 (2012)
J.M. Herreros, S.S. Gill, I. Lefort, A. Tsolakis, P. Millington, E. Moss, Enhancing the low temperature oxidation performance over a Pt and a Pt-Pd diesel oxidation catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 147, 835–841 (2014)
H. Wang, Q. Zhang, M. Qiu, B. Hu, Synthesis and application of perovskite-based photocatalysts in environmental remediation: a review. J. Mol. Liq. 334, 116029 (2021)
B. Białobok, J. Trawczyński, T. Rzadki, W. Miśta, M. Zawadzki, Catalytic combustion of soot over alkali doped SrTiO3. Catal. Today 119(1–4), 278–285 (2007)
P. Legutko, T. Jakubek, W. Kaspera, P. Stelmachowski, Z. Sojka, A. Kotarba, Soot oxidation over K-doped manganese and iron spinels - How potassium precursor nature and do** level change the catalyst activity. Catal. Commun. 43, 34–37 (2014)
C. Zhang, D. Yu, C. Peng, L. Wang, X. Yu, Y. Wei, J. Liu, Z. Zhao, Research progress on preparation of 3DOM-based oxide catalysts and their catalytic performances for the combustion of diesel soot particles. Appl. Catal. B Environ.Catal. B Environ. 319(Augest), 121946 (2022)
X. Wu, X. Yu, Z. Chen, Z. Huang, G. **g, Low-valence or tetravalent cation do** of manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve (K-OMS-2) materials for nitrogen oxide emission abatement. Catal. Sci. Technol. 9(15), 4108–4117 (2019)
J. Peng, C. Ren, Y. Yu, D. Wang, L. Zhang, C. Fan et al., K-modified. Nano Res. J. 16(5), 6187–6199 (2023)
S. Wagloehner, M. Nitzer-noski, S. Kureti, Oxidation of soot on manganese oxide catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 492–504 (2015)
W. Hong, T. Zhu, Y. Sun, H. Wang, X. Li, F. Shen, Enhancing oxygen vacancies by introducing Na+ into OMS-2 tunnels to promote catalytic ozone decomposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53(22), 13332–13343 (2019)
F. Sabaté, M.J. Sabater, Recent manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (Oms–2) with isomorphically substituted cationic dopants and their catalytic applications. Catalysts 11(10), 1147 (2021)
Y. Qin, X. Liu, T. Zhu, T. Zhu, Catalytic oxidation of ethyl acetate over silver catalysts supported on CeO2 with different morphologies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 229(June 2018), 32–38 (2019)
Z. Qu, Y. Bu, Y. Qin, Y. Wang, Q. Fu, The improved reactivity of manganese catalysts by Ag in catalytic oxidation of toluene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 132–133, 353–362 (2013)
H.E. Emam, M.A. Attia, F.M.S.E. El-Dars, H.B. Ahmed, Emerging use of homogenic and heterogenic nano-colloids synthesized via size-controllable technique in catalytic potency. J. Polym. Environ. 28(2), 553–565 (2020)
H.E. Emam, M.M. Mikhail, S. El-Sherbiny, K.S. Nagy, H.B. Ahmed, Metal-dependent nano-catalysis in reduction of aromatic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27(6), 6459–6475 (2020)
L. Ma, D. Wang, J. Li, B. Bai, L. Fu, Y. Li, Ag/CeO2 nanospheres: efficient catalysts for formaldehyde oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 148–149, 36–43 (2014)
L. Yu, R. Peng, L. Chen, M. Fu, J. Wu, D. Ye, Ag supported on CeO2 with different morphologies for the catalytic oxidation of HCHO. Chem. Eng. J. 334(October 2017), 2480–2487 (2018)
M. Liu, X. Wu, S. Liu, Y. Gao, Z. Chen, Y. Ma, R. Ran, D. Weng, Study of Ag/CeO2 catalysts for naphthalene oxidation: Balancing the oxygen availability and oxygen regeneration capacity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 219, 231–240 (2017)
R. Nithya, H. Dasari, S. Nethaji, S. Sriram, A.L. Vikram, M.S. Murari, Effect of do** copper on K-OMS-2 over soot oxidation activity. Mater. Today Proc. 80, 1130–1134 (2023)
Y. Li, Z. Fan, J. Shi, Z. Liu, J. Zhou, W. Shangguan, Modified manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves M″-OMS-2 (M″ = Co, Ce, Cu) as catalysts in post plasma-catalysis for acetaldehyde degradation. Catal. Today 256, 178–185 (2015)
