Abstract
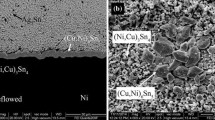
The predicted growth behavior of intermetallic compound (IMC) induced by electromigration of a Cu/organic solderability preservative (OSP)/Sn-2.5Ag solder/electroless nickel electroless palladium immersion gold (ENEPIG)/Cu joint was calculated for a current density of 14 kA/cm2 and current application time of 600 h and validated experimentally. Under as-reflow conditions, thin Cu3Sn and scallop-shaped Cu6Sn5 layers were produced near the OSP interface, and a (Cu, Ni)6Sn5 layer was formed near the ENEPIG interface. Cu6Sn5 islands and Ag3Sn with a β-Sn matrix were formed in the solder. The mobilities of Cu, Ni, and Sn atoms at the OSP and ENEPIG interfaces were calculated, and a relationship was found between IMC thickness and current application time. Under electron flow from the OSP to ENEPIG interface, the predicted total thickness (26.6 μm) of the IMCs (Cu3Sn, Cu6Sn5, and (Cu, Ni)6Sn5), was in agreement with the experimental value (24.7 μm). With electron flow reversed, the predicted IMC thickness (14.2 μm) was similar to the experimental value (13.2 μm). The application of current during electromigration only coarsened Cu6Sn5, regardless of the direction of electron flow. Finally, the Ni plating layer on the ENEPIG surface finish prevented the diffusion of Cu and suppressed electromigratory IMC growth by approximately 50%.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, P., Xue, S., Wang, J.: New challenges of miniaturization of electronic devices: electromigration and thermomigration in lead-free solder joints. Mater. Des 192, 108726 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108726
Liang, C.L., Lin, Y.S., Kao, C.L., Tarng, D., Wang, S.B., Hung, Y.C., Lin, G.T., Lin, K.L.: Electromigration reliability of advanced high-density fan-out packaging with fine-pitch 2-/2-μm L/S Cu redistribution lines. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag Manuf Technol. 10, 1438–1445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCPMT.2020.2997824
Kim, G., Son, K., Lee, J.H., Joo, Y.C., Park, Y.B.: Size effect on the electromigration characteristics of flip chip Pb-free solder bumps. Electron. Mater. Lett 18, 431–439 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00356-6
Kuan, W.C., Liang, S.W., Chen, C.: Effect of bump size on current density and temperature distributions in flip-chip solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 49, 544–550 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2009.03.001
Jeong, H., Lee, C.J., Kim, J.H., Son, J.Y., Jung, S.B.: Electromigration behavior of Cu core solder joints under high current density. Electron. Mater. Lett. 16, 513–519 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-020-00239-8
Sun, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, X., Yang, C., Hu, A., Hang, T., Wu, Y., Ling, H., Li, M.: Low-temperature insertion bonding using Electroless Cu-Co-P Micro-Cones array with controllable morphology. Electron. Mater. Lett. 17, 459–470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-021-00302-y
Kim, S., Hong, W., Nam, H., Kang, N.: Growth behavior of Intermetallic Compounds in various solder joints Induced by Electromigration. J. Weld. Join. 39, 89–102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5781/JWJ.2021.39.1.11
Vianco, P.T.: An overview of surface finishes and their role in printed circuit board solderability and solder joint performance. Circuit World. 25, 6–24 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1108/03056129910244518
Kim, M.S., Hong, W.S., Kim, M.: Flip chip-chip scale package bonding technology with type 7 solder paste printing. J. Weld. Join 39, 359–367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5781/JWJ.2021.39.4.3
Karthik, M., Abhinav, J., Shankar, K.V.: Morphological and mechanical behaviour of Cu–Sn alloys—A review. Met. Mater. Int 27, 1915–1946 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00899-z
Yoon, J.W., Lee, D.H., Lee, B.S.: A study of transient liquid phase bonding using an Ag-Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu hybrid solder paste. J. Weld. Join 39, 376–383 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5781/JWJ.2021.39.4.5
El-Taher, A.M., Razzk, A.F.: Controlling Ag3Sn plate formation and its effect on the creep resistance of Sn–3.0Ag–0.7Cu lead-free solder by adding minor alloying elements Fe, Co, Te and Bi. Met. Mater. Int 27, 4294–4305 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00856-w
Kim, J., Jung, S.B., Yoon, J.W.: Effect of Ni(P) thickness in Au/Pd/Ni(P) surface finish on the electrical reliability of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder joints during current-stressing. J. Alloys Compd. 850, 156729 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156729
Yoon, J.W., Noh, B.I., Jung, S.B.: Comparative study of ENIG and ENEPIG as surface finishes for a Sn-Ag-Cu solder joint. J. Electron. Mater. 40, 1950–1955 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-011-1686-x
Park, G.T., Lee, B.R., Son, K., Park, Y.B.: Ni barrier symmetry effect on electromigration failure mechanism of Cu/Sn–Ag microbump. Electron. Mater. Lett 15, 149–158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-00108-5
Yoon, J.W., Bang, J.H., Lee, C.W., Jung, S.B.: Interfacial reaction and intermetallic compound formation of Sn-1Ag/ENIG and Sn-1Ag/ENEPIG solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 627, 276–280 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.208
Yang, F., Liu, L.W., Huang, M.L.: Comparative study on interfacial reactions between Sn-3.5Ag, Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder balls and ENEPIG pad after multiple reflows, pp. 280–286. IEEE (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISAPM.2011.6105717
Baek, S.M., Park, Y., Oh, C., Chun, E.J., Kang, N.: Modeling and experimental verification of intermetallic compounds grown by electromigration and thermomigration for Sn-0.7Cu solders. J. Electron. Mater 48, 142–151 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6786-4
