Abstract
Background
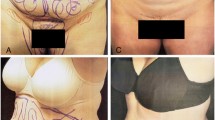
In cases where the upper arm exhibits an irregular cylindrical appearance with subcutaneous fat concentrated primarily in the posterior lateral aspect, traditional localized fat suction techniques may lead to uneven or disharmonious results when addressing this concern. Many practitioners have turned to circumferential fat suction methods using multi-incision approaches to ensure effective results and fat removal. However, these methods often involve numerous incisions and complex procedures, necessitating the development of new, more efficient surgical techniques.
Methods
We collected and screened patients who underwent upper arm circumferential liposuction with a double incision technique at our hospital from October 2020 to February 2023. A total of 496 cases were included in our retrospective analysis, in which we examined factors such as the length of surgery, arm circumference before and after surgery, subcutaneous tissue thickness before and after surgery, fat suction volume, postoperative satisfaction, and postoperative complications of the patients.
Results
The average length of surgery was 71.7 min. 458 cases (92.3%) showed significant improvement, 23 cases (4.6%) reported satisfaction, and 10 cases (2.0%) were essentially satisfied. Additionally, 339 cases (68.3%) experienced an improvement in skin laxity. Four cases (0.8%) developed localized hard nodules with slight tenderness in the early postoperative period, which resolved without special treatment after observation and follow-up for 1–3 months. Three cases (0.6%) reported localized pain or numbness, and they were given oral medication. Their symptoms disappeared after 1–3 months of observation and follow-up. Three cases (0.6%) had localized pain or numbness, and their symptoms disappeared. All of these cases improved and resolved after one month of taking mecobalamin tablets. There were also three cases (0.6%) with mild pigmentation of the incision and two cases (0.4%) with mild limitation of unilateral upper arm abduction movement. However, upper arm activities were not affected after three months to one year of follow-up. No serious complications were reported, resulting in an overall satisfaction rate of 99.0%.
Conclusion
The double incision upper arm liposuction is safe, effective, time-saving, with high satisfaction and fewer complications, and is worthy of clinical popularization and application.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these evidence-based medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Vasilakis V et al (2020) Four-position four-entry site circumferential arm liposuction: technique overview and experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg 44(5):1596–1603
Stevens WG, Pietrzak LK, Spring MA (2013) Broad overview of a clinical and commercial experience with CoolSculpting. Aesthet Surg J 33(6):835–846
Stevens WG (2014) Does cryolipolysis lead to skin tightening? A first report of cryodermadstringo. Aesthet Surg J 34(6):NP32–NP34
Carruthers JD, Humphrey S, Rivers JK (2017) Cryolipolysis for reduction of arm fat: safety and efficacy of a prototype coolcup applicator with flat contour. Dermatol Surg 43(7):940–949
Sugawara J et al (2017) Application for lower facial fat reduction and tightening by static type monopolar 1-MHz radio frequency for body contouring. Lasers Surg Med 49(8):750–755
Wu DC et al (2016) Subdermal radiofrequency for skin tightening of the posterior upper arms. Dermatol Surg 42(9):1089–1093
Alster TS, Tanzi EL (2012) Noninvasive lifting of arm, thigh, and knee skin with transcutaneous intense focused ultrasound. Dermatol Surg 38(5):754–759
Putra IB, Jusuf NK, Dewi NK (2019) Utilisation of cryolipolysis among asians: a review on efficacy and safety. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 7(9):1548–1554
Chia CT et al (2015) Radiofrequency-assisted liposuction compared with aggressive superficial, subdermal liposuction of the arms: a bilateral quantitative comparison. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 3(7):e459
Leclere FM et al (2015) Laser-assisted lipolysis for arm contouring in Teimourian grades I and II: a prospective study of 45 patients. Lasers Med Sci 30(3):1053–1059
Nilforoushzadeh MA et al (2023) Efficacy of endolift laser for arm and under abdomen fat reduction. J Cosmet Dermatol 22(7):2018–2022
Katz B, Doherty S (2018) Safety and efficacy of a noninvasive 1,060-nm diode laser for fat reduction of the flanks. Dermatol Surg 44(3):388–396
Apfelberg DB (1996) Results of multicenter study of laser-assisted liposuction. Clin Plast Surg 23(4):713–719
Shermak MA (2014) Aesthetic refinements in body contouring in the massive weight loss patient: part 2. Arms. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(5):726e–735e
Nagrath N, Winters R (2023) Brachioplasty. In: StatPearls. 2023: Treasure Island, FL
Sergesketter AR, Erdmann D (2022) A personal approach to brachioplasty. Ann Plast Surg 88(5 Suppl 5):S433–S438
(2022) Aesthetic Plastic Surgery National Databank Statistics 2020–2021. Aesthet Surg J 42(Suppl 1):1-18
Hoyos A, Perez M (2012) Arm dynamic definition by liposculpture and fat grafting. Aesthet Surg J 32(8):974–987
Hong JY et al (2020) Efficacy and safety of high-intensity focused ultrasound for noninvasive abdominal subcutaneous fat reduction. Dermatol Surg 46(2):213–219
Duncan DI (2012) Improving outcomes in upper arm liposuction: adding radiofrequency-assisted liposuction to induce skin contraction. Aesthet Surg J 32(1):84–95
Paul M, Mulholland RS (2009) A new approach for adipose tissue treatment and body contouring using radiofrequency-assisted liposuction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 33(5):687–694
Flynn TC et al (2000) History of liposuction. Dermatol Surg 26(6):515–520
Klein JA (1990) Tumescent technique for regional anesthesia permits lidocaine doses of 35 mg/kg for liposuction. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 16(3):248–263
Collins PS, Moyer KE (2018) Evidence-based practice in liposuction. Ann Plast Surg 80(6S Suppl 6):S403–S405
Holt NF (2017) Tumescent anaesthesia: its applications and well tolerated use in the out-of-operating room setting. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 30(4):518–524
Hong YG et al (2012) Three-dimensional circumferential liposuction of the overweight or obese upper arm. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36(3):497–503
Lillis PJ (1999) Liposuction of the arms. Dermatol Clin 17(4):783–797
Deng M, Gu Y, Lei H, Liu Z, Ma G (2014) Application of adjacent aesthetic unit combined liposuction in upper arm. Chin J Plast Surg 30(6):439–442
Gu Y et al (2021) Application of a proposed multi-positional circumferential arm liposuction method and quantification of its clinical efficacy evaluation. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(3):1115–1124
Garibyan L et al (2014) Three-dimensional volumetric quantification of fat loss following cryolipolysis. Lasers Surg Med 46(2):75–80
Leclere FM et al (2016) Laser-assisted lipolysis for arm contouring in Teimourian grades III and IV: a prospective study involving 22 patients. Plast Surg (Oakv) 24(1):35–40
Acknowledgements
No.
Funding
No.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All the participants in this work gave their informed consent in writing.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 159462 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Han, W., Deng, Q. et al. Clinical Efficacy Analysis of Circumferential Upper Arm Liposuction with Double Incision: A Study of 496 Cases. Aesth Plast Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-03875-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-03875-9