Abstract
The estuary of River Badung is a containment for the Nusa Dua Estuary Reservoir, which requires an assessment of sedimentation and sediment transport to determine potential reductions in its storage capacity. Therefore, this study aims to quantify and optimize the transported sediment obtained through various control measures, accompanied by the analysis of sedimentation distribution patterns in the lower reaches of River Badung. In this study, three simulation methods were used, (1) Hydrologic Engineering Center’s-River Analysis System (HEC-RAS) was applied to analyze sediment transport, (2) Aeronautical Reconnaissance Coverage Geographic Information System (ArcGIS) was implemented to process geometry data and then exported with Hydrologic Engineering Center’s-Geospatial River Analysis System (HEC-GeoRAS), and (3) Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) method was used to optimize sedimentation control. The results showed that River Badung had significant erosion, with sediment volume determined by USLE and HEC-RAS methods being 8040 m3 and 8740 m3, respectively. This emphasized a difference of 697 m3 or 8.66%, with the condition of sediment control structures yielding the following outputs, (1) the structures of check dams 1 and 4 required a thorough repair, (2) the capacity of check dams 2 was almost full, and (3) check dams 3 was full. Based on these results, check dams 5 and groundsill were capable of accommodating sediment, with reservoir (check dams 5) needing adjustment for appropriate functioning.



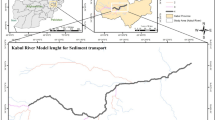
Source: Secondary data processing

Source: Secondary data processing

Source: Secondary data processing




Source: Adapted map sourced from Abd.Rahman As-Syakur, Udayana University [30]

