Abstract
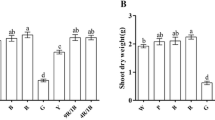
Light is a crucial signal for plant growth, development, and secondary metabolism. Exploring the effects of light on autotoxin secretion in lettuce can be helpful for improving the utilization efficiency of the nutrient solution in plant factories. The effects of white light (WL) and the combination of red (R) and blue (B) light (RB, 4R:1B) at different intensities (150, 200, and 250 μmol m−2 s−1) on the growth and root exudates of hydroponic lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) were studied in a closed plant factory. The lettuce biomass and photosynthetic rate increased with the increasing light intensity, and the photosynthetic rate was significantly lower under WL than under RB at both 200 and 250 μmol m−2 s−1. Lettuce under WL had the longest root length and highest root surface area at 200 μmol m−2 s−1, while the root length, root surface area, and root volume under RB were the highest at 250 μmol m−2 s−1. Total organic carbon (TOC) content of root exudates in the nutrient solution based on shoot or root dry weight decreased with the increasing light intensity. With the increase in light intensity, the secretion of four autotoxins (benzoic acid, ferulic acid, gallic acid, and tannic acid) based on shoot dry weight and root dry weight decreased under WL. Compared with RB, WL significantly reduced the secretion of autotoxins at 250 μmol m−2 s−1. In conclusion, 250 μmol m−2 s−1 white light should be used for high lettuce yield, and it could also decrease the autotoxins in the nutrient solution and the occurrence of autotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arena C, Tsonev T, Doneva D, De Micco V, Michelozzi M, Brunetti C, Centritto M, Fineschi S, Velikova V, Loreto F (2016) The effect of light quality on growth, photosynthesis, leaf anatomy and volatile isoprenoids of a monoterpene-emitting herbaceous species (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and an isoprene-emitting tree (Platanus orientalis L.). Environ Exp Bot 130:122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.05.014
Aulakh MS, Wassmann R, Bueno C, Kreuzwieser J, Rennenberg H (2001) Characterization of root exudates at different growth stages of ten rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Plant Biol 3:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-12905
Cao G, Zhang G, Yu J, Ma Y (2013) Effects of different LED light qualities on cucumber seedling growth and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters. Sci Agric Sin 46:1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.06.024
Chen X, Yang Q (2018) Effects of intermittent light exposure with red and blue light emitting diodes on growth and carbohydrate accumulation of lettuce. Sci Hortic 234:220–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.02.055
Cluis CP, Mouchel CF, Hardtke CS (2004) The Arabidopsis transcription factor HY5 integrates light and hormone signaling pathways. Plant J 38:332–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02052.x
Dijkstra FA, Cheng W (2007) Moisture modulates rhizosphere effects on C decomposition in two different soil types. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2264–2274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.03.026
Duan KX (2009) Experiments of instrument analysis. Chemical Industry Press, Bei**g
Fu W, Li P, Wu Y (2012) Effects of different light intensities on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and yield in lettuce. Sci Hortic 135:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2011.12.004
Fu YR, Zhang WM, Chen GM, Bai XM (2006) Determination of gallic acid and total phenolic acid in Sedum Aizoon L. Chin Tradit Pat Med 28:1016–1018
Goins GD, Yorio NC, Sanwo MM, Brown CS (1997) Photomorphogenesis, photosynthesis, and seed yield of wheat plants grown under red light-emitting diodes (LEDs) with and without supplemental blue lighting. J Exp Bot 48:1407–1413. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/48.7.1407
Gundel PE, Pierik R, Mommer L, Ballaré CL (2014) Competing neighbors: light perception and root function. Oecologia 176:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-014-2983-x
Hao W, Ren L, Ran W, Shen Q (2010) Allelopathic effects of root exudates from watermelon and rice plants on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum. Plant Soil 336:485–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0505-0