H. Yang, X. Zhang, Y. Yu, Z. Chen, Q. Liu, Y. Li, W.C. Cheong, D. Qi, Z. Zhuang, Q. Peng, X. Chen, H. **ao, C. Chen, Y. Li, Manganese vacancy-confined single-atom Ag in cryptomelane nanorods for efficient Wacker oxidation of styrene derivatives. Chem. Sci. 12(17), 6099–6106 (2021)
G.D. Yadav, R.V. Sharma, Biomass derived chemicals: environmentally benign process for oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-diformylfuran by using nano-fibrous Ag-OMS-2-catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 147, 293–301 (2014)
F.M. Kalimani, A. Khorshidi, Ag-embedded manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve (Ag-OMS-2) nanorods as efficient heterogeneous catalysts for hydration of nitriles to amides in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 13(10), 6909–6918 (2023)
N.J. Mazumdar, G. Deshmukh, A. Rovea, P. Kumar, M. Arredondo-Arechavala, H. Manyar, Insights into selective hydrogenation of levulinic acid using copper on manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves. R. Soc. Open Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.220078
M. Frenklach, Z. Liu, R.I. Singh, G.R. Galimova, V.N. Azyazov, A.M. Mebel, Detailed, sterically-resolved modeling of soot oxidation: role of O atoms, interplay with particle nanostructure, and emergence of inner particle burning. Combust. Flame 188, 284–306 (2018)
Z. Wu, C. Ji, L. Li, J. Kong, Z. Sun, S. Zhao, S. Wang, M. Hong, J. Luo, Alloying n-butylamine into CsPbBr 3 to give a two-dimensional Bilayered perovskite ferroelectric material. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 57(27), 8140–8143 (2018)
H.C. Genuino, M.S. Seraji, Y. Meng, D. Valencia, S.L. Suib, Combined experimental and computational study of CO oxidation promoted by Nb in manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 163, 361–369 (2015)
T. Jakubek, K. Ralphs, A. Kotarba, H. Manyar, Nanostructured potassium-manganese oxides decorated with Pd nanoparticles as efficient catalysts for low-temperature soot oxidation. Catal. Letters 149(1), 100–106 (2019)
C. Calvert, R. Joesten, K. Ngala, J. Villegas, A. Morey, X. Shen, S.L. Suib, Synthesis, characterization, and rietveld refinement of tungsten-framework-doped porous manganese oxide (K-OMS-2) material. Chem. Mater. 20(20), 6382–6388 (2008)
S.S.P. Sultana, D.H.V. Kishore, M. Kuniyil, M. Khan, M.R.H. Siddiqui, A. Alwarthan, K.R.S. Prasad, N. Ahmad, S.F. Adil, Promoting effects of thoria on the nickel-manganese mixed oxide catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Arab. J. Chem. 10(4), 448–457 (2017)
W. Song, A.S. Poyraz, Y. Meng, Z. Ren, S.Y. Chen, S.L. Suib, Mesoporous Co3O4 with controlled porosity: Inverse micelle synthesis and high-performance catalytic Co oxidation at − 60 °C. Chem. Mater. 26(15), 4629–4639 (2014)
F. Sabaté, J.L. Jordà, M.J. Sabater, Ruthenium isomorphic substitution into manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve OMS-2: comparative physic-chemical and catalytic studies of Ru versus abundant metal cationic dopants. Catal. Today. Today 394–396(March 2021), 414–424 (2022)
H. Zhao, L. Sun, M. Fu, L. Mao, X. Zhao, X. Zhang, Y. **ao, G. Dong, Effect of A-site substitution on the simultaneous catalytic removal of NOx and soot by LaMnO3 perovskites. New J. Chem. 43(29), 11684–11691 (2019)
Q.S. Cao, W.Z. Lu, Z.Y. Zou, G.F. Fan, M. Fu, W. Lei, Phase compositions and reaction models of zinc manganese oxides with different Zn/Mn ratios. J. Alloys Compd. 661, 196–200 (2016)
W. Yu, F. Chen, Y. Wang, L. Zhao, Rapid evaluation of oxygen vacancies-enhanced photogeneration of the superoxide radical in nano-TiO2 suspensions. RSC Adv. 10(49), 29082–29089 (2020)
F. Sabaté, J.L. Jordá, M.J. Sabater, A. Corma, Synthesis of isomorphically substituted Ru manganese molecular sieves and their catalytic properties for selective alcohol oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 8(7), 3771–3784 (2020)