Source: Secondary data processing

Source: Denpasar Government Website, 2020






Source: Water resources research and development center, 2014
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, X.; Dalrymple, R.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Lin, C.M.; Wang, P.: Provenance of Holocene sediments in the outer part of the Paleo-Qiantang River Estuary, China. Mar. Geol. 366, 1–15 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2015.04.008
Mohammad, M.E.; Al-Ansari, N.; Issa, I.E.; Knutsson, S.: Sediment in Mosul Dam Reservoir using the HEC-RAS model. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 21(3), 235–244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12142
Van Maren, D.S.; Winterwerp, J.C.; Vroom, J.: Fine sediment transport into the hyper-turbid lower Ems River: the role of channel deepening and sediment-induced drag reduction. Ocean Dyn. 65, 589–605 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-015-0821-2
Zhang, G.; Cheng, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Gong, W.: Transport of riverine sediment from different outlets in the pearl river estuary during the wet season. Mar. Geol. 415, 105957 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2019.06.002
Damte, F.; G-Mariam, B.; Ayana, M.T.; Lohani, T.K.; Dhiman, G.; Shabaz, M.: Computing the sediment and ensuing its erosive activities using HEC-RAS to surmise the flooding in Kulfo River in Southern Ethiopia. World J. Eng. 18(6), 948–955 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/WJE-01-2021-0002
Joshi, N.; Lamichhane, G.R.; Rahaman, M.M.; Kalra, A.; Ahmad, S.: Application of HEC-RAS to study the sediment transport characteristics of Maumee River in Ohio. In: World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019 (pp. 257-267). Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers.Reston, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784482353.024
Hidayati, A.M.; Yekti, M.I.; Sujana, G.F.E.A.: Analysis of sedimentation quantity and its handling in the downstream of Tukad Unda Klungkung using Hec-GeoRAS. MEDIA KOMUNIKASI TEKNIK SIPIL 27(2), 161–169 (2021)
Dai, Z.; Mei, X.; Darby, S.E.; Lou, Y.; Li, W.: Fluvial sediment transfer in the Changjiang (Yangtze) river-estuary depositional system. J. Hydrol. 566, 719–734 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.09.019
Shabani, A.; Woznicki, S.A.; Mehaffey, M.; Butcher, J.; Wool, T.A.; Whung, P.Y.: A coupled hydrodynamic (HEC-RAS 2D) and water quality model (WASP) for simulating flood-induced soil, sediment, and contaminant transport. J. Flood Risk Manage. 14(4), e12747 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12747
Sathya, A.; Thampi, S.G.; Chithra, N.R.: Development of a framework for sand auditing of the Chaliyar River basin, Kerala, India using HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS model coupling. Int. J. River Basin Manage. 21(1), 67–80 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2021.1909604
Tadesse, A.; Dai, W.: Prediction of sedimentation in reservoirs by combining catchment based model and stream based model with limited data. Int. J. Sedim. Res. 34(1), 27–37 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2018.08.001
Boothroyd, R.; Williams, R.; Hoey, T.; Barrett, B.; Prasojo, O.A.: Applications of google earth engine in fluvial geomorphology for detecting river channel change. WIREs Water 8(1), e21496 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1496
Mihi, A.; Benarfa, N.; Arar, A.: Assessing and map** water erosion-prone areas in Northeastern Algeria using analytic hierarchy process, USLE/RUSLE equation, GIS, and remote sensing. Appl. Geomat. 12(2), 179–191 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-019-00289-0
Dubey, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Mundetia, N.: Morphometric analysis of the Banas River Basin using geographical information system, Rajasthan India. Hydrology 3(5), 47–57 (2015). https://doi.org/10.11648/j.hyd.20150305.11
Gibson, S.; Sánchez, A.; Piper, S.; Brunner, G.: ew One-Dimensional Sediment Features in HEC-RAS 5.0 and 5.1. In: World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2017: Hydraulics and Waterways and Water Distribution Systems Analysis - Selected Papers from the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2017. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784480625.018
Kiran, S.; Poudyal, A.; Pradhan, S.; Gautom, M.: Application of ArcGIS and HEC-RAS in Assessing Sedimentation in Godavari River Reach. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, Springer, Singapore, Singapore (2022)
Mahapatra, S.K.; Obi Reddy, G.P.; Nagdev, R.; Yadav, R.P.; Singh, S.K.; Sharda, V.N.: Assessment of soil erosion in the fragile himalayan ecosystem of Uttarakhand, India using USLE and GIS for sustainable productivity. Curr. Sci. 115(1), 108–121 (2018)
Zhao, N.; Ghaemi, A.; Wu, C.; Band, S.S.; Chau, K.W.; Zaguia, A.; Mosavi, A.H.: A decomposition and multi-objective evolutionary ozation model for suspended sediment load prediction in rivers. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 15(1), 1811–1829 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2021.1990133
Indraswari, D.; Hanifah, N.; Ramadani, M.J.; dan Priyana, Y.: Analisis Aplikasi ArcGIS 10.3 Untuk Pembuatan Daerah Aliran Sungai Dan Penggunaan Lahan Di DAS Samajid Kabupaten Sampang, Madura. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Geografi UMS IX 2018. Yogyakarta, Indonesia. (2018).
Ali, S.A.; Hagos, H.: Estimation of soil erosion using USLE and GIS in Awassa catchment, Rift Valley Central Ethiopia. Geoderma Reg. 7(2), 159–166 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2016.03.005
Karamage, F.; Zhang, C.; Kayiranga, A.; Shao, H.; Fang, X.; Ndayisaba, F.; Nahayo, L.; Mupenzi, C.; Tian, G.: USLE-based assessment of soil erosion by water in the Nyabarongo River Catchment, Rwanda. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 13(8), 835 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080835
Azouagh, A.; El Bardai, R.; Hilal, I.; Stitou el Messari, J.: Integration of GIS and HEC-RAS in floods modeling of Martil River (Northern Morocco). European Sci. J., ESJ 14(12), 130 (2018)
Yulistiyanto, B.; Kironoto, B.; Giarto, B.; Kiptiah, M.; Tantowi, M.L.: The simplified of suspended sediment measurement method in Natural River (Case Study of Kuning River in Yogyakarta, Indonesia). J. Civ. Eng. Forum. 5(3), 243–254 (2019)
