Summary
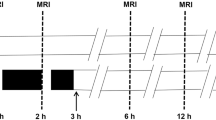
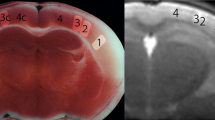
The chronological and spatial rules of changes during focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in different brain regions with magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in a model of occlusion of middle cerebral artery (MCAO) and the development of cytotoxic edema in acute phase were explored. Fifteen healthy S-D rats with MCA occluded by thread-emboli were randomly divided into three groups. 15 min after the operation, the serial imaging was scanned on DWI for the three groups. The relative mean signal intensity (RMSI) of the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, lateral cauda-putamen, medial cauda-putamen and the volume of regions of hyperintense signal on DWI were calculated. After the last DWI scanning, T2WI was performed for the three groups. After 15 min ischemia, the rats was presented hyperintense signals on DWI. The regions of hyperintense signal were enlarged with prolonging ischemia time. The regions of hyperintense signal were back to normal after 60 min reperfusion with a small part remaining to show hyperintense signal. The RMSIs of parietal lobe and lateral cauda-putamen were higher than that of the frontal lobe and medial cauda-putamen both in ischemia phase and recanalization phase. The three groups were normal on T2WI imaging. DWI had good sensitivity to acute cerebral ischemia, which was used to study the chronological and spatial rules of development of early cell edema in ischemia regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loubinoux I, Volk A, Borredon Jet al. Spreading of vasogenic edema and cytotoxic edema assessed by quantitative diffusion and T2 magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke, 1997, 28: 419
Nagasawa H, Kogure K. Correlation between cerebral blood flow and histologic changes in a new rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke, 1989, 20: 1037
Vorkapic P, Bevan J A, Bevan R D. Longitudinal time course of reversible and irreversible components of chronic verebrovasospasm of the rabbit basilar artery. J Neurosurg, 1991, 14: 951
Delgado-Zygmunt T J, Arbab M A, Shiokawa Yet al. A primate model for acute and late cerebral vasospasm: angiographic findings. Acta Nearochir, 1992, 118: 130
Busza A L, Allen K L, Van Bzuggen Net al. Diffusion-weighted imaging studies of cerebral ischemia in Gerbils. Stroke, 1992, 23: 1602
Moseley M E, Chen Y, Mintorovitch Jet al. Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion- and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med, 1990, 14: 330
Tatlisumak T, Takano K, Carano R Aet al. Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor on experimental focal ischemia studied by diffusion-weighted and perfusion imaging. Stroke, 1996, 27: 2292
Tomlinson F H, Anderson R E, Meyer T B. Acidic Foci within the ischemic penumbra of the New Zealand white rabbit. Stroke, 1993, 24: 2030
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
YI Li, female, born in 1970, M. D., Ph. D.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Siyu, F. & Suming, Z. An early continuous experimental study on magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted image of focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 25, 594–596 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896028
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896028