Hwang, J.H., Lee, J.H.: Transient liquid phase bonding process using Sn-coated Cu dendritic particles. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 4638–4644 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00702-z
Wierzbicka-Miernik, A., Miernik, K., Filipek, R., Szyszkiewicz, K.: Kinetics of intermetallic phase growth and determination of diffusion coefficients in solid-solid-state reaction between Cu and (sn + 1at.% ni) pads. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 10533–10544 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1187-2
Chao, B.H.L., Zhang, X., Chae, S.H., Ho, P.S.: Recent advances on kinetic analysis of electromigration enhanced intermetallic growth and damage formation in Pb-free solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 49, 253–263 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2009.01.006
Yu, J.E., Kim, S.J., Hong, W.S., Kang, N.H.: Intermetallic compound growth induced by electromigration in Sn-2.5 ag solder joints with ENEPIG surface finish. J. Weld. Join 40, 225–232 (2022). https://doi.org/10.5781/JWJ.2022.40.3.3
International, A.S.M.: ASM handbook volume 3: Alloy phase diagrams, (1998)
Baheti, V.A.: Diffusion controlled growth of phases in metal-tin systems related to microelectronics packaging. Ar**v 1804, 09595 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.1804.09595
Wang, Y., Ho, P.S.: Mode II electromigration failure mechanism in Sn-based Pb-free solder joints with ni under-bump metallization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 121909 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4821819
Chao, B., Chae, S.H., Zhang, X., Lu, K.H., Im, J., Ho, P.S.: Investigation of diffusion and electromigration parameters for Cu–Sn intermetallic compounds in Pb-free solders using simulated annealing. Acta Mater. 55, 2805–2814 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.12.019
Chao, H.L.: Electromigration enhanced kinetics of Cu-Sn intermetallic compounds in Pb free solder joints and Cu low-k dual Damascene processing using step and flash imprint lithography. The University of Texas at Austin (2009). http://hdl.handle.net/2152/7607
Paul, A., Ghosh, C., Boettinger, W.J.: Diffusion parameters and growth mechanism of phases in the Cu-Sn system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 42, 952–963 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0592-9
Ho, C.E., Lee, P.T., Chen, C.N., Yang, C.H.: Electromigration in 3D-IC scale Cu/Sn/Cu solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 676, 361–368 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.134
Ho, C.E., Yang, C.H., Lee, P.T., Chen, C.T.: Real-time X-ray microscopy study of electromigration in microelectronic solder joints. Scr. Mater. 114, 79–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.12.001
Yang, P.C., Kuo, C.C., Chen, C.: The effect of pre-aging on the electromigration of flip-chip SnAg solder joints. JOM. 60, 77–80 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-008-0077-0
Wei, C.C., Chen, C.F., Liu, P.C., Chen, C.: Electromigration in Sn-Cu intermetallic compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 023715 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3072662
Frederikse, H.P.R., Fields, R.J., Feldman, A.: Thermal and electrical properties of copper-tin and nickel-tin intermetallics. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 2879–2882 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351487
Ho, C.Y., Duh, J.G.: Quantifying the dependence of Ni (P) thickness in ultrathin-ENEPIG metallization on the growth of Cu–Sn intermetallic compounds in soldering reaction. Mater. Chem. Phys. 148, 21–27 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.06.072
Tseng, C.F., Lee, T.K., Ramakrishna, G., Liu, K.C., Duh, J.G.: Suppressing Ni3Sn4 formation in the Sn–Ag–Cu solder joints with Ni–P/Pd/Au surface finish. Mater. Lett. 65, 21–22 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.07
Huang, M.L., Zhang, Z.J., Ma, H.T., Chen, L.D.: Different diffusion behavior of Cu and Ni undergoing liquid-solid electromigration. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 1235–1242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2014.11.013
Wang, Y.W., Zhu, Z.X., Shih, W.L., Kao, C.R.: Abnormal Cu3Sn growth through grain boundary penetration in space-confined Ni-Sn-Cu diffusion couples. J. Alloys Compd. 799, 108–112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.328
Ho, C.E., Yang, S.C., Kao, C.R.: Interfacial reaction issues for lead-free electronic solders. Lead-Free Electron. Solders. 18, 155–174 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-48433-4_10
Wu, W.H., Chung, H.L., Chen, C.N., Ho, C.E.: The influence of current direction on the Cu-Ni cross-interaction in Cu/Sn/Ni diffusion couples. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2563–2572 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0876-2
Gan, H., Tu, K.N.: Polarity effect of electromigration on kinetics of intermetallic compound formation in Pb-free solder V-groove samples. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 063514 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1861151
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Technology Innovation Program Materials and Components Development Program (Grant No. 20011427) funded by the Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE) and the Competency Development Program for Industry Specialists of the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) (Grant No. P0002019) of the Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Choi, M., Yu, DY. et al. In-situ Observation and Modeling of Intermetallic Compound Growth Induced by Electromigration in Sn-2.5Ag Solder Joints with OSP and ENEPIG Surface Finish. Electron. Mater. Lett. 19, 229–238 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00405-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00405-0