Abstract
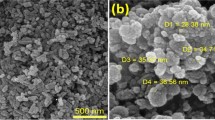
The present study is designed to investigate the antibacterial efficacy of B. mori silk fibroin based silver and gold ultra bio-nanocomposites (SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC) against Enterococcus faecalis for endodontic disinfection. The SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC based irrigant solution was tested in- vitro against Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC: 29212). In this direction, SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC synthesized by silk fibroin are very important as they are economically cheap and easy to biosynthesize. The synthesis of SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC was accomplished by dissolving 1 mM silver nitrate and 0.5 mM auric chloride respectively in 10 ml of fibroin as precursors. The structural and morphological analysis was executed by UV-Vis Spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis (FTIR), Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDAX) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The qualitative antimicrobial activity of SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC were performed against inoculum of Enterococcus faecalis containing 1⨯105 CFU/ ml. The same solutions were tested on dentine specimens inoculated with bacterial cultures and found remarkable biofilm reduction. The structural and morphological analysis reveals the formation of SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC having quasi-spherical morphology. The average particle size for SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC was same (~ 8 nm). The XRD study confirms that, both SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC were crystalline in nature. The bacterial growth inhibition and significant biofilm reduction was observed on dentine specimens treated with SF-AgUNC, SF-AuUNC and positive control. In antibacterial study, at 30 μg/well concentration of SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC, 3.13 ± 0.22 and 1.13 ± 0.22 cm of zone of inhibition was noted respectively. Moreover, growth of Enterococcus faecalis was completely inhibited at 20 μg/ml and 30 μg/ml when treated with SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC respectively. Hence, the present study concludes that SF-AgUNC and SF-AuUNC can be used as an effective intracanal medicament for the treatment of dental problems with no cyto toxicity.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data is included in the manuscript.
References
S.M. Cirino, S. Scantlebury, Dental caries in develo** countries: preventive and restorative approaches to treatment. N. Y. State Dent. J. 64(2), 32–39 (1998) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9542392/
N.J. Kassebaum, A.G. Smith, E. Bernabe, T.D. Fleming, A.E. Reynolds, T. Vos, C.J.L. Murray, W. Marcenes, GBD 2015, Oral Health Collaborators, Global, regional, and national prevalence, incidence, and disability-adjusted life years for oral conditions for 195 countries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. J Dental Res. 96(4), 380–387 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034517693566
T. Vos, A.A. Abajobir, K.H. Abate, C. Abbafati, K.M. Abbas, F. Abd-Allah, R.S. Abdulkader, A.M. Abdulle, T.A. Abebo, S.F. Abera, V. Aboyans, Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390(10100), 1211–1259 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2
W.H. Bowen, R.A. Burne, H. Wu, H. Koo, Oral biofilms: pathogens, matrix, and polymicrobial interactions in microenvironments. Trends Microbial 26(3), 229–242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2017.09.008
P.C. Baehni, Y. Takeuchi, Anti-plaque agents in the prevention of biofilm-associated oral diseases. Oral Dis. 9(suppl 1), 23–29 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1601-0825.9.s1.5.x
P. Bhardwaj, S. Krishnappa, Various approaches for prevention of dental caries with emphasis on probiotics: a review. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 1, 62–67 (2014) https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jdms/papers/Vol13-issue2/Version-1/O013216267.pdf
H.Y. Wang, J.W. Cheng, H.Y. Yu, L. Lin, Y.H. Chih, Y.P. Pan, Efficacy of a novel antimicrobial peptide against periodontal pathogens in both planktonic and polymicrobial biofilm states. Acta Biomater. 25, 150–161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.07.031
P.C. Mane, M.D. Shinde, S. Varma, B.P. Chaudhari, A. Fatehmulla, M. Shahabuddin, D.P. Amalnerkar, A.M. Aldhafiri, R.D. Chaudhari, Highly sensitive label-free bio-interfacial colorimetric sensor based on silk fibroin-gold nanocomposite for facile detection of chlorpyrifos pesticide. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61130-y
P.C. Mane, R.D. Chaudhari, M.D. Shinde, D.D. Kadam, C.K. Song, D.P. Amalnerkar, H. Lee, Designing ecofriendly bionanocomposite assembly with improved antimicrobial and potent on-site zika virus vector larvicidal activities with its mode of action. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15537-9
