Abstract
Key message
In two Spanish barley landraces with outstanding resistance to scald, the Rrs1 Rh4 locus was fine mapped including all known markers used in previous studies and closely linked markers were developed.
Abstract
Scald, caused by Rhynchosporium commune, is one of the most prevalent barley diseases worldwide. A search for new resistance sources revealed that Spanish landrace-derived lines SBCC145 and SBCC154 showed outstanding resistance to scald. They were crossed to susceptible cultivar Beatrix to create large DH-map** populations of 522 and 416 DH lines that were scored for disease resistance in the greenhouse using two R. commune isolates. To ascertain the pattern of resistance, parents and reference barley lines with known scald resistance were phenotyped with a panel of differential R. commune isolates. Subpopulations were genotyped with the Illumina GoldenGate 1,536 SNP Assay and a large QTL in the centromeric region of chromosome 3H, known to harbour several scald resistance genes and/or alleles, was found in both populations. Five SNP markers closest to the QTL were converted into CAPS markers. These CAPS markers, together with informative SSR markers used in other scald studies, confirmed the presence of the Rrs1 locus. The panel of differential scald isolates indicated that the allele carried by both donors was Rrs1 Rh4 . The genetic distance between Rrs1 and its flanking markers was 1.2 cM (11_0010) proximally and 0.9 cM (11_0823) distally, which corresponds to a distance of just below 9 Mbp. The number and nature of scald resistance genes on chromosome 3H are discussed. The effective Rrs1 allele found and the closely linked markers developed are already useful tools for molecular breeding programs and provide a good step towards the identification of candidate genes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SBCC:
-
Spanish barley core collection
- SARDI:
-
South Australian Research and Development Institute
- BOPA1:
-
Barley oligonucleotid pool assay
- Rs:
-
Rhynchosporium secalis
- DH:
-
Doubled haploid
References
Aghnoum R, Marcel TC, Johrde A, Pecchioni N, Schweizer P, Niks RE (2010) Basal host resistance of barley to powdery mildew: connecting quantitative trait loci and candidate genes. MPMI 23:91–102
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Avrova A, Knogge W (2012) Rhynchosporium commune: a persistent threat to barley cultivation. Mol Plant Pathol 13:986–997
Ayres G, Owen H (1971) Resistance of barley varieties to establishment of subcuticular mycelia by Rhynchosporium secalis. Trans Br Mycol Soc 57:233–240
Baba T, Tanno K, Furusho M, Komatsuda T (2011) Allelic variation at the EF-G locus among northern Moroccan six-rowed barleys. Plant Genetic Resour: Charact Util 9:240–242
Behn A, Hartl L, Schweizer G, Wenzel G, Baumer M (2004) QTL map** for resistance against non-parasitic leaf spots in a spring barley doubled haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 108:1229–1235
Bjørnstad Å, Patil V, Tekauz A, Marøy AG, Skinnes H, Jensen A, Magnus H, MacKey J (2002) Resistance to scald (Rhynchosporium secalis) in barley (Hordeum vulgare) studied by near-isogenic lines. I. Markers and differential isolates. Phytopathol 92:710–720
Casao MC, Igartua E, Karsai I, Lasa JM, Gracia MP, Casas AM (2011) Expression analysis of vernalization and day-length response genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) indicates that VRNH2 is a repressor of PPDH2 (HvFT3) under long days. J Exp Bot 6:1939–1949
Cheong J, Williams K, Wallwork H (2006) The identification of QTLs for adult plant resistance to leaf scald in barley. Aust J Agric Res 57:961–965