Hogewoning SW, Trouwborst G, Maljaars H, Poorter H, van Ieperen W, Harbinson J (2010) Blue light dose-esponses of leaf photosynthesis, morphology, and chemical composition of Cucumis sativus grown under different combinations of red and blue light. J Exp Bot 61:3107–3117. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq132
Hosseinzadeh S, Verheust Y, Bonarrigo G, Van Hulle S (2017) Closed hydroponic systems: operational parameters, root exudates occurrence and related water treatment. Rev Environ Sci Bio 16:59–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-016-9418-6
Jiang NX, Liu ZM, Ren HQ, Han SY, Zhu CY (2010) Changes of phenolic acids and total phenolic acids contents in cell walls of moso bamboos at different ages. J Bamboo Res 29:24–28
Jones HG (2014) Plants and microclimate: a quantitative approach to environmental plant physiology, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kozai T (2013) Resource use efficiency of closed plant production system with artificial light: concept, estimation and application to plant factory. Proc Jpn Acad 89:447–461. https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.89.447
Lee JG, Lee BY, Lee HJ (2006) Accumulation of phytotoxic organic acids in reused nutrient solution during hydroponic cultivation of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Sci Hortic 110:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2006.06.013
Li FM, Hu HY (2005) Isolation and characterization of a novel antialgal allelochemical from Phragmites communis. Appl Environ Microb 71:6545–6553. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.11.6545-6553.2005
Li SS, Pan RC (1994) Effects of blue light on the growth of rice seedlings. Chin J Rice Sci 8:115–118. https://doi.org/10.16819/j.1001-7216.1994.02.010
Liu WK, Yang QC, Wei LL (2012) Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and their applications in protected horticulture as light sources. China agricultural science and technology press, Bei**g
Lynch JM, Whipps JM (1990) Substrate flow in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 129:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011685
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Meier S, Alvear M, Borie F, Aguilera P, Ginocchio R, Cornejo P (2012) Influence of copper on root exudate patterns in some metallophytes and agricultural plants. Ecotox Environ Safe 75:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.08.029
Molas ML, Kiss JZ, Correll MJ (2006) Gene profiling of the red light signalling pathways in roots. J Exp Bot 57:3217–3229. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erl086
Pramanik MHR, Nagai M, Asao T, Matsui Y (2000) Effects of temperature and photoperiod on phytotoxic root exudates of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) in hydroponic culture. J Chem Ecol 26:1953–1967. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005509110317
Qiu Z, Yang Q, Liu W (2013a) Photocatalytic degradation of phytotoxic substances in waste nutrient solution by various immobilized levels of nano-TiO2. Water Air Soil Poll 224:1461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1461-0
Qiu Z, Yang Q, Liu W (2013b) Effect of nano-TiO2 photocatalysis on yield and quality of hydroponic lettuce. Acta Agric Boreali Sin 28:103–107
Renella G, Egamberdiyeva D, Landi L, Mench M, Nannipieri P (2006) Microbial activity and hydrolase activities during decomposition of root exudates released by an artificial root surface in Cd-contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 38:702–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.06.021
Sæbø A, Krekling T, Appelgren M (1995) Light quality affects photosynthesis and leaf anatomy of birch plantlets in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss Org 41:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00051588
Satbhai SB, Ristova D, Busch W (2015) Underground tuning: quantitative regulation of root growth. J Exp Bot 66:1099–1112. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru529
Savvides A, Fanourakis D, van Ieperen W (2012) Co-ordination of hydraulic and stomatal conductances across light qualities in cucumber leaves. J Exp Bot 63:1135–1143. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err348
Son KH, Oh MM (2015) Growth, photosynthetic and antioxidant parameters of two lettuce cultivars as affected by red, green, and blue light-emitting diodes. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 56:639–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-1064-3
Sunada K, Ding XG, Utami MS, Kawashima Y, Miyama Y, Hashimoto K (2008) Detoxification of phytotoxic compounds by TiO2 photocatalysis in a recycling hydroponic cultivation system of asparagus. J Agric Food Chem 56:4819–4824. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8001075