H. Zhao, A. Wang, Q. Zhang, C. Han, Highly efficient removal of ozone by amorphous manganese oxides synthesized with a simple hydrothermal method. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 134, 96–107 (2022)
C. Su, Y. Wang, A. Kumar, P.J. McGinn, Simulating real world soot-catalyst contact conditions for lab-scale catalytic soot oxidation studies. Catalysts 8(6), 247 (2018)
C. Díaz, L. Urán, A. Santamaria, Preparation method effect of La0.9K0.1Co0.9Ni0.1O3 perovskite on catalytic soot oxidation. Fuel 295(March), 120605 (2021)
M. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Yu, W. Shan, H. He, Insight into the better performance of Co than Pt on Ce-Sn catalyst for soot oxidation. Fuel 346(March), 128379 (2023)
Ke. Xu, Y. Zhang, W. Shan, H. He, Promotional effects of Sm/Ce/La do** on soot oxidation over MnCo2O4 spinel catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 125(48), 26484–26491 (2021)
N.E. Olong, K. Stöwe, W.F. Maier, A combinatorial approach for the discovery of low temperature soot oxidation catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 74(1–2), 19–25 (2007)
J. Xu, J. Liu, Z. Zhao, J. Zheng, G. Zhang, A. Duan, G. Jiang, Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous LaCoxFe1–xO3 perovskite-type complex oxide catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Catal. Today 153(3–4), 136–142 (2010)
S. Jian, Y. Yang, W. Ren, L. **ng, D. Zhao, Y. Tian, T. Ding, X. Li, Kinetic analysis of morphologies and crystal planes of nanostructured CeO2 catalysts on soot oxidation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 226, 115891 (2020)
F. Zhang, X. Zhu, Wu. Hanpeng, Wu. **qiang, Z. Zhou, G. Chen, G. Yang, Activity and stability of cu-based spinel-type complex oxides for diesel soot combustion. ChemistrySelect 6(48), 14019–14026 (2021)
M. Wang, Y. Zhang, W. Shan, Y. Yu, J. Liu, H. He, Develo** a thermally stable Co/Ce-Sn catalyst via adding Sn for soot and CO oxidation. IScience 25(4), 104103 (2022)
X. Wu, H.-R. Lee, S. Liu, D. Weng, Regeneration of sulfated MnOx–CeO2–Al2O3 soot oxidation catalyst by reduction with hydrogen. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52(2), 716–721 (2013)
C. Hu, Z. Chen, C. Wei, X. Wan, W. Li, Q. Lin, Au Nanoparticles supported on iron-based oxides for soot oxidation: physicochemical properties before and after the reaction. ACS Omega 6(17), 11510–11518 (2021)
Y. Wei, Q. Wu, J. **ong, J. Li, J. Liu, Z. Zhao, S. Hao, Efficient catalysts of supported PtPd nanoparticles on 3D ordered macroporous TiO2 for soot combustion: synergic effect of Pt-Pd binary components. Catal. Today. Today 327(18), 143–153 (2019)
J.H. Lee, D.Y. Jo, J.W. Choung, C.H. Kim, H.C. Ham, K.Y. Lee, Roles of noble metals (M= Ag, Au, Pd, Pt and Rh) on CeO2 in enhancing activity toward soot oxidation: active oxygen species and DFT calculations. J. Hazard. Mater. 403, 124085 (2021)
Neha, R. Prasad, S.V. Singh, A review on catalytic oxidation of soot emitted from diesel fuelled engines. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8(4), 103945 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank MIT, MAHE for funding this work by providing the Intramural Fund.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RN: conceptualization, methodology, visualization, investigation, writing—original draft. ALV: formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, validation. HD: supervision, conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, writing—review and editing. SN: supervision, conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, writing—review and editing. MSM: resources, supervision, investigation, writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors reported no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Nithya, R., Vikram, A.L., Dasari, H. et al. Improved catalytic performance of Ag-doped K-OMS-2 for soot oxidation. Appl. Phys. A 130, 112 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07282-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07282-4