Abstract
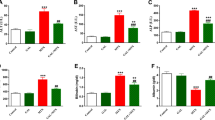
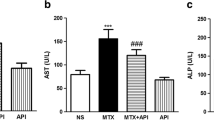
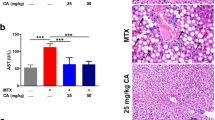
Methotrexate (MTX), as a folic acid antagonist, is an effective drug in treating a wide range of malignancies and autoimmune diseases. However, the clinical use of MTX has been limited due to its side effects, the most common of which is hepatotoxicity. In this study, rats were randomly divided into six groups: three treatment groups received methotrexate and different doses of astaxanthin (AX) for 14 days. At the end of the study, blood samples were collected to determine serum levels of ALT, AST, ALP, and LDH. Also, liver tissues were isolated to evaluate antioxidant enzymes and markers of oxidative stress, histopathological damage, and expression of NF-E2-related transcription factor (Nrf2) and Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) genes. The results showed that administration of MTX significantly increased the levels of ALT, AST, ALP, and LDH in the blood, markers of oxidative stress, and histopathological damage in liver tissue and significantly reduced the levels of antioxidant enzymes and the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 genes. On the other hand, treatment with AX decreased blood levels of ALT, AST, ALP, and LDH and oxidative stress markers and remarkably raises the activity of antioxidant enzymes and expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 genes in liver tissue. In addition, histopathological lesions were improved with AX administration. The findings of this study indicated that AX may be useful for the prevention of MTX-induced hepatotoxicity by improving oxidative and inflammatory changes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to [REASON(S) WHY DATA ARE NOT PUBLIC] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdelaziz RM, Abdelazem AZ, Hashem KS, Attia YA (2020) Protective effects of hesperidin against MTX-induced hepatotoxicity in male albino rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393:1405–1417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01843-z
Abo-Haded HM, Elkablawy MA, Al-Johani Z, Al-Ahmadi O, El-Agamy DS (2017) Hepatoprotective effect of sitagliptin against methotrexate induced liver toxicity. PLoS ONE 12: e0174295. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174295
Akca G, Eren H, Tumkaya L, Mercantepe T, Horsanali MO, Deveci E, Dil E, Yilmaz A (2018) The protective effect of astaxanthin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. B Biomed Pharmacother 100:575–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.042
Al Maruf A, O’Brien PJ, Naserzadeh P, Fathian R, Salimi A, Pourahmad J (2018) Methotrexate induced mitochondrial injury and cytochrome c release in rat liver hepatocytes. Drug Chem Toxicol 41:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2017.1289221
Ali N, Rashid S, Nafees S, Hasan SK, Sultana S (2014) Beneficial effects of chrysin against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity via attenuation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 385:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1830-4
Badary OA, Abdel-Maksoud S, Ahmed WA, Owieda GH (2005) Naringenin attenuates cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats. Life Sci 76:2125–2135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2004.11.005
Bresciani G, da Cruz IBM, González-Gallego J (2015) Manganese superoxide dismutase and oxidative stress modulation. Adv Clin Chem 68:87–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2014.11.001
Bu T, Wang C, Meng Q, Huo X, Sun H, Sun P, Zheng S, Ma X, Liu Z, Liu K (2018) Hepatoprotective effect of rhein against methotrexate-induced liver toxicity. Eur J Pharmacol 834:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.07.031
Chang L-C, Fan C-W, Tseng W-K, Chen J-R, Chein H-P, Hwang C-C, Hua C-C (2013) Immunohistochemical study of the Nrf2 pathway in colorectal cancer: Nrf2 expression is closely correlated to Keap1 in the tumor and Bach1 in the normal tissue. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 21:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0b013e318282ac20
Chen Y, Li D, Lu W, **ng J, Hui B, Han Y (2003) Screening and characterization of astaxanthin-hyperproducing mutants of Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol Lett 25:527–529. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022877703008
Choi HD, Kim JH, Chang MJ, Kyu-Youn Y, Shin WG (2011) Effects of astaxanthin on oxidative stress in overweight and obese adults. Phytother Res 25:1813–1818. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3494
Farzaei MH, Zobeiri M, Parvizi F, El-Senduny FF, Marmouzi I, Coy-Barrera E, Naseri R, Nabavi SM, Rahimi R, Abdollahi M (2018) Curcumin in liver diseases: a systematic review of the cellular mechanisms of oxidative stress and clinical perspective. Nutrients 10:855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070855
Golestaneh E, Aslani A, Aghaei M, Hashemnia M, Aarabi MH (2023) Preparation and characterisation of a new form of silymarin as a potential antidiabetic agent in the adult male rat. Arch Physiol Biochem 129:799–809. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2021.1874018
Goudarzi F, Mohammadalipour A, Bahabadi M, Goodarzi MT, Sarveazad A, Khodadadi I (2018) Hydrogen peroxide: a potent inducer of differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into chondrocytes. Free Radic Res 52:763–774. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2018.1466121
Goudarzi M, Khodayar MJ, Hosseini Tabatabaei SMT, Ghaznavi H, Fatemi I, Mehrzadi S (2017) Pretreatment with melatonin protects against cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress and renal damage in mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 31:625–635. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12303
Guerin M, Huntley ME, Olaizola M (2003) Haematococcus astaxanthin: applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol 21:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7799(03)00078-7
Halliwell B (1991) Reactive oxygen species in living systems: source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am J Med 91:S14–S22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(91)90279-7
Heidari Khoei H, Fakhri S, Parvardeh S, Shams Mofarahe Z, Baninameh Z, Vardiani M (2019) Astaxanthin prevents the methotrexate-induced reproductive toxicity by targeting oxidative stress in male mice. Toxin Rev 38:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2018.1452263
Higuera-Ciapara I, Felix-Valenzuela L, Goycoolea F (2006) Astaxanthin: a review of its chemistry and applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 46:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690590957188