S.C. Motshekga, S.S. Ray, M.S. Onyango, M.N. Momba, Microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of Ag/ZnO nanoparticles supported bentonite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 262, 439–446 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.074
Z. Cheng, A. Al Zaki, J.Z. Hui, V.R. Muzykantov, A. Tsourkas, Multifunctional nanoparticles: cost versus benefit of adding targeting and imaging capabilities. Science 338(6109), 903–910 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1226338
E.M. Decker, R. Weiger, I. Wiech, P.E. Heide, M. Brecx, Comparison of antiadhesive and antibacterial effects of antiseptics on Streptococcus sanguinis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 111(2), 144–148 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0722.2003.00025.x
T. Asakura, M. Kitaguchi, M. Demura, H. Sakai, K. Komatsu, Immobilization of glucose oxidase on nonwoven fabrics with Bombyx mori silk fibroin gel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 46, 49–53 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1992.070460106
G. Cheng, Z. Davoudi, X. **ng, X. Yu, X. Cheng, Z. Li, H. Deng, Q. Wang, Advanced silk fibroin biomaterials for cartilage regeneration advanced silk fibroin biomaterials for cartilage regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng 4, 2704–2715 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00150
W.P. Xu, W. Zhang, R. Asrican, H.J. Kim, D.L. Kaplan, P.C. Yelick, Accurately shaped tooth bud cell-derived mineralized tissue formation on silk scaffolds. Tissue Eng. – Part A 14, 549–557 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1089/tea.2007.0227
R.L. Moy, A. Lee, A. Zalka, Commonly used suture materials in skin surgery. Am. Fam. Physician 44, 2123–2128 (1991) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1746393/
N. Kasoju, U. Bora, Silk fibroin in tissue engineering. Adv. Healthcare Mater 1, 393–412 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201200097
B.M. Min, G. Lee, S.H. Kim, Y.S. Nam, T.S. Lee, W.H. Park, Electrospinning of silk fibroin nanofibers and its effect on the adhesion and spreading of normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. Biomater 25, 1289–1297 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.08.045
Y. Wang, D.D. Rudym, A. Walsh, L. Abrahamsen, H.J. Kim, H.S. Kim, C. Kirker-Head, D.L. Kaplan, In vivo degradation of three-dimensional silk fibroin scaffolds. Biomater 29, 3415–3428 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.05.002
J.W. Yang, Y.F. Zhang, Z.Y. Sun, G.T. Song, Z. Chen, Dental pulp tissue engineering with bFGF-incorporated silk fibroin scaffolds. J. Biomater. Appl. 30(2), 221–229 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328215577296
M.J.R. Virlan, B. Calenic, C. Zaharia, M. Greabu, Silk fibroin and potential uses in regenerative Dental Medicine. Stoma. Edu. J 1(2), 108–115 (2014). https://doi.org/10.25241/stomaeduj.2014.1(2).art.5
A. Kopp, R. Smeets, M. Gosau, R.E. Friedrich, S. Fuest, M. Behbahani, M. Barbeck, R. Rutkowski, S. Burg, L. Kluwe, Production and characterization of porus fibroin scafolds for regenerative medical application. In Vivo 33, 757–762 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11536
C. Martıínez-Mora, A. Mrowiec, E.M. Garcia-Vizcaino, A. Alcaraz, J.L. Cenis, F.J. Nicolas, Fibroin and sericin from Bombyx mori silk stimulate cell migration through upregulation and phosphorylation of c-Jun. PLoS One 7, e42271 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042271
A.A. Lozano-Pérez, A.L. Gil, S.A. Pérez, N. Cutillas, H. Meyer, M. Pedreno, S.D. Aznar-Cervantes, C. Janiak, J.L. Cenis, J. Ruiz, Antitumor properties of platinum [IV] prodrug-loaded silk fibroin nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 44, 13513–13521 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5DT00378D
D.N. Rockwood, R.C. Preda, T. Yucel, X. Wang, M.L. Lovett, D.L. Kaplan, Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 6, 1612–1631 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.379
J.N. Chin, R.N. Jones, H.S. Sader, P.B. Savage, M.J. Rybak, Potential synergy activity of the novel ceragenin, CSA-13, against clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 61(2), 365–370 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkm457
H.J. Heipieper, R. Diefenbach, H. Kewelol, Conversion of cis unsaturated fatty acids to trans, a possible mechanism for the protection of phenol-degrading Pseudomonas putida P8 from substrate toxicity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 1847–1852 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.58.6.1847-1852.1992
P. Mane, R. Chaudhari, N. Qureshi, M. Shinde, T. Kim, D. Amalnerkar, Silver nanoparticles-silk fibroin nanocomposite based colorimetric bio-interfacial sensor for on-site ultra-trace impurity detection of mercury ions. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 20(4), 2122–2129 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.17335
M. Amina, N.M.A. Musayeib, N.A. Alarfaj, M.F. El-Tohamy, G.A. Al-Hamoud, Antibacterial and immunomodulatory potentials of biosynthesized Ag, Au, Ag-Au bimetallic alloy nanoparticles using the Asparagus racemosus root extract. Nanomater 10, 2453 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122453