Talukder MR, Asaduzzaman M, Tanaka H, Asao T (2019) Electro-degradation of culture solution improves growth, yield and quality of strawberry plants grown in closed hydroponics. Sci Hortic 243:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.08.024
Urbonaviciute A, Pinho P, Samuoliene G, Duchovskis P, Vitta P, Stonkus A, Tamulaitis G, Zukauskas A, Halonen L (2007) Effect of short-wavelength light on lettuce growth and nutritional quality. Sodininkystė Ir Daržininkystė 26:157–165
Wang J, Lu W, Tong Y, Yang Q (2016) Leaf morphology, photosynthetic performance, chlorophyll fluorescence, stomatal development of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) exposed to different ratios of red light to blue light. Front Plant Sci 7:250. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00250
Wang XY, Xu XM, Cui J (2015) The importance of blue light for leaf area expansion, development of photosynthetic apparatus, and chloroplast ultrastructure of Cucumis sativus grown under weak light. Photosynthetica 53:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-015-0083-8
Wang X, Zhang T, Dai C (2010) Advance in mechanism and countermeasures of peanut succession monocrop** obstacles. Soils 42:505–512
Wu FZ, Wang W (1999) Research on soil microflora of greenhouse tomato. North Hortic 3:1–2
Yan J, Bi HH, Liu YZ, Zhang M, Zhou ZY, Tan JW (2010) Phenolic compounds from Merremia umbellata subsp. orientalis and their allelopathic effects on Arabidopsis seed germination. Molecules 15:8241–8250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15118241
Yan XH, Yu JH, **e JM (2016) Effects of supplemental light quality and durations of illumination on growth and root activity of cucumber seedling. J Nucl Agric Sci 30:1211–1217. https://doi.org/10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.06.1211
Yang CM, Lee CN, Chou CH (2002) Effects of three allelopathic phenolics on chlorophyll accumulation of rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings: I. Inhibition of supply-orientation. Bot Bull Acad Sin 43:299–304
Yang J, Pan T, Wang J, Bao E, Zou Z (2018) Effects of different light quality on tomato seedlings growth and root. North Hortic 12:77–82. https://doi.org/10.11937/bfyy.20174675
Yang Q, Zhang C (2005) Serial interview on plant factory (IV): plant factory based cultivation system (I). Appl Eng Technol Rural Area (greenh Hortic) 8:38–39
Yu JQ, Matsui Y (1994) Phytotoxic substances in root exudates of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Chem Ecol 20:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02065988
Yu JQ, Ye SF, Zhang MF, Hu WH (2003) Effects of root exudates and aqueous root extracts of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) and allelochemicals, on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzymes in cucumber. Biochem Syst Ecol 31:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-1978(02)00150-3
Zha LY, Liu WK (2017) Effect of continuous light with red and blue LED lamps on growth and characteristics of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of five lettuce cultivars. Plant Physiol J. 53:1735–1741. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2017.0086
Zha L, Zhang Y, Liu W (2019) Dynamic responses of ascorbate pool and metabolism in lettuce to long-term continuous light provided by red and blue LEDs. Environ Exp Bot 163:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.04.003
Zhou W, Liu W, Yang Q (2013) Reducing nitrate content in lettuce by pre-harvest continuous light delivered by red and blue light-emitting diodes. J Plant Nutr 36:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2012.748069
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 31672202) and The Key R&D Projects of Ningxia, China (No. 2017BY085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL was the recipient of funds. WL and CZ designed the experiment. CZ, QW, BL, MS, and YZ prepared the plant materials, collected samples, and undertook experiments. CZ analyzed the data and prepared the manuscript. WL revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Young Yeol Cho.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Wang, Q., Liu, W. et al. Effects of red/blue versus white LED light of different intensities on the growth and organic carbon and autotoxin secretion of hydroponic lettuce. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 63, 195–205 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00394-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00394-3