Close TJ, Bhat PR, Lonardi S, Wu Y, Rostoks N, Ramsay L, Druka A, Stein N, Svensson J, Wanamaker S, Bozdag S, Roose M, Moscou M, Chao S, Varshney R, Szucs P, Sato K, Hayes P, Matthews D, Kleinhofs A, Muehlbauer G, DeYoung J, Marshall D, Madishetty K, Fenton R, Condamine P, Graner A, Waugh R (2009) Development and implementation of high-throughput SNP genoty** in barley. BMC Genomics 10:582
Collinge DB, Kragh KM, Mikkelsen JD, Nielsen KK, Rasmussen U, Vad K (1993) Plant chitinases. Plant J 3:31–40
Dyck PL, Schaller CW (1961) Inheritance of resistance in barley to several physiologic races of the scald fungus. Can J Genet Cytol 3:153–164
Garvin DF, Brown AHD, Raman H, Read BJ (2000) Genetic map** of the barley Rrs14 scald resistance gene with RFLP, isozyme and seed storage protein markers. Plant Breed 119:193–196
Genger RK, Brown AHD, Knogge W, Nesbitt K, Burdon JJ (2003) Development of SCAR markers linked to a scald resistance gene derived from wild barley. Euphytica 134:149–159
Graner A, Tekauz A (1996) RFLP map** of a dominant gene conferring resistance to scald (Rhynchosporium secalis). Theor Appl Genet 93:421–425
Grønnerød S, Marøy AG, MacKey I, Tekauz A, Penner GA, Bjørnstad A (2002) Genetic analysis of resistance to barley scald (Rhynchosporium secalis) in the Ethiopian line ‘Abyssinian’ (CI668). Euphytica 126:235–250
Habgood MR, Hayes JD (1971) The inheritance of resistance to Rhynchosporium secalis in barley. Heredity 27:25–37
Hanemann A, Schweizer GF, Cossu R, Wicker T, Röder MS (2009) Fine map**, physical map** and development of diagnostic markers for the Rrs2 scald resistance gene in barley. Theor Appl Genet 119:1507–1522
Hillocks RJ (2012) Farming with fewer pesticides: EU pesticide review and resulting challenges for UK agriculture. Crop Prot 31:85–93
IBSC International Barley Genome Sequencing Consortium (2012) A physical, genetic and functional sequence assembly of the barley genome. Nature 491:711–716
Igartua E, Gracia MP, Lasa JM, Medina B, Molina-Cano JL, Montoya JL, Romagosa I (1998) The Spanish barley core collection. Genet Resour Crop Ev 45:475–481
Igartua E, Moralejo M, Casas AM, Torres L, Molina-Cano JL (2013) Whole-genome analysis with SNPs from BOPA1 shows clearly defined grou**s of Western Mediterranean, Ethiopian, and Fertile Crescent barleys. Genet Resour Crop Ev 60:251–264
Jackson LF, Webster RK (1976) Race differentiation, distribution, and frequency of Rhynchosporium secalis in California. Phytopathol 66:719–725
Jansen R, Stam P (1994) High resolution of quantitative traits into multiple loci via interval map**. Genetics 136:1447–1455
Jensen J, Backes G, Skinnes H, Giese H (2002) Quantitative trait loci for scald resistance in barley localized by a non-interval map** procedure. Plant Breed 121:124–128
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Langridge P, Karakousis A, Kretschmer J, Manning S, Chalmers K (1996) Molecular relationship between barley varieties. http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ggpages/DEM/Polymorphism/Waite/Barley_dend.gif. Accessed 26 Feb 2013
Lasa JM (2008) Spanish barley core collection. Monografias INIA: Serie Agricola, n25. ISBN 978-84-7498-526-9
Li HB, Zhou MX (2011) Quantitative trait loci controlling barley powdery mildew and scald resistances in two different barley doubled haploid populations. Mol Breed 27:479–490
Li JZ, Sjakste TG, Röder MS, Ganal MW (2003) Development and genetic map** of 127 new microsatellite markers in barley. Theor Appl Genet 107:1021–1027