Janaszewska A, Bartosz G (2002) Assay of total antioxidant capacity: comparison of four methods as applied to human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 62:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/003655102317475498
Kansanen E, Jyrkkänen H-K, Levonen A-L (2012) Activation of stress signaling pathways by electrophilic oxidized and nitrated lipids. Free Radic Biol Med 52:973–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.038
Kazemi M, Mohammadifar M, Aghadavoud E, Vakili Z, Aarabi MH, Talaei SA (2020) Deep skin wound healing potential of lavender essential oil and licorice extract in a nanoemulsion form: biochemical, histopathological and gene expression evidences. J Tissue Viability 29:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtv.2020.03.004
Kremer JM (2004) Toward a better understanding of methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 50:1370–1382. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20278
Kuduban O, Mazlumoglu MR, Kuduban SD, Erhan E, Cetin N, Kukula O, Yarali O, Cimen FK, Cankaya M (2016) The effect of Hippophae rhamnoides extract on oral mucositis induced in rats with methotrexate. J Appl Oral Sci 24:423–430. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-775720160139
Leitão RF, Brito GA, Oriá RB, Braga-Neto MB, Bellaguarda EA, Silva JV, Gomes AS, Lima-Júnior RC, Siqueira FJ, Freire RS (2011) Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway on methotrexate-induced intestinal mucositis in rodents. BMC Gastroenterol 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-11-90
Liu A, Ma T, Chen Y, Wang Y, Tao D, Zhang H (2010) Protective effect of astaxanthin on the acute liver injury induced by CCl4 in mice. Mod Food Sci Technol 26:1197–1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090628
Mahmoud AM, Hussein OE, Hozayen WG, Abd el-Twab SM, (2017) Methotrexate hepatotoxicity is associated with oxidative stress, and down-regulation of PPARγ and Nrf2: protective effect of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid. Chem Biol Interact 270:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.04.009
Mehrzadi S, Fatemi I, Esmaeilizadeh M, Ghaznavi H, Kalantar H, Goudarzi M (2018) Hepatoprotective effect of berberine against methotrexate induced liver toxicity in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 97:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.113
Mohammadalipour A, Hashemnia M, Goudarzi F, Ravan AP (2019) Increasing the effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) in combination with a statin in reducing liver fibrosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 46:1183–1193. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.13157
Montasser AO, Saleh H, Ahmed-Farid OA, Saad A, Marie M-AS (2017) Protective effects of Balanites aegyptiaca extract, melatonin and ursodeoxycholic acid against hepatotoxicity induced by methotrexate in male rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med 10:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.06.003
Pınar N, Kaplan M, Özgür T, Özcan O (2018) Ameliorating effects of tempol on methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 102:758–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.147
Shahzad S, Mateen S, Kausar T, Naeem SS, Hasan A, Abidi M, Nayeem SM, Faizy AF, Moin S (2020) Effect of syringic acid and syringaldehyde on oxidative stress and inflammatory status in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients of myocardial infarction. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393:691–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01768-2
Soliman MM, Aldhahrani A, Alkhedaide A, Nassan MA, Althobaiti F, Mohamed WA (2020) The ameliorative impacts of Moringa oleifera leaf extract against oxidative stress and methotrexate-induced hepato-renal dysfunction. Biomed Pharmacother 128: 110259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110259
Sporn MB, Liby KT (2012) NRF2 and cancer: the good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat Rev Cancer 12:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3278
Suresh D, Annam V, Pratibha K, Prasad BM (2009) Total antioxidant capacity–a novel early bio-chemical marker of oxidative stress in HIV infected individuals. J Biomed Sci 16:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-16-61
Tayeb W, Nakbi A, Trabelsi M, Attia N, Miled A, Hammami M (2010) Hepatotoxicity induced by sub-acute exposure of rats to 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid based herbicide “Désormone lourd.” J Hazard Mater 180:225–233
Ueki M, Ueno M, Morishita J, Maekawa N (2013) Curcumin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting renal inflammation in mice. J Biosci Bioeng 115:547–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.018
Wu L, Qiu W, Sun J, Wang J (2018) SENP1 attenuates the liver fibrosis through down-regulating the expression of SMAD2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495:755–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.047
Zakaria ZA, Mahmood ND, Omar MH, Taher M, Basir R (2019) Methanol extract of Muntingia calabura leaves attenuates CCl4-induced liver injury: possible synergistic action of flavonoids and volatile bioactive compounds on endogenous defence system. Pharm Biol 57:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2019.1606836
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant (No: 298058) from Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Iran. The authors would like to extend their deep and sincere gratitude to each and every one of those who helped them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A: Razieh Azadian, B: Adel Mohammadalipour, C: Mohammad Reza Memarzadeh, D: Mohammad Hashemnia, E: Mohammad Hosein Aarabi. A.B. and B.C. carried out the experiment. A.E. wrote the manuscript with support from B. D.E. fabricated the AB sample. E conceived the original and supervised the project. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All measures of experimental study were approved by the Ethics Committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (Isfahan, Iran), ethical code IR.MUI.RESEARCH.REC.1398.213.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Azadian, R., Mohammadalipour, A., Memarzadeh, M.R. et al. Examining hepatoprotective effects of astaxanthin against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats through modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway genes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 371–380 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02581-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02581-8