S. Yallappa, J. Manjanna, B.L. Dhananjaya, Phytosynthesis of stable Au, Ag and Au–Ag alloy nanoparticles using J. Sambac leaves extract, and their enhanced antimicrobial activity in presence of organic antimicrobials. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectro 137, 236–243 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.08.030
L. Lv, C. Chen, H.W. Hou, X.H. Zhang, P. Lan, Structure analysis and cesium adsorption mechanism evaluation of sodium copper ferrocyanide. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 331, 5835–5842 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08633-2
C. Singh, R.K. Baboota, P.K. Naik, H. Singh, Biocompatible synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Dalbergia Sissoo. Adv. Mater. Lett. 3(4), 279–285 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2011.10312
A.C. Joshi, G.B. Markad, S.K. Haram, Rudimentary simple method for the decoration of graphene oxide with silver nanoparticles: Their application for the amperometric detection of glucose in the human blood samples. Electrochim. Acta 161, 108–114 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.02.077
K. Hareesh, J.F. Williams, N.A. Dhole, K.M. Kodam, V.N. Bhoraskar, S.D. Dhole, Bio-green synthesis of Ag–GO, Au–GO and Ag–Au–GO nanocomposites using Azadirachta indica: its application in SERS and cell viability. Mater. Res. Expr 3, 075010 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/3/7/075010
D. Briggs, M.P. Seah, in Vol. 1: Auger and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy John Willey & Sons, Chichester-New York-Brisbane-Toronto-Singapore, Salle+ Sauerlander. Practical Surface Analysis (Willey, New York, 1990) https://books.google.co.in/books/about/Practical_Surface_Analysis_Auger_and_X_r.html?id=D9pTAAAAMAAJ&redir_esc=y
W. Liu, D. Sun, J. Fu, R. Yuan, Z. Li, Assembly of evenly distributed Au nanoparticles on thiolated reduced graphene oxide as an active and robust catalyst for hydrogenation of 4-nitroarenes. RSC Adv. 4, 11003–11011 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA47829G
S. Das, B.B. Dhar, Green synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles using cysteine-modified silk fibroin: catalysis and antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 4(86), 46285–46292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA06179A
X. Fei, M. Jia, X. Du, Y. Yang, R. Zhang, Z. Shao, X. Zhao, X. Chen, Green synthesis of silk fibroin-silver nanoparticle composites with effective antibacterial and biofilm-disrupting properties. Biomacromol 14(12), 4483–4488 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/bm4014149
A.M. Grant, H.S. Kim, T.L. Dupnock, K. Hu, Y.G. Yingling, V.V. Tsukruk, Silk Fibroin-Substrate interactions at Heterogeneous nanocomposite interface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 6380–6392 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201601268
X.W. Huang, J.J. Wei, T. Liu, X.L. Zhang, S.M. Bai, H.H. Yang, Silk fibroin-assisted exfoliation and functionalization of transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets for antibacterial wound dressings. Nanoscale 9(44), 17193–17198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR06807G
M.C. Belda, V. Fitzpatrick, D.L. Kaplan, J. Landoulsi, E. Guenin, C. Egles, Silk polymers and nanoparticles: a powerful combination for the design of versatile biomaterials. Front Chem 8, 604398 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.604398
S. Priyadarsini, S. Mukherjee, M. Mishra, Nanoparticles used in dentistry: A review. J Oral Biol Craniofacial Res 8(1), 58–67 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobcr.2017.12.004
I.X. Yin, I.S. Zhao, M.L. Mei, Q. Li, O.Y. Yu, C.H. Chu, Use of silver nanomaterials for caries prevention: a concise review. Int J Nanomed 15, 3181–3191 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S253833
Y. Abo-zeid, G.R. Williams, The potential anti-infective applications of metal oxide nanoparticles: A systematic review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol 12(2), e1592 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1592
F. Morgan-Sagastume, P. Larsen, J.L. Nielsen, P.H. Nielsen, Characterization of the loosely attached fraction of activated sludge bacteria. Water Res. 42(4-5), 843–854 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.08.026
Y. Jiao, F.R. Tay, L.N. Niu, J.H. Chen, Advancing antimicrobial strategies for managing oral biofilm infections. Int J Oral Sci 11(3), 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-019-0062-1
N.S. Re**old, G. Choi, J.H. Choy, Chitosan hybrids for cosmeceutical applications in skin, hair and dental care: an update. Emerg. Mater. 4(5), 1125–1142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00280-9
O.A. El Seoud, K. Jedvert, M. Kostag, S. Possidonio, Cellulose, chitin and silk: the cornerstones of green composites. Emerg. Mater. 5, 785–810 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00308-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mane, P.C., Pawar, J., Mane, D.P. et al. Green synthesis of silver and gold ultra nanocomposites from silk fibroin and their application for treatment of endodontic infections. emergent mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-024-00757-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-024-00757-3