Liu ZW, Biyashev RM, Saghai Maroof MA (1996) Development of simple sequence repeat DNA markers and their integration into a barley linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 93:869–876
Looseley ME, Newton AC, Atkins SD, Fitt BDL, Fraije B, Thomas WTB, Keith R, Lynott J, Harrap D (2012) Genetic basis of control of Rhynchosporium secalis infection and symptom expression in barley. Euphytica 184:47–56
Mayer KFX, Martis M, Hedley PE, Šimková H, Liu H, Morris JA, Steuernagel B, Taudien S, Roessner S, Gundlach H, Kubaláková M, Suchánková P, Murat F, Felder M, Nussbaumer T, Graner A, Salse J, Endo T, Sakai H, Tanaka T, Itoh T, Sato K, Platzer M, Matsumoto T, Scholz U, Dolezél J, Waugh R, Stein N (2011) Unlocking the barley genome by chromosomal and comparative genomics. Plant Cell 23:1249–1263
Muñoz-Amatriaín M, Moscou MJ, Bhat PR, Svensson JT, Bartoš J, Suchánková P, Šimková H, Endo TR, Fenton RD, Lonardi S, Castillo AM, Chao S, Cistué L, Cuesta-Marcos A, Forrest KL, Hayden MJ, Hayes PM, Horsley RD, Makoto K, Moody D, Sato K, Vallés MP, Wulff BBH, Muehlbauer GJ, Doležel J, Close TJ (2011) An improved consensus linkage map of barley based on flow-sorted chromosomes and single nucleotide polymorphism markers. Plant Genome 4:238–249
Patil V, Bjørnstad A, Mackey J (2003) Molecular map** of a new gene Rrs4 CI11549 for resistance to barley scald (Rhynchosporium secalis). Mol Breed 12:169–183
Paulitz TC, Steffenson BJ (2011) Biotic stress in barley: disease problems and solutions. In: Ullrich SE (ed) Barley: production, improvement and uses. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, London, pp 307–354
Penner GA, Tekauz A, Reimer E, Scoles GJ, Rossnagel BG, Eckstein PE, Legge WG, Burnett PA, Ferguson T, Helm JF (1996) The genetic basis of scald resistance in western Canadian barley cultivars. Euphytica 92:367–374
Phillips D, Nibau C, Ramsay L, Waugh R, Jenkins G (2010) Development of a molecular cytogenetic recombination assay for barley. Cytogenet Genome Res 129:154–161
Pickering R, Ruge-Wehling B, Johnston PA, Schweizer G, Ackermann P, Wehling P (2006) The transfer of a gene conferring resistance to scald (Rhynchosporium secalis) from Hordeum bulbosum into H. vulgare chromosome 4HS. Plant Breed 125:576–579
Ponce-Molina LJ, Casas AM, Gracia MP, Silvar C, Mansour E, Thomas WBT, Schweizer G, Herz M, Igartua E (2012) Quantitative trait loci and candidate loci for heading date in a large population of a wide barley cross. Crop Sci 52:2469–2480
Ramsay L, Macaulay M, degli Ivanissevich S, MacLean K, Cardle L, Fuller J, Edwards KJ, Tuvesson S, Morgante M, Massari A, Maestri E, Marmiroli N, Sjakste T, Ganal M, Powell W, Waugh R (2000) A simple sequence repeat-based linkage map of barley. Genetics 156:1997–2005
Read BJ, Macdonald AF (1991) Hordeum vulgare (barley) cv. Yerong. Aust J Exp Agric 31:866
Rostoks N, Mudie S, Cardle L, Russell J, Ramsay L, Booth A, Svensson J, Wanamaker S, Walia H, Rodriguez E, Hedley P, Liu H, Morris J, Close T, Marshall D, Waugh R (2005) Genome-wide SNP discovery and linkage analysis in barley based on genes responsive to abiotic stress. Mol Gen Genomics 274:515–527
Sayed H, Kayyal H, Ramsay L, Ceccarelli S, Baum M (2002) Segregation distortion in doubled haploid lines of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) detected by simple sequence repeat (SSR). Euphytica 225:265–272
Schweizer GF, Baumer M, Daniel G, Rugel H, Röder MS (1995) RFLP markers linked to scald (Rhynchosporium secalis) resistance gene Rh2 in barley. Theor Appl Genet 90:920–924