Mejía-Veintimilla, D.; Ochoa-Cueva, P.; Samaniego-Rojas, N.; Félix, R.; Arteaga, J.; Crespo, P.; Fries, A.: River discharge simulation in the high andes of southern ecuador using high-resolution radar observations and meteorological station data. Remote Sens. 11(23), 2804 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232804
Tukimat, N.N.A.; Syukri, N.A.; Malek, M.A.: Projection the long-term ungauged rainfall using integrated statistical downscaling model and geographic information system (SDSM-GIS) model. Heliyon 5(9), e02456 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02456
Triatmodjo, B. 2008. Hidrologi Terapan (Applied Hydrology). Yogyakarta, Indonesia: Beta Offset.
Shrestha, N.K.; Qamer, F.M.; Pedreros, D.; Murthy, M.S.R.; Wahid, S.M.; Shrestha, M.: Evaluating the accuracy of Climate Hazard Group (CHG) satellite rainfall estimates for precipitation based drought monitoring in Koshi basin. Nepal. J. Hydrol.: Reg. Stud. 13, 138–151 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2017.08.004
Utomo, W.: Soil Conservation in Indonesia, A Record and Analysis. Publisher Rajawali, Jakarta (1989)
Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Guan, Y.: Improved USLE-K factor prediction: a case study on water erosion areas in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 4(3), 168–176 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.08.003
Macklin, P. A. 2019. Hydrological drivers of carbon dioxide cycling from headwaters to the coastal ocean on a tropical island (Doctoral dissertation, Southern Cross University).
Lelyana, N.: Analisis Sedimentasi Sebagai Evaluasi Umur Layanan Waduk Benel di Kabupaten Jembrana Provinsi Bali (Sedimentation Analysis as an Evaluation of the Service Life of the Benel Reservoir in Jembrana Regency. Universitas Udayana, Bali Province) (2018)
Khattak, M.S.; Anwar, F.; Saeed, T.U.; Sharif, M.; Sheraz, K.; Ahmed, A.: Floodplain map** using HEC-RAS and ArcGIS: a case study of Kabul River. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41(4), 1375–1390 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1915-3
Ngadisih, N.; Satriagasa, M.C.; Kumolo, C.; Suryatmojo, H.; Annisa, M.: Komparasi Tiga Model Infiltrasi Pada Lahan Pertanian dan Agroforestri Di Das Merawu—Banjarnegara (Comparison of Three Infiltration Models on Agricultural and Agroforestry Land in the Merawu Basin—Banjarnegara). Jurnal Ilmiah Rekayasa Pertanian Dan Biosistem, 8 (Maret). (2020). https://doi.org/10.29303/jrpb.v8i1.157
Bera, A.: Assessment of soil loss by universal soil loss equation (USLE) model using GIS techniques: a case study of Gumti River Basin, Tripura. India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 3(1), 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0289-9
Arsyad, S.: Konservasi Tanah dan Air (Conservation Soil and Water), 2nd edn. IPB Press, Bogor (2010)
Abdurachman, A.; Abuyamin, S.; Kurnia, U.: Pengelolaan Tanah dan Tanaman untuk Usaha Konservasi (Management of Soil and Plants for Conservation Effort). Center for Soil Research, Bogor (1984)
Palupi, L.D. 2019. Upaya Konservasi Tanah Berdasarkan Penetapan Indeks Bahaya Erosi (IBE) Di Kelurahan Kejajar, Kecamatan Kejajar, Kabupaten Wonosobo (Soil Conservation Efforts Based on Erosion Hazard Index (IBE) Determination in Kejajar Village, Kejajar District, Wonosobo Regency). Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Veteran. http://eprints.upnyk.ac.id/id/eprint/21208
Istiarto. 2014. Modul Pelatihan Simulasi Aliran 1-Dimensi Dengan Bantuan Paket Program Hidrodinamika HEC-RAS. https://istiarto.staff.ugm.ac.id/index.php/hec-ras/modul-hec-ras/
Brunner, G.W.; Gibson, S.: Sediment transport modeling in HEC RAS. In Impacts of global climate change (pp. 1–12). (2005). https://doi.org/10.1061/40792(173)442
Brunner, G.W.: HEC-RAS river analysis system: hydraulic reference manual version 5.0; US army corps of engineers-hydrologic engineering center (HEC). Davis, CA, USA (2016)
Sisinggih, D.; Wahyuni, S.; Nugroho, R.; Hidayat, F.; Rahman, K.I.: Sediment transport functions in HEC-RAS 4.0 and their evaluation using data from sediment flushing of Wlingi reservoir-Indonesia. In: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, IOP Publishing. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/437/1/012014
Legowo, D.: Volcanic debris control applied in Indonesia. J. Hydrol. (New Zealand) 20(1), 71–79 (1981)
Abd Rahman, N.F.; Mohammed, L.; Mohammad, M.; Khalid, K.; Tai, V.C.; Sharif, M.S.M.; Haron, S.H.: Modeling of 1D sediment transport in the langat river using quasi-unsteady HEC-RAS. J. Biol. Stud. 5(3), 378–387 (2022)
Mateusz, H.; Tomasz, K.; Stanisław, Z.: Sediment Transport and Changes in the River Bottom Topology Downstream of the Jeziorsko Reservoir. CRC Press, Florida, USA, In Flood Handbook (2022) https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429463938
Asriadi, A.; dan Pristianto, H.: Ringkasan Teori Erosi dan Sedimentasi (Summary of Erosion and Sedimentation Theory). Universitas Muhammadiyah Sorong, Sorong (2018)
De Ploey, J.; Poesen, J.: Aggregate stability, runoff generation and interrill erosion. Routledge, London, UK, In Geomorphology and soils (2020) https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429320781
Water Resources Research and Development Center. 2014. Scientific Manuscript of Sediment Control Building. Ministry of Public Works Republic Indonesia.
Funding
“The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support was received during the preparation of this manuscript.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
“All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Ni Made Vania Sukmasari Marsha, Mawiti Infantri Yekti, Anissa Maria Hidayati and Bart Schultz. The first draft of the manuscript was revised and edited by Mawiti Infantri Yekti, Ni Made Vania Sukmasari Marsha and Bart Schultz, all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.”
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
“The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.” This study originally academic study in our faculty, Faculty of Engineering, Udayana University, Bali, Indonesia and collaboration writing with Prof. em Bart Schultz, Land and Water Development, IHE-Delft, Lelystad, the Netherlands”.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yekti, M.I., Marsha, N.M.V.S., Hidayati, A.M. et al. Sedimentation Evaluation of Downstream Reaches of River Badung by Applying HEC-GeoRAS and USLE Method. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09232-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09232-x