Schweizer G, Herz M, Mikolajewski S, Brenner M, Hartl L, Baumer M (2004) Genetic map** of a novel scald resistance gene Rrs15 CI8288 in barley. In: Proceedings of 9th Int Barley Genet Symposium, Brno, Czech Republic, 20–26 June 2004, pp 258–265
Shipton WA, Boyd WJR, Ali SM (1974) Scald of Barley. Rev Plant Pathol 53:839–861
Silvar C, Casas AM, Kopahnke D, Habekuß A, Schweizer G, Gracia MP, Lasa JM, Ciudad FJ, Molina-Cano JL, Igartua E, Ordon F (2010) Screening the Spanish barley core collection for disease resistance. Plant Breed 129:45–52
Silvar C, Casas AM, Igartua E, Ponce-Molina LJ, Gracia MP, Schweizer G, Herz M, Flath K, Waugh R, Kopahnke D, Ordon F (2011) Resistance to powdery mildew in Spanish barley landraces is controlled by different sets of quantitative trait loci. Theor Appl Genet 123:1019–1028
Starling TM, Roane CW, Chi KR (1971) Inheritance of reaction to Rhynchosporium secalis in winter barley cultivars. In: Proceedings of 2nd Int Barley Genetics Symposium, Pullman, WA, pp 513–519
Stein N, Prasad M, Scholz U, Thiel T, Zhang H, Wolf M, Kota R, Varshney RK, Perovic D, Grosse I, Graner A (2007) A 1,000-loci transcript map of the barley genome: new anchoring points for integrative grass genomics. Theor Appl Genet 114:823–839
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development of cDNA derived microsatellite markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422
Thirugnanasambandam A, Wright KM, Atkins SD, Whisson SC, Newton AC (2011) Infection of Rrs1 barley by an incompatible race of the fungus Rhynchosporium secalis expressing the green fluorescent protein. Plant Pathol 60:513–521
Thomas WTB, Powell W, Waugh R, Chalmers KJ, Barua UM, Jack P, Lea V, Forster BP, Swanston JS, Ellis RP, Hanson PR, Lance RCM (1995) Detection of quantitative trait loci for agronomic, yield, grain and disease characters in spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 91:1037–1047
van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTL® 5, Software for the map** of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap 4, software for the calculation of genetics linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
Varshney RK, Grosse I, Hähnel U, Siefken R, Prasad M, Stein N, Langridge P, Altschmied L, Graner A (2006) Genetic map** and BAC assignment of EST-derived SSR markers shows non-uniform distribution of genes in the barley genome. Theor Appl Genet 113:239–250
Varshney RK, Marcel TC, Ramsay L, Russell J, Röder MS, Stein N, Waugh R, Langridge P, Niks RE, Graner A (2007) A high density barley microsatellite consensus map with 775 SSR loci. Theor Appl Genet 114:1091–1103
von Korff M, Wang H, Léon J, Pillen K (2005) AB-QTL analysis in spring barley. I. Detection of resistance genes against powdery mildew, leaf rust and scald introgressed from wild barley. Theor Appl Genet 111:583–590
VSN International (2011) Genstat for Windows 14th edn. VSN International, Hemel Hempstead, UK http://www.vsni.co.uk/software/genstat?ref=genstat.co.uk. Accessed 03 Oct 2011
Wagner C, Schweizer G, Krämer M, Dehmer-Badani AG, Ordon F, Friedt W (2008) The complex quantitative barley—Rhynchosporium secalis interaction: newly identified QTL may represent already known resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 118:113–122
Wallwork H, Grcic M (2011) The use of differential isolates of Rhynchosporium secalis to identify resistance to leaf scald in barley. Aust Plant Pathol 40:490–496
Williams KJ, Bogacki P, Scott L, Karakousis A, Wallwork H (2001) Map** a gene for scald resistance in barley Line ‘B87/14’ and validation of microsatellite and RFLP markers for marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed 120:301–304
** K, Xue AG, Burnett PA, Helm JH, Turkington TK (2000) Quantitative resistance of barley cultivars to Rhynchosporium secalis. Can J Plant Pathol 22:221–227
Yun SJ, Gyenis L, Hayes PM, Matus I, Smith KB, Steffenson BJ, Muehlbauer GJ (2005) Quantitative trait loci for multiple disease resistance in wild barley. Crop Sci 45:2563–2572
Zaffarano PL, McDonald BA, Linde CC (2011) Two new species of Rhynchosporium. Mycologia 103:195–202
Zhan J, Fitt BDL, Pinnschmidt HO, Oxley SJP, Newton AC (2008) Resistance, epidemiology and sustainable management of Rhynchosporium secalis populations on barley. Plant Pathol 57:01–14
Zhan J, Yang L, Zhu W, Shang L, Newton AC (2012) Pathogen populations evolve to greater race complexity in agricultural systems—evidence from analysis of Rhynchosporium secalis virulence data. PLoS One 6:e38611
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the German BMELV and BLE through the project “Rhynchosporium secalis-resistance” in barley (project 28-1-41.009-06) and PLANT KBBE II “ExpResBar” AZ 0315702C and by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (projects GEN2006-28560-E, AGL2007-63625, RFP2012-00015-00-00 and PLANT KBBE “ExpResBar”, EUI2009-04075) and co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund. CS held an I3P contract from CSIC. BCM is supported by Fundación ARAID, Zaragoza, Spain. Barley-SSR markers were kindly provided by Andreas Graner and Marion Röder, IPK Gatersleben. Isolates UK7 and AU2 were kindly provided by W. Knogge, Leibnitz Institute for Plant Biochemistry, Halle. The authors would like to thank Alfred Barth and Alexandra Jestadt for the high level of commitment in the laboratory, greenhouse and field and Carlos P. Cantalapiedra for assistance in the work with the physical map of barley. The Grains Research and Development Corporation (GRDC) and SARDI funded the work in Australia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. M. Hayes.
K. Hofmann and C. Silvar contributed equally to this publication.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
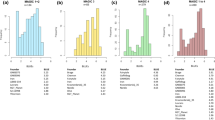
Figure S1 Response of SBCC145 × Beatrix and SBCC154 × Beatrix DH lines to R. commune isolates 271 and LfL07 for the subpopulations genotyped with BOPA1 (n = 190/SBCC145 × Beatrix, n = 168/SBCC154 × Beatrix). The Jackson and Webster (1976) scale extended by half steps was used. In addition occurrence of the marker allele of 11_0205 is shown (red “SBCCxxx”, blue “Beatrix” - allele). Black vertical arrows indicate mean disease scores, red vertical arrows the resistant parent SBCC145 or SBCC154 respectively and blue vertical arrows the susceptible parent Beatrix. A) SBCC145 × Beatrix, isolate 271. B) SBCC154 × Beatrix, isolate 271. C) SBCC145 × Beatrix, isolate LfL07. D) SBCC154 × Beatrix, isolate LfL07.
Figure S2 Genetic map of the population SBCC154 x Beatrix, genotyped with BOPA1.
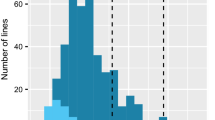
Figure S3 MQM LOD scans for resistance scores to R. commune isolates 271 and LfL07 in 190 DH lines of SBCC145 × Beatrix and 168 DH lines of SBCC154 × Beatrix. The horizontal dotted lines and the numbers above them indicate the significance threshold for QTL detection based on an experiment-wise error rate of less than 5 %, estimated with 1,000 permutations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofmann, K., Silvar, C., Casas, A.M. et al. Fine map** of the Rrs1 resistance locus against scald in two large populations derived from Spanish barley landraces. Theor Appl Genet 126, 3091–3102 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2196-